我的第一次Blog,我对本学期所学知识的总结
一.前言
我在大一下学期第一次接触java以及面向对象,我在上学期刚刚学习了c语言,所以了解一些基本语法,比如if,else等基本方法的使用,但是和c语言相比java还有很多新东西需要学习,比如类,继承和包等相关知识。所以我在刚刚学习的时候遇到了一些困难并且不太适应。以下是我对学习的知识点和题目的总结
二.学习总结
1.在学习中学习到并使用的知识点
(1)对象和类(class):
对象和类的关系:类为对象定义属性和行为,类是一个模板,用来定义对象的状态和行为。
类是由属性和方法组成,期中属性就是根据类创建对象的状态,比如一个圆的半径,颜色等等,方法是对象的行为,让对象完成一个动作,例如让圆返回他的周长,面积等等。
类可以分为三种:MVC
M:Model 实体类.模型类
V:View 展示类.接口类
C:Controller 控制类/业务类
类之间的关系:关联 依赖 聚集:聚合.组合 泛化 实现
耦合:类和类之间的紧密程度(追求弱耦合性)
内聚:类内部的紧密程度(追求强聚合性)
解耦:通过某种手段降低耦合性
类的七大设计原则:(目前只了解2个原则)
(1)单一职责原则:类或方法职责单一
(7)迪米特法则:不和陌生人说话,只和直接朋友说话,最少知识原则
(2)继承(extends):
继承使你可以定义一个通用的类(父类),之后通过继承得到一个更特殊的类(子类)
什么时候可以继承呢?
一般继承用于两种语境
(1)整体与部分之间的关系(不常用)
例如计算机和cpu的关系,我们一般采用聚集表示
因为继承的耦合性大于聚合的耦合性
(2)大类到小类的关系
例如人类和教师,学生,工人之间的关系
复制兼容性原则:可以将子类的对象赋给父类的引用
抽象类是专门做父类的,不能创建对象
2. 作业总结
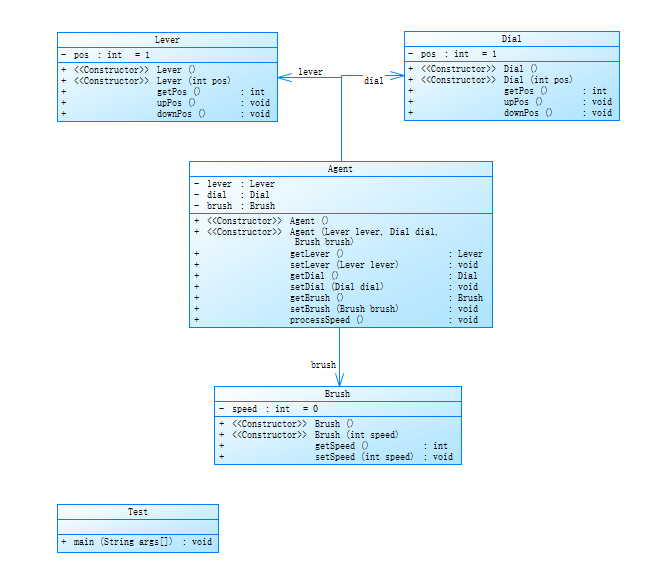
1. 雨刷器控制杆(简单的功能实现)
实现功能:
通过输入需要的功能对应的数字来完成此功能
1:升档位 2:将档位 3:升刻度 4:降刻度
零档位雨刷速度 0
间歇档位:刻度一速度:4
刻度二速度:6
刻度三速度:12
低速档位:30
高速档位:60
类图:
主函数代码:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = input.nextInt(); Lever lever = new Lever(); Dial dial = new Dial(); Brush brush = new Brush(); Agent agent = new Agent(lever,dial,brush); while(true) { switch(choice) { case 1:lever.upPos();break; //升档 case 2:lever.downPos();break; //降档 case 3:dial.upPos();break; //升刻度 case 4:dial.downPos();break; //降刻度 } agent.processSpeed(); System.out.println("Lever's pos is:" + lever.getPos()); System.out.println("Dial's pos is:" + dial.getPos()); System.out.println("Brush's speed is:" + brush.getSpeed()); choice = input.nextInt(); } } }
