01numpy数组创建
Numpy是什么
Numpy是一个科学计算数据库,提供大量的科学计算相关的功能,比如数据统计,随机数的生成等。其提供的核心类型为多维数组类型(ndarray),支持大量的 维度数组与矩阵运算,numpy支持处理ndarray对象,提高程序的运算速度。
安装numpy库
在 Anaconda3中创建虚拟环境当中安装numpy的方式如下:
激活虚拟环境
activate 自己的虚拟环境名字
pip install numpy
[示例]测试我们安装的numpy是否成功
在VScode中新建一个jupyter文件,测试代码如下
import numpy as np
如果未发生报错,说明我们的numpy安装成功
下面总结一下安装过程中需要注意的问题
-
如何配置和创建虚拟环境,请参考我的博客下载和安装anaconda以及pytorch安装教程
-
在测试过程中,需要注意选择内核时,选择我们刚刚安装过
numpy的环境名,之后再输入测试代码 -
在测试代码中,我们将
numpy重命名为np,那么在该jupyter文件内,只要使用到了numpy,可以直接输入np,以节省重复工作量
创建数组
array函数的创建数组
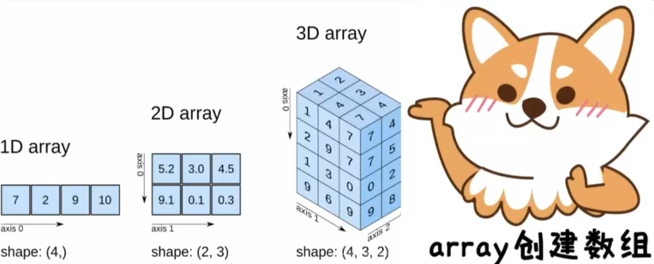
numpy模块的array函数可以生成多维数组,语法格式如下
numpy.array(object, dtype = None, copy = True, order = None, subok = False, ndmin = 0)
参数说明:
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| object | 数组或嵌套的数列 |
| dtype | 数组元素的数据类型,可选 |
| copy | 对象是否需要复制,可选 |
| order | 创建数组的样式,C为行方向,F为列方向,A为任意方向(默认) |
| subok | 默认返回一个与基类类型一致的数组 |
| ndmin | 指定生成数组的最小维度 |
实例
object 参数
一维数组
import numpy as np
my_array1 = np.array([7,2,9,10])
my_array1
# 输出:
> array([7,2,9,10])
二维数组
import numpy as np
my_array2 = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
my_array2
# 输出:
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])
三维数组
import numpy as np
my_array2 = np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]])
my_array2
# 输出:
array([[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]]])
dtype参数 - 指定数组中的类型
我们拿一维数组举例:
import numpy as np
my_array_int = np.array([7,2,9,10],dtype= np.int)
my_array_float = np.array([7,2,9,10],dtype= np.float)
print(my_array_int)
print(my_array_float)
# 输出:
> [ 7 2 9 10]
> [ 7. 2. 9. 10.]
经常用到的数据类型列举:
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| bool_ | 布尔型数据类型(True 或者 False) |
| int16 | 整数(-32768 to 32767) |
| int32 | 整数(-2147483648 to 2147483647) |
| int64 | 整数(-9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807) |
| float16 | 半精度浮点数,包括:1 个符号位,5 个指数位,10 个尾数位 |
| float32 | 单精度浮点数,包括:1 个符号位,8 个指数位,23 个尾数位 |
| float64 | 双精度浮点数,包括:1 个符号位,11 个指数位,52 个尾数位 |
ndmin参数 - 指定数组的维度大小
import numpy as np
a = np.array([7,2,9,10], ndmin = 2)
print (a)
# 输出
> [[ 7 2 9 10]]
arange函数创建数组
语法格式
numpy.arange(start,stop,step,dtype)
- 参数说明:
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| start | 起始值,默认为0 |
| stop | 终止值,不包含该值 |
| step | 步长,默认值为1 |
| dtype | 返回ndarray的数据类型,如果没有提供,则默认与输入数据的类型一致 |
实例
import numpy as np
# stop-终止值
np.arange(20)
# 输出
> array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,17, 18, 19])
# start-起始值,stop-终止值
np.arange(1,20) # [1,20),即左闭右开集合
# 输出:
> array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,18, 19])
# start-起始值,stop-终止值, step-步长
np.arange(1,20,2)
# 输出
> array([ 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19])
# start-起始值,stop-终止值, step-步长,dtype-输出数据类型
np.arange(1,20,2,float)
# 输出
> array([ 1., 3., 5., 7., 9., 11., 13., 15., 17., 19.])
