FTP-COMMAND
FTP Commands and Extensions
- Created
- 2010-01-07
- Last Updated
- 2014-03-14
- Available Formats

XML
HTML
Plain text
Registry included below
FTP Commands and Extensions
- Expert(s)
-
Unassigned
- Reference
- [RFC5797]
- Note
-
Note: An IESG Standards Action is allowed to direct IANA to change the Conformance Requirements listed for any entry. The following commands are part of the base FTP specification [RFC0959] and are listed in the registry with the immutable pseudo FEAT code "base". Mandatory commands: ABOR, ACCT, ALLO, APPE, CWD, DELE, HELP, LIST, MODE, NLST, NOOP, PASS, PASV, PORT, QUIT, REIN, REST, RETR, RNFR, RNTO, SITE, STAT, STOR, STRU, TYPE, USER Optional commands: CDUP, MKD, PWD, RMD, SMNT, STOU, SYST Note: STD 3 [RFC1123] clarified and updated the status and implementation requirements of these standard FTP commands, and it contains important complementary information for the following commands: LIST, NLST, PASV, REST, SITE, STOU The following commands were specified as experimental in an extension to an early version of the FTP specification [RFC0775] but later deprecated by RFC 1123 [RFC1123], because Standard FTP [RFC0959] specifies their standard successors. They are listed in the registry with the immutable pseudo FEAT code "hist". XCUP, XCWD, XMKD, XPWD, XRMD Implementation note: Deployed FTP clients still make use of the deprecated commands and most FTP servers support them as aliases for the standard commands. The following commands were specified as part of the "FOOBAR" IPng effort in RFC 1545 [RFC1545] and, later, RFC 1639 [RFC1639] and are now obsolete. They are listed in the registry with the immutable pseudo FEAT code "hist". LPRT, LPSV Legend for the registry: o cmd (Command Name) Amended versions of commands are tagged with a trailing "+" o FEAT Code Keyword returned in FEAT response line for this command/extension: - actual FEAT codes are given in upper case - placeholders (pseudo FEAT codes) are shown in lower case - "-N/A-" indicates a feature not related to one particular command See the "Extension name" clause in Section 2.2 of [RFC5797] for details. o description Brief description of command / extension o type (Command Type) Type or "kind" of command, based on Section 4.1 of [RFC959]: 'a' ... access control 'p' ... parameter setting 's' ... service execution Combinations like 'p/s' are possible. o conf (Conformance Requirements) Expectation for support in modern FTP implementations: 'm' ... mandatory to implement 'o' ... optional 'h' ... historic - Available Formats

CSV
Range  | Registration Procedures  |
|---|---|
| registration marked "mandatory" ('m' in the "conf" column) | Standards Action |
| all other registrations | Specification Required |
cmd  | FEAT code  | description  | type  | conf  | References and Notes  |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABOR | base | Abort | s | m | [RFC959] |
| ACCT | base | Account | a | m | [RFC959] |
| ADAT | secu | Authentication/Security Data | a | o | [RFC2228] [RFC2773] [RFC4217] |
| ALGS | FTP64 ALG status | o | [RFC6384] Section 11 | ||
| ALLO | base | Allocate | s | m | [RFC959] |
| APPE | base | Append (with create) | s | m | [RFC959] |
| AUTH | secu | Authentication/Security Mechanism | a | o | [RFC2228] |
| AUTH+ | AUTH | Authentication/Security Mechanism | a | o | [2][RFC2773][RFC4217] |
| CCC | secu | Clear Command Channel | a | o | [RFC2228] |
| CDUP | base | Change to Parent Directory | a | o | [RFC959] |
| CONF | secu | Confidentiality Protected Command | a | o | [RFC2228] |
| CWD | base | Change Working Directory | a | m | [RFC959] |
| DELE | base | Delete File | s | m | [RFC959] |
| ENC | secu | Privacy Protected Command | a | o | [RFC2228] [RFC2773] [RFC4217] |
| EPRT | nat6 | Extended Port | p | o | [RFC2428] |
| EPSV | nat6 | Extended Passive Mode | p | o | [RFC2428] |
| FEAT | feat | Feature Negotiation | a | m [1] | [RFC2389] |
| HELP | base | Help | s | m | [RFC959] |
| HOST | HOST | Hostname | a | o | [RFC7151] |
| LANG | UTF8 | Language (for Server Messages) | p | o | [RFC2640] |
