springboot,WebFlux,Bean对象循环依赖问题解决
Spring WebFlux是一套全新的Reactive Web技术栈,实现完全非阻塞、支持Reactive Streams、背压等特性,而且运行的环境除了Servlet容器(Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow),还有Netty等。WebFlux可以和WebMVC共存,在springboot中,mvc的优先级更高。
编程模型
编程模型有两种,注解驱动和函数式编程
WebFlux与WebMVC在注解驱动方面的异同:
定义:都是@Controller或@RestController
映射:都是@RequestMapping、@GetMapping、@PostMapping等等
请求:都是@RequestParam、@RequestHeader、@CookieValue、@RequestBo、@PathVariable、RequestEntity
响应:都是@ResponseBody、ResponseEntity、ResponseCookie
拦截:都是@ControllerAdvice、@RestControllerAdvice
跨域:跨域方面有差异
| 特性 | Spring Web MVC | Spring WebFlux |
| 资源跨域声明注解 | @CrossOrigin | 相同 |
| 资源跨域拦截器 | CorsFilter | CorsWebFilter |
| 注册资源跨域信息 | webMvcConfigurer#addCorsMappings | WebFluxConfigurer#addCorsMappings |
关于函数式编程
函数式编程是java1.8引入的新特性,在之前其实我们就已经用过了。函数式编程的接口必须有@FunctionalInterface注解,进去看这个注解的源码
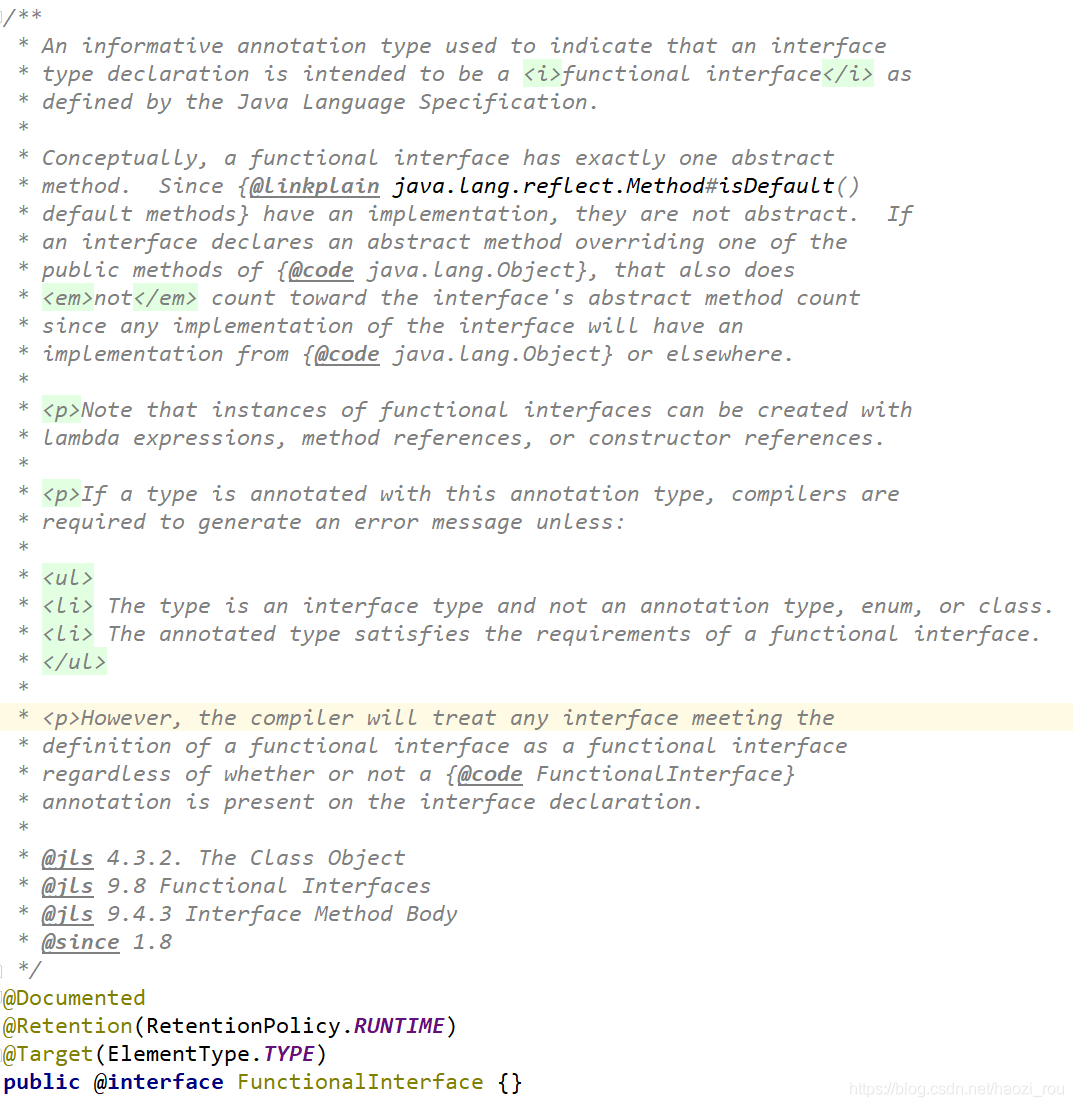
看注释可以知道:这是用于函数式接口类型生命的信息性注解类型,这种接口只能有一个抽象方法,因为接口都有个默认方法Method#isDefault,所以这个方法也需要被覆盖。并且@FunctionalInterface不能标注在注解、类或枚举上。否则就不能被视为函数是接口,引起编译错误。函数是借口可以使用lambda表达式、方法引用或构造器来创建功能接口的实例。
对于函数是接口有四种函数类型,列出来,具体的可以去看源码:
消费函数-Consumer:只有输入,没有输出
生产函数-Supplier:没有输入,只有输出
处理函数-Function:既有输入,也有输出
判定函数-Predicate:判定输入的真伪性
核心接口-RouterFunction
例:
-
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route =
-
route(GET("/person/{id}").and(accept(APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::getPerson)
