【Java】日期 / 事件字符串包含 TZ
前言
- 这个时间是什么格式?
2021-09-02T15:25:03Z - jdk1.8
T、Z 的含义
2021-09-02T15:25:03Z 中 T 是表示时间段开始的关键字,Z 是表示 UTC 时间(通用协调时,Universal Time Coordinated)。
UTC 与格林尼治平均时 (GMT, Greenwich Mean Time) 一样,都与英国伦敦的本地时间相同。
包含 T、Z 的日期的出处
包含 T、Z 的日期的出自 ISO 8601 Extended Format。ISO 8601 Extended Format 的时间看起来是这样的 YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.sssZ。
Z 的规律
- 以 Z 结尾表示 UTC 时间 (可理解为,英国伦敦时间)
+HH表示时区,比如+08表示东八区-HH表示时区,比如-08表示西八区+HHmm表示时区,比如+0800表示东八区-HHmm表示时区,比如-0800表示西八区+HH:mm表示时区,比如+08:00表示东八区-HH:mm表示时区,比如-08:00表示西八区
date format pattern
| 日期字符串 | 日期格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 2021-09-02T15:25:03Z | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssX |
一个 X 可以识别 Z 字符 |
| 2021-09-02T15:25:03Z | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXX |
两个 XX 可以识别 Z 字符 |
| 2021-09-02T15:25:03Z | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXXX |
三个 XXX 可以识别 Z 字符 |
| 2021-09-02T15:25:03+00 | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssX |
一个 X 可以识别 +HH |
| 2021-09-02T15:25:03-08 | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssX |
一个 X 可以识别 -HH |
| 2021-09-02T15:25:03+8000 | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXX |
两个 X 可以识别 -HHmm |
| 2021-09-02T15:25:03-0800 | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXX |
两个 X 可以识别 -HHmm |
| 2021-09-02T15:25:03+08:00 | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXXX |
三个 X 可以识别 -HH:mm |
| 2021-09-02T15:25:03-08:00 | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXXX |
三个 X 可以识别 -HH:mm |
示例
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXXX");
Date d = null;
d = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssX").parse("2021-09-01T16:19:10Z");
System.out.println(df.format(d));
d = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXX").parse("2021-09-01T16:19:10Z");
System.out.println(df.format(d));
d = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXXX").parse("2021-09-01T16:19:10Z");
System.out.println(df.format(d));
d = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssX").parse("2021-09-01T16:19:10-00");
System.out.println(df.format(d));
d = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXX").parse("2021-09-01T16:19:10+0800");
System.out.println(df.format(d));
d = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXXX").parse("2021-09-01T16:19:10+08:00");
System.out.println(df.format(d));
d = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXXX").parse("2021-09-01T16:19:10+08:30");
System.out.println(df.format(d));
}
}输出
2021-09-02T00:19:10+08:00
2021-09-02T00:19:10+08:00
2021-09-02T00:19:10+08:00
2021-09-02T00:19:10+08:00
2021-09-01T16:19:10+08:00
2021-09-01T16:19:10+08:00
2021-09-01T15:49:10+08:00参考
【日期、时间】javascript 字符串转日期类型
java string 类型时间段 转换 date 类型
Date 的构造方法
new Date();
new Date(value);
new Date(dateString);
new Date(year, monthIndex [, day [, hours [, minutes [, seconds [, milliseconds]]]]]);- 无参数 : 取当前时间。
- value : 相对于 “January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 UTC” 的毫秒。
- dateString : 符合 IETF-compliant RFC 2822 timestamps 或 ISO 8601 Extended Format(es5 开始支持),以及非标格式。
- year, monthIndex [, day [, hours [, minutes [, seconds [, milliseconds]]]]] : 年月日时分秒
ISO 8601 Extended Format 示例
chrome console> console.log(new Date('2019-12-11T08:30:05+08:00'));
Wed Dec 11 2019 08:30:05 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
chrome console> console.log(new Date('2019-12-11T08:30:05'));
Wed Dec 11 2019 08:30:05 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
chrome console> console.log(new Date('2019-12-11T08:30:05+00:00'));
Wed Dec 11 2019 16:30:05 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
chrome console> console.log(new Date('2019-12-11T08:30:05Z'));
Wed Dec 11 2019 16:30:05 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)浏览器兼容
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Date#Browser_compatibility
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/beta_xiyan/article/details/76991635
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000017579541
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Date
IETF-compliant RFC 2822 timestamps
Date and Time Specification
Date and time occur in several header fields. This section specifies
the syntax for a full date and time specification. Though folding
white space is permitted throughout the date-time specification, it
is RECOMMENDED that a single space be used in each place that FWS
appears (whether it is required or optional); some older
implementations may not interpret other occurrences of folding white
space correctly.
