Java多线程(一)
Java多线程(一)
1.1多线程
1.1.1 基本概念
进程(process)是程序运行的实体,程序运行内部的一些资源调动由进程内部的线程完成。线程可以理解为进程中独立运行的子任务。线程也可以理解为一个轻量级进程。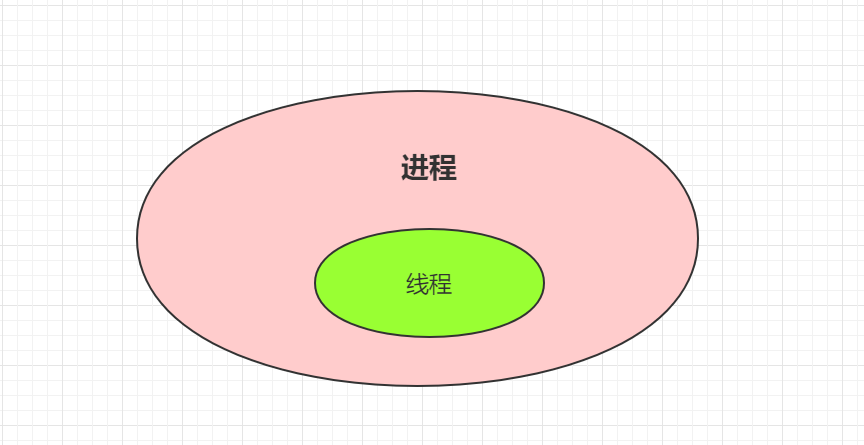
1.1.2单任务环境与多任务环境
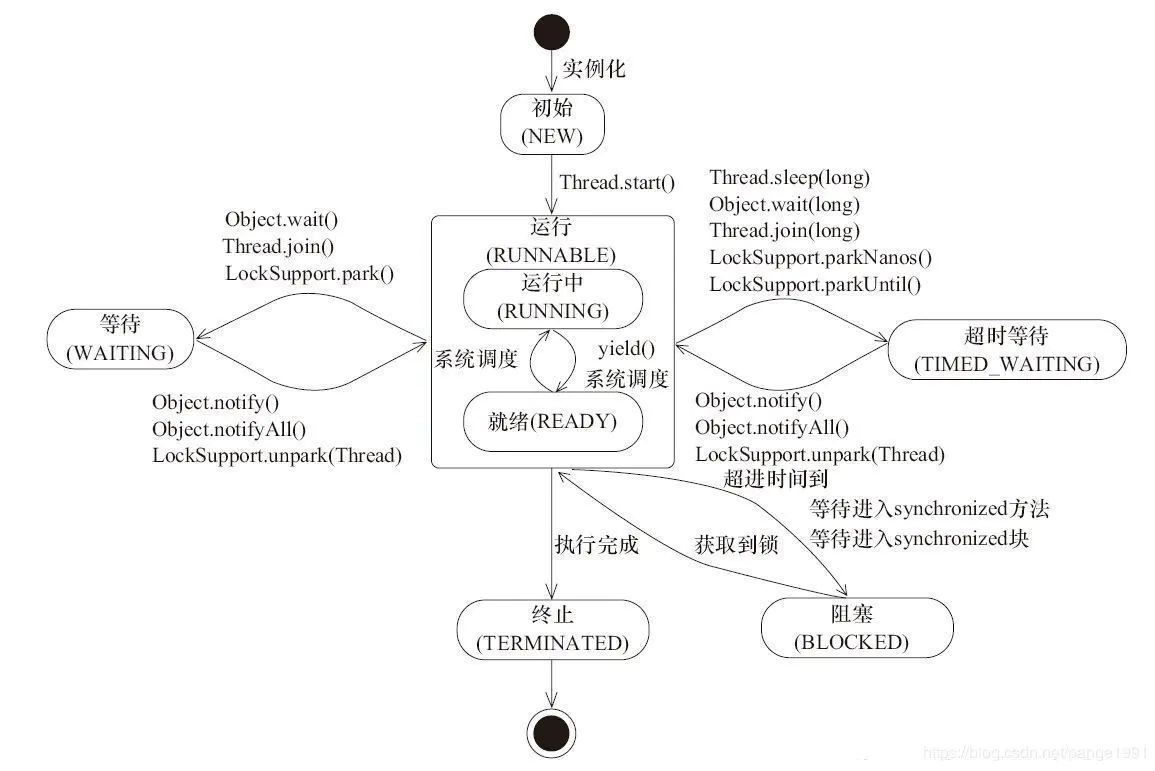
1.1.3线程的状态
public class MainThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取当前线程
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run Thread");
Thread.currentThread().setName("MyThread-1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
//运行一个线程是start()
myThread.start();
//因为线程的调用具有随机性,所以这一句输出的位置不确定
//我们先调用的main()函数
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("run over");
}
}
/**
* 线程执行是随机的
*/
public class RandomThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++) {
int time = (int) (Math.random() * 1000);
try {
Thread.sleep(time);
System.out.println("run = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new RandomThread();
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.setName("RandomThread");
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++) {
int time = (int) (Math.random() * 1000);
try {
Thread.sleep(time);
System.out.println("run = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadStartTest extends Thread{
private int i;
public ThreadStartTest(int i){
this.i = i;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(i);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadStartTest t1 = new ThreadStartTest(1);
ThreadStartTest t2 = new ThreadStartTest(2);
ThreadStartTest t3 = new ThreadStartTest(3);
ThreadStartTest t4 = new ThreadStartTest(4);
ThreadStartTest t5 = new ThreadStartTest(5);
//线程的启动顺序与start()的调用顺序无关
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
t5.start();
}
}
public class ThreadUnsafe {
/**
* 多线程访问变量的线程安全问题
*/
private int count = 5;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadUnsafe threadSafe = new ThreadUnsafe();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() ->{
while(threadSafe.getCount() > 0){
/**
* JVM:
* 取到count的值
* 计算count-1
* 对count赋值
*/
threadSafe.count--;
System.out.println("cal by " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + threadSafe.getCount());
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() ->{
while(threadSafe.getCount() > 0){
threadSafe.count--;
System.out.println("cal by " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + threadSafe.getCount());
}
});
t1.setName("thread-1");
t2.setName("thread-2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
public class ThreadSafeWithSync implements Runnable {
private int count = 5;
/**
* synchronized对同步代码块加锁,一次只允许一个线程执行这段同步代码块,
* 在有线程执行的过程中,其他线程不能执行当前代码块。正在执行的线程是一个