运行结果:
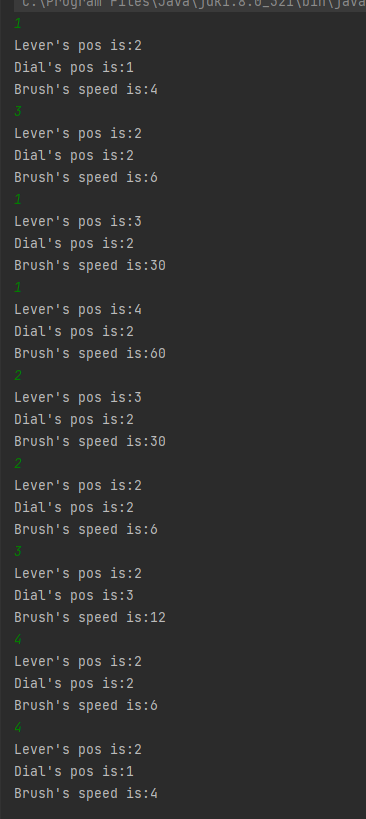
遇到的困难:
实现方法和逻辑的实现
再不发基本报错的情况下,犯了一些比较低级的错误,并且难以发现,
解决方法:
通过在编写程序之前先画类图实现方法和逻辑
通过idea的debug调试,推荐大家使用,非常的方便,可以观看运行过程中的每个变量的值,
缺点:此种写法只能完成最基本的功能实现,并且工作部分都在主函数里,耦合性太强,一个模块的修改会产生涟漪效应,其它模块也需要随之修改,由于这种原因模块的组合需要更多的经历和时间,导致代码无法复用,并且没有执行单一职责原则,代码质量较低,不符合面向对象的基本要求,为了改进有了雨刷2.0,
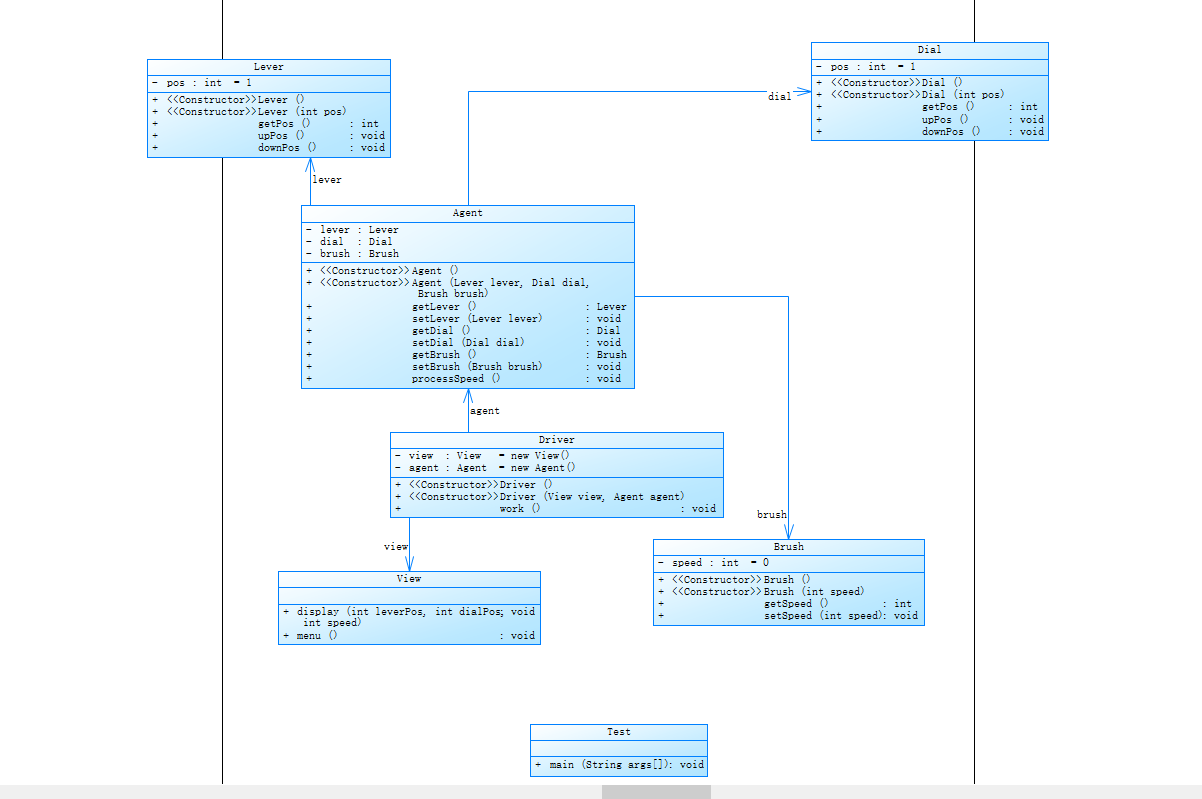
2.雨刷器控制杆(1.0降低耦合性)
实现功能:
通过输入需要的功能对应的数字来完成此功能
1:升档位 2:将档位 3:升刻度 4:降刻度 0:退出程序
零档位雨刷速度 0
间歇档位:刻度一速度:4
刻度二速度:6
刻度三速度:12
低速档位:30
高速档位:60
新增菜单功能
在1.0版本基础上进行扩展,基本功能保持不变
类图:
main代码:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Driver driver = new Driver(); driver.work(); } }
运行结果:
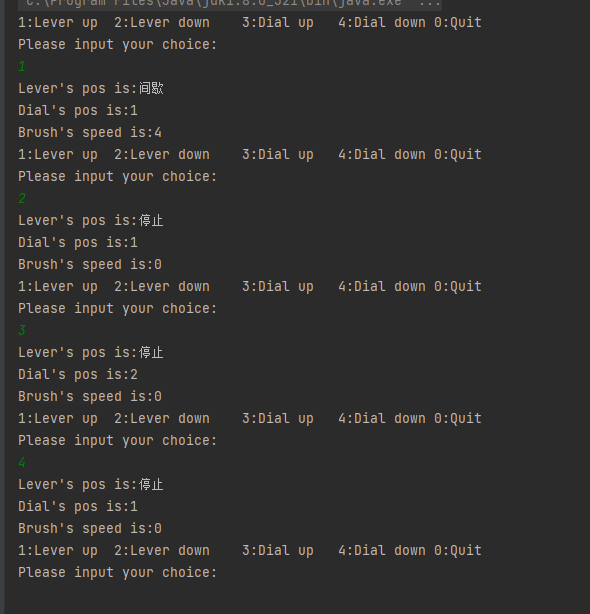
降低耦合性方法:通过创建Driver类来简化main方法使M和V解耦
缺点:暂时没有发现,这是通过学习完成的我觉得最优化的方法,如果发现缺点请读者指出
1和2的小总结
因为是在老师的一部分讲解后开始开始实现,所以没有遇见太多的困难,只遇到一些通过调试可以解决的小问题,所以接着往下看,下面是我的Pta题目,全部或大部分由自己完成,可以有更真实的困难,以及我的解决方法,和实践方法
3.日期类设计1.0(只有一个类,简单完成功能)
功能:
设计一个类DateUtil,该类有三个私有属性year、month、day(均为整型数),其中,year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 除了创建该类的构造方法、属性的getter及setter方法外,
public boolean checkInputValidity();//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法
public boolean isLeapYear(int year);//判断year是否为闰年
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n);//取得year-month-day的下n天日期
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n);//取得year-month-day的前n天日期
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date);//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后)
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date);//判断两个日期是否相等