-
.andRoute(GET("/person").and(accept(APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::listPeople)
-
.andRoute(POST("/person"), handler::createPerson);
函数式处理接口:
-
public class PersonHandler {
-
-
public Mono<ServerResponse> listPeople(ServerRequest request) {
-
-
}
-
public Mono<ServerResponse> createPerson(ServerRequest request) {
-
-
}
-
public Mono<ServerResponse> getPerson(ServerRequest request) {
-
-
}
-
}
上面就是函数式映射的例子,如果用传统的mvc的形式,其实就是
-
-
public void getPerson(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse) {
-
-
}
自定义一个简单的demo
加依赖
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
-
</dependency>
-
-
public class WebFluxApplication {
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
SpringApplication.run(WebFluxApplication.class, args);
-
}
-
-
-
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> routerFunction() {
-
return RouterFunctions.route(
-
request -> { // 判断请求是否匹配
-
URI uri = request.uri();
-
return "/haozirou".equals(uri.getPath());
-
},
-
request -> { //绑定实现
-
return ServerResponse
-
.status(HttpStatus.OK)
-
.body(Mono.just("haozirou") , String.class);
-
});
-
}
-
}
运行的控制台:
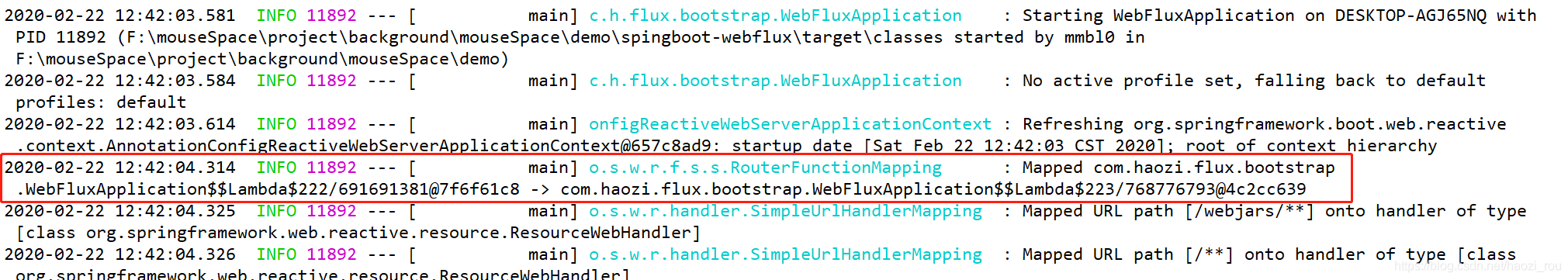
从控制台可以看出,我们自己写的由于映射写的比较深,所以控制台输出不出来具体的情况,而且我们自己实现起来比较麻烦,所以改成官方写法
-
-
public class WebFluxApplication {
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
