牛客刷题-Day21
牛客刷题-Day21
今日刷题:\(1031-1035\)
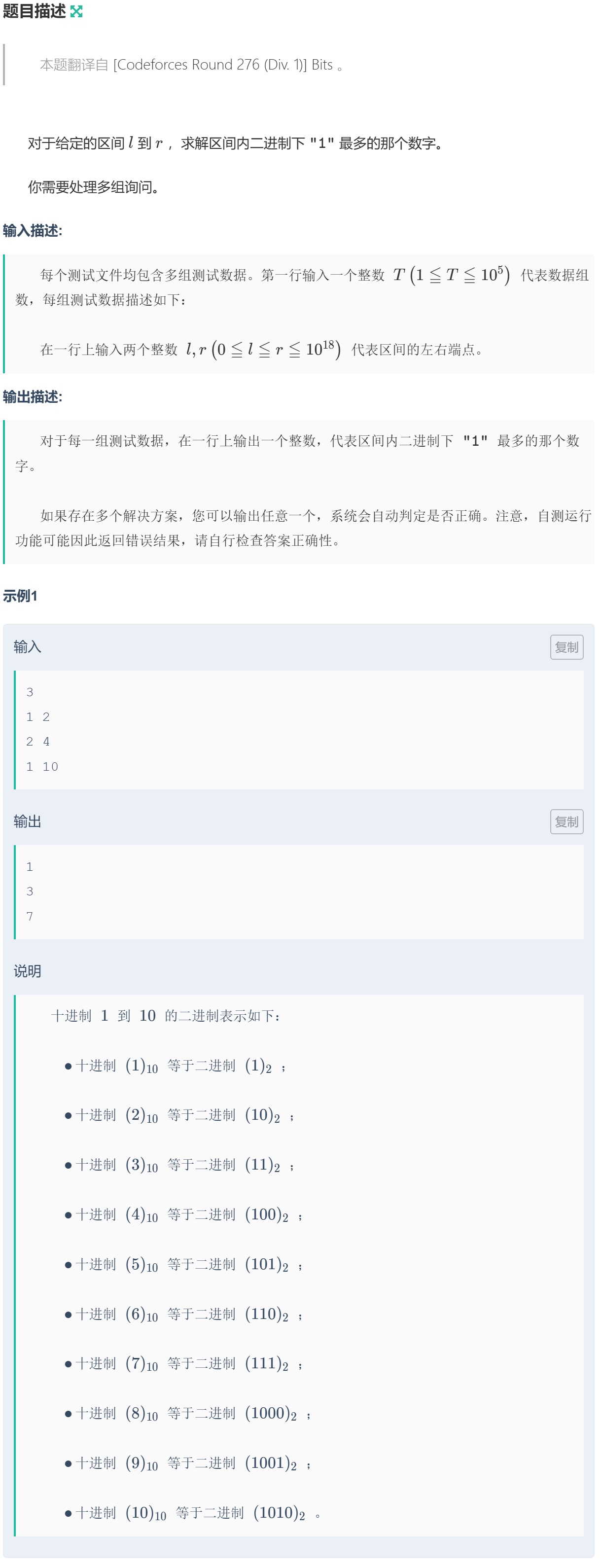
1031 贪心 · 例10-Bits
解题思路
贪心。假设开始每一位都是 \(1\),从高位 \(i\) 开始枚举,如果当前数 \(>r\),且减去 \(1<<i\) 后仍 \(>=l\),就减 \(1<<i\)。当当前数在 \([l,r]\) 之间时,输出。
因为从高位开始减,所以保证当前数是最小的。
参考:Codeforces Round #276 (Div. 1) A. Bits
C++ 代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 70;
int T;
LL bit[N];
int main() {
scanf("%d", &T);
bit[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 60; i++)
bit[i] = bit[i - 1] * 2;
while (T--) {
LL l, r;
scanf("%lld%lld", &l, &r);
LL res = ((LL) 1 << 61) - 1;
for (int i = 60; i >= 0; i--) {
if (res > r && res - bit[i] >= l)
res -= bit[i];
if (res >= l && res <= r)
break;
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
return 0;
}
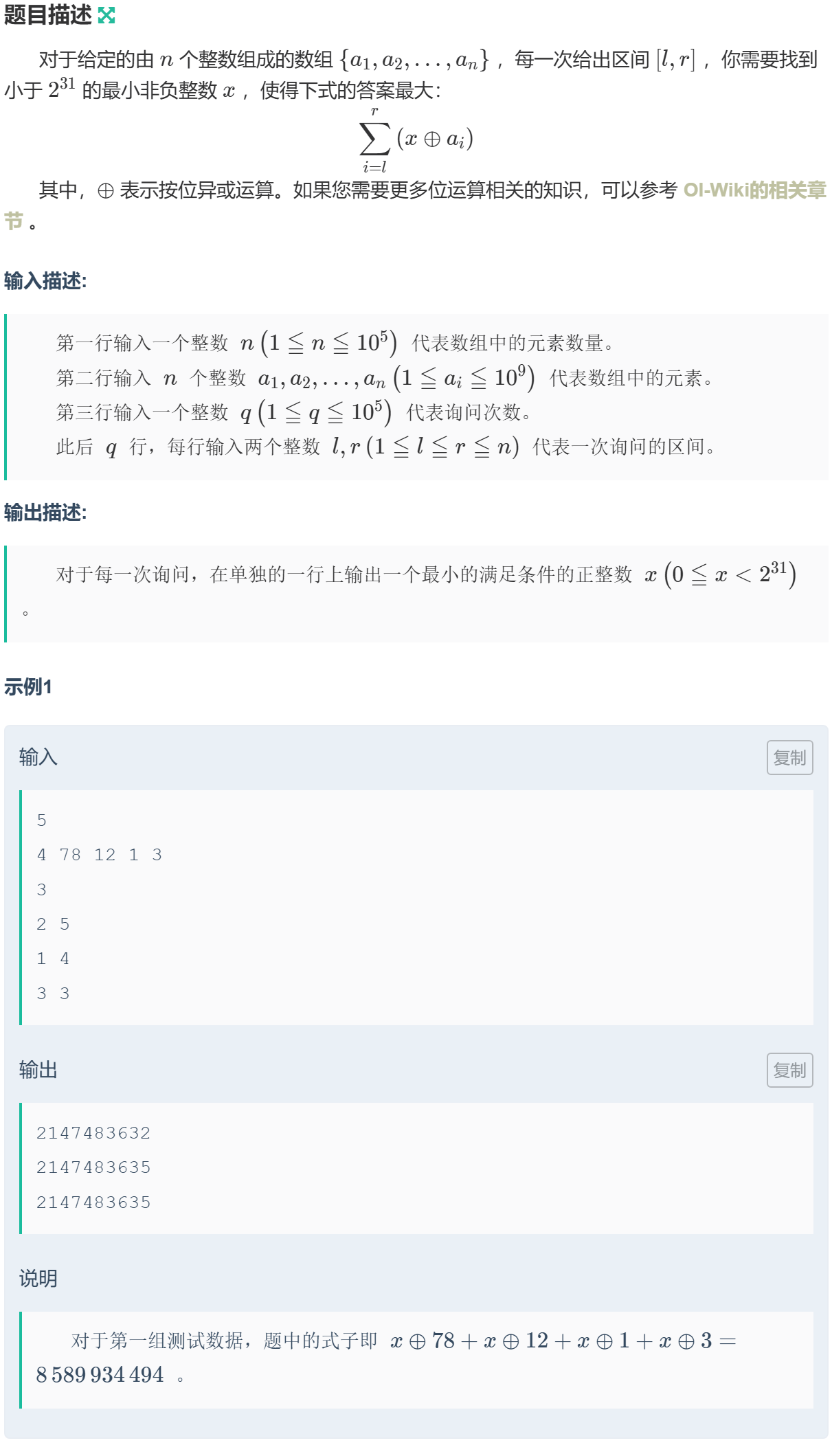
1032 贪心 · 例11-毒瘤xor
解题思路
异或运算每一位是独立的,因此,对于每一位,统计该区间内所有数在该位的 \(0\) 和 \(1\) 的个数。
因为要在异或操作之后保留更多的 \(1\),因此对于 \(x\) 的对应位,如果 \(1\) 多则取 \(0\),反之取 \(1\)。
C++ 代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = 35;
typedef long long LL;