| LIST | base | List | s | m | [RFC959][RFC1123] |
| LPRT | hist | Data Port {FOOBAR} | p | h | [RFC1545][RFC1639] |
| LPSV | hist | Passive Mode {FOOBAR} | p | h | [RFC1545][RFC1639] |
| MDTM | MDTM | File Modification Time | s | o | [RFC3659] |
| MIC | secu | Integrity Protected Command | a | o | [RFC2228][RFC2773] [RFC4217] |
| MKD | base | Make Directory | s | o | [RFC959] |
| MLSD | MLST | List Directory (for machine) | s | o | [RFC3659] |
| MLST | MLST | List Single Object | s | o | [RFC3659] |
| MODE | base | Transfer Mode | p | m | [RFC959] |
| NLST | base | Name List | s | m | [RFC959][RFC1123] |
| NOOP | base | No-Op | s | m | [RFC959] |
| OPTS | feat | Options | p | m [1] | [RFC2389] |
| PASS | base | Password | a | m | [RFC959] |
| PASV | base | Passive Mode | p | m | [RFC959][RFC1123] |
| PBSZ | secu | Protection Buffer Size | p | o | [RFC2228] |
| PBSZ+ | PBSZ | Protection Buffer Size | p | o | [RFC4217] |
| PORT | base | Data Port | p | m | [RFC959] |
| PROT | secu | Data Channel Protection Level | p | o | [RFC2228] |
| PROT+ | PROT | Data Channel Protection Level | p | o | [RFC4217] |
| PWD | base | Print Directory | s | o | [RFC959] |
| QUIT | base | Logout | a | m | [RFC959] |
| REIN | base | Reinitialize | a | m | [RFC959] |
| REST | base | Restart | s/p | m | [RFC959][RFC1123] |
| REST+ | REST | Restart (for STREAM mode) | s/p | m | [3][RFC3659] |
| RETR | base | Retrieve | s | m | [RFC959] |
| RMD | base | Remove Directory | s | o | [RFC959] |
| RNFR | base | Rename From | s/p | m | [RFC959] |
| RNTO | base | Rename From | s | m | [RFC959] |
| SITE | base | Site Parameters | s | m | [RFC959][RFC1123] |
| SIZE | SIZE | File Size | s | o | [RFC3659] |
| SMNT | base | Structure Mount | a | o | [RFC959] |
| STAT | base | Status | s | m | [RFC959] |
| STOR | base | Store | s | m | [RFC959] |
| STOU | base | Store Unique | a | o | [RFC959][RFC1123] |
| STRU | base | File Structure | p | m | [RFC959] |
| SYST | base | System | s | o | [RFC959] |
| TYPE | base | Representation Type | p | m | [4][RFC959] |
| USER | base | User Name | a | m | [RFC959] |
| XCUP | hist | {precursor for CDUP} | s | h | [RFC775] [RFC1123] |
| XCWD | hist | {precursor for CWD} | s | h | [RFC775] [RFC1123] |
| XMKD | hist | {precursor for MKD} | s | h | [RFC775] [RFC1123] |
| XPWD | hist | {precursor for PWD} | s | h | [RFC775] [RFC1123] |
| XRMD | hist | {precursor for RMD} | s | h | [RFC775] [RFC1123] |
| -N/A- | TVFS | Trivial Virtual File Store | p | o | [RFC3659] |
Footnotes
FTP Commands and Extensions: https://www.iana.org/assignments/ftp-commands-extensions/ftp-commands-extensions.xml
List of raw FTP commands
(Warning: this is a technical document, not necessary for most FTP use.)
Note that commands marked with a * are not implemented in a number of FTP servers.
Common commands
- ABOR - abort a file transfer
- CWD - change working directory
- DELE - delete a remote file
- LIST - list remote files
- MDTM - return the modification time of a file
- MKD - make a remote directory
- NLST - name list of remote directory
- PASS - send password
- PASV - enter passive mode
- PORT - open a data port
- PWD - print working directory
- QUIT - terminate the connection
- RETR - retrieve a remote file
- RMD - remove a remote directory
- RNFR - rename from
- RNTO - rename to
- SITE - site-specific commands
- SIZE - return the size of a file
- STOR - store a file on the remote host
- TYPE - set transfer type
- USER - send username
Less common commands
- ACCT* - send account information
- APPE - append to a remote file
- CDUP - CWD to the parent of the current directory
- HELP - return help on using the server
- MODE - set transfer mode
- NOOP - do nothing
- REIN* - reinitialize the connection
- STAT - return server status
- STOU - store a file uniquely
- STRU - set file transfer structure
- SYST - return system type
ABOR
Syntax: ABOR
Aborts a file transfer currently in progress.
ACCT*
Syntax: ACCT account-info
This command is used to send account information on systems that require it. Typically sent after a PASS command.
