Java面向对象(七)
Java面向对象(七)
1.1文件与IO
** I/O --- input / output ---> /File/Data**
1.1.1分类
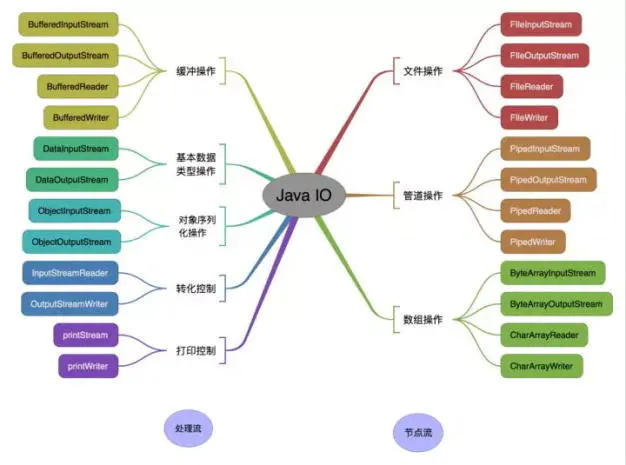
从数据来源或者说是操作对象角度看,IO 类可以分为:
- 1、文件(file):FileInputStream、FileOutputStream、FileReader、FileWriter
- 2、数组([]):
- 2.1、字节数组(byte[]):ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream
- 2.2、字符数组(char[]):CharArrayReader、CharArrayWriter
- 3、管道操作:PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream、PipedReader、PipedWriter
- 4、基本数据类型:DataInputStream、DataOutputStream
- 5、缓冲操作:BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
- 6、打印:PrintStream、PrintWriter
- 7、对象序列化反序列化:ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream
- 8、转换:InputStreamReader、OutputStreWriter
- 9、
字符串(String)Java8中已废弃:StringBufferInputStream、StringBufferOutputStream、StringReader、StringWriter
从数据传输方式或者说是运输方式角度看,可以将 IO 类分为:
- 1、字节流
- 2、字符流
字节流是以一个字节单位来运输的,比如一杯一杯的取水。而字符流是以多个字节来运输的,比如一桶一桶的取水,一桶水又可以分为几杯水。
字节流和字符流的区别:
字节流读取单个字节,字符流读取单个字符(一个字符根据编码的不同,对应的字节也不同,如 UTF-8 编码是 3 个字节,中文编码是 2 个字节。)字节流用来处理二进制文件(图片、MP3、视频文件),字符流用来处理文本文件(可以看做是特殊的二进制文件,使用了某种编码,人可以阅读)。简而言之,字节是个计算机看的,字符才是给人看的。
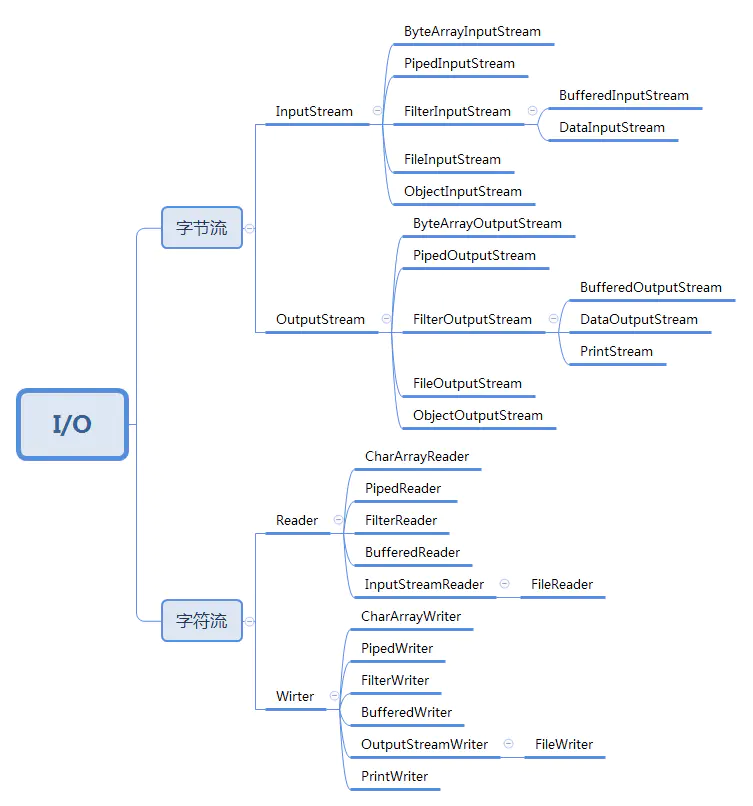
IO 类虽然很多,但最基本的是 4 个抽象类:InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer。最基本的方法也就是一个读 read() 方法、一个写 write() 方法。方法具体的实现还是要看继承这 4 个抽象类的子类。注意这里的读取和写入,其实就是获取(输入)数据和输出数据。
InputStream 类
| 方法 | 方法介绍 |
|---|---|
| public abstract int read() | 读取数据 |
| public int read(byte b[]) | 将读取到的数据放在 byte 数组中,该方法实际上是根据下面的方法实现的,off 为 0,len 为数组的长度 |
| public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) | 从第 off 位置读取 len 长度字节的数据放到 byte 数组中,流是以 -1 来判断是否读取结束的(注意这里读取的虽然是一个字节,但是返回的却是 int 类型 4 个字节,这里当然是有原因,这里就不再细说了,推荐这篇文章,链接) |
| public long skip(long n) | 跳过指定个数的字节不读取,想想看电影跳过片头片尾 |
| public int available() | 返回可读的字节数量 |
| public void close() | 读取完,关闭流,释放资源 |
| public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) | 标记读取位置,下次还可以从这里开始读取,使用前要看当前流是否支持,可以使用 markSupport() 方法判断 |
| public synchronized void reset() | 重置读取位置为上次 mark 标记的位置 |
| public boolean markSupported() | 判断当前流是否支持标记流,和上面两个方法配套使用 |
OutputStream 类
| 方法 | 方法介绍 |
|---|---|
| public abstract void write(int b) | 写入一个字节,可以看到这里的参数是一个 int 类型,对应上面的读方法,int 类型的 32 位,只有低 8 位才写入,高 24 位将舍弃。 |
| public void write(byte b[]) | 将数组中的所有字节写入,和上面对应的 read() 方法类似,实际调用的也是下面的方法。 |
| public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) | 将 byte 数组从 off 位置开始,len 长度的字节写入 |
| public void flush() | 强制刷新,将缓冲中的数据写入 |
| public void close() | 关闭输出流,流被关闭后就不能再输出数据了 |
再来看 Reader 和 Writer 类中的方法,你会发现和上面两个抽象基类中的方法很像。
Reader 类
| 方法 | 方法介绍 |
|---|---|
| public int read(java.nio.CharBuffer target) | 读取字节到字符缓存中 |
| public int read() | 读取单个字符 |
| public int read(char cbuf[]) | 读取字符到指定的 char 数组中 |
| abstract public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) | 从 off 位置读取 len 长度的字符到 char 数组中 |
| public long skip(long n) | 跳过指定长度的字符数量 |
| public boolean ready() | 和上面的 available() 方法类似 |
| public boolean markSupported() | 判断当前流是否支持标记流 |