SpringApplication.run(WebFluxApplication.class, args);
-
}
-
-
-
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> routerFunction() {
-
return route(GET("/haozirou"), this::haozirou);
-
}
-
-
private Mono<ServerResponse> haozirou(ServerRequest serverRequest) {
-
return ServerResponse.status(HttpStatus.OK)
-
.body(Mono.just("haozirou"), String.class);
-
}
-
}
控制台
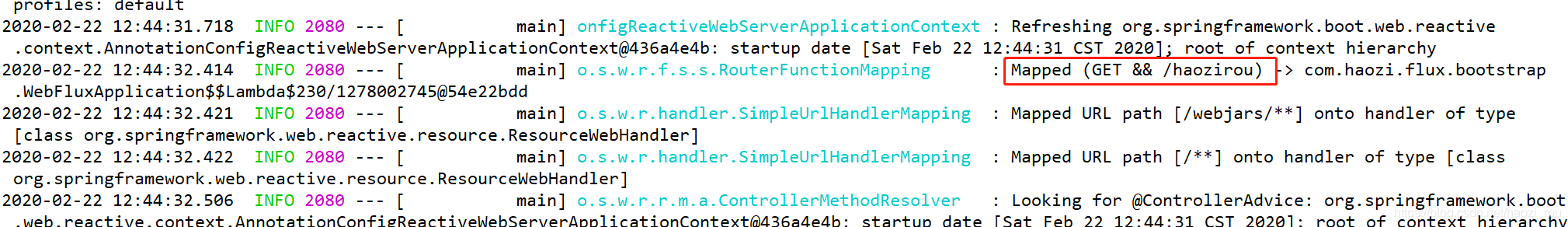
关于函数式编程的好处,相对于传统mvc的写法,可以很轻松的自定义请求的判断逻辑,mvc只能通过@Profile的方式,这里自定义代码更自由。
WebFlux核心组件
HttpHandler API
HttpHandler是一种带有处理http请求和响应方法的简单契约。
看一下源码:
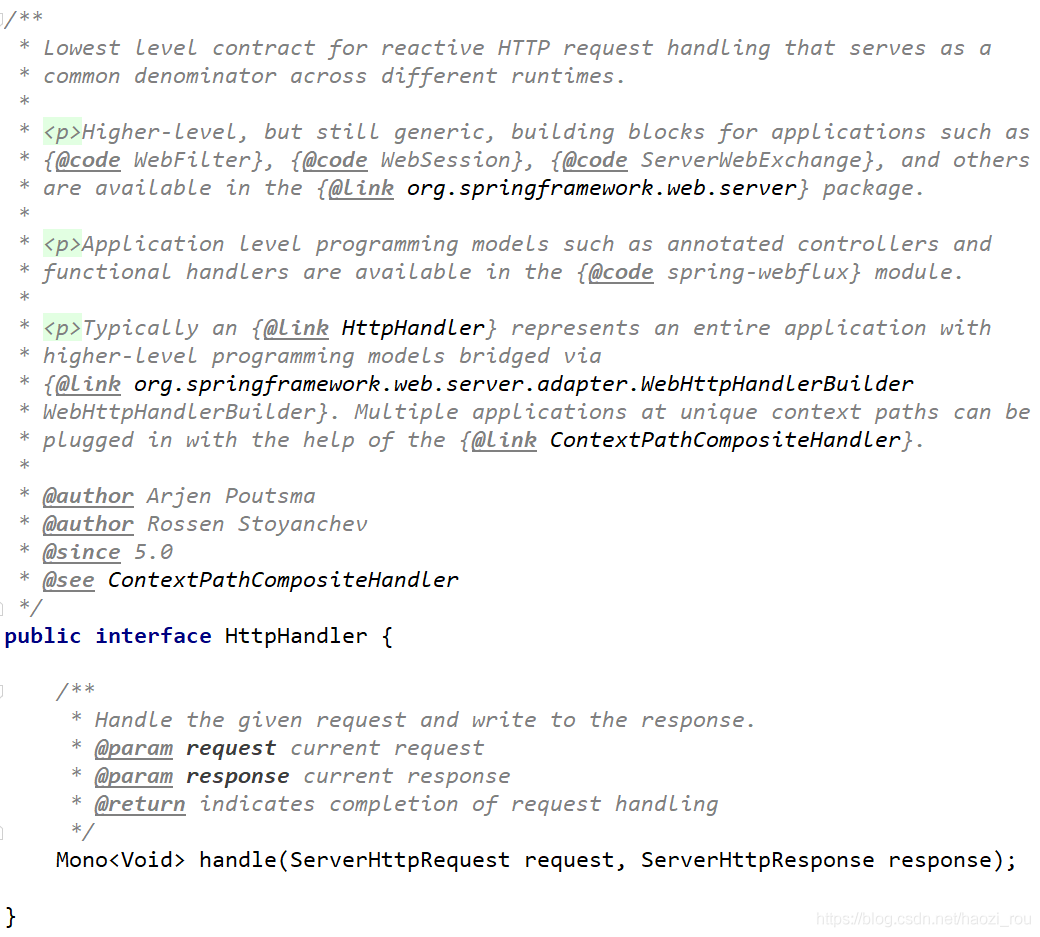
可以看到,这个方法跟Servlet#service的传值很类似,而且返回值虽然格式不同,但都是void
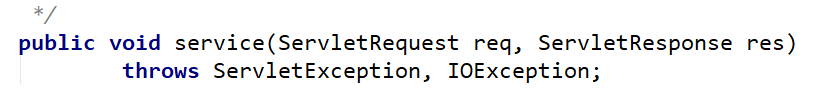
Servlet再找子类HttpServlet#service

可以对照ContextPathCompositeHandler和HttpServlet源码看一下,实现的大多数功能其实都差不多。
webHandle API
| Bean类型 | 数量 | 描述 | 类比mvc |
| webExceptionHandler | 0-N | 提供对来自WebFilter和目标WebHandler链的异常的处理 | ExceptionHandler |
| webFilter | 0-N | 拦截器 | Filter#doFilter |
| webHandler | 1 | 请求的处理程序 | Servlet#service |
| webSessionManager | 0-1 | WebSession的管理器通过ServerWebExchange上的方法公开。 默认实现为DefaultWebSessionManager | session |
| serverCodecConfigurer | 0-1 | 用于解析、转义数据 | HttpMessageConverter |
| localeContextResolver | 0-1 | 处理国际化上下文的 | LocaleContextResolver |
WebFlux的核心组件与WebMVC对比
| 核心组件 | Spring WebMVC | Spring WebFlux |
| 前端控制器 | DispatcherServlet | DispatcherHandler |