ALLO
Syntax: ALLO size [R max-record-size]
Allocates sufficient storage space to receive a file. If the maximum size of a record also needs to be known, that is sent as a second numeric parameter following a space, the capital letter "R", and another space.
APPE
Syntax: APPE remote-filename
Append data to the end of a file on the remote host. If the file does not already exist, it is created. This command must be preceded by a PORT or PASV command so that the server knows where to receive data from.
CDUP
Syntax: CDUP
Makes the parent of the current directory be the current directory.
CWD
Syntax: CWD remote-directory
Makes the given directory be the current directory on the remote host.
DELE
Syntax: DELE remote-filename
Deletes the given file on the remote host.
HELP
Syntax: HELP [command]
If a command is given, returns help on that command; otherwise, returns general help for the FTP server (usually a list of supported commands).
LIST
Syntax: LIST [remote-filespec]
If remote-filespec refers to a file, sends information about that file. If remote-filespec refers to a directory, sends information about each file in that directory. remote-filespec defaults to the current directory. This command must be preceded by a PORT or PASV command.
MDTM
Syntax: MDTM remote-filename
Returns the last-modified time of the given file on the remote host in the format "YYYYMMDDhhmmss": YYYY is the four-digit year, MM is the month from 01 to 12, DD is the day of the month from 01 to 31, hh is the hour from 00 to 23, mm is the minute from 00 to 59, and ss is the second from 00 to 59.
MKD
Syntax: MKD remote-directory
Creates the named directory on the remote host.
MODE
Syntax: MODE mode-character
Sets the transfer mode to one of:
- S - Stream
- B - Block
- C - Compressed
The default mode is Stream.
NLST
Syntax: NLST [remote-directory]
Returns a list of filenames in the given directory (defaulting to the current directory), with no other information. Must be preceded by a PORT or PASV command.
NOOP
Syntax: NOOP
Does nothing except return a response.
PASS
Syntax: PASS password
After sending the USER command, send this command to complete the login process. (Note, however, that an ACCT command may have to be used on some systems.)
PASV
Syntax: PASV
Tells the server to enter "passive mode". In passive mode, the server will wait for the client to establish a connection with it rather than attempting to connect to a client-specified port. The server will respond with the address of the port it is listening on, with a message like:
227 Entering Passive Mode (a1,a2,a3,a4,p1,p2)
where a1.a2.a3.a4 is the IP address and p1*256+p2 is the port number.
PORT
Syntax: PORT a1,a2,a3,a4,p1,p2
Specifies the host and port to which the server should connect for the next file transfer. This is interpreted as IP address a1.a2.a3.a4, port p1*256+p2.
PWD
Syntax: PWD
Returns the name of the current directory on the remote host.
QUIT
Syntax: QUIT
Terminates the command connection.
REIN*
Syntax: REIN
Reinitializes the command connection - cancels the current user/password/account information. Should be followed by a USER command for another login.
REST
Syntax: REST position
Sets the point at which a file transfer should start; useful for resuming interrupted transfers. For nonstructured files, this is simply a decimal number. This command must immediately precede a data transfer command (RETR or STOR only); i.e. it must come after any PORT or PASV command.
RETR
Syntax: RETR remote-filename
Begins transmission of a file from the remote host. Must be preceded by either a PORT command or a PASV command to indicate where the server should send data.
RMD
Syntax: RMD remote-directory
Deletes the named directory on the remote host.
RNFR
Syntax: RNFR from-filename
Used when renaming a file. Use this command to specify the file to be renamed; follow it with an RNTO command to specify the new name for the file.
RNTO
Syntax: RNTO to-filename
Used when renaming a file. After sending an RNFR command to specify the file to rename, send this command to specify the new name for the file.
SITE*
Syntax: SITE site-specific-command
Executes a site-specific command.
SIZE
Syntax: SIZE remote-filename
Returns the size of the remote file as a decimal number.
STAT
Syntax: STAT [remote-filespec]
If invoked without parameters, returns general status information about the FTP server process. If a parameter is given, acts like the LIST command, except that data is sent over the control connection (no PORT or PASV command is required).
STOR
Syntax: STOR remote-filename
Begins transmission of a file to the remote site. Must be preceded by either a PORT command or a PASV command so the server knows where to accept data from.
STOU
Syntax: STOU
Begins transmission of a file to the remote site; the remote filename will be unique in the current directory. The response from the server will include the filename.
STRU
Syntax: STRU structure-character
Sets the file structure for transfer to one of:
- F - File (no structure)
- R - Record structure
- P - Page structure
The default structure is File.
