字节跳动-文远知行杯”广东工业大学第十四届程序设计竞赛
题目链接
简单数学题
题目

思路
前置知识:
\[\sum_{i=m}^{n}C_{i}^{m}=C_{n+1}^{m+1}
\]
此题化简:
\[\begin{aligned}
&\sum_{i=1}^{n}i\sum_{j=i}^{n}C_{j}^{i}& \\
=&\sum_{i=1}^{n}iC_{n+1}^{i+1}& \\
=&(n+1)\sum_{i=1}^{n}C_{n}^{i}-\sum_{i=1}^{n}C_{n+1}^{i+1}&\\
=&(n+1)(2^n-1)-(2^{n+1}-C_{n+1}^{0}-C_{n+1}^{1})&\\
=&(n-1)2^{n}+1
\end{aligned}
\]
代码实现如下:
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> piL;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define lson rt<<1
#define rson rt<<1|1
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
#define name2str(name) (#name)
#define bug printf("*********\n")
#define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl
#define FIN freopen("in","r",stdin)
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 7;
const double pi = acos(-1);
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
LL n;
LL qpow(LL x, LL n) {
LL res = 1;
while(n) {
if(n & 1) res = res * x % mod;
x = x * x % mod;
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main() {
while(~scanf("%lld", &n)) {
printf("%lld\n", ((n - 1) % mod * qpow(2, n) % mod + 1) % mod);
}
return 0;
}
Count
题目
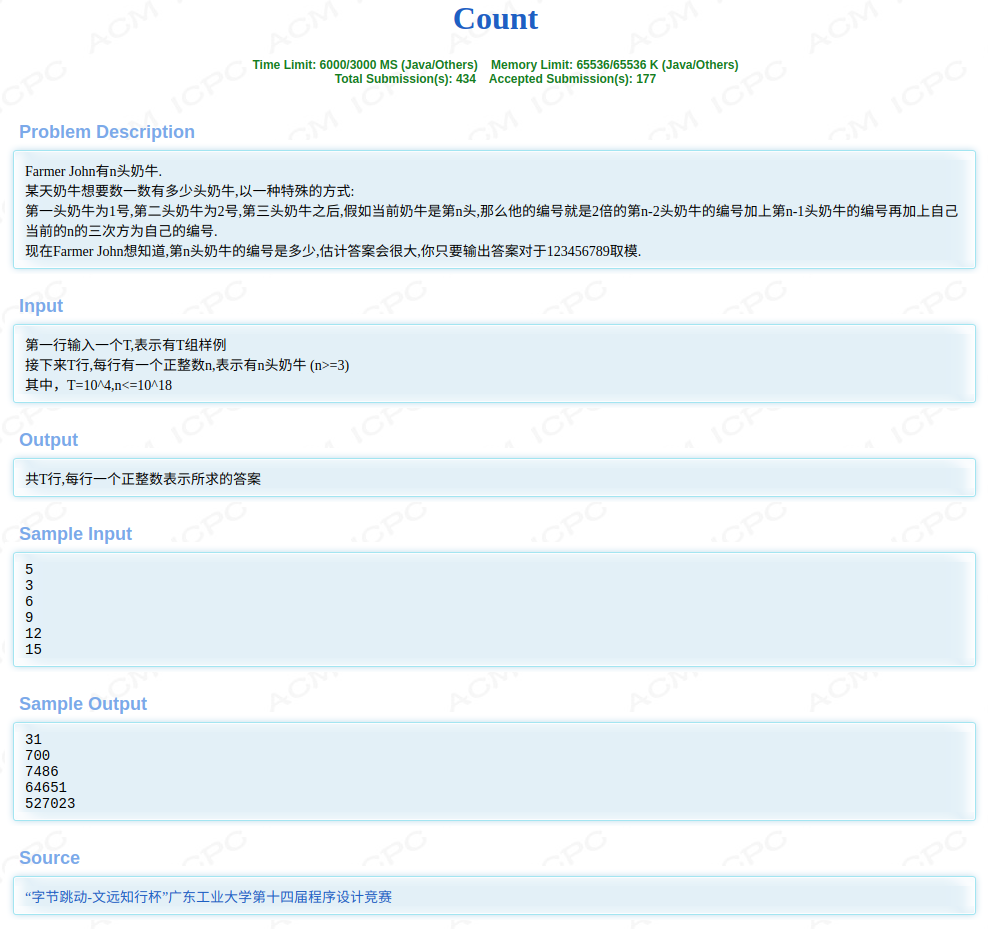
思路
我们假设第n头牛的编号为\(f_{n}\),由题意可知递推式为\(f_{n}=f_{n-1}+2 \times f_{n-2}+n^{3}\),根据这个我们可以推得矩阵快速幂的系数矩阵为:
\[\left\{
\begin{matrix}
1 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
2 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
1 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
3 & 0 & 3 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\
3 & 0 & 3 & 2 & 1 & 0 \\
1 & 0 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1
\end{matrix}
\right\}
\]
代码实现如下
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> piL;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define lson rt<<1
#define rson rt<<1|1
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
#define name2str(name) (#name)
#define bug printf("*********\n")
#define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl
#define FIN freopen("in","r",stdin)
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 123456789;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 7;
const double pi = acos(-1);
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
int t;
LL n;
int f[10], a[10][10];
void mulself(int a[10][10]) {
int c[10][10];
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
for(int k = 0; k < 10; k++) {
c[i][j] = (c[i][j] + (long long)a[i][k] * a[k][j]) % mod;
}
}
}
memcpy(a, c, sizeof(c));
}
void mul(int f[10], int a[10][10]) {
int c[10];
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
c[i] = (c[i] + (long long)f[j] * a[j][i] ) % mod;
}
}
memcpy(f, c, sizeof(c));
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--) {
scanf("%lld", &n);
f[0] = 2, f[1] = 1, f[2] = 8, f[3] = 4, f[4] = 2, f[5] = 1;
a[0][0] = 1, a[0][1] = 1, a[0][2] = 0, a[0][3] = 0, a[0][4] = 0, a[0][5] = 0;
a[1][0] = 2, a[1][1] = 0, a[1][2] = 0, a[1][3] = 0, a[1][4] = 0, a[1][5] = 0;
a[2][0] = 1, a[2][1] = 0, a[2][2] = 1, a[2][3] = 0, a[2][4] = 0, a[2][5] = 0;
a[3][0] = 3, a[3][1] = 0, a[3][2] = 3, a[3][3] = 1, a[3][4] = 0, a[3][5] = 0;
a[4][0] = 3, a[4][1] = 0, a[4][2] = 3, a[4][3] = 2, a[4][4] = 1, a[4][5] = 0;
a[5][0] = 1, a[5][1] = 0, a[5][2] = 1, a[5][3] = 1, a[5][4] = 1, a[5][5] = 1;
if(n <= 2) {
printf("%d\n", f[n]);
continue;
}
n -= 2;
while(n) {
if(n & 1) mul(f, a);
mulself(a);
n >>= 1;
}
printf("%d\n", f[n]);
}
return 0;
}
版权声明:本文允许转载,转载时请注明原博客链接,谢谢~


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号