| Handler请求映射 | o.s.w.servlet.HandlerMapping | o.s.w.reactive.HandlerMapping |
| Handler请求适配器 | o.s.w.servlet.HandlerAdapter | o.s.w.reactive.HandlerAdapter |
| Handler异常处理器 | o.s.w.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver | o.s.w.reactive.HandlerResult #exceptionHandler |
| 视图处理器 | o.s.w.servlet.ViewResolver | o.s.w.reactive.ViewResolver |
| Locale解析器 | o.s.w.servlet.LocaleResolver/LocaleContextResolver | o.s.w.server.i18n.LocaleContextResolver |
| @Enable模块注解 | @EnableWebMvc | @EnableWebFlux |
| 自定义配置器 | webMvcConfigurer | webFluxConfigurer |
| 内容协商配置器 | ContentNegotiationConfigurer | RequestedContentTypeResolverBuilder |
| 内容协商管理器 | ContentNegotiationManager | 无 |
| 内容协商策略 | ContentNegotiationStrategy | RequestedContentTypeResolver |
| 资源跨域注册器 | o.s.w.servlet.c.a.CorsRegistry | o.s.w.reactive.c.CorsRegistry |
| HandlerMethod参数解析器 | o.s.w.m.s.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver | o.s.w.reactive.r.m.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver |
| HandlerMethod返回值解析器 | HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler | HandlerResultHandler |
核心组件初始化流程
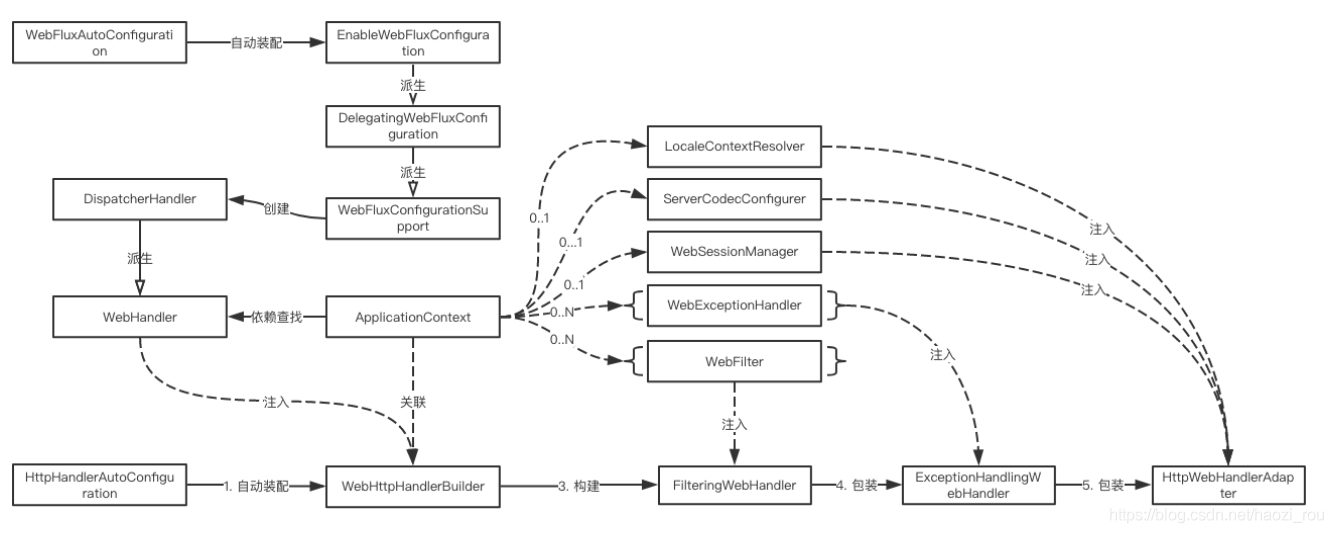
其实看着源码对照着流程图,很容易就能看懂流程是什么样,这里只是描述一下,具体源码就不贴了,自己去看吧。
首先上面部分:自动装配WebFluxAutoConfiguration,他import了EnableWebFluxConfiguration,这个类的作用就是把springboot配置的spring.webflux导进来,用于后面配置。这个类找父类可以找到WebFluxConfigurationSupport,里面会创建DispatcherHandler,而这个类会根据ApplicationContext来初始化(加载mapping、adapter、handler),而这个类实现了WebHandler接口。