date-time = [ day-of-week "," ] date FWS time [CFWS]
day-of-week = ([FWS] day-name) / obs-day-of-week
day-name = "Mon" / "Tue" / "Wed" / "Thu" /
"Fri" / "Sat" / "Sun"
date = day month year
year = 4*DIGIT / obs-year
month = (FWS month-name FWS) / obs-month
month-name = "Jan" / "Feb" / "Mar" / "Apr" /
"May" / "Jun" / "Jul" / "Aug" /
"Sep" / "Oct" / "Nov" / "Dec"
day = ([FWS] 1*2DIGIT) / obs-day
time = time-of-day FWS zone
time-of-day = hour ":" minute [ ":" second ]
hour = 2DIGIT / obs-hour
minute = 2DIGIT / obs-minute
second = 2DIGIT / obs-second
zone = (( "+" / "-" ) 4DIGIT) / obs-zone
The day is the numeric day of the month. The year is any numeric
year 1900 or later.
The time-of-day specifies the number of hours, minutes, and
optionally seconds since midnight of the date indicated.
The date and time-of-day SHOULD express local time.
The zone specifies the offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC,
formerly referred to as "Greenwich Mean Time") that the date and
time-of-day represent. The "+" or "-" indicates whether the
time-of-day is ahead of (i.e., east of) or behind (i.e., west of)
Universal Time. The first two digits indicate the number of hours
difference from Universal Time, and the last two digits indicate the
number of minutes difference from Universal Time. (Hence, +hhmm
means +(hh * 60 + mm) minutes, and -hhmm means -(hh * 60 + mm)
minutes). The form "+0000" SHOULD be used to indicate a time zone at
Universal Time. Though "-0000" also indicates Universal Time, it is
used to indicate that the time was generated on a system that may be
in a local time zone other than Universal Time and therefore
indicates that the date-time contains no information about the local
time zone.
A date-time specification MUST be semantically valid. That is, the
day-of-the-week (if included) MUST be the day implied by the date,
the numeric day-of-month MUST be between 1 and the number of days
allowed for the specified month (in the specified year), the
time-of-day MUST be in the range 00:00:00 through 23:59:60 (the
number of seconds allowing for a leap second; see [STD12]), and the
zone MUST be within the range -9959 through +9959.形如:
Sun 30 Dec 2018 19:42:44 +0800ISO 8601 Extended Format
ECMAScript defines a string interchange format for date-times based upon a simplification of the ISO 8601 Extended Format. The format is as follows: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.sssZ
Where the fields are as follows:
YYYY is the decimal digits of the year 0000 to 9999 in the Gregorian calendar.
- “-” (hyphen) appears literally twice in the string.
MM is the month of the year from 01 (January) to 12 (December).
DD is the day of the month from 01 to 31.
T “T” appears literally in the string, to indicate the beginning of the time element.
HH is the number of complete hours that have passed since midnight as two decimal digits from 00 to 24.
: “:” (colon) appears literally twice in the string.
mm is the number of complete minutes since the start of the hour as two decimal digits from 00 to 59.
ss is the number of complete seconds since the start of the minute as two decimal digits from 00 to 59.