* 获得锁的状态,其他线程在等待锁
*/
@Override
public synchronized void run() {
count--;
System.out.println("cal by " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + count);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadSafeWithSync safeWithSync = new ThreadSafeWithSync();
Thread t1 = new Thread(safeWithSync,"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(safeWithSync,"t2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(safeWithSync,"t3");
Thread t4 = new Thread(safeWithSync,"t4");
Thread t5 = new Thread(safeWithSync,"t5");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
t5.start();
}
}
public class ThreadSafeWithSync2 implements Runnable {
private int count = 3;
/**
* synchronized对于同一个线程,锁是可重入的。
*/
@Override
public void run() {
sub1();
}
public synchronized void sub1() {
count--;
System.out.println(count);
sub2();
}
public synchronized void sub2() {
count--;
System.out.println(count);
sub3();
}
public synchronized void sub3() {
count--;
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadSafeWithSync2 safeWithSync = new ThreadSafeWithSync2();
Thread t1 = new Thread(safeWithSync, "t1");
t1.start();
}
}
一个小案例
public class LoginServlet {
private static String username;
private static String password;
/**
* 同步代码块
* @param username
* @param password
*/
public synchronized static void doPost(String username,String password){
try {
LoginServlet.username = username;
if ("YCL".equals(username)){
//休眠5s,让线程没有同步时足以完成线程切换
Thread.sleep(5000L);
}
LoginServlet.password = password;
System.out.println("username= " + LoginServlet.username + " password= " + LoginServlet.password);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class TOMLogin extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
LoginServlet.doPost("TOM","12121");
}
}
public class YCLLogin extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
LoginServlet.doPost("YCL","1234");
}
}
public class LoginTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
YCLLogin yclLogin = new YCLLogin();
yclLogin.start();
TOMLogin tomLogin = new TOMLogin();
tomLogin.start();
}
}
public class IsAliveDemo extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run= " + this.isAlive());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
IsAliveDemo aliveDemo = new IsAliveDemo();
System.out.println("begin ----" + aliveDemo.isAlive());
aliveDemo.start();
//等待线程停止
Thread.sleep(2000L);
System.out.println("end ----" + aliveDemo.isAlive());
}
}
public class SleepTest extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("run ----> " + currentThread().getName() + " begin ---" + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(2000L);
