LeetCode - 字符串操作问题(另附以上题目解析)
14. 最长公共前缀
编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。
如果不存在公共前缀,返回空字符串 “”。
示例 1:
输入: [“flower”,“flow”,“flight”]
输出: “fl”
示例 2:
输入: [“dog”,“racecar”,“car”]
输出: “”
解释: 输入不存在公共前缀。
说明:
所有输入只包含小写字母 a-z 。
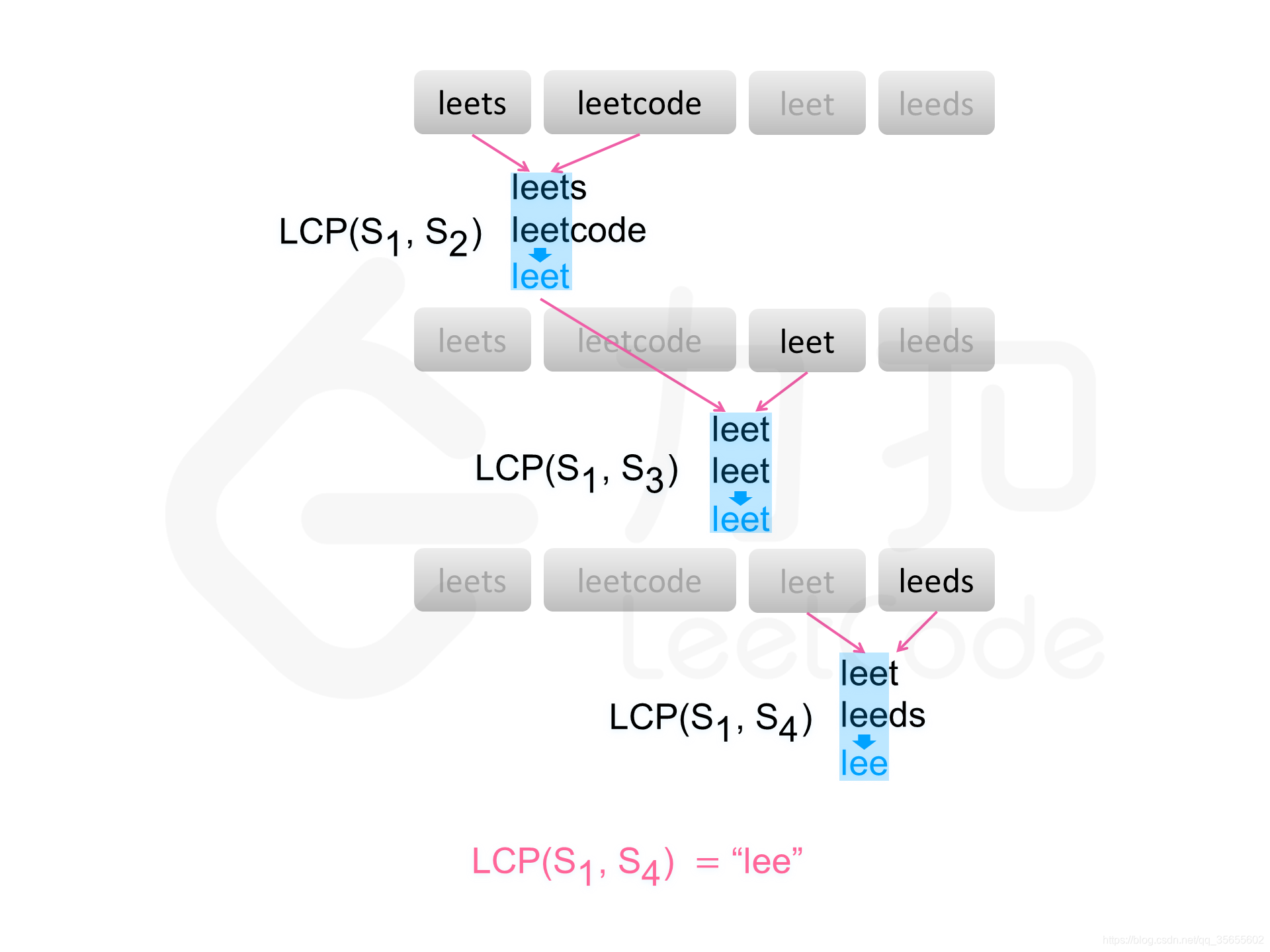
方法一:横向扫描
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) {
return "";
}
String prefix = strs[0];
int count = strs.length;
for (int i = 1; i < count; i++) {
prefix = longestCommonPrefix(prefix, strs[i]);
if (prefix.length() == 0) {
break;
}
}
return prefix;
}
public String longestCommonPrefix(String str1, String str2) {
int length = Math.min(str1.length(), str2.length());
int index = 0;
while (index < length && str1.charAt(index) == str2.charAt(index)) {
index++;
}
return str1.substring(0, index);