SYST
Syntax: SYST
Returns a word identifying the system, the word "Type:", and the default transfer type (as would be set by the TYPE command). For example: UNIX Type: L8
TYPE
Syntax: TYPE type-character [second-type-character]
Sets the type of file to be transferred. type-character can be any of:
- A - ASCII text
- E - EBCDIC text
- I - image (binary data)
- L - local format
For A and E, the second-type-character specifies how the text should be interpreted. It can be:
- N - Non-print (not destined for printing). This is the default if second-type-character is omitted.
- T - Telnet format control (<CR>, <FF>, etc.)
- C - ASA Carriage Control
For L, the second-type-character specifies the number of bits per byte on the local system, and may not be omitted.
USER
Syntax: USER username
Send this command to begin the login process. username should be a valid username on the system, or "anonymous" to initiate an anonymous login.
The STOR, APPE, STOU, ALLO, MKD, RMD, DELE, RNFR, and RNTO verbs
The STOR verb
A STOR request asks the server to read the contents of a file from the data connection already established by the client. The STOR parameter is an encoded pathname of the file. The file is either a binary file or a text file, depending on the most recent TYPE request.
If the server is willing to create a new file under that name, or replace an existing file under that name, it responds with a mark using code 150. It then stops accepting new connections, attempts to read the contents of the file from the data connection, and closes the data connection. Finally it
- accepts the STOR request with code 226 if the entire file was successfully received and stored;
- rejects the STOR request with code 425 if no TCP connection was established;
- rejects the STOR request with code 426 if the TCP connection was established but then broken by the client or by network failure; or
- rejects the STOR request with code 451, 452, or 552 if the server had trouble saving the file to disk.
The server may reject the STOR request (code 450, 452, or 553) without first responding with a mark. In this case the server does not touch the data connection.
Some servers allow REST immediately before STOR for binary files, if a previous STOR for the same file transmitted at least the number of bytes given by the start position.
The APPE verb
APPE is just like STOR except that, if the file already exists, the server appends the client's data to the file.
The STOU verb
STOU is just like STOR except that it asks the server to create a file under a new pathname selected by the server. The STOU parameter is optional; if it is supplied, it is a suggested pathname, which the server will ignore if there is already a file with that pathname. (RFC 959 prohibited STOU parameters, but this prohibition is obsolete.)
If the server accepts STOU, it provides the pathname in a human-readable format in the text of its response.
The ALLO verb
ALLO is obsolete. The server should accept any ALLO request with code 202.
The MKD verb
A MKD request asks the server to create a new directory. The MKD parameter is an encoded pathname specifying the directory.
If the server accepts MKD (required code 257), its response includes the pathname of the directory, in the same format used for responses to PWD.
A typical server accepts MKD with code 250 if the directory was successfully created, or rejects MKD with code 550 if the creation failed.
RFC 1123 requires that the server treat XMKD as a synonym for MKD.
The RMD verb
An RMD request asks the server to remove a directory. The RMD parameter is an encoded pathname specifying the directory.
A typical server accepts RMD with code 250 if the directory was successfully removed, or rejects RMD with code 550 if the removal failed.
RFC 1123 requires that the server treat XRMD as a synonym for RMD.
The DELE verb
A DELE request asks the server to remove a regular file. The DELE parameter is an encoded pathname specifying the file.
A typical server accepts DELE with code 250 if the file was successfully removed, or rejects DELE with code 450 or 550 if the removal failed.
The RNFR verb
A RNFR request asks the server to begin renaming a file. The RNFR parameter is an encoded pathname specifying the file.
A typical server accepts RNFR with code 350 if the file exists, or rejects RNFR with code 450 or 550 otherwise.
The RNTO verb
A RNTO request asks the server to finish renaming a file. The RNTO parameter is an encoded pathname specifying the new location of the file. RNTO must come immediately after RNFR; otherwise the server may reject RNTO with code 503.
A typical server accepts RNTO with code 250 if the file was renamed successfully, or rejects RNTO with code 550 or 553 otherwise.
https://cr.yp.to/ftp/stor.html
vsftpd的安装和使用
vsftpd的安装和使用_Aaron_Run的博客-CSDN博客_vsftpd
1、vsftpd的简介
vsftpd是“very secure TTP daemon”的缩写,是一个完全免费的、开放源代码的ftp服务器软件
2、特点
vsftpd是一款在Linux发行版中最受推崇的ftp服务器程序,小巧轻快,安全易用,支持虚拟用户,支持带宽限制等功能
3、安装
检查Linux系统是否安装了vsftpd的命令:rpm -qa|grep vsftpd
卸载vsftpd的命令yum remove vsftpd
执行yum -y install vsftpd
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install vsftpd

使用whereis vsftpd 查看安装路径
[root@localhost ~]#whereis vsftpd
![]()
注:
(1)是否使用sudo权限执行,请根据具体环境决定
(2)yum安装vsftpd的默认配置文件在/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
4、创建虚拟用户
(1)选择在根目录或用户目录下创建ftp文件目录:mkdir ftpfile,如/ftpfile,
[root@localhost ~]# cd /
[root@localhost /]# mkdir ftpfile
[root@localhost /]# ls
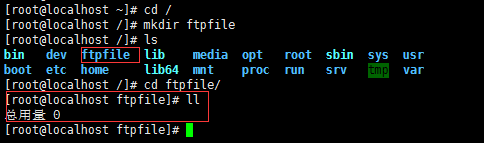
通过ftp上传时就会传到这个文件夹下
(2)添加匿名用户:useradd ftpuser -d /ftpfile/ -s /sbin/nologin #添加用户没有登录机器的权限,只有上传ftpfile有权限.