随机数创建数组
numpy中的random模块包含了很多方法可以用来生成随机数
随机数 - random函数
-
返回
[0.0,1.0)范围的随机数 -
语法格式
numpy.random.random(size=None)
-
参数说明
size:输出数组的维度大小 -
实例
import numpy as np # 设置随机种子,保证每次随机生成的x,y值一致 # 这里的数值0,可以指定,并不一定非得是0 np.random.seed(0) # 一维数组,数组内包含五个元素 x = np.random.random(size=4) # 二维数组 y = np.random.random(size=(3,4)) print(x.shape) print(y.shape) # 输出 > (4,) > (3, 4) -
说明
np.random.seed(0):设置随机种子,保证每次随机生成的x,y值一致, 这里的数值0,可以指定,并不一定非得是0.shape:查看生成数组的维度大小
随机整数 - randint函数
- 返回整数随机数
- 语法格式
numpy.random.randint(low,high,size)
- 参数说明
low:起始值(若不指定,默认为0)high:终止值(不包括该值)size:输出数组的维度大小(若不指定,默认生成一个整数值)
- 实例
import numpy as np x = np.random.randint(5) y = np.random.randint(1,11) # 一维数组,数组中包含20个元素,元素的取值范围为[1,11) z1 = np.random.randint(1,11, size=20) # 二维数组 z2 = np.random.randint(1,21, size=(3,5)) print(z1) print(z1.shape) print(z2) print(z2.shape) # 输出 > [ 4 7 8 3 1 4 6 10 5 5 7 5 5 4 5 5 9 5 4 8] > (20,) > [[16 14 17 18 6] > [10 4 1 6 1] > [18 19 5 3 17]] > (3, 5)
正态分布 - randn函数
- 返回一个或一组样本,具有标准正态分布(期望值为0,方差为1)
- 语法格式
numpy.random.randn(d0,d1,...,dn)
- 参数说明
dn:表格每个维度
- 实例
# 一维数组,数组中包含3个元素 z1 = np.random.randn(3) #二维数组,维度为3行4列 z2 = np.random.randn(3,4) # 三维数组,维度为(2,3,4) z3 = np.random.randn(2,3,4) print("一维数组") print(z1) print("二维数组") print(z2) print("三维数组") print(z3) 一维数组 [0.97663904 0.3563664 0.70657317] 二维数组 [[ 0.01050002 1.78587049 0.12691209 0.40198936] [ 1.8831507 -1.34775906 -1.270485 0.96939671] [-1.17312341 1.94362119 -0.41361898 -0.74745481]] 三维数组 [[[ 1.92294203 1.48051479 1.86755896 0.90604466] [-0.86122569 1.91006495 -0.26800337 0.8024564 ] [ 0.94725197 -0.15501009 0.61407937 0.92220667]] [[ 0.37642553 -1.09940079 0.29823817 1.3263859 ] [-0.69456786 -0.14963454 -0.43515355 1.84926373] [ 0.67229476 0.40746184 -0.76991607 0.53924919]]]
正态分布变形 - normal函数
- 返回值为指定期望值和方差的正态分布
- 语法格式
numpy.random.normal(loc,scale,size)
- 参数说明
loc:期望值scale:方差size:数组维度大小
- 实例