System.out.println("run ----> " + currentThread().getName() + " end---" + System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SleepTest test = new SleepTest();
System.out.println("begin ====>" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +" "+ System.currentTimeMillis());
//main 和 Thread-0是异步执行的 所以是先打印begin,end再打印 Thread-0中的信息
//test.start();
//都是main线程去同步执行
test.run();
System.out.println("end ====>" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +" "+ System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(3000L);
//子线程运行结束就终止
System.out.println(test.isAlive());
//在程序终止前,主线程不会死亡
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isAlive());
}
}
public class PrintThread extends Thread {
private volatile int count = 5;
@Override
public void run() {
/**
*count--发生在println()之前,所以println()的
* synchronized (this) {
* print(x);
* newLine();
* }
* 没有生效,有概率发生同步问题
*
*/
System.out.println("count="+ (count--) + "--" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
if (count == 0){
System.out.println(count);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintThread printThread = new PrintThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(printThread);
Thread t2 = new Thread(printThread);
Thread t3 = new Thread(printThread);
Thread t4 = new Thread(printThread);
Thread t5 = new Thread(printThread);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
t5.start();
}
}
public class CanNotStop extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+(i+1));
}
}
/**
* 判断线程停止的方法
* Thread.interrupted(),测试当前线程是否已经中断
* this.isInterrupted(),测试线程是否中断
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
CanNotStop canNotStop = new CanNotStop();
canNotStop.start();
try {
// Thread.sleep(2000L);
//停止当前thread的线程---main
//所以结果为false
canNotStop.interrupt();
//中断当前线程
//Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
//System.out.println("Thread is stop 1?---->" + Thread.interrupted());
//当前线程已经被中断,线程中断的状态就有该方法清除,所以第二次调用返回false
//例外情况,当第一次线程中断状态清除以后,第二次调用中断检测签,当前线程再次中断会返回true
//System.out.println("Thread is stop 2?---->" + Thread.interrupted());
//两个返回值都是true,因为isInterrupted()不会清除状态,所以两次中断结果一致
System.out.println("stop 1 "+ canNotStop.isInterrupted());
System.out.println("stop 2 "+ canNotStop.isInterrupted());
//避免主线程因睡眠导致Thread-0提前执行完结束,导致停止失效
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
public class ExceptionStop extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50000 ; i++) {
if (interrupted()){
System.out.println("statue : stop,I'm out");
break;
}
System.out.println("i="+(i+1));
}
//让线程停止了,但是为什么还能输出呢?