| public void mark(int readAheadLimit) | 标记读取位置,下次还可以从这里开始读取,使用前要看当前流是否支持,可以使用 markSupport() 方法判断 |
| public void reset() | 重置读取位置为上次 mark 标记的位置 |
| abstract public void close() | 关闭流释放相关资源 |
Writer 类
| 方法 | 方法介绍 |
|---|---|
| public void write(int c) | 写入一个字符 |
| public void write(char cbuf[]) | 写入一个字符数组 |
| abstract public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) | 从字符数组的 off 位置写入 len 数量的字符 |
| public void write(String str) | 写入一个字符串 |
| public void write(String str, int off, int len) | 从字符串的 off 位置写入 len 数量的字符 |
| public Writer append(CharSequence csq) | 追加吸入一个字符序列 |
| public Writer append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) | 追加写入一个字符序列的一部分,从 start 位置开始,end 位置结束 |
| public Writer append(char c) | 追加写入一个 16 位的字符 |
| abstract public void flush() | 强制刷新,将缓冲中的数据写入 |
| abstract public void close() | 关闭输出流,流被关闭后就不能再输出数据了 |
import java.io.*;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//readTest1();
//outToFile();
//inToSys();
//writeToFile();
//readBufferToSys();
//readToSys();
//defineEncode();
//getEncode();
//copyBuffer();
//copy2();
//copy3();
copy4();
}
public static void readTest1() throws IOException {
//字符流缓冲区 <---字符流 <-- 来源于标准输入(通过字符转换流转换)
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// char c;
// do {
// //读取输入流的一个字符
// c = (char) bf.read();
// System.out.println(c);
// }while (c != 'q');
//读取完整的一行
String s = bf.readLine();
System.out.println(s);
// /n /t /0
}
public static void outToFile() throws IOException {
byte[] b ={1,2,3,4,5};
/**
* D:\New-Java\dev\byte.txt
* D:\New-Java\dev\a.txt
* D:\New-Java\b.txt
* 绝对路径:就是文件在存储系统中的真实位置
* 相对路径:相对于某个基准目录的路径 ./ ../ /
* byte.txt ---> 访问a.txt a.txt
* byte.txt ---> 访问b.txt ../b.txt
*/
//文件字节输出流,输出到文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("").getAbsolutePath()+"/dev/byte.txt");
//写入二进制文件
fos.write(b);
//冲刷缓冲区
fos.flush();
//关闭资源
fos.close();
}
public static void inToSys() throws IOException {
//文件字节输入流读入到系统
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("D:\\New-Java\\dev\\byte.txt"));
int c;
//读取文件中的二进制信息
while ((c = fis.read()) != -1){
System.out.print(c +" ");
}
}
public static void writeToFile() throws IOException {
//字符流写入文件
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(new File("D:\\New-Java\\dev\\mono.txt"));
/**
* 两个方法一致,append可以直接把null作为字符写入,write如果写入null需要进行转化
*/
fw.write("学习不刻苦,不如卖红薯.");
fw.append("~~~~");
fw.append(null);
//fw.write(null);
fw.write("学习若刻苦,月薪一万五");
fw.flush();
System.out.println(fw.getEncoding());
fw.close();
}
public static void readBufferToSys() throws IOException {
//字符流读出文件
FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File("D:\\New-Java\\dev\\mono.txt"));
//将字符输入流加入输入流缓冲区
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(fr);
String str="";
while ((str=bf.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(str);
}
bf.close();
fr.close();
}
public static void readToSys() throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File("D:\\New-Java\\dev\\mono.txt"));
int c;
//不加人缓冲区就是一个字符一个字符的读取