}
}
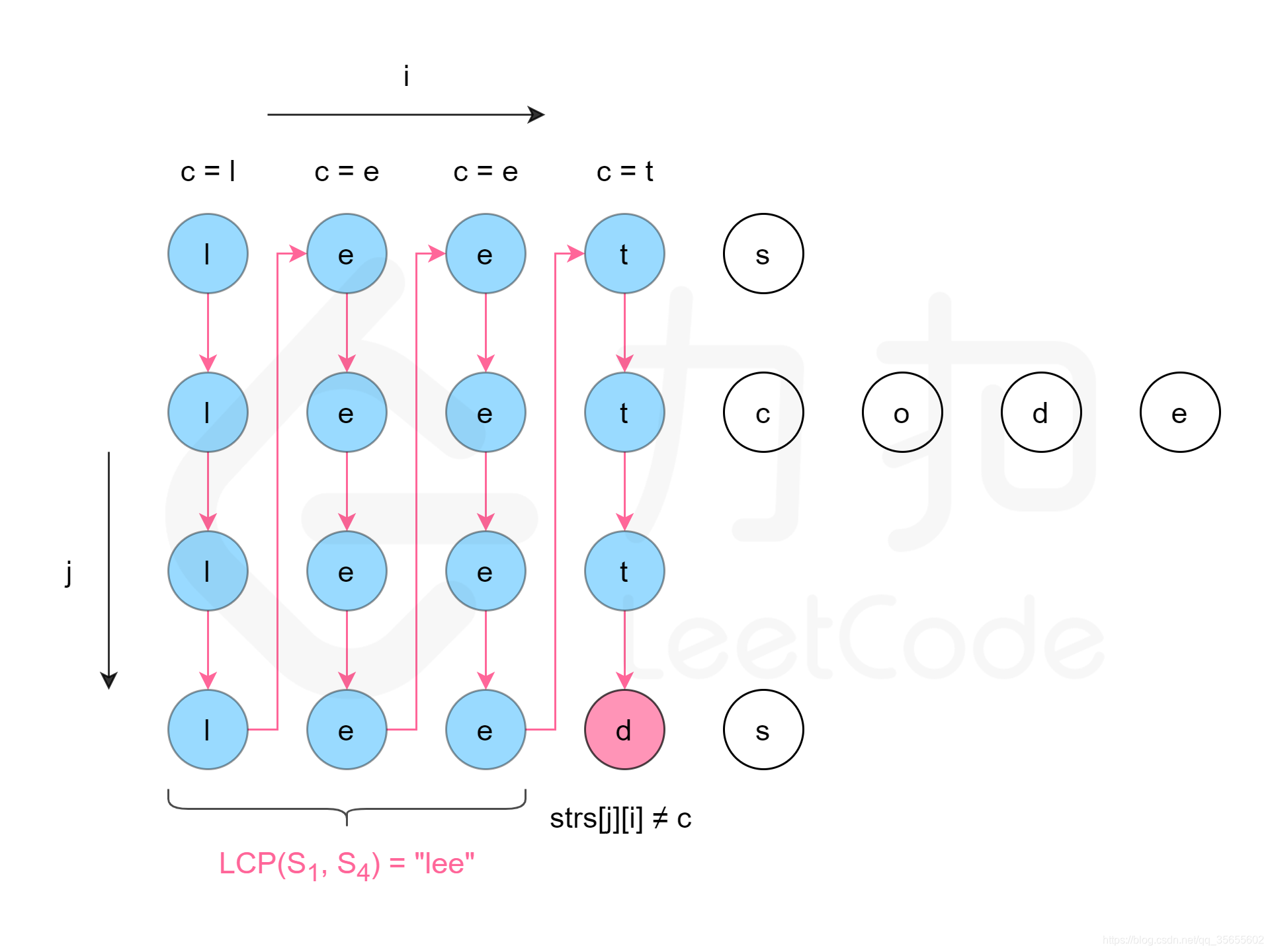
方法二:纵向扫描
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) {
return "";
}
int length = strs[0].length();
int count = strs.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = strs[0].charAt(i);
for (int j = 1; j < count; j++) {
if (i == strs[j].length() || strs[j].charAt(i) != c) {
return strs[0].substring(0, i);
}
}
}
return strs[0];
}
}
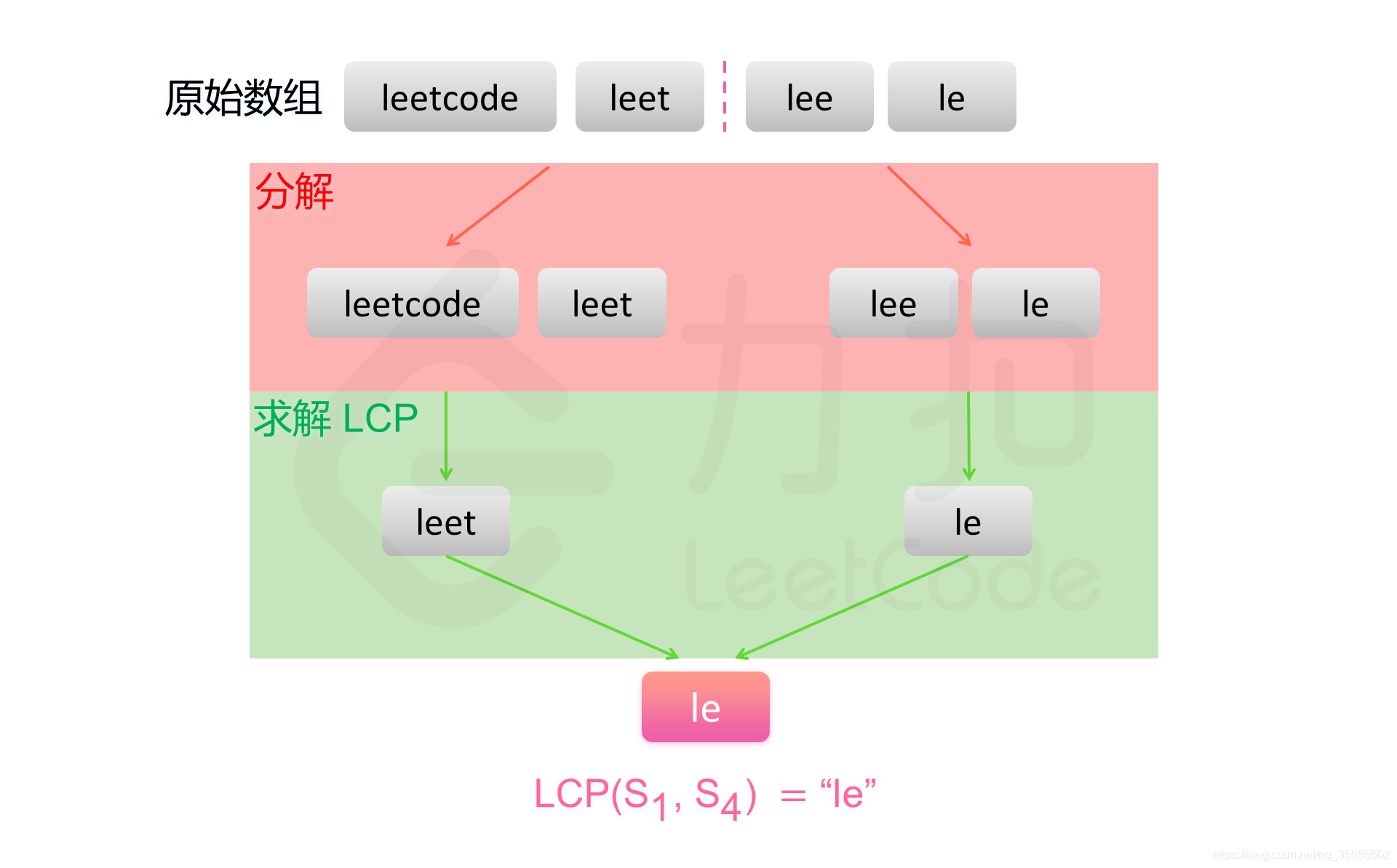
方法三:分治
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) {
return "";
} else {
return longestCommonPrefix(strs, 0, strs.length - 1);
}
}
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs, int start, int end) {
if (start == end) {
return strs[start];
} else {
int mid = (end - start) / 2 + start;
String lcpLeft = longestCommonPrefix(strs, start, mid);