System.out.println("Really stop?");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExceptionStop exceptionStop = new ExceptionStop();
exceptionStop.start();
try {
exceptionStop.interrupt();
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
public class ExceptionStop2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
if (interrupted()) {
System.out.println("statue : stop,I'm out");
throw new InterruptedException();
}
System.out.println("i=" + (i + 1));
}
//抛出异常之后线程没有得到执行,说明线程停止了
System.out.println("Really stop?");
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("Threed-0-catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExceptionStop2 exceptionStop = new ExceptionStop2();
exceptionStop.start();
try {
exceptionStop.interrupt();
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
public class SleepStop extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("run begin...");
//先让线程sleep再停止线程
Thread.sleep(200000L);
System.out.println("run end...");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Sleep stop thread");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SleepStop sleepStop = new SleepStop();
sleepStop.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
sleepStop.interrupt();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
public class StopSleep extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000 ; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+(i+1));
}
System.out.println("run begin...");
Thread.sleep(200000L);
System.out.println("run end...");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("stop --> sleep");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StopSleep stopSleep = new StopSleep();
stopSleep.start();
//先停止再睡眠
stopSleep.interrupt();
System.out.println("end");
}
}
public class StopSleep extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000 ; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+(i+1));
}
System.out.println("run begin...");
Thread.sleep(200000L);
System.out.println("run end...");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("stop --> sleep");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StopSleep stopSleep = new StopSleep();
stopSleep.start();
//先停止再睡眠
stopSleep.interrupt();
System.out.println("end");
}
}
public class StopTest1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
this.stop();
//在stop时会抛出这样一个异常,不要显式捕获
}catch (ThreadDeath e){
System.out.println("Thread-0 catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StopTest1 stopTest1 = new StopTest1();
stopTest1.start();
}
}
public class StopTest2SyncObject {
private String username = "YCL";
private String password = "123456";
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public synchronized void getMsg(String username,String password){
try {
this.username = username;
Thread.sleep(100000);
this.password = password;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class StopTest2 extends Thread {
private StopTest2SyncObject stopTest2SyncObject;
public StopTest2(StopTest2SyncObject stopTest2SyncObject){
this.stopTest2SyncObject = stopTest2SyncObject;
}
@Override
public void run() {
stopTest2SyncObject.getMsg("Tom","1231");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StopTest2SyncObject object = new StopTest2SyncObject();
StopTest2 stopTest2 = new StopTest2(object);
stopTest2.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
//stop()释放锁造成数据不一致。
stopTest2.stop();
System.out.println(object.getUsername() + " " + object.getPassword());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class ReturnStop extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
if (this.isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("Stop");
//使用return停止一个线程
return;
}
System.out.println("timer=" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReturnStop returnStop = new ReturnStop();
returnStop.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
returnStop.interrupt();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class SuspendThread extends Thread {
private long i = 0;
public long getI() {
return i;
}
public void setI(long i) {
this.i = i;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
i++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SuspendThread suspendThread = new SuspendThread();
suspendThread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(5000L);
//第一次暂停(多线程情况下会造成死锁)
suspendThread.suspend();
System.out.println("ONE=" + System.currentTimeMillis() + " i=" + suspendThread.getId());
Thread.sleep(5000L);
System.out.println("ONE=" + System.currentTimeMillis() + " i=" + suspendThread.getId());
//恢复线程
suspendThread.resume();
Thread.sleep(5000L);
//第二次暂停
suspendThread.suspend();
System.out.println("TWO=" + System.currentTimeMillis() + " i=" + suspendThread.getId());
Thread.sleep(5000L);
System.out.println("TWO=" + System.currentTimeMillis() + " i=" + suspendThread.getId());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class SyncSuspend {
public synchronized void getMsg(){
System.out.println("begin");
if("t1".equals(Thread.currentThread().getName())){
System.out.println("forever suspend t1");
//suspend()暂停线程不会释放锁,是独占的
Thread.currentThread().suspend();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
public class SuspendThread2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
final SyncSuspend syncSuspend = new SyncSuspend();
//线程1
Thread t1 = new Thread(() ->{
//t1获得锁
syncSuspend.getMsg();
});
t1.setName("t1");
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000L);
//线程2
Thread t2 = new Thread(() ->{
System.out.println("t2 run,but can access getMsg()");
System.out.println("t1 is suspend");
//t2一直在等待t1释放锁,但是t1处于一直持有的状态故死锁
syncSuspend.getMsg();
});
t2.setName("t2");
t2.start();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class SuspendThread3 extends Thread {
private long i = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
i++;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SuspendThread3 suspendThread3 = new SuspendThread3();
suspendThread3.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
//子线程暂停,导致程序阻塞
suspendThread3.suspend();
System.out.println("main end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class SuspendAndResumeTest {
private String username = "YCL";
private String password = "123456";
public void setValue(String username,String password){
this.username = username;
if ("t1".equals(Thread.currentThread().getName())){
System.out.println("t1 suspend");
Thread.currentThread().suspend();
}
this.password = password;
}
public void getMsg(){
System.out.println(username + "===" + password);
}
}
public class SuspendAndResumeRun {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final SuspendAndResumeTest test = new SuspendAndResumeTest();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
test.setValue("Tom","12121");
});
t1.setName("t1");
t1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(500L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Thread t2 = new Thread(() ->{
test.getMsg();
});
t2.start();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号