int n, q;
int a[N], s[N][M]; // s[i][j] 表示前 i 个数第 j 位 1 的个数
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= 30; j++)
s[i][j] = s[i - 1][j] + ((a[i] >> j) & 1);
}
scanf("%d", &q);
while (q--) {
int l, r, res = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
for (int j = 0; j <= 30; j++) {
if (2 * (s[r][j] - s[l - 1][j]) <= r - l + 1)
res |= 1 << j;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
}
return 0;
}
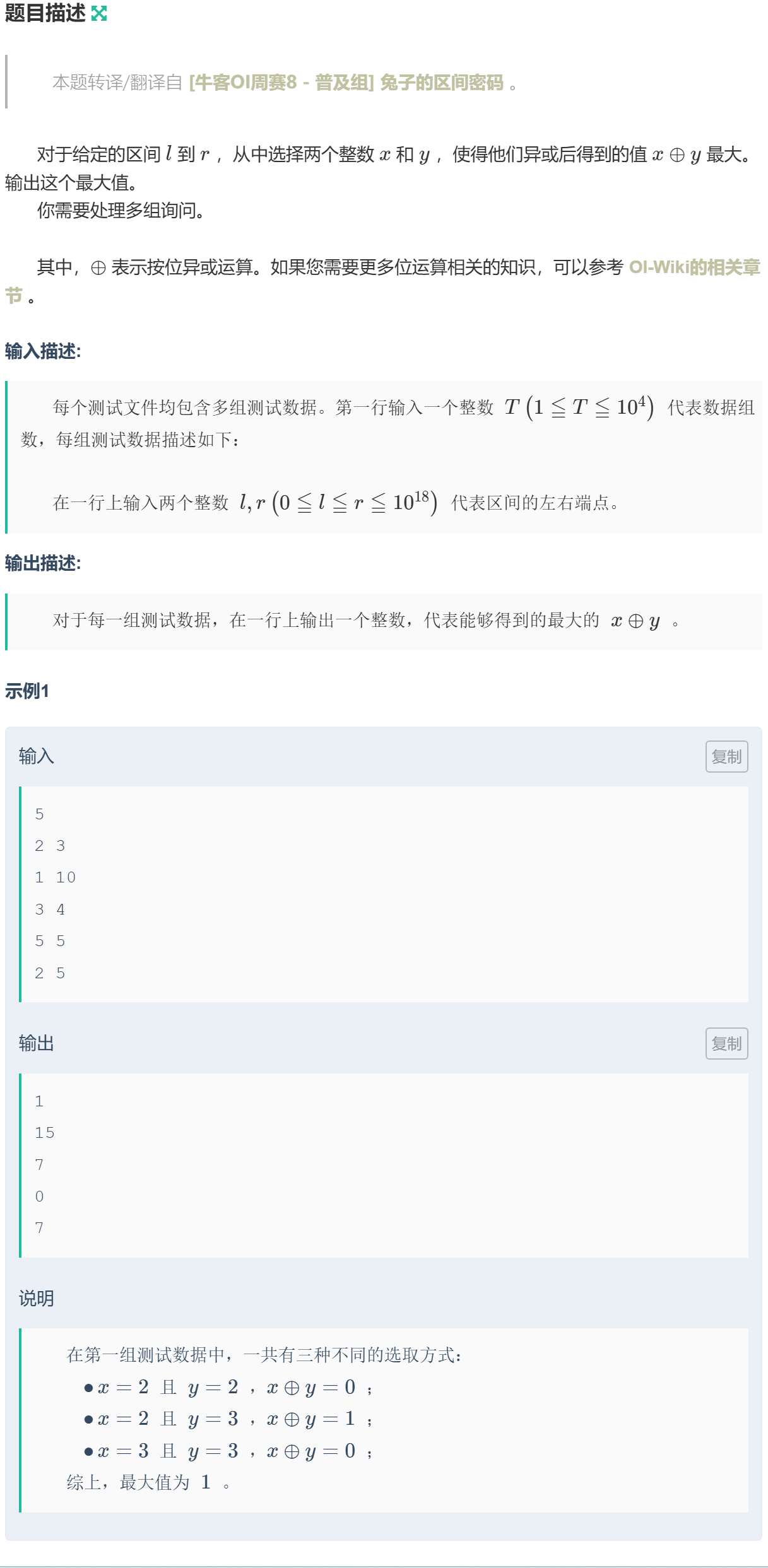
1033 贪心 · 例12-兔子的区间密码
解题思路
对于区间端点 \(l\) 和 \(r\),按位来遍历,如果高位都相同,那么高位是无法改变的,继续遍历,只要某位开始不同,那么异或的结果就是这一位往低位都可以变为全 \(1\)。
假设前 \(k\) 位相同,第 \(k+1\) 位不同。
注意:第 \(k+1\) 位不同,则 \(l\) 的 \(k+1\) 位必然为 \(0\),\(r\) 的 \(k+1\) 位必然为 \(1\)。如果反之,则 \(l\) 为 \(xxx1aaa\),\(r\) 为 \(xxx0bbb\),很明显 \(l>r\)。
\(l\) 的从 \(k+2\) 位到最后都可以取到 \(1\),这样得到的数必然大于等于 \(l\);\(r\) 的从 \(k+2\) 位到最后都可以取到 \(0\),这样得到的数必然小于等于 \(r\)。这样得到的两个数存在 \(k+1\) 到最低位都不同,异或之后值最大。
C++ 代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int T;
void solve(LL l, LL r) {
for (int i = 63; i >= 0; i--) {
