四则运算——结对项目报告
写在前面:这次的作业我们是用Web做的,搭服务器的部分已经完成,老师们可以通过这个链接查看我们的页面http://47.93.197.5:8080/chenf/。附加功能1我们加了英语这个语种,其他的基础功能已经全部实现。这次的结对作业完成得很艰难,但是也学到了很多,在这里想特别感谢自己的队友陈芳,以及互帮互助搭建服务器的马玲、王雪小组。
一、项目地址
二、PSP(1)
| PSP | 任务内容 | 计划共完成需要的时间(min) | 实际完成需要的时间(min) | ||
| Planning | 计划 | 1*60 | |||
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间,并规划大致工作步骤 | 1*60 | |||
| Development | 开发 |
|
|||
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 5*60 | |||
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 2*60 | |||
| Design Review | 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
|
|||
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 1*60 | |||
| Design | 具体设计 | 3*60 | |||
| Coding | 具体编码 | 26*60 | |||
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 4*60 | |||
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 8*60 | |||
| Reporting | 报告 | 7*60 | |||
| Test Report | 测试报告 |
|
|||
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 30 | |||
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 1*60 |
三、接口设计
(1)Information Hiding(信息隐藏)

我们在这次的作业中在不同层次上利用到了信息隐藏,例如用具名常量代替字面常量、数据类型的创建,当然最重要的还是对接口的设计,我们用层次分明的几个包分别代表不同模块的代码,其中dao层中设计的Algorithm接口将所有的四则运算生成功能中的方法封装起来,用AlgorithmImpl类来实现该接口。
(2)Interface Design(接口设计)
这里引用一篇在网上找到的博文:http://www.cnblogs.com/zfc2201/p/3423370.html
其中接口设计包含六大原则,因为我们这个项目对接口的设计运用的还不算很多很复杂,因此我们对接口的实现主要是满足单一职责原则和里氏替换原则。
(3)Loose Couling(松耦合)
耦合:一个软件结构内不同模块之间互连程度的度量
(转)对于低耦合的理解是:
一个完整的系统,模块与模块之间,尽可能的使其独立存在。也就是说,让每个模块,尽可能的独立完成某个特定的子功能。模块与模块之间的接口,尽量的少而简单。如果某两个模块间的关系比较复杂的话,最好首先考虑进一步的模块划分。这样有利于修改和组合。
在我们的项目中,我们很好地保证了耦合度的松紧,每个模块之间的联系都很清晰且元素的紧密度不会导致有元素错误时每个模块都要跟着改动。
四、计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
由于我跟我的搭档陈芳都在工作室学习过有关JAVAWEB的后台开发,我们对于接口模块的设计都是工作室学习到的同一个结构层次,在结对项目过程中,我们的后台代码选择分三个包,分别是dao,servlet,util,当然最后还有一个测试类。dao层写的是生成四则运算的代码,其中包含一个接口类和一个实现类,里面的方法包括(1)algorithm(不包含括号的四则运算);(2)BracketsAlgo(包含括号的四则运算);(3)getNum(求最大公因数);(4)priority(判断优先级);(5)symbol(判断符号)。其中前两个方法是dao层算法的主体核心,保证实现五个参数的功能。
五、计算模块接口部分的性能改进
在接口的性能改进上,我大概用了4个小时,我的思路主要就是尽量缩短生成特定要求的运算式的时间。比如说:我以前在判断条件时,如果产生的不符合要求,则重新产生随机数,直至符合要求为止。这样有时就会一直随机产生,需要好久可能才产生一个符合要求的运算式。因此,在改进时,我主要是将不符合要求的直接舍弃,重新生成。这样会在一定程度上节约使劲按并且不会产生死循环。
关于性能分析图,我以前没有接触过,因此我上网搜了一下,发现关于java的性能分析工具在jdk的bin目录直接有,只需按自己的需求下载相应的插件即可。我看了一下博客,关于java VisualVM的推荐使用最多。关于这个工具的使用方法,推荐这篇博客【Java VisualVM】使用 VisualVM 进行性能分析及调优,是我看过比较详细比较详细的一篇啦。
部分截图:


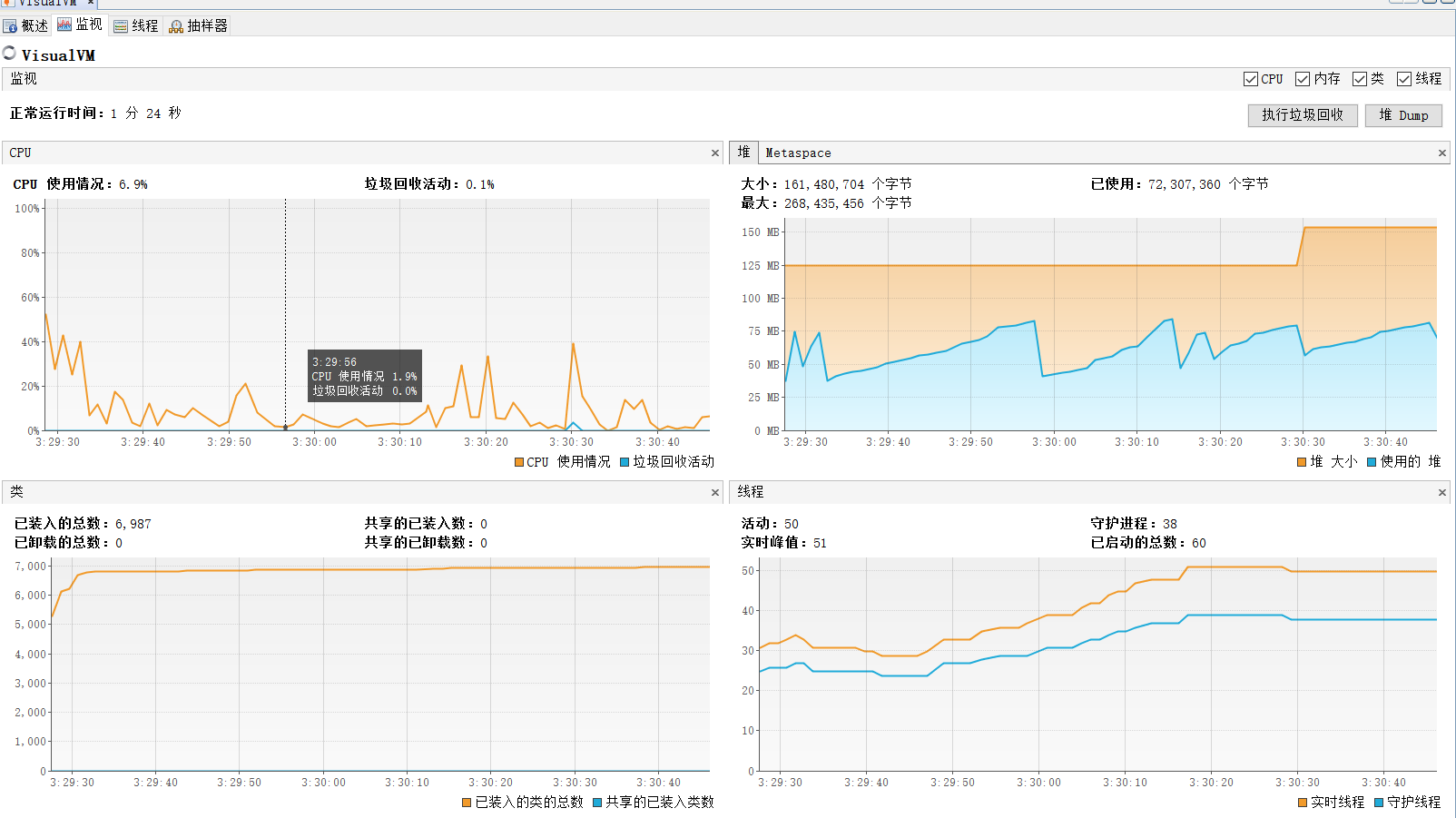
关于程序中消耗最大的函数就是 生成不产生括号,运算符大于一位的符合要求的运算式 的函数。
六、计算模块部分单元测试展示
以下是对dao中所有方法的测试代码:
package com.dao; import com.dao.impl.AlgorithmImpl; import org.junit.Test; import static org.junit.Assert.*; /** * PairProgram2 * Created by TestUser on 2018/4/8. */ public class AlgorithmTest { @Test public void algorithm() throws Exception { Algorithm algorithm =new AlgorithmImpl(); for(int i =0;i<10;i++){ System.out.println(algorithm.algorithm(5,100,7,1)); System.out.println(algorithm.algorithm(1,100,1,1)); System.out.println(algorithm.algorithm(10,200,1,2)); System.out.println(algorithm.algorithm(10,100,2,2)); System.out.println(algorithm.algorithm(10,200,2,1)); System.out.println(algorithm.algorithm(5,200,4,1)); System.out.println(algorithm.algorithm(1,100,4,2)); } } @Test public void bracketsAlgo() throws Exception { Algorithm algorithm =new AlgorithmImpl(); for(int i =0;i<10;i++){ System.out.println(algorithm.BracketsAlgo(10,100,1,1)); System.out.println(algorithm.BracketsAlgo(10,100,1,2)); System.out.println(algorithm.BracketsAlgo(1,100,5,1)); // System.out.println(algorithm.BracketsAlgo(5,100,1,2)); // System.out.println(algorithm.BracketsAlgo(5,100,5,1)); System.out.println(algorithm.BracketsAlgo(5,200,4,2)); // System.out.println(algorithm.BracketsAlgo(5,200,2,1)); } } @Test public void getNum() throws Exception { Algorithm algorithm =new AlgorithmImpl(); System.out.println(algorithm.getNum(1,2)); System.out.println(algorithm.getNum(4,2)); System.out.println(algorithm.getNum(24,3)); } @Test public void priority() throws Exception { Algorithm algorithm =new AlgorithmImpl(); System.out.println(algorithm.priority(1)); System.out.println(algorithm.priority(2)); } @Test public void symbol() throws Exception { Algorithm algorithm =new AlgorithmImpl(); System.out.println(algorithm.symbol(1)); System.out.println(algorithm.symbol(2)); System.out.println(algorithm.symbol(3)); System.out.println(algorithm.symbol(0)); } }
以下是五个方法的测试覆盖率:
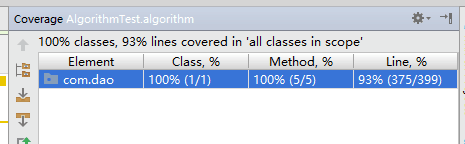
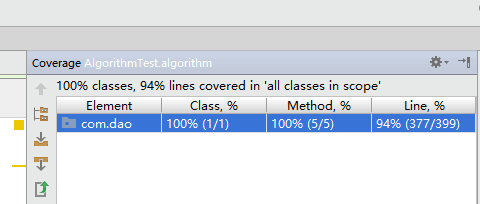
七、计算模块部分异常处理说明
(1)是否含有“-c”判断有无乘除