下面部分比较简单:自动装配HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,里面有build方法,以ApplicationContext为参数,关联到了WebHttpHandlerBuilder,里面将FilteringWebHandler带着context中的webHandler、filters构建出来,并加上exceptionHandler包装成ExceptionHandlingWebHandler,最后返回HttpWebHandlerAdapter。
至于图中WebFilter等如何跟ApplicationContext关联,通过看源码可以知道,WebFilter这些接口的初始化方法参数都是ServerWebExchange,里面就有getApplicationContext方法。
注解驱动(Annotated Controllers)组件请求处理流程
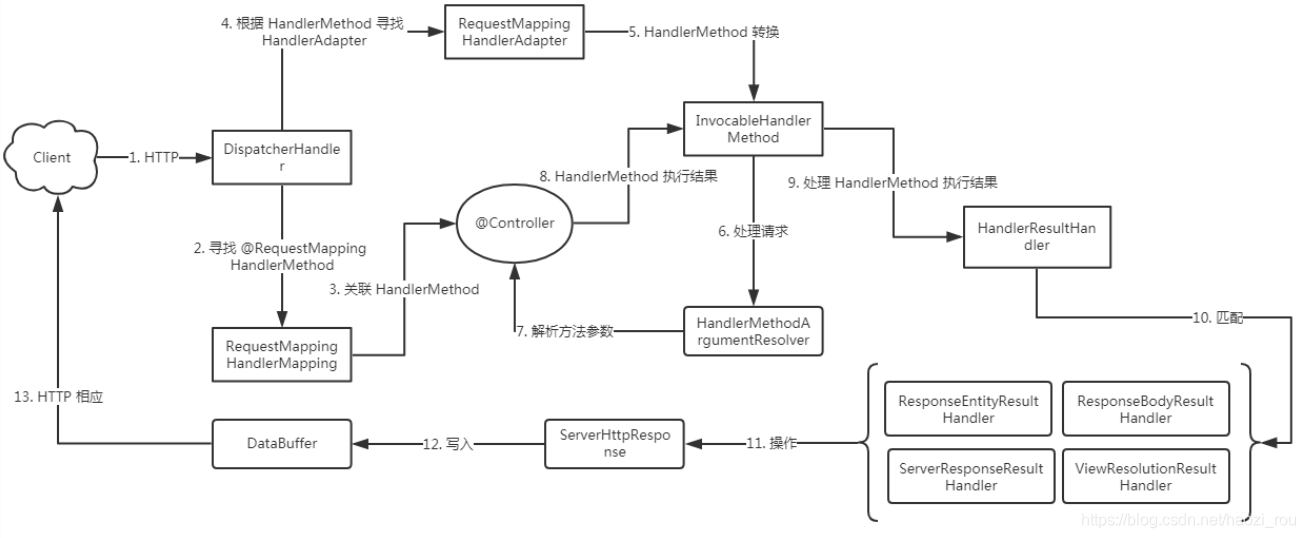
注解驱动的方式和SpringMVC非常相似,这里就不再多说,可以根据之前表格的对比来看,都是大同小异的。
函数式端点(Functional Endpoints)组件请求处理流程
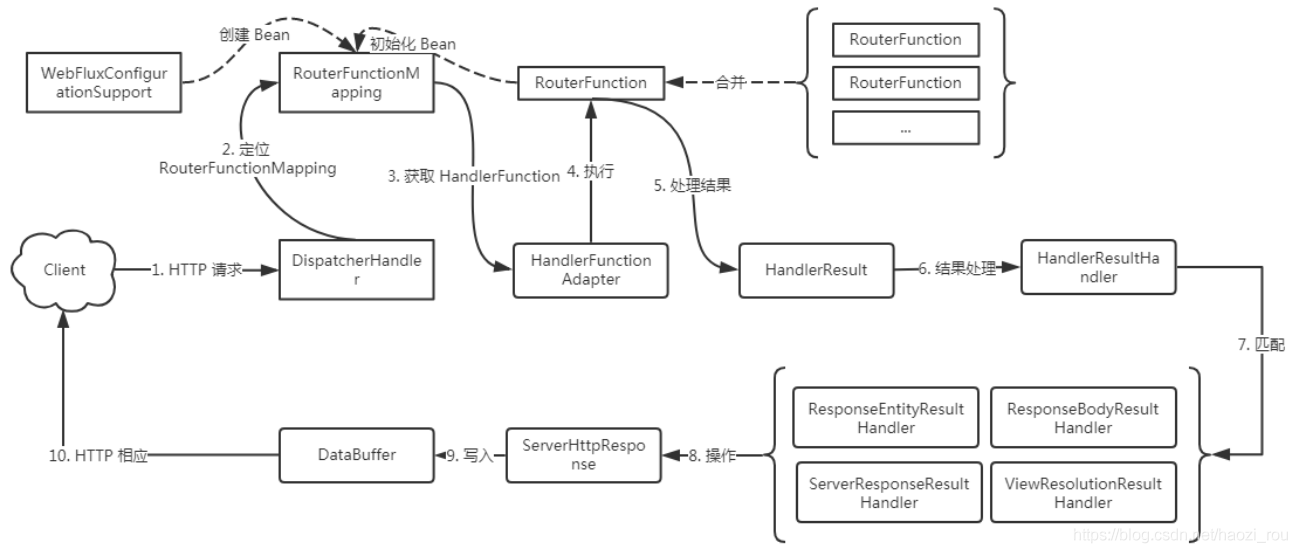
这个图分为两部分,上面一部分是在系统启动的时候运行的,下面是请求的过程,首先先看一下上面的。
先放一下bean
-
-
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> routerFunction() {
-
return route(GET("/haozirou"), this::haozirou)
-
.andRoute(GET("/haozirou2"), this::haozirou)
-
.andRoute(GET("/haozirou3"), this::haozirou)
-
.andRoute(GET("/haozirou4"), this::haozirou)
-
.andRoute(GET("/haozirou5"), this::haozirou);
-
}
-
-
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> anotherRouterFunction() {
-
return route(GET("/anotherhaozirou"), this::haozirou);
-
}
首先看RouterFunctionMapping,向上查找,很明显是由WebFluxConfigurationSupport创建,看下源码:

看注释,优先级是在RequestMappingHandlerMapping前面,也就是说函数式的映射会在注解驱动之前。看RouterFunctionMapping的父类可以知道,他也属于HandlerMapping,也可以向成mvc的RequestMapping了。再往下看,里面有一个initRouterFunctions初始化方法