while ((c = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) c);
}
}
public static void defineEncode() throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\New-Java\\dev\\a.txt"));
//指定写入文件内容的编码,字符输出流自行包装
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"GBK");
osw.write("hello,你好");
osw.flush();
System.out.println(osw.getEncoding());
osw.close();
fos.close();
}
public static void getEncode() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("D:\\New-Java\\dev\\a.txt"));
//指定读出文件的编码
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"GBK");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String str="";
while((str = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(str);
}
br.close();
isr.close();
fis.close();
}
public static void copyBuffer() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\New-Java\\dev\\周杰伦 - Mojito.flac");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("周杰伦 - Mojito.flac");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//记录长度
int len = 0;
//1kb
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//源文件读入
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){
//写入新文件
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
System.out.println("Time is "+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
bis.close();
fis.close();
bos.close();
fos.close();
}
public static void copy2() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\New-Java\\dev\\周杰伦 - Mojito.flac");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
//输出流不使用缓冲区
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("周杰伦 - Mojito.flac");
//记录长度
int len = 0;
//1kb
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//源文件读入
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){
//写入新文件
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
System.out.println("Time is "+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
bis.close();
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
public static void copy3() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\New-Java\\dev\\周杰伦 - Mojito.flac");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("周杰伦 - Mojito.flac");
//记录长度
int len = 0;
//1kb,缓冲区数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//源文件读入
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){
//写入新文件
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
System.out.println("Time is "+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
public static void copy4() throws IOException {
//完全不用缓冲区
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\New-Java\\dev\\周杰伦 - Mojito.flac");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("周杰伦 - Mojito.flac");
//记录长度
int len = 0;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//源文件读入
while ((len = fis.read()) != -1){
//写入新文件
fos.write(len);
}
System.out.println("Time is "+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
/**
* 使用缓冲区可以加速文件的处理
*/
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号