[root@localhost ftpfile]# useradd ftpuser -d /ftpfile/ -s /sbin/nologin
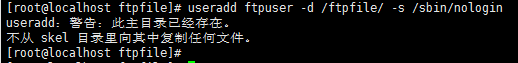
(3)修改ftpfile权限:chown -R ftpuser.ftpuser /ftpfile/ #把创建的用户和创建的文件夹的权限对应上。-R表示遍历,把用户或者用户组赋予到/ftpfile这个文件夹的权限上
[root@localhost ftpfile]# chown -R ftpuser.ftpuser /ftpfile/
![]()
查看该文件目录的权限
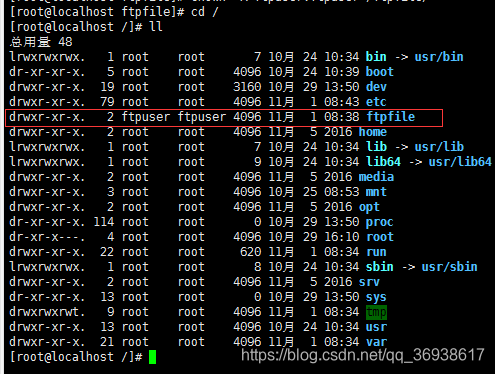
此时的用户名和用户组的权限都为ftpuser
(4)重设ftpuser密码:passwd ftpuser 123456(这里设置的密码为123456)
[root@localhost /]# passwd ftpuser
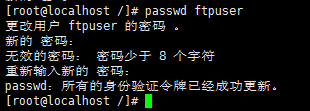
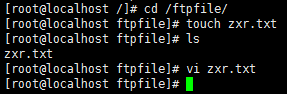
(5)在vsftpd文件目录下创建测试文件zxr.txt
[root@localhost /]# cd ftpfile/
[root@localhost ftpfile]# touch zxr.txt
[root@localhost ftpfile]# ls
zxr.txt
[root@localhost ftpfile]# vi zxr.txt
5、vsftpd服务器的配置
(1)vsftpd.conf文件
查看ftp服务器的安装路径
[root@localhost ftpfile]# whereis vsftpd
![]()
进入/etc/vsftpd/目录下
[root@localhost ftpfile]# cd /etc/vsftpd/
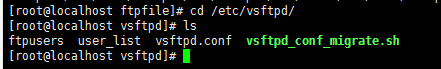
编辑vsftpd.conf文件,把创建的用户配置上
修改客户端登录,提示的欢迎信息(vi打开文件输入/然后将banner输入,再点击enter键,能快速找到banner信息)
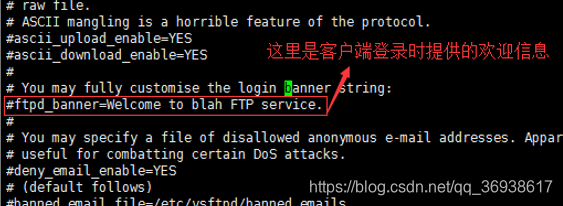
需要将注释取消掉,改为自己想要的提示信息
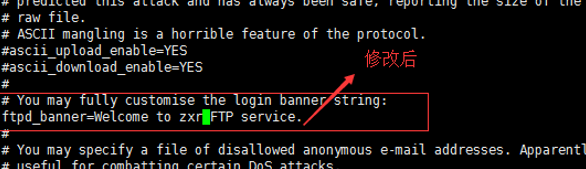
还需要添加一些重要的属性节点
local_root=/ftpfile #把本地账户指向创建的ftpfile文件夹
anon_root=/ftpfile #添加匿名账户访问ftpfile目录
use_localtime=YES #ftp服务器用到的是本地的时间
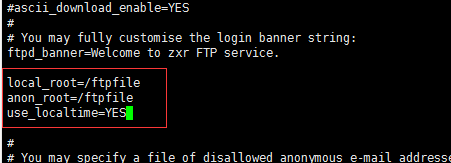
查找chroot_list节点
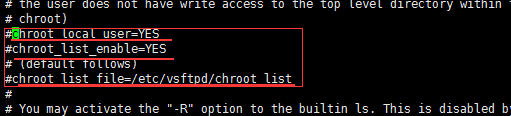
#chroot_local_user=YES #这个节点为是否锁定创建的/ftpfile为根目录,不解除注释,默认为chroot_local_user=NO,锁定创建的/ftpfile为根目录,如果解除后设置为chroot_local_user=YES,那么就没有锁定创建的/ftpfile为根目录,在命令行是可以访问到/ftpfile的上级目录,也就是系统的根目录,这是绝对不安全的。所以这个节点不用解除注释,或者解除更改为chroot_local_user=NO。
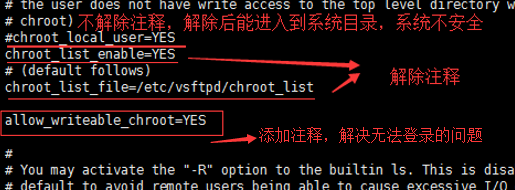
编辑该节点,解除
chroot_list_enable=YES
chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list