(2)是否生成题目的数值上下限是否为上限1~100,下限50~1000
(3)判断“-o”参数输入是否有误

(4)判断result.txt文件创建是否成功

(5)判断前台获取的参数是否正确
(6)判断输入参数是否有误

以下是异常类的设计:

八、界面模块的详细设计过程
前端的页面展示我们是主用jsp写的,分为六个jsp页面,以下是大概的页面结构:
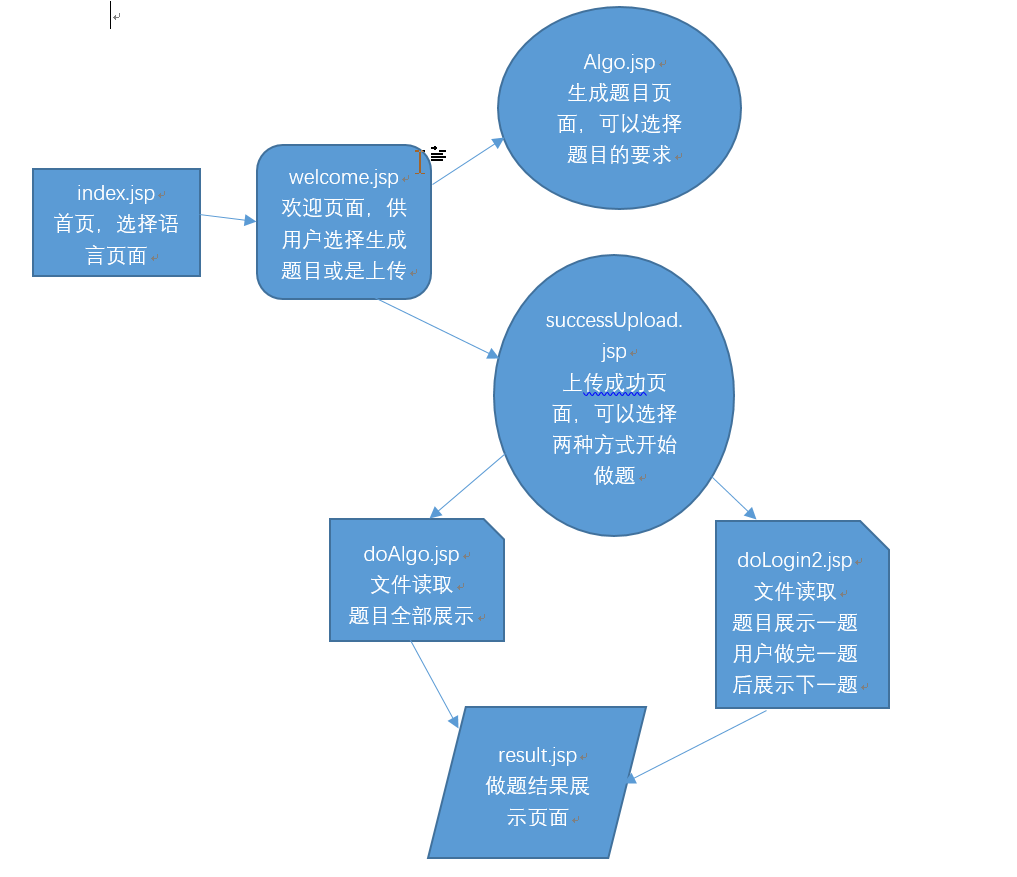
下面是部分代码的展示:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>欢迎页面</title>
<style type="text/css">
body{
background-image: url("../../ti432mg.jpg");
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="margin-top: 130px;margin-left: 300px">
<c:if test="${language==1}">
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/Algo?state=Algo1" ><button><font size="4" >题目生成</font></button> </a>
<br><br>
<font size="5" ><strong>OR</strong></font><br><br>
<table border="1" >
<tr>
<td>
<button><font size="4" >上传文件</font></button>
</td>
<td>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/upTitle?state=up" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
<input type="file" name="myfile" value="选择文件"/><br/><br>
<input type="submit" size="3"/>
</form>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</c:if>
</div>
<div style="margin-top: 130px;margin-left: 300px">
<c:if test="${language==2}">
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/Algo?state=Algo1"><button><font size="4" >Subject generated</font></button> </a>
<br><br>
<font size="5" ><strong>OR</strong></font><br><br>
<table border="1" >
<tr>
<td>
<button><font size="4" >Files Upload</font></button>
</td>
<td>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/upTitle?state=up" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
<input type="file" id="browsefile" style="visibility:hidden" name="file" onchange=filepath.value=this.value ><br>
<input type="textfield" id="filepath">
<input type="button" id="filebutton" value="Select a File" onclick="browsefile.click()"><br/><br>
<input type="submit" value="submit" />
</form>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</c:if>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>做题</title>
<style type="text/css">
body{
background-image: url("../../ti432mg.jpg");
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<table border="1" style="margin-top: 200px">