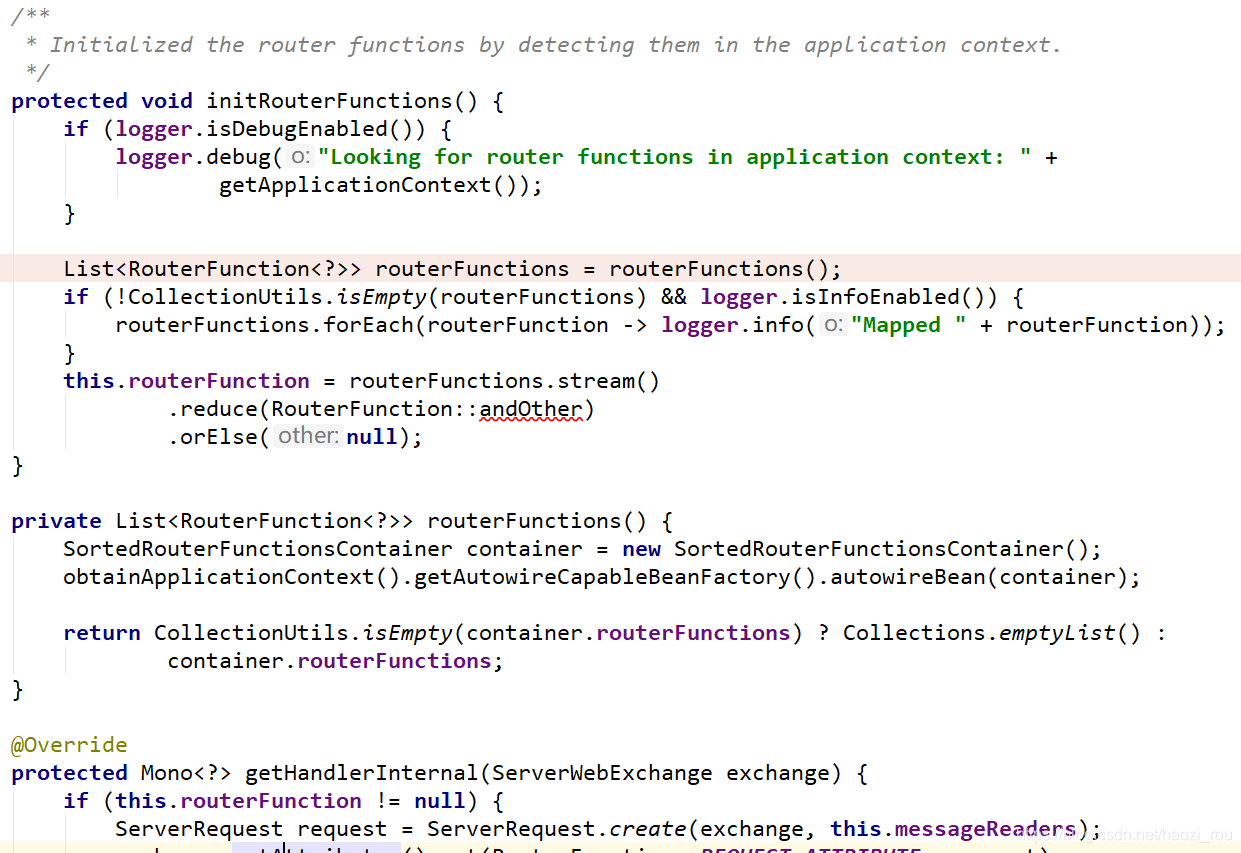
图中打断点的routerFunctions是获取所有路由的,如果有多个路由,那么就会有多个
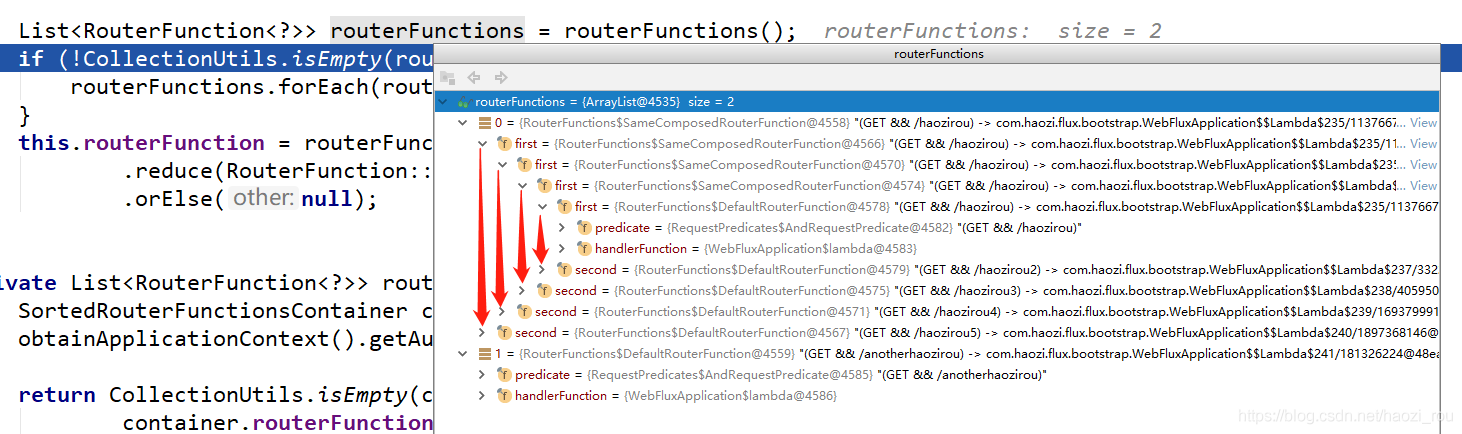
上面这种结构有点奇怪,具体怎么运行,自己看设置的时候andRoute的源码。
找到所有routerFunction后,最下面有一个合并的操作,将所有路由以集合的形式传给routerFunction。
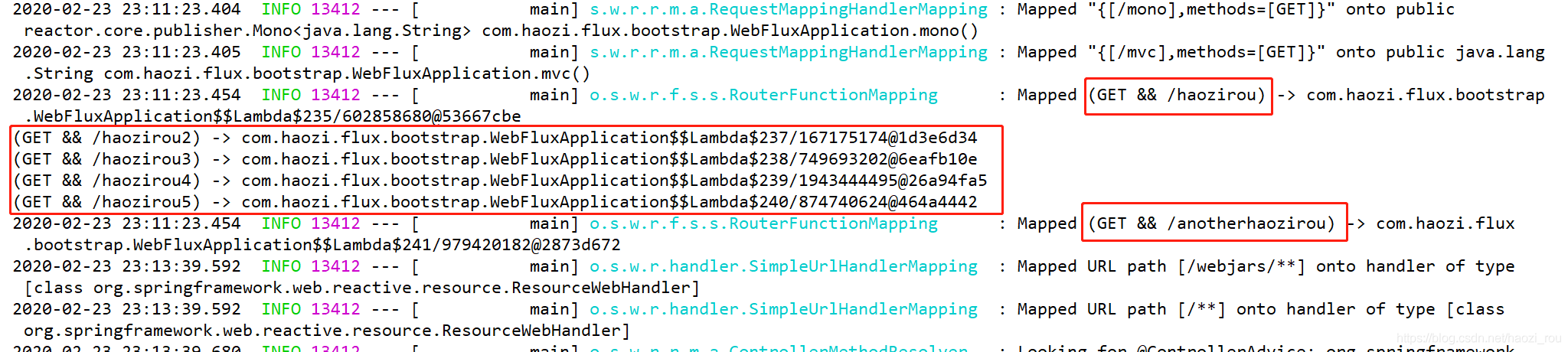
由此RouterFunctionMapping就初始化完成了,可以看一下控制台输出
接下来当请求进来的时候:
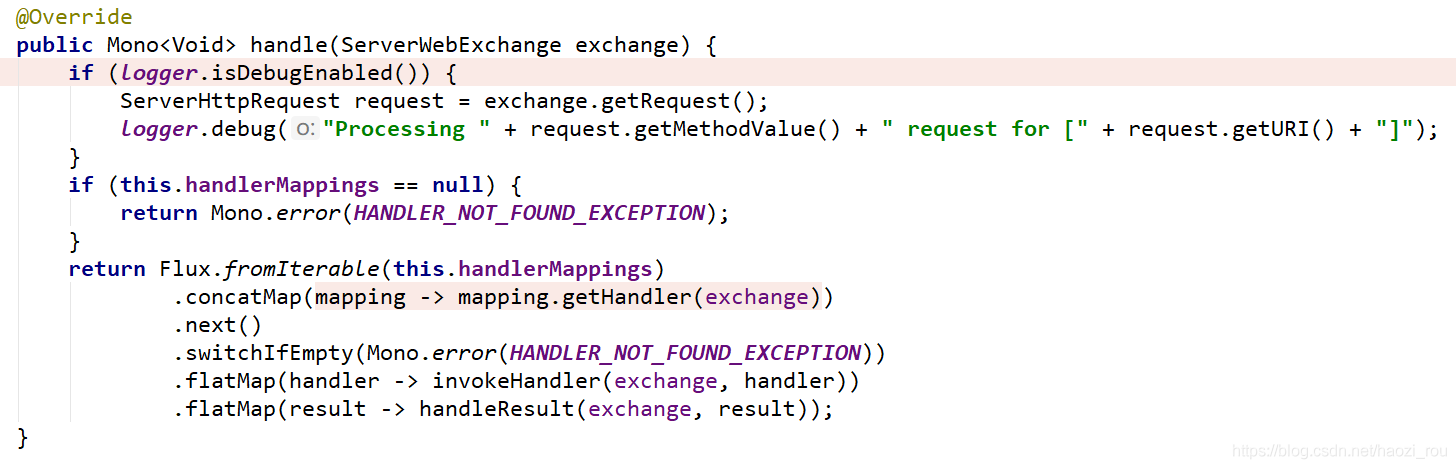
有三种mapping,最前面的就是我们前面定义的。
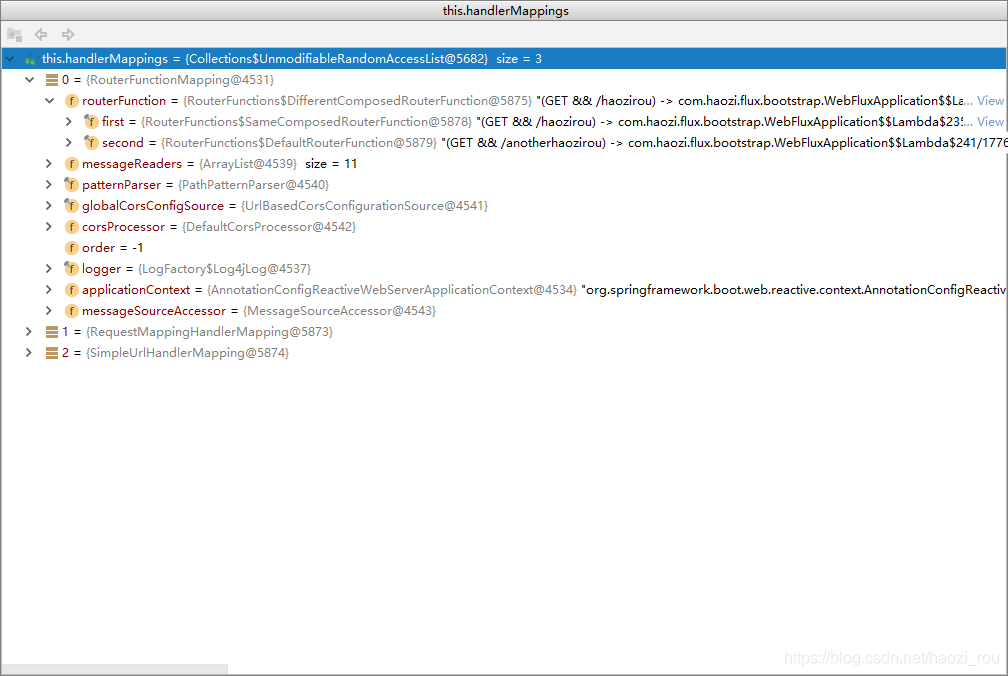
在mapping.getHandler源码中往里看,可以看到下面的方法,这个方法会routerFunction匹配我们的请求
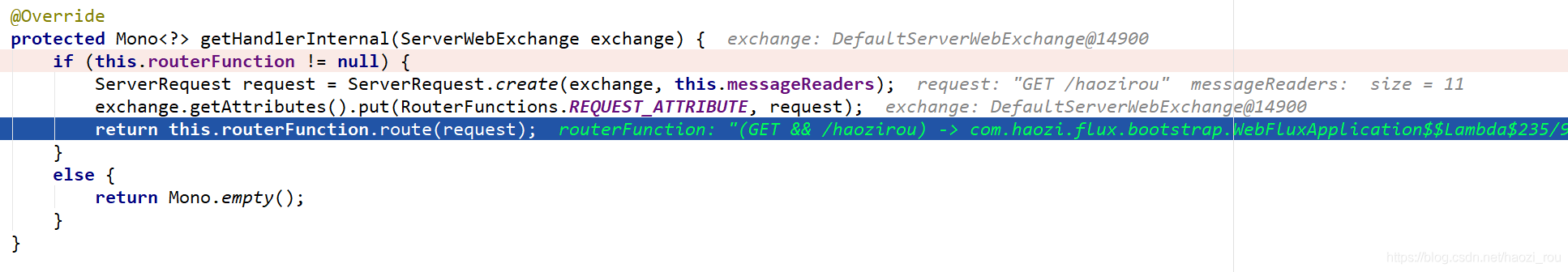
多个路由会逐一进行匹配
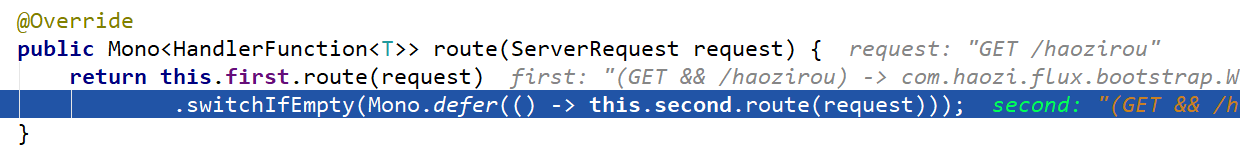
匹配成功的时候,就会返回lambda方法了,也就是HandlerFunction。
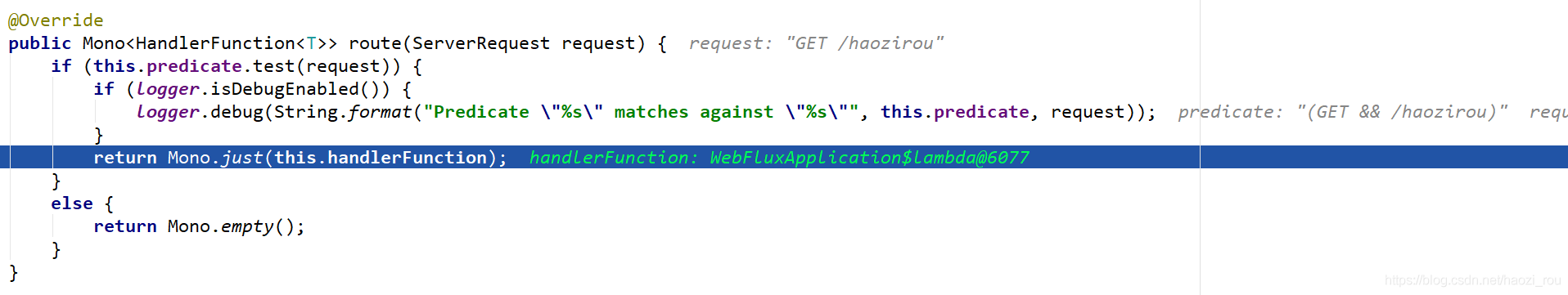
再往下,执行RouterFunction
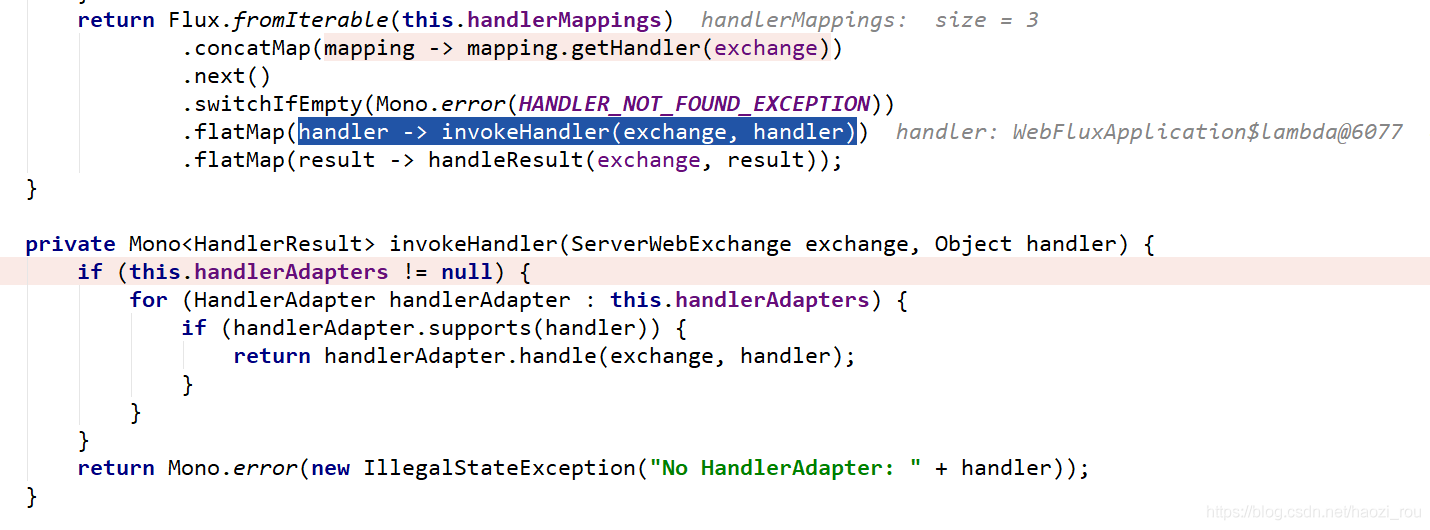
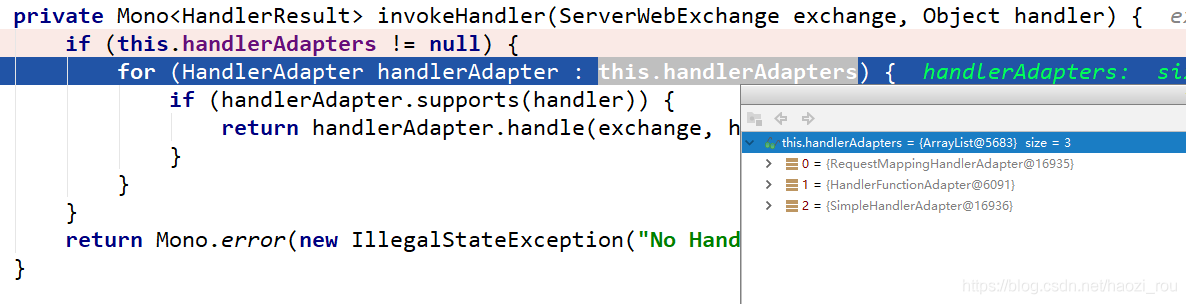
可以看到这里有三种适配器,我们选择了HandlerFunctionAdapter
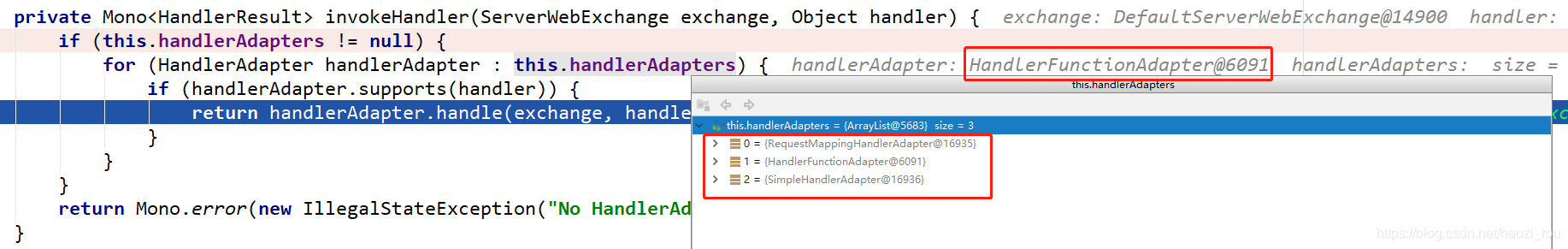
接下来进入我们自己的方法,完成后开始处理返回数据
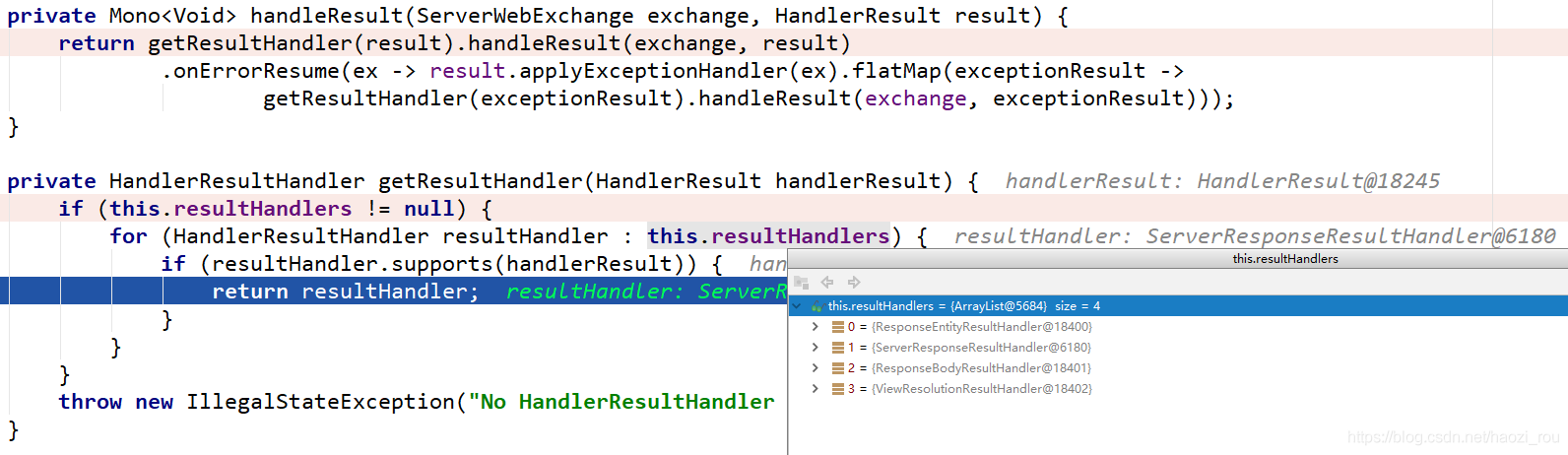
接下来输出
函数式端点的处理流程就完成了。
Performance has many characteristics and meanings. Reactive and non-blocking generally do not make applications run faster. They can, in some cases, for example if using the WebClient to execute remote calls in parallel. On the whole it requires more work to do things the non-blocking way and that can increase slightly the required processing time.