添加节点
allow_writeable_chroot=YES #加上这行解决了无法登陆的问题
两条命令的注释,将新建的用户添上。
查找节点anonymous_enable
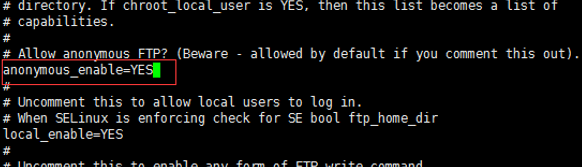
将该节点改为anonymous_enable=NO,不允许匿名用户登录
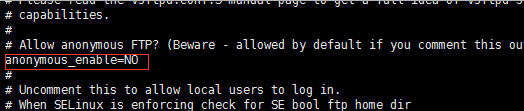
在该文件的末尾添加传输接口的范围,最大接口61001,最大接口62000,限定严格的设置防火墙。
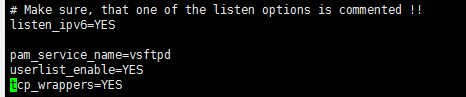
添加范围
pasv_min_port=61001
pasv_max_port=62000
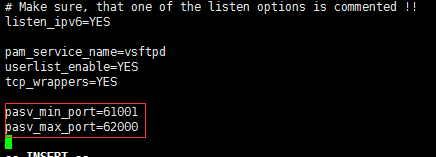
编辑完成保存退出。
(2)配置chroot_list文件
该文件目录的节点在上一步配置vsftpd.conf文件中已解除注释。
进入到/etc/vsftpd/目录下创建文件chroot_list
[root@localhost vsftpd]# cd /etc/vsftpd/
[root@localhost vsftpd]# vi chroot_list
#用编辑器打开文件时,如果没有这个文件,会默认自动创建一个该文件。
![]()
将用户添加进入该新建的chroot_list文件中

保存退出。
(5)编辑文件/etc/selinux/config文件
[root@localhost vsftpd]# vi /etc/selinux/config
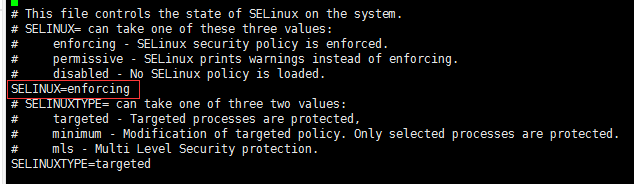
修改为SELINUX=disabled,如果不改的话,匿名账户无法创建文件文件或者文件目录
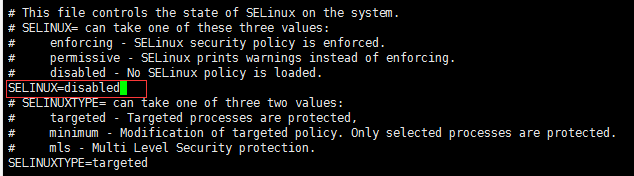
:wq保存退出
注:如果在验证的时候碰到550拒绝访问请执行:
sudo setsebool -P ftp_home_dir 1
然后重启Linux服务器,执行reboot命令。
6、vsftpd配置文件说明
sudo vi /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
vsftpd.conf文件的配置文件的添加或更新配置
本项目要用到的配置项:
1)local_root=/ftpfile(当本地用户登入时,将被更换到定义的目录下,默认值为各用户的家目录)
2)anon_root=/ftpfile(使用匿名登入时,所登入的目录)
3)use_localtime=YES(默认是GMT时间,改成使用本机系统时间)
4)anonymous_enable=NO(不允许匿名用户登录)
5)local_enable=YES(允许本地用户登录)
6)write_enable=YES(本地用户可以在自己家目录中进行读写操作)
7)local_umask=022(本地用户新增档案时的umask值)
8)dirmessage_enable=YES(如果启动这个选项,那么使用者第一次进入一个目录时,会检查该目录下是否有.message这个档案,如果有,则会出现此档案的内容,通常这个档案会放置欢迎话语,或是对该目录的说明。默认值为开启)
9)xferlog_enable=YES(是否启用上传/下载日志记录。如果启用,则上传与下载的信息将被完整纪录在xferlog_file 所定义的档案中。预设为开启。)
10)connect_from_port_20=YES(指定FTP使用20端口进行数据传输,默认值为YES)
11)xferlog_std_format=YES(如果启用,则日志文件将会写成xferlog的标准格式)
12)ftpd_banner=Welcome to mmall FTP Server(这里用来定义欢迎话语的字符串)