. “.” (dot) appears literally in the string.
sss is the number of complete milliseconds since the start of the second as three decimal digits.
Z is the time zone offset specified as “Z” (for UTC) or either “+” or “-” followed by a time expression HH:mm
This format includes date-only forms:
- YYYY
- YYYY-MM
- YYYY-MM-DD
It also includes “date-time” forms that consist of one of the above date-only forms immediately followed by
one of the following time forms with an optional time zone offset appended:
- THH:mm
- THH:mm:ss
- THH:mm:ss.sss
All numbers must be base 10. If the MM or DD fields are absent “01” is used as the value. If the HH, mm, or ss fields are absent “00” is used as the value and the value of an absent sss field is “000”. The value of an absent time zone offset is “Z”.
Illegal values (out-of-bounds as well as syntax errors) in a format string means that the format string is not a valid instance of this format.
NOTE 1 : As every day both starts and ends with midnight, the two notations 00:00 and 24:00 are available to distinguish the two midnights that can be associated with one date. This means that the following two notations refer to exactly the same point in time: 1995-02-04T24:00 and 1995-02-05T00:00
NOTE 2 : There exists no international standard that specifies abbreviations for civil time zones like CET, EST, etc. and sometimes the same abbreviation is even used for two very different time zones. For this reason, ISO 8601 and this format specifies numeric representations of date and time.
精简一下:
ISO 8601 Extended Format : YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.sssZ示例:
1995-12-17T03:24:00+00:00 //标准时间
1995-12-17T03:24:00Z //标准时间
1995-12-17T03:24:00+08:00 //东8区时间 前言
- string 类型时间段 : 2019-08-30 14:01-16:01
- org.apache.commons:commons-lang3
date format pattern
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm-KK:KK解析结果:2019-08-30 14:01
yyyy-MM-dd KK:KK-HH:mm解析结果:2019-08-30 16:01
示例
实例代码:
import java.util.Date;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.time.DateFormatUtils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.time.DateUtils;
public class TestTimeInterval {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String str1 = "2019-08-30 14:01-16:01";
Date d1 = DateUtils.parseDate(str1, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm-ss:ss");
System.out.println(DateFormatUtils.format(d1, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + "\t" + d1.getTime());
Date d2 = DateUtils.parseDate(str1, "yyyy-MM-dd ss:ss-HH:mm");
System.out.println(DateFormatUtils.format(d2, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + "\t" + d2.getTime());
Date d3 = DateUtils.parseDate(str1, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm-SS:SS");
System.out.println(DateFormatUtils.format(d3, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + "\t" + d3.getTime());