The key expected benefit of reactive and non-blocking is the ability to scale with a small, fixed number of threads and less memory. That makes applications more resilient under load because they scale in a more predictable way. In order to observe those benefits however you need to have some latency including a mix of slow and unpredictable network I/O. That’s where the reactive stack begins to show its strengths and the differences can be dramatic.
彻底找到Spring Webflux与WebMVC 冲突原因 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
一、问题(Spring Cloud Gateway Webflux启动报错)
最近运行一年的网关突然报错,无法启动,报错内容如下:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Unable to start web server; nested exception is org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing ServletWebServerFactory bean.
at org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.onRefresh(ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java:156) ~[spring-boot-2.2.5.RELEASE.jar:2.2.5.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:544) ~[spring-context-5.2.4.RELEASE.jar:5.2.4.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.refresh(ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java:141) ~[spring-boot-2.2.5.RELEASE.jar:2.2.5.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh(SpringApplication.java:747) [spring-boot-2.2.5.RELEASE.jar:2.2.5.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext(SpringApplication.java:397) [spring-boot-2.2.5.RELEASE.jar:2.2.5.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:315) [spring-boot-2.2.5.RELEASE.jar:2.2.5.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1226) [spring-boot-2.2.5.RELEASE.jar:2.2.5.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1215) [spring-boot-2.2.5.RELEASE.jar:2.2.5.RELEASE]
at com.ncmed.eos.gateway.GatewayApplication.main(GatewayApplication.java:22) [classes/:na]
Caused by: org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing ServletWebServerFactory bean.二、问题分析
从报错内容上来看是找不到ServletWebServerFactory这个bean导致的错误。从Spring Framework 5.0开始,引入的新的响应式Web框架(Spring WebFlux),与Spring MVC不同,它不需要Servlet API,完全异步和非阻塞。Spring Cloud Gateway 运用了响应式编程(WebFlux),因此它需要依赖于Servlet API,但是启动的时候为什么还是去找Servlet呢?百思不得其解。
1、相关代码如下:
Spring Cloud 版本:Hoxton.RELEASE
Nacos版本:2.1.0.RELEASE
pom文件
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--2. nacos-服务发现功能依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--alibaba nacos config-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ncmed.eos</groupId>
<artifactId>ncmed-common</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ncmed.eos</groupId>
<artifactId>ncmed-auth-client</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ncmed.eos</groupId>
<artifactId>ncmed-system-feign</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
package com.ncmed.eos.gateway;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
/**
* @author 努力的码农(Liiy)
* @email manliyi@163.com
* @date 2019/9/23 14:47
*/
@EnableFeignClients({"com.ncmed.eos.system.feign","com.ncmed.eos.auth.client.feign"})
@EnableDiscoveryClient
// 阻止注入数据库连接
@SpringBootApplication(exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class GatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GatewayApplication.class, args);
}
}2、源码追踪
由于不清楚工程启动时为什么会调用Servlet API,只好去追踪源码,了解Spring内部真相。由SpringApplication.run(GatewayApplication.class, args)进入追踪源码。
SpringApplication部分源码(按执行顺序贴出了部分调用关键代码)
/**
* Static helper that can be used to run a {@link SpringApplication} from the
* specified source using default settings.
* @param primarySource the primary source to load
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return the running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
/**
* Static helper that can be used to run a {@link SpringApplication} from the
* specified sources using default settings and user supplied arguments.
* @param primarySources the primary sources to load
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return the running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
/**
* Refresh the underlying {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param applicationContext the application context to refresh
*/
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}以上是Spring Boot启动相关主要代码,重点关注以上代码第88行((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh(),这行代码是Spring Boot启动核心,继续跟进去。
AbstractApplicationContext部分源码
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
/**
* Template method which can be overridden to add context-specific refresh work.
* Called on initialization of special beans, before instantiation of singletons.
* <p>This implementation is empty.
* @throws BeansException in case of errors
* @see #refresh()
*/
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}重点关注上面第30行代码onRefresh(),Spring Boot在这里对一些特殊化bean进行初始化,继续追踪进去,发现该方法为抽象方法,由其子类进行实现,AbstractApplicationContext 在spring boot中有两个实现类ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext和ServletWebServerApplicationContext。
从报错的第二行内容来看(ServletWebServerApplicationContext.onRefresh),启动的时候是调用了ServletWebServerApplicationContext的onRefresh方法,继续进入ServletWebServerApplicationContext进行追踪。
ServletWebServerApplicationContext部分源码
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
/**
* Returns the {@link ServletWebServerFactory} that should be used to create the
* embedded {@link WebServer}. By default this method searches for a suitable bean in
* the context itself.
* @return a {@link ServletWebServerFactory} (never {@code null})
*/
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() {
// Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);
if (beanNames.length == 0) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory bean.");
}
if (beanNames.length > 1) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames));
}
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);
}重点关注以上38行到40行代码,找到了最终抛出异常的地方。这里会去找ServletWebServerFactory bean,因为找不到该Bean导致报错。
深入思考:该类为Spring MVC的上下文启动类,WebFlux不依赖于Servlet API,为何会调用到该类,按道理应该调用ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext类。
知识点补充:
ServletWebServerApplicationContext:Servlet Web服务
ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext:响应式Web服务
此刻需要对applicationContext进行追踪,追踪其在哪里进行初始化,返回到SpringApplication源码
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
/**
* Strategy method used to create the {@link ApplicationContext}. By default this
* method will respect any explicitly set application context or application context
* class before falling back to a suitable default.
* @return the application context (not yet refreshed)
* @see #setApplicationContextClass(Class)
*/
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}重点关注第20行代码context = createApplicationContext()继续追踪,在createApplicationContext方法找到了ApplicationContext初始化代码,通过属性webApplicationType来决定初始化上下文对象是ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext还是ServletWebServerApplicationContext,如果webApplicationType属性值为SERVLET则初始化ServletWebServerApplicationContext,如果为REACTIVE则初始化ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext,很显然这里的属性值为SERVLET。继续追踪webApplicationType在哪里赋值?
/**
* Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load
* beans from the specified primary sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level}
* documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling
* {@link #run(String...)}.
* @param primarySources the primary bean sources
* @see #run(Class, String[])
* @see #SpringApplication(ResourceLoader, Class...)
* @see #setSources(Set)
*/
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
/**
* Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load
* beans from the specified primary sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level}
* documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling
* {@link #run(String...)}.