13)chroot_local_user=NO(用于指定用户列表文件中的用户是否允许切换到上级目录)
14)chroot_list_enable=YES(设置是否启用chroot_list_file配置项指定的用户列表文件)
15)chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list(用于指定用户列表文件)
16)listen=YES(设置vsftpd服务器是否以standalone模式运行,以standalone模式运行是一种较好的方式,此时listen必须设置为YES,此为默认值。建议不要更改,有很多与服务器运行相关的配置命令,需要在此模式下才有效,若设置为NO,则vsftpd不是以独立的服务运行,要受到xinetd服务的管控,功能上会受到限制)
17)pam_service_name=vsftpd(虚拟用户使用PAM认证方式,这里是设置PAM使用的名称,默认即可,与/etc/pam.d/vsftpd对应) userlist_enable=YES(是否启用vsftpd.user_list文件,黑名单,白名单都可以
18)pasv_min_port=61001(被动模式使用端口范围最小值)
19)pasv_max_port=62000(被动模式使用端口范围最大值)
20)pasv_enable=YES(pasv_enable=YES/NO(YES)
若设置为YES,则使用PASV工作模式;若设置为NO,则使用PORT模式。默认值为YES,即使用PASV工作模式。
FTP协议有两种工作方式:PORT方式和PASV方式,中文意思为主动式和被动式。
一、PORT(主动)方式的连接过程是:客户端向服务器的FTP端口(默认是21)发送连接请求,服务器接受连接,建立一条命令链路。
当需要传送数据时,客户端在命令链路上用 PORT命令告诉服务器:“我打开了****端口,你过来连接我”。于是服务器从20端口向客户端的****端口发送连接请求,建立一条数据链路来传送数据。
二、PASV(被动)方式的连接过程是:客户端向服务器的FTP端口(默认是21)发送连接请求,服务器接受连接,建立一条命令链路。
当需要传送数据时,服务器在命令链路上用 PASV命令告诉客户端:“我打开了****端口,你过来连接我”。于是客户端向服务器的****端口发送连接请求,建立一条数据链路来传送数据。
从上面可以看出,两种方式的命令链路连接方法是一样的,而数据链路的建立方法就完全不同。而FTP的复杂性就在于此。
)
7、防火墙的配置
防火墙的配置(这里采用的是centos6,用的还是Iptables文件设置防火墙)
(1)编辑防火墙文件
sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
(2)添加防火墙规则到配置文件中
-A INPUT -p TCP --dport 61001:62000 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -p TCP --sport 61001:62000 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p TCP --dport 20 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -p TCP --sport 20 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p TCP --dport 21 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -p TCP --sport 21 -j ACCEPT
(3):wq保存退出
(4)sudo service iptables restart 执行命令重启防火墙