Date d4 = DateUtils.parseDate(str1, "yyyy-MM-dd SS:SS-HH:mm");
System.out.println(DateFormatUtils.format(d4, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + "\t" + d4.getTime());
Date d5 = DateUtils.parseDate(str1, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm-KK:KK");
System.out.println(DateFormatUtils.format(d5, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + "\t" + d5.getTime());
Date d6 = DateUtils.parseDate(str1, "yyyy-MM-dd KK:KK-HH:mm");
System.out.println(DateFormatUtils.format(d6, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + "\t" + d6.getTime());
Date d7 = DateUtils.parseDate(str1, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm-hh:hh");
System.out.println(DateFormatUtils.format(d7, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + "\t" + d7.getTime());
Date d8 = DateUtils.parseDate(str1, "yyyy-MM-dd hh:hh-HH:mm");
System.out.println(DateFormatUtils.format(d8, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + "\t" + d8.getTime());
}
}执行结果:
2019-08-30 14:01:01 1567144861000
2019-08-30 16:01:01 1567152061000
2019-08-30 14:01:00 1567144860001
2019-08-30 16:01:00 1567152060001
2019-08-30 14:01:00 1567144860000
2019-08-30 16:01:00 1567152060000
2019-08-30 14:01:00 1567144860000
2019-08-30 16:01:00 1567152060000参考
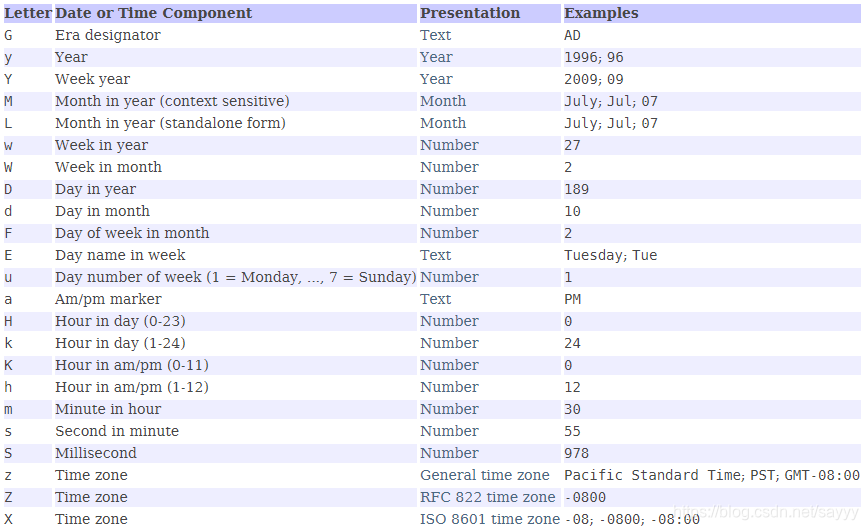
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/text/SimpleDateFormat.html
- 当前时区
带时区格式化时间
为 SimpleDateFormat 对象指定时区后,再执行格式化。
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXXX");
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.ofOffset("GMT", ZoneOffset.ofHours(9));
TimeZone timeZone = TimeZone.getTimeZone(zoneId);
df.setTimeZone(timeZone);
System.out.println(df.format(cal.getTime()));- 将时间格式化成东九区的时间
示例
package com.example.demo;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.TimeZone;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXXX");
TimeZone timeZone;
ZoneId zoneId;
System.out.println("user.timezone = " + System.getProperty("user.timezone"));
zoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault();
System.out.println("zoneId = " + zoneId);
timeZone = TimeZone.getTimeZone(zoneId);
df.setTimeZone(timeZone);
System.out.println(df.format(cal.getTime()));
for (int i=0;i<=12;i++) {
zoneId = ZoneId.ofOffset("GMT", ZoneOffset.ofHours(i));
System.out.println("zoneId = " + zoneId);
timeZone = TimeZone.getTimeZone(zoneId);
df.setTimeZone(timeZone);
System.out.println(df.format(cal.getTime()));
}
for (int i=-0;i>=-12;i--) {
zoneId = ZoneId.ofOffset("GMT", ZoneOffset.ofHours(i));
System.out.println("zoneId = " + zoneId);
timeZone = TimeZone.getTimeZone(zoneId);
df.setTimeZone(timeZone);
System.out.println(df.format(cal.getTime()));
}
}
}输出
user.timezone = Asia/Shanghai
zoneId = Asia/Shanghai
2021-09-26T18:20:09+08:00
zoneId = GMT