String lcpRight = longestCommonPrefix(strs, mid + 1, end);
return commonPrefix(lcpLeft, lcpRight);
}
}
public String commonPrefix(String lcpLeft, String lcpRight) {
int minLength = Math.min(lcpLeft.length(), lcpRight.length());
for (int i = 0; i < minLength; i++) {
if (lcpLeft.charAt(i) != lcpRight.charAt(i)) {
return lcpLeft.substring(0, i);
}
}
return lcpLeft.substring(0, minLength);
}
}
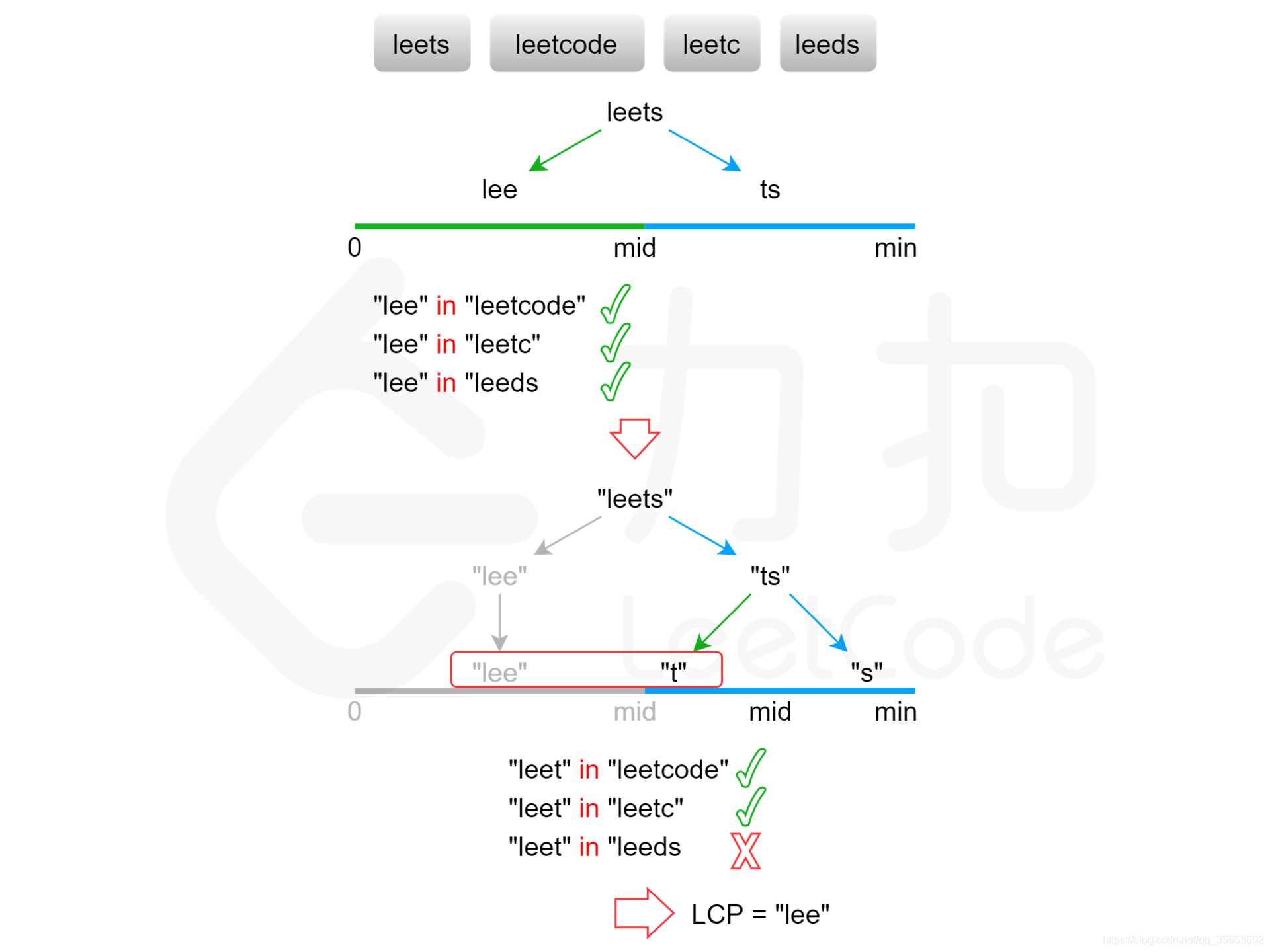
方法四:二分查找
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) {
return "";
}
int minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (String str : strs) {
minLength = Math.min(minLength, str.length());
}
int low = 0, high = minLength;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (high - low + 1) / 2 + low;
