System
System 类常见的成员方法:
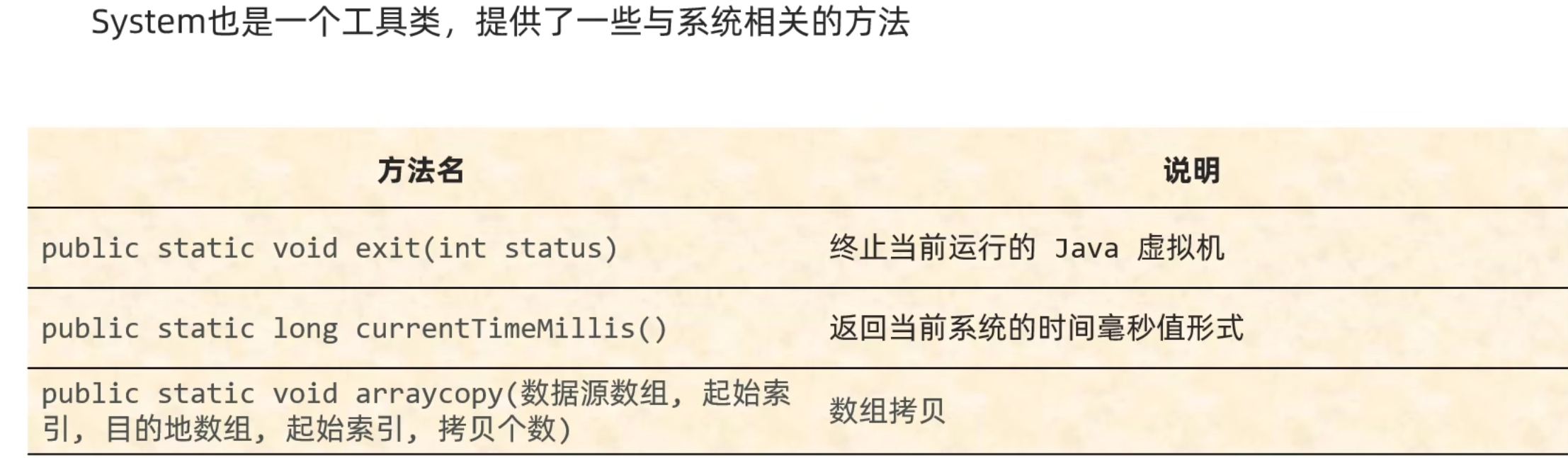
图1
System 是一个工具类, 提供了一些与系统相关的方法.
public static void exit(int status) // 终止当前运行的 Java 虚拟机
status 是一个状态码, 有两种情况, 第一种情况是等于 0, 表示当前虚拟机是正常停止的. 第二种情况是非零, 一般是写 1, 表示当前虚拟机是异常停止.
不管是正常停止还是异常停止, 程序执行到这一步之后, 程序都会停止, 也就是说写在这一句话后面的语句都不会被执行.
在计算机中, 时间是有原点的, 表示最初的开始时间, 是 1970 年 1 月 1 号 00:00:00
1970 年 1 月 1 号是 C 语言的生日.
中国位于东八区, 跟标准时间有 8 个小时的时差. 所以在我们的操作系统中获取到的时间原点是 1970 年 1 月 1 号 08:00:00
时间的单位:
1 秒 = 1000 毫秒
1 毫秒 = 1000 微秒
1 微秒 = 1000 纳秒
还有其他不常用的单位: 皮秒, 飞秒, 阿托秒, 仄秒, 幺秒, 都是以 1000 为换算单位的.
public static long currentTimeMillis() // 返回从时间原点开始, 到代码运行时, 一共度过了多少毫秒
程序示例:
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(l);
}
}
程序示例:
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double sum = 0.0;
double avg = 0.0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// 获取程序开始运行时的时间
long n1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
int count = 0;
for (int j = 2; j <= 200000; j++) {
if (isPrime2(j)) {
++count;
}
}
// 获取程序运行结束时的时间
long n2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 获取程序运行总时间
double res = n2 - n1;
System.out.println(res);
// // 打印 count
// System.out.println(count);
sum += res;
}
avg = sum / 5;
System.out.println(avg); // isPrime1: 2344.8, isPrime2: 9.6
}
// 判断一个整数是否为素数, 方法一
public static boolean isPrime1(int num) {
for (int i = 2; i < num; i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 判断一个整数是否为素数, 方法二 (改进的方法, 效率更高)
public static boolean isPrime2(int num) {
for (int i = 2; i * i <= num; i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
public static void arraycopy(数据源数组, 起始索引, 目的地数组, 起始索引, 拷贝个数) // 数组拷贝
程序示例:
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 拷贝数组
int[] arr1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int[] arr2 = new int[10];
// 把 arr1 数组中的数据拷贝到 arr2 中
// 参数一: 数据源, 要拷贝的数据从哪个数组而来
// 参数二: 从数据源数组中的第几个索引开始拷贝
// 参数三: 目的地, 我要把数据拷贝到哪个数组中
// 参数四: 目的地数组的索引
// 参数五: 拷贝的个数
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 0, 10);
// 验证
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr2[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
int[] arr3 = new int[10];
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr3, 0, 5);
for (int i = 0; i < arr3.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr3[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
int[] arr4 = new int[10];
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr4, 4, 3);
for (int i = 0; i < arr4.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr4[i] + " ");
}
}
}
程序示例:
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public static void arraycopy(数据源数组, 起始索引, 目的地数组, 起始索引, 拷贝个数) // 数组拷贝
// 细节:
// 如果数据源数组和目的地数组都是基本数据类型, 那么两者的类型必须保持一致, 否则会报错
int[] arr1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
double[] arr2 = new double[10];
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 0, 10); // ArrayStoreException: arraycopy: type mismatch: can not copy int[] into double[]
// 验证
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr2[i] + " ");
}
}
}
程序示例:
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public static void arraycopy(数据源数组, 起始索引, 目的地数组, 起始索引, 拷贝个数) // 数组拷贝
// 细节:
// 在拷贝的时候需要考虑数组的长度, 如果超出范围也会报错
int[] arr1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int[] arr2 = new int[5];
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 0, 10); // ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: arraycopy: last destination index 10 out of bounds for int[5]
// 验证
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr2[i] + " ");
}
}
}
程序示例:
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public static void arraycopy(数据源数组, 起始索引, 目的地数组, 起始索引, 拷贝个数) // 数组拷贝
// 细节:
// 如果数据源数组和目的地数组都是引用数据类型, 那么子类类型可以复制给父类类型
Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan", 23);
Student s2 = new Student("lisi", 24);
Student s3 = new Student("wangwu", 25);
Student[] arr1 = {s1, s2, s3}; // 子类
Person[] arr2 = new Person[3]; // 父类
// 把 arr1 中对象的地址值复制给 arr2 中
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 0, 3);
// 遍历数组 arr2
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
// Student stu = (Student) arr2[i]; // 强制类型转换
// System.out.println(stu.getName() + "," + stu.getAge());
System.out.println(arr2[i].getName() + "," + arr2[i].getAge());
}
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
class Student extends Person {
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号