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date);//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
public String showDate();//以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值
类图过于简单无法看出什么所以省略
困难:
方法的编写很难实现,逻辑错误
具体困难:
只能年跨年,没法月跨年,在十二月走到一月后年份没有重新判断,导致闰年判断错误
最开始我是先更改月份在调用月份减一的数组,在十二月回到一月后,1-1=0,导致数组里的数引用错误
解决方法:
依旧还是通过边写边调试的方法来寻找自己的逻辑错误
缺点:所有工作和方法都写在一个类里,完全不符合代码编写的基本要求,既没有做到断耦,也没有做到单一职责,所以后两道题是此题的升级版本2.1和2.2
4.日期类设计2.1(类里包含类在包含类)
功能:和1.0版本基本相同
类图:
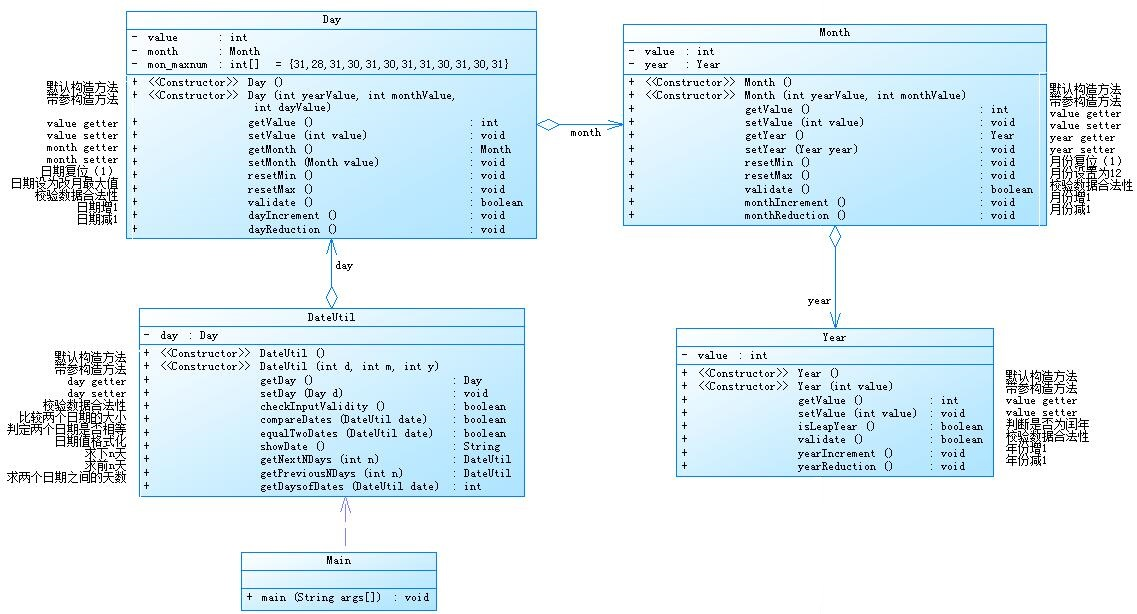
主函数:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day,month,year); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } // System.out.print(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " next " + m + " days is:"); date.getNextNDays(m); System.out.println(date.day.month.year.getValue()+"-"+date.day.month.getValue()+"-"+date.day.getValue()); } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method int n = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day,month,year); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } n = input.nextInt(); if (n < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } // System.out.print( // year +"-"+month+"-"+day +" previous " + n + " days is:"); date.getPreviousNDays(n); System.out.println(date.day.month.year.getValue()+"-"+date.day.month.getValue()+"-"+date.day.getValue()); } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(day,month,year); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherDay,anotherMonth,anotherYear); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println(fromDate.getDsysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } }
因为功能没有变化,所以困难和1.0版本相同,解决方法也类似
缺点:相较于于1.0版本来说主函数类的功能减少了很多,但是年月日三个类的耦合性还是很高,一个模块的修改会产生涟漪效应,其它模块也需要随之修改,由于这种原因模块的组合需要更多的经历和时间,导致代码无法复用,并且没有执行单一职责原则,代码质量较低,不符合面向对象的基本要求,所以下一道题我们有了2.2版本
5.日期类设计(降低耦合性)
检测输入的年、月、日是否合法
判断year是否为闰年
/取得year-month-day的下n天日期
/取得year-month-day的前n天日期
/比较当前日期与date的大小(先后)
/判断两个日期是否相等
/求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
/以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值
功能基本不变
类图:
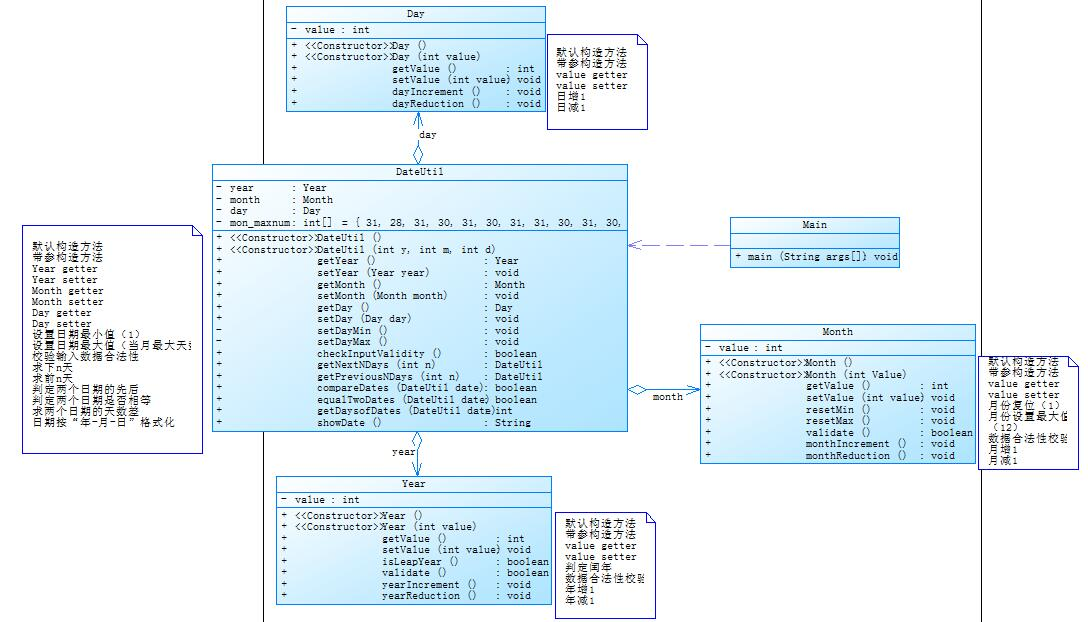
主函数代码:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(); date.year.setValue(year); date.month.setValue(month); date.day.setValue(day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " next " + m + " days is:"); date.getNextNDays(m); System.out.println(date.year.getValue()+"-"+date.month.getValue()+"-"+date.day.getValue()); } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method int n = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(); date.year.setValue(year); date.month.setValue(month); date.day.setValue(day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } n = input.nextInt(); if (n < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print( year +"-"+month+"-"+day +" previous " + n + " days is:"); date.getPreviousNDays(n); System.out.println(date.year.getValue()+"-"+date.month.getValue()+"-"+date.day.getValue()); } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(); fromDate.year.setValue(year); fromDate.month.setValue(month