if (isCommonPrefix(strs, mid)) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return strs[0].substring(0, low);
}
public boolean isCommonPrefix(String[] strs, int length) {
String str0 = strs[0].substring(0, length);
int count = strs.length;
for (int i = 1; i < count; i++) {
String str = strs[i];
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
if (str0.charAt(j) != str.charAt(j)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
344. 反转字符串
编写一个函数,其作用是将输入的字符串反转过来。输入字符串以字符数组 char[] 的形式给出。
不要给另外的数组分配额外的空间,你必须原地修改输入数组、使用 O(1) 的额外空间解决这一问题。
你可以假设数组中的所有字符都是 ASCII 码表中的可打印字符。
示例 1:
输入:[“h”,“e”,“l”,“l”,“o”]
输出:[“o”,“l”,“l”,“e”,“h”]
示例 2:
输入:[“H”,“a”,“n”,“n”,“a”,“h”]
输出:[“h”,“a”,“n”,“n”,“a”,“H”]
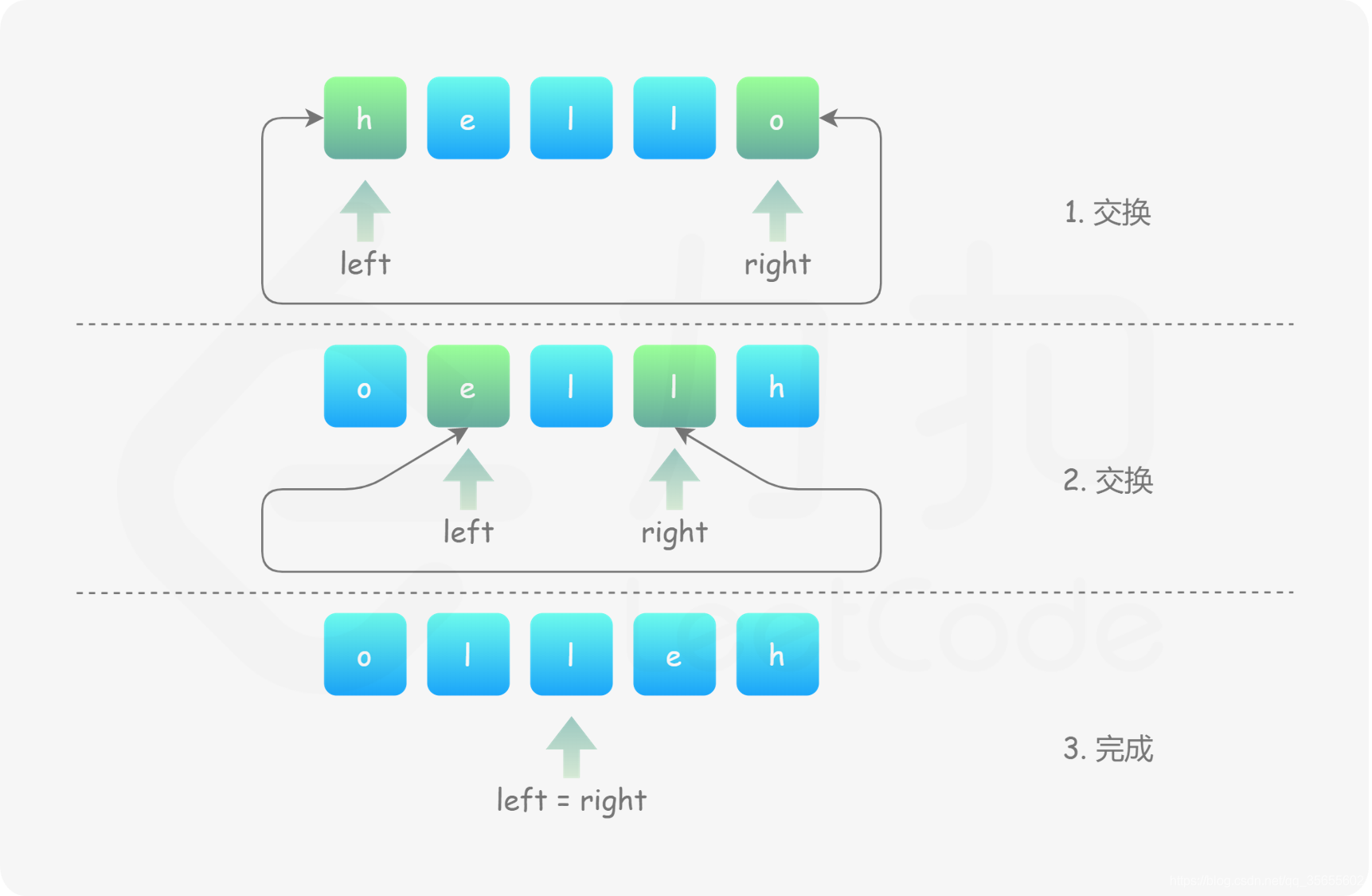
- 将 left 指向字符数组首元素,right 指向字符数组尾元素。