if ((l >> i) == (r >> i))
continue;
printf("%lld\n", ((LL) 1 << (i + 1)) - 1);
return;
}
printf("0\n");
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
LL l, r;
scanf("%lld%lld", &l, &r);
solve(l ,r);
}
return 0;
}
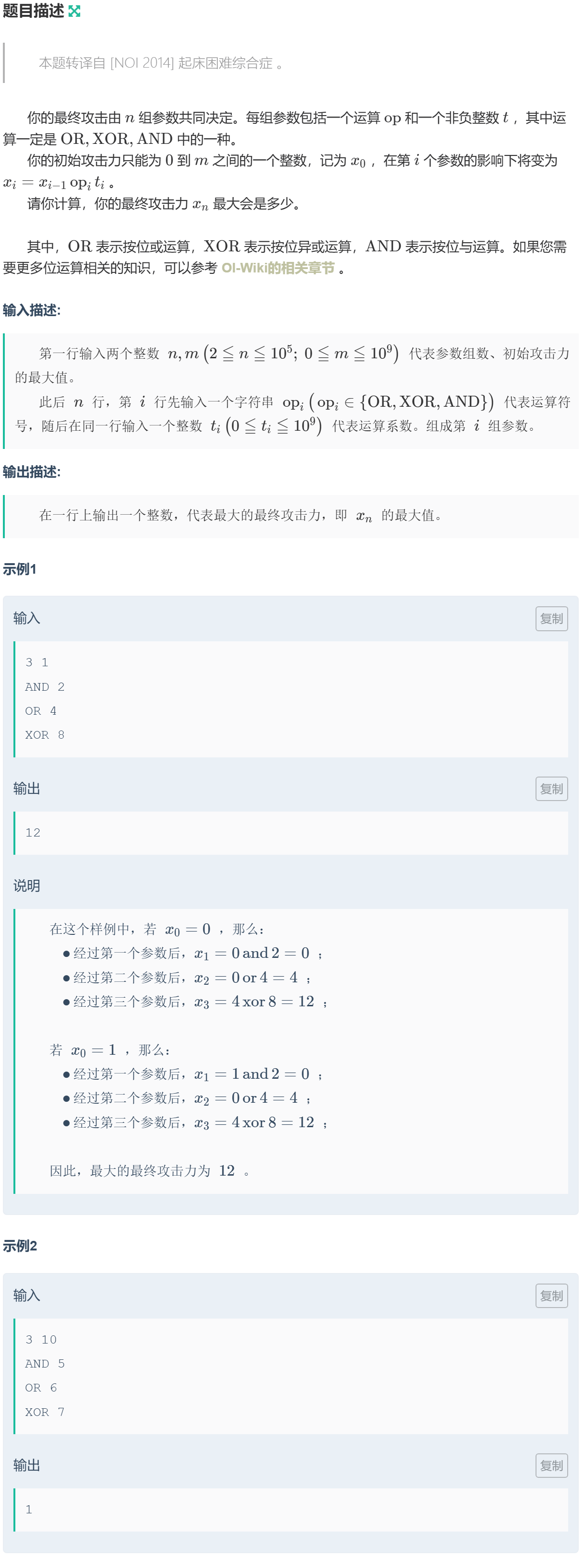
1034 贪心 · 例13-起床困难综合征
解题思路
取 \(a=0\) 和 \(b=-1\) 进行一边操作,这样就可以得到每一位在初始为 \(0\) 或者 \(1\) 经过操作得到的结果。
因为初始攻击力要在 \([0,m]\) 之间,因此每一位可以从 \(0\) 经过操作得到 \(1\),则该位优先取 \(0\);否则取 \(1\),并计算剩余可用值(范围限制)。
因为要保证答案最大,因此从高位开始遍历。
for (int j = 29; j >= 0; j--) {
if ((a >> j) & 1)
res += (1 << j);
else if ((b >> j) & 1 && ((1 << j) <= m))
res += (1 << j), m -= (1 << j);
}
C++ 代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
int n, m, t;
string op;
int main() {
int a = 0, b = -1;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // 每一位为 0 或者 1 进行操作
cin >> op >> t;
if (op == "OR") {
a |= t, b |= t;
} else if (op == "XOR") {
a ^= t, b ^= t;
} else {
a &= t, b &= t;
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int j = 29; j >= 0; j--) {
if ((a >> j) & 1)