* @param resourceLoader the resource loader to use
* @param primarySources the primary bean sources
* @see #run(Class, String[])
* @see #setSources(Set)
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}继续关注SpringApplication源码,发现SpringApplication初始化时对webApplicationType进行了赋值(上面第30行代码),继续追踪。
WebApplicationType部分源码
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";
private static final String SERVLET_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext";
private static final String REACTIVE_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebApplicationContext";
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}从源码可以看出,默认是SERVLET,当org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler能加载,org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet和org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer不能加载的时候才是REACTIVE,定位到这里的时候,发现相关jar包中引入了DispatcherServlet类,导致无法正常使用响应式上下文(ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext)。DispatcherServlet类位于Spring WebMVC的jar包中,在pom文件中剔除Spring MVC jar包即可。
ClassUtils部分源码
/**
* Resolve the given class name into a Class instance. Supports
* primitives (like "int") and array class names (like "String[]").
* <p>This is effectively equivalent to the {@code forName}
* method with the same arguments, with the only difference being
* the exceptions thrown in case of class loading failure.
* @param className the name of the Class
* @param classLoader the class loader to use
* (may be {@code null}, which indicates the default class loader)
* @return a class instance for the supplied name
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the class name was not resolvable
* (that is, the class could not be found or the class file could not be loaded)
* @throws IllegalStateException if the corresponding class is resolvable but
* there was a readability mismatch in the inheritance hierarchy of the class
* (typically a missing dependency declaration in a Jigsaw module definition
* for a superclass or interface implemented by the class to be loaded here)
* @see #forName(String, ClassLoader)
*/
public static Class<?> resolveClassName(String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader)
throws IllegalArgumentException {
try {
return forName(className, classLoader);
}
catch (IllegalAccessError err) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Readability mismatch in inheritance hierarchy of class [" +
className + "]: " + err.getMessage(), err);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unresolvable class definition for class [" + className + "]", err);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not find class [" + className + "]", ex);
}
}如果没有排除Spring WebMVC相关jar包,还可以采用另外一种方式去指定webApplicationType为REACTIVE
package com.ncmed.eos.gateway;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.WebApplicationType;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
/**
* @author 努力的码农(Liiy)
* @email manliyi@163.com
* @date 2019/9/23 14:47
*/
@EnableFeignClients({"com.ncmed.eos.system.feign","com.ncmed.eos.auth.client.feign"})
@EnableDiscoveryClient
// 阻止注入数据库连接
@SpringBootApplication(exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class GatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// SpringApplication.run(GatewayApplication.class, args);
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(GatewayApplication.class);
// 该设置方式
application.setWebApplicationType(WebApplicationType.REACTIVE);
application.run(args);
}
}总结:名面上来看,我并没有引入Spring WebMVC相关jar包,但是其他的包中引入了,因此要特别注意pom文件中的引入,包与包之间存在许多依赖关系,需要仔细检查其依赖。
WebFlux切换Web容器Tomcat、undertow、jetty、netty_ywb201314的博客-CSDN博客
没有比较就没有伤害!Web 容器我们用的最多的还是 Tomcat,但是 Tomcat 的性能现在比起其他容器来说有点劣势!很多人可能更喜欢 Jetty 或者 netty,那么这么多 Web 容器,我们在使用 WebFlux 的时候该如何切换呢?一起来看本文的教程吧!
Spring WebFlux支持Netty,Undertow,Tomcat,Jetty和Servlet 3.1+容器。他们都适用于一个通用的Reactive Streams API。Spring WebFlux编程模型基于该通用API。
Spring WebFlux 默认是使用 Netty 作为 Web 容器的。如果要切换 Web 容器,只需要在 Maven 中做一下配置即可。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-netty</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加 Undertow依赖 -->
<!-- <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId>
</dependency> -->
<!-- <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency> -->思路就是,先在 spring-boot-starter-webflux 容器中排除 netty 的 starter。然后添加需要的 Web 容器的 starter 即可。
那么怎么看自己是否配置成功呢?
有两种验证方法。第一种是在你的 idea 编辑器中的项目工程的 External Libraries 中查看你引入的 Web 容器的 starter 是否被加了进来。
第二种方法是,把你的工程跑起来,看看启动日志。以 Tomcat 为例,它在启动的日志可可以看到很多关于 tomcat 的日志信息。比如下面的内容:
Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''Undertow是一个Java开发的灵活的高性能Web服务器,提供包括阻塞和基于NIO的非阻塞机制。Undertow是红帽公司的开源产品,是Wildfly默认的Web服务器。Undertow 用的人比较少,但是它性能不错。具体用法上面的配置中也有,其他的我就不在多说了。你都可以用起来,比较比较!
Circular Dependencies in Spring | Baeldung
Spring源码学习--Bean对象循环依赖问题解决(四)_原型bean循环依赖_军伟@的博客-CSDN博客
循环依赖就是N个类相互嵌套引用,如果通过new对象的方式产生循环依赖的话会导致程序内存溢出报错,接下来我们了解一下spring是如何解决循环依赖问题。
第一种:prototype原型bean循环依赖
AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean()方法:
-
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
-
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
-
}
-
protected boolean isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName) {
-
Object curVal = this.prototypesCurrentlyInCreation.get();
-
return (curVal != null &&
-
(curVal.equals(beanName) || (curVal instanceof Set && ((Set<?>) curVal).contains(beanName))));
-
}
在获取bean之前如果这个原型bean正在被创建则直接抛出异常。原型bean在创建之前会进行标记这个beanName正在被创建,等创建结束之后会删除标记
-
try {
-
//创建原型bean之前添加标记
-
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
-
//创建原型bean
-
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
-
}
-
finally {
-
//创建原型bean之后删除标记
-
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
-
}
总结:简单来说Spring不支持原型bean的循环依赖。
第二种:单例bean 构造器参数循环依赖
1、Spring创建ClassA时首先会调用beforeSingletonCreation(beanName),判断单例bean是否正在被创建,如果正在被创建则报错,如果没有被创建则做标记
-
protected void beforeSingletonCreation(String beanName) {
-
//singletonsCurrentlyInCreation是一个集合,不可重复,add返回true则表明没有创建,返回false则说明bean在创建
-
if (!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && !this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(beanName)) {
-
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
-
}
-
}
此时刚开始创建ClassA,因此不会报异常错误,当初始化ClassA的构造器时需要用到ClassB的实例。
2、Spring从容器中无法获取ClassB的实例,接下来Spring按照步骤1创建ClassB的实例,在构造ClassB的构造函数时需要用到ClassA的实例。
3、Spring还是首先尝试从容器中获取ClassA的实例,由于第1步还没有执行结束,此时还没有ClassA实例,Spring容器认为就需要初始化ClassA了,重复第1步,
但是ClassA一开始就已经进行了第1步,并且做标记bean正在创建,当再次进入第一步时就会抛出异常错误。
总结:Spring在创建构造器循环依赖时其实就是循环初始化操作 A-> B -> A 当A要被初始化第二次时就直接抛出异常。
第三种 :单例bean通过setXxx或者@Autowired进行循环依赖
1、Spring容器初始化ClassA通过构造器初始化对象后提前暴露到Spring容器。
-
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
-
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
-
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
-
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
-
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
-
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
-
}
-
//将初始化后的对象提前已ObjectFactory对象注入到容器中
-
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
-
-
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
-
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
-
}
-
});
-
}
2、ClassA调用setClassB方法,Spring首先尝试从容器中获取ClassB,此时ClassB不存在Spring容器中。
3、Spring容器初始化ClassB,同时也会将ClassB提前暴露到Spring容器中
4、ClassB调用setClassA方法,Spring从容器中获取ClassA ,因为第一步中已经提前暴露了ClassA,因此可以获取到ClassA实例
5、ClassA通过spring容器获取到ClassB,完成了对象初始化操作。
6、这样ClassA和ClassB都完成了对象初始化操作,解决了循环依赖问题。
总结:简单来说就是对象通过构造函数初始化之后就暴露到容器中,这样就不会存在循环初始化对象的情况了。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号