import numpy as np z = np.random.normal(loc=2,scale=1,size=(4,3,2)) print(z) # 输出 [[[1.32566734 2.03183056] [1.36415392 2.67643329] [2.57659082 1.79170124]] [[2.39600671 0.90693849] [0.50874241 2.4393917 ] [2.1666735 2.63503144]] [[4.38314477 2.94447949] [1.08717777 3.11701629] [0.68409259 1.5384154 ]] [[1.93175839 3.71334272] [1.25524518 1.17356146] [1.90154748 1.33652171]]]
zeros函数创建数组
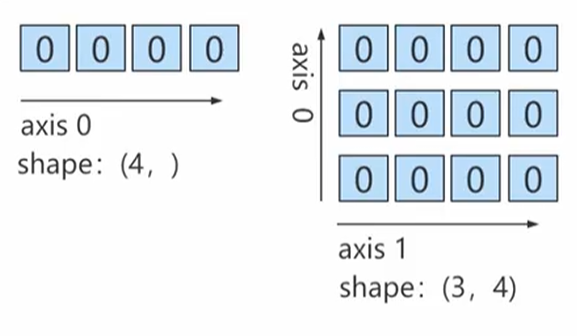
创建指定大小的数组,数组元素使用0来填充
- 语法格式
numpy.zeros(shape,dtype=float,order='C')
- 参数说明
shape:指定数组的维度大小dtype:元素0的数据类型,默认为floatorder:默认即可
- 实例
import numpy as np # 一维数组 np.zeros(10) # 指定维度为1维的,元素个数为20个 np.zeros(shape=(20)) # 指定参数dtype np.zeros(5,dtype=int) # 二维数组 np.zeros((3,4),dtype=int) zeros_like:根据传入的数组形状创建全为0的数组
【示例】zeros_like的使用
z = np.arange(4)
n3 = np.zeros_like(z)
ones函数创建数组
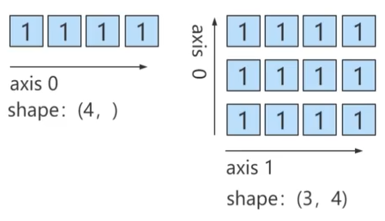
创建指定大小的数组,数组元素使用1来填充
- 语法格式
numpy.ones(shape,dtype=float,order='C')
- 参数说明
shape:指定数组的维度大小dtype:元素1的数据类型,默认为floatorder:默认即可
- 实例
import numpy as np # 一维数组 np.ones(4) # 指定维度为1维的,元素个数为10个 np.ones(shape=(10)) # 指定参数dtype np.ones(5,dtype=int) # 二维数组, 即3行4列 np.ones((3,4),dtype=int) ones_like:根据传入的数组形状创建全为1的数组
【示例】ones_like的使用
z = np.arange(4)
n3 = np.ones_like(z)
empty函数创建数组
创建一个指定形状(shape),数据类型(dtype)且未初始化的数组,每面的元素的值是之前内存中的值,之开辟空间,并不赋值
- 语法格式
numpy.empty(shape,dtype = float,order = 'C')
- 参数说明
shape:指定数组的维度大小dtype:默认为floatorder:默认即可
- 实例
import numpy as np # 一维数组 np.empty(4) # 指定维度为1维的,元素个数为16个 np.empty(shape=(16)) # 指定参数dtype np.empty(5,dtype=int) # 二维数组, 即3行4列 np.empty((3,4),dtype=int)
【示例】empty_like的使用
y = np.empty_like(10,dtype=int)
x = np.empty_like(z)
empty创建数组的使用
x = np.arange(5)
y = np.empty_like(x, dtype=int) # y 和 x 具有相同 shape 和 dtype
np.add(2, x, out=y)
- 说明
已知数组x,我们对数组x的每个值均加2,并将值传入数组y
full函数创建数组
- 返回值为某个指定的数组
- 语法格式
numpy.full(shape,fill_value)
- 参数说明
shape:指定数组的维度大小fill_value:指定的元素值fill_value元素来填充数组
- 实例
import numpy as np # 一维数组,数组中的元素个数为10,以18来填充 np.full(10,18) # 二维数组 np.full((3,5),11)
【示例】full_like函数的使用
a = np.arange(4,9)
np.full_like(a,10)
指定数据类型
np.full_like(a,10,dtype=int)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号