8、vsftpd的验证
(1)执行sudo service vsftpd restart
[root@localhost vsftpd]# service vsftpd restart
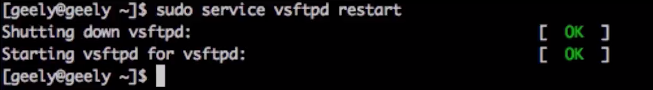
注:第一次启动时Shutting down vsftpd是failed不用理会,因为这是重启命令,保证Starting vsftpd for vsftpd是OK即代表vsftpd服务成功。、
service vsftpd stop #表示关闭vsftpd
(2)执行ifconfig查看运行vsftpd服务器的ip地址
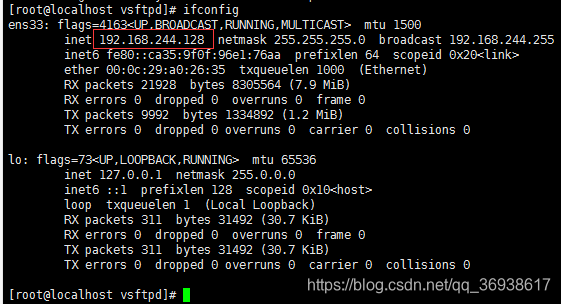
(3)打开浏览器访问:ftp://192.168.244.128/
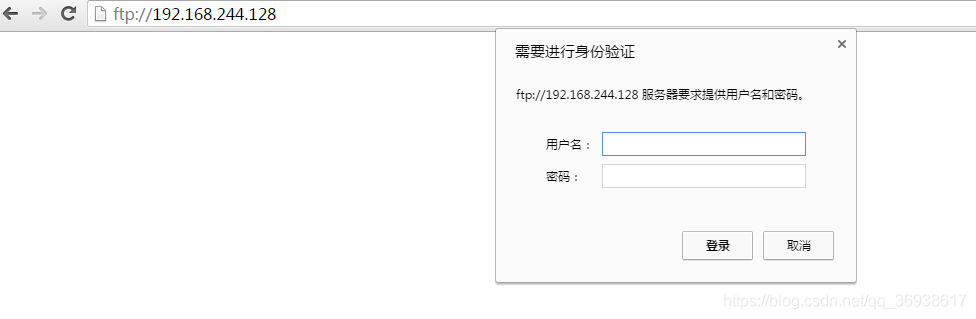
(4)输入之前创建的ftp匿名用户账号和密码
例如:用户名:ftpuser,密码:123456
(5)看到如图界面代表访问成功
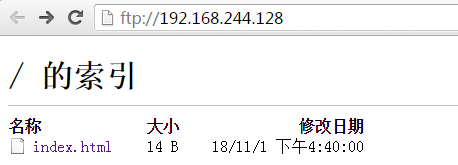
或者通过ftp客户端软件
例如:cuteftp、filezilla、viperftp、flashftp、leapftp等进行连接ftp服务器,进行上传文件、下载验证
9、vsftpd的常用命令
(1)启动:sudo service vsftpd start
(2)关闭:sudo service vsftpd stop
(3)重启:sudo service vsftpd restart
10、反复需要验证ftp身份问题解决
在安装vsftpd的时候如果在浏览器中一直提示需要身份验证,此时在命令行行登录会报530 Login incorrect错误。
在vsftpd的配置文件目录/etc/vsftpd下中的vsftpd.conf文件中会配置有pam_service_name=vsftpd指定pam下的文件在该文件中内容如下:
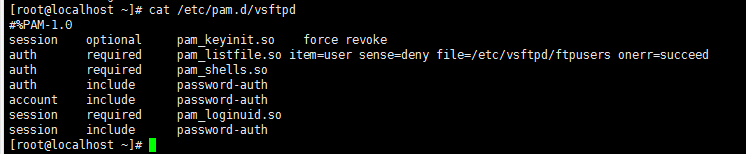
其中可能导致登录不成功(反复需要身份验证)的问题主要在于以下两个配置
问题配置一
![]()
在/etc/vsftpd/ftpusers这个文件中的用户是禁止登录的用户,先检查需要登录的账户是否在该文件中,如果在,就将该账户注释或者从该文件中去除
问题配置二:
![]()
该配置是允许用户的shell为 /etc/shells文件内的shell命令时,才能够成功
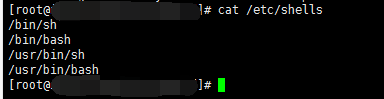
此处多留意有的系统里面的shells中的bash会多一些,比如
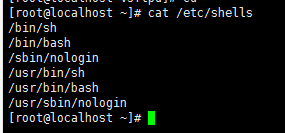
所以就需要查看当前系统shells文件中的内容与创建ftp用户的时候,为了禁止ssh登录,跟上的命令在shells中是否存在;
比如:我当前的shells文件内容为
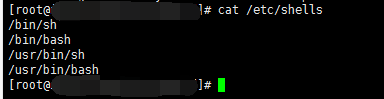
但是我在创建ftp用户的时候的命令为
[root@localhost ~]# useradd ftpuser -d /ftpfile/ -s /sbin/nologin
所以此时创建用户后-s /sbin/nologin并不是有效的。
这时的解决方案为修改/etc/pam.d/vsftpd文件中的
auth required pam_shells.so
修改为auth required pam_nologin.so
最后重启vsftpd
[root@localhost ~]# service vsftpd restart



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号