); fromDate.day.setValue(day); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(); toDate.year.setValue(anotherYear); toDate.month.setValue(anotherMonth); toDate.day.setValue(anotherDay); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("The days between " + year +"-"+month+"-"+day + " and " + anotherYear +"-"+anotherMonth+"-"+anotherDay + " are:" + fromDate.getDsysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } }
因为功能没有变化,所以困难和1.0版本相同,解决方法也类似
与前两种方法相比较,通过DateUtil类的建立,断了年月日之间的耦合性,代码的复用性也随之提高
缺点:此代码和控制杆相比的断耦合方式相似,但是工作部分还是在main函数中,main函数的内容过多过于繁琐
总结:
1.bug的主要来源:
自己的疏忽,发生一些细节的小问题,比如字符数字没有加‘ ’,这也是我起初没有注意最困扰我的问题,导致判断不通过
没有认真读题导致题意理解错误或有偏差
2.学习到了什么:
除了类和继承的相关知识点,在其它题目集中学会了使用正则表达式,字符串的分割,在做最近一次的作业中我起初是使用字符串的分割,但是没法实现要求的全部功能,后来学习了正则表达式来解决这个问题,在正则表达式的使用时也会遇到很多问题,需要的形式自己没法正确表达出来,只能通过不断的调试来寻找自己需要的表达式,在课堂上老师也是教会了我很多,比如MVC,耦合性,聚合性,类之间的关系,以及断耦和降低耦合度的方法,还有很多基本概念也是通过网课学习
3.心得体会:
这是我第一次接触java这门语言,也是我第一次写学习总结,总而言之这种总结方法对我来说起到很大的作用,这是我第一次写学习总结,我认为在梳理过后我对知识在脑海里梳理的更加清晰,有助于对这些知识点的再次使用,这也是我第一次编写博客,所以有很多表达不清楚的地方,我因为过于追求pta的分数,所以我很多时间都花在了题目集上,导致自己没有太多时间来编写学习总结和博客,所以我会在下次编写中进行优化,尽可能写出更好的学习总结以及博客,也是很感谢老师在课堂上和课堂下做出的贡献,网课的购买以及对我们免费的开放让我甚是感动。
关于Java,这是我在第一次学习之后的第一次学习总结,我对java学习还是不够,所以还需要继续在课上课下继续努力,继续在优秀的代码中学习,多看教程,多培养自己的逻辑
4.小建议:
因为我是一个新手,所以还不能给出太多的权威的建议,但是我还是总结出了一些经验,在语法通关的情况下,我们要尽可能去提升自己的逻辑推理能力,因为只有这样才能去解决生活中的实际问题,逻辑能力就像基本功,所以我们的数学专业在这个方面就体现了很强的重要性,再有就是培养自己的兴趣,因为我能感觉到我只有在兴趣高涨的时候才能写进去代码,坐得住板凳才能写得出好代码,多去实践,很多人为了快速学会java而不去时间,不要把所有时间都放在学上,快餐式学习不可取,更多的是去自己编写代码,从而学好java






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号