res += (1 << j);
else if ((b >> j) & 1 && ((1 << j) <= m))
res += (1 << j), m -= (1 << j);
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
1035 习题-[NOIP2017]时间复杂度
解题思路
首先判断循环是否可执行:
- 如果 \(x=n\):\(y=n\),为 \(O(1)\);\(y\) 为常数,无法执行;
- 如果 \(y=n\):\(x\) 为常数,为 \(O(n^1)\);
- 如果 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 都为常数,且 \(x\le y\),为 \(O(1)\)。
当输入为循环开始语句,判断变量是否已声明,已声明为 \(ERR\),否则(当前循环判断值为 \(t\)):
- 栈为空:当前不存在嵌套循环,上述判断的值直接入栈,可更新答案 \(res=max(res,t)\);
- 栈不空:当前存在嵌套循环,判断外层循环是否可执行,若外层不可执行或者当前循环不可执行,则 \(-1\) 入栈;否则 \(top+t\) 入栈,可更新答案 \(res=max(res,t+top)\)。
当输入为循环结束语句:
- 栈为空:不合法。
- 栈不空:栈顶弹出,变量弹出,一个循环结束。
C++ 代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int T, L;
string complexity, loop[N];
int get(string x, string y) {
if (x == "n" && y == "n") return 0;
else if (x == "n") return -1;
else if (y == "n") return 1;
else if (stoi(x) <= stoi(y)) return 0;
else return -1;
}
string calc(int L) {
int res = 0;
stack<int> stk;
string vars;
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
auto &s = loop[i];
if (s[0] == 'F') {
char var[2], x[4], y[4];
sscanf(s.c_str(), "F %s %s %s", var, x, y);
if (vars.find(var) != -1)
return "ERR";
vars += var;
int t = get(x, y);
if (stk.empty()) {
stk.push(t);
res = max(res, t);
} else {
int top = stk.top();
if (top == -1 || t == -1)
stk.push(-1);
else {
stk.push(top + t);
res = max(res, top + t);
}
}
} else {
if (stk.empty())
return "ERR";
stk.pop();
vars.pop_back();
}
}
if (stk.size()) return "ERR";
if (!res) return "O(1)";
return "O(n^" + to_string(res) + ")";
}
int main() {
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
cin >> L >> complexity;
getchar();
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
getline(cin, loop[i]);
string res = calc(L);
if (res == "ERR")
cout << res << endl;
else if (res == complexity)
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
本文来自博客园,作者:Cocoicobird,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Cocoicobird/p/19210995

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号