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/upTitle?state=begin2" method="post">
<c:forEach items="${list}" var="algo" varStatus="status">
<c:if test="${status.index+1==i}">
<tr>
<td>
${count}/${i}
</td>
<td>
${algo} = <input type="text" value="" name="${i}.2" style="width:50px;" required="required" onkeyup="(this.v=function(){this.value=this.value.replace(/[^0-9-]+/,'');}).call(this)" onblur="this.v();">
</td>
<td hidden><input type="text" value="${algo}" name="${i}.1" style="width:50px;" ></td>
<td hidden><input type="text" value="${i}" name="i" style="width:50px;" ></td>
<td hidden><input type="text" value="${right}" name="right" style="width:50px;" ></td>
<td>
<c:if test="${i==count}">
<c:if test="${language==1}">
<input type="submit" value="结束做题">
</c:if>
<c:if test="${language==2}">
<input type="submit" value="The end of the problem">
</c:if>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${i<count}">
<c:if test="${language==1}">
<input type="submit" value="下一题">
</c:if>
<c:if test="${language==2}">
<input type="submit" value="Next question">
</c:if>
</c:if>
</td>
</tr>
</c:if>
</c:forEach>
<c:forEach items="${titleResult}" var="Tresult" varStatus="status">
<tr hidden >
<td hidden><input type="text" value="${Tresult}" name="${status.index}.5" style="width:50px;" ></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
<c:forEach items="${rightNum}" var="algo" varStatus="status">
<tr hidden >
<td hidden><input type="text" value="${algo}" name="${status.index}.6" style="width:50px;" ></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</form>
</table>
</center>
</body>
</html>
九、界面模块与计算模块的对接
通过两个Servlet:AlgorithmServlet和UploadTitleServlet,以及如下的变量定义,我们可以实现前后台的代码连接和前台页面的跳转。
public class WebContents { public static final String Algorithm = "/WEB-INF/views/Algo.jsp"; public static final String WELCOME = "/WEB-INF/views/welcome.jsp"; public static final String DOALGO ="/WEB-INF/views/doAlgo.jsp"; public static final String DOALGO2 ="/WEB-INF/views/doLogin2.jsp"; public static final String RESULT="/WEB-INF/views/result.jsp"; public static final String SSUCCESSUPLOAD ="/WEB-INF/views/successUpload.jsp"; }
以下是部分实现前后台功能的连接代码(三张不同页面的截图):
![]()