2021-09-26T10:20:09Z
zoneId = GMT+01:00
2021-09-26T11:20:09+01:00
zoneId = GMT+02:00
2021-09-26T12:20:09+02:00
zoneId = GMT+03:00
2021-09-26T13:20:09+03:00
zoneId = GMT+04:00
2021-09-26T14:20:09+04:00
zoneId = GMT+05:00
2021-09-26T15:20:09+05:00
zoneId = GMT+06:00
2021-09-26T16:20:09+06:00
zoneId = GMT+07:00
2021-09-26T17:20:09+07:00
zoneId = GMT+08:00
2021-09-26T18:20:09+08:00
zoneId = GMT+09:00
2021-09-26T19:20:09+09:00
zoneId = GMT+10:00
2021-09-26T20:20:09+10:00
zoneId = GMT+11:00
2021-09-26T21:20:09+11:00
zoneId = GMT+12:00
2021-09-26T22:20:09+12:00
zoneId = GMT
2021-09-26T10:20:09Z
zoneId = GMT-01:00
2021-09-26T09:20:09-01:00
zoneId = GMT-02:00
2021-09-26T08:20:09-02:00
zoneId = GMT-03:00
2021-09-26T07:20:09-03:00
zoneId = GMT-04:00
2021-09-26T06:20:09-04:00
zoneId = GMT-05:00
2021-09-26T05:20:09-05:00
zoneId = GMT-06:00
2021-09-26T04:20:09-06:00
zoneId = GMT-07:00
2021-09-26T03:20:09-07:00
zoneId = GMT-08:00
2021-09-26T02:20:09-08:00
zoneId = GMT-09:00
2021-09-26T01:20:09-09:00
zoneId = GMT-10:00
2021-09-26T00:20:09-10:00
zoneId = GMT-11:00
2021-09-25T23:20:09-11:00
zoneId = GMT-12:00
2021-09-25T22:20:09-12:00zoneId = Asia/Shanghai是系统默认时区。zoneId = Asia/Shanghai也就是东八区,其时间与zoneId = GMT+08:00一样。zoneId = GMT+00:00与zoneId = GMT+00:00是同一个时区,因此时间一样。zoneId = GMT+12:00与zoneId = GMT-12:00是国际日期变更线所在,因此时间相差 24 小时。
前言
- 从头捋捋,将时间捋明白。
- 计算机使用的是 UTC 时间。这里的计算机可以理解为:操作系统、BIOS、CMOS、数据库等。
计算机中日期、时间表示方法
UNIX 认为 1970 年 1 月 1 日 0 点是时间纪元,现在的计算机世界沿用此规则。
比如:Java 中,Date 类构造方法的注释中说 “使用 GMT(同 UTC) 1970 年 1 月 1 日 0 点作为时间纪元”。
/**
* Allocates a <code>Date</code> object and initializes it to
* represent the specified number of milliseconds since the
* standard base time known as "the epoch", namely January 1,
* 1970, 00:00:00 GMT.
*
* @param date the milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 GMT.
* @see java.lang.System#currentTimeMillis()
*/
public Date(long date) {...}JavaScript 示例
var d = new Date(0); // 0是距 UTC 时间1970年1月1日0点的毫秒数
console.log(d.toLocaleString()); // 显示成本地时间
console.log(d.toString());
console.log(d.toUTCString()); // 显示成UTC时间(世界时间)执行结果:
1970/1/1 上午8:00:00
Thu Jan 01 1970 08:00:00 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
Thu, 01 Jan 1970 00:00:00 GMT说明:
- 1970 年 1 月 1 日 0 点是时间纪元。
- 除了操作系统外,还有编程语言、BIOS、数据库,均用计算机代表。
- 计算机使用的是 UTC 时间。系统时间指的就是这个。
- 计算机中用数字表示 UTC 时间,该数字是
距UTC时间1970年1月1日0点的毫秒数。 - 计算机将数字表示的 UTC 时间转化为人类可读的时间。在 JavaScript 中用 toUTCString () 获取。
- 在 JavaScript 中 toLocaleString () 获取本地时区的本地时间。本地时区是由操作系统设置的。操作系统的时区设置成北京时间,就获得北京时间。上例中,数字 0 是 UTC 时间,运行代码的电脑设置的时区是北京时间,因此,toLocaleString () 获得北京时间 8 点(此时的世界时间是 0 点)。
- 计算机中 GMT 时间视同 UTC 时间。
- 采用不同时区的数据进行数据交换时,最好采用标准时间格式(上例中输出的第 1 个时间无法在不同时区中进行数据交换)。
参考
计算机系统的时间
日期类的时间从为什么是从 1970 年 1 月 1 日
UTC
javascript 字符串转日期类型
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Date



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号