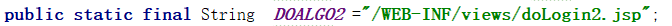
十、结对过程
这次结对编程我们主要在工作室进行,虽然常常遇到bug和一些功能的实现问题,但是我们在一起讨论并解决的过程还是很有作用和意义的。昨天因为测试率的问题忙了好久,两个人都精疲力竭,但是我们还是坚持下来把它解决了。
放几张图片吧!



十一、结对编程的优缺点
我认为结对编程的优点主要是体现在两个人能交流并讨论项目的内容,可以分享展示自己对项目的看法,可以从对方的身上学到不同的东西,可以取长补短。在项目遇到问题,代码遇到bug时,两个人的力量也比一个人要强,两个人能注意到不同的问题点,对于问题的解决方式也会有不同的想法,能够更高效率地解决问题、完成任务。当然,结对编程也会有它的缺点,但是在我们的编程中,我们的合作和配合还是很令人满意的,结对编程的缺点可能有:两个人的工作方式不同,可能在工作时会被对方所影响,工作的状态可能也会被对方所影响干扰,项目的思路和对项目的理解可能也会不同而在编程中产生冲突。
陈芳的优点:编程时非常专注、每天能够合理约束自己的作息时间直到完成任务、代码能力相当强;陈芳的缺点:不解决bug不睡觉。
我的优点:解决问题和bug时有独特的想法、有问题多百度并向陈芳请教、会调整我们编程的状态和气氛;我的缺点:代码能力较弱。
十二、PSP(2)
| PSP | 任务内容 | 计划共完成需要的时间(min) | 实际完成需要的时间(min) | ||||||
| Planning | 计划 | 1*60 | 1*60 | ||||||
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间,并规划大致工作步骤 | 1*60 | 1*60 | ||||||
| Development | 开发 | 50*60 | 50*60 | ||||||
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 5*60 |
|
||||||
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 2*60 | 2*60 | ||||||
| Design Review | 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 1*60 | 1*60 | ||||||
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 1*60 | 1*60 | ||||||
| Design | 具体设计 | 3*60 | 3*60 | ||||||
| Coding | 具体编码 | 26*60 | 26*60 | ||||||
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 4*60 | 4*60 | ||||||
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 8*60 | 8*60 | ||||||
| Reporting | 报告 | 7*60 |
|
||||||
| Test Report | 测试报告 | 5.5*60 | 5.5*60 | ||||||
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 30 | 30 | ||||||
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 1*60 | 1*60 |





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号