- 当 left < right:
- 交换 s[left] 和 s[right];
- left 指针右移一位,即 left = left + 1;
- right 指针左移一位,即 right = right - 1。
- 当 left >= right,反转结束,返回字符数组即可。
双指针:
class Solution {
public void reverseString(char[] s) {
int n = s.length;
for (int left = 0, right = n - 1; left < right; ++left, --right) {
char tmp = s[left];
s[left] = s[right];
s[right] = tmp;
}
}
}
541. 反转字符串 II
给定一个字符串 s 和一个整数 k,你需要对从字符串开头算起的每隔 2k 个字符的前 k 个字符进行反转。
如果剩余字符少于 k 个,则将剩余字符全部反转。
如果剩余字符小于 2k 但大于或等于 k 个,则反转前 k 个字符,其余字符保持原样。
示例:
输入: s = “abcdefg”, k = 2
输出: “bacdfeg”
提示:
该字符串只包含小写英文字母。
给定字符串的长度和 k 在 [1, 10000] 范围内。
class Solution {
public String reverseStr(String s, int k) {
char[] a = s.toCharArray();
for(int start = 0;start < a.length;start += 2 * k){
int i = start,j = Math.min(start + k - 1,a.length - 1);
while(i < j){
char tmp = a[i];
a[i++] = a[j];
a[j--] = tmp;
}
}
return new String(a);
}
}
☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆下面都是反转字符串字母的题目☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆:
151. 翻转字符串里的单词 ☆☆☆
给定一个字符串,逐个翻转字符串中的每个单词。
说明:
无空格字符构成一个 单词 。
输入字符串可以在前面或者后面包含多余的空格,但是反转后的字符不能包括。
如果两个单词间有多余的空格,将反转后单词间的空格减少到只含一个。
示例 1:
输入:“the sky is blue”
输出:“blue is sky the”
示例 2:
输入:" hello world! "
输出:“world! hello”
解释:输入字符串可以在前面或者后面包含多余的空格,但是反转后的字符不能包括。
示例 3:
输入:“a good example”
输出:“example good a”
解释:如果两个单词间有多余的空格,将反转后单词间的空格减少到只含一个。
示例 4:
输入:s = " Bob Loves Alice "
输出:“Alice Loves Bob”
示例 5:
输入:s = “Alice does not even like bob”
输出:“bob like even not does Alice”
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104
s 包含英文大小写字母、数字和空格 ’ ’
s 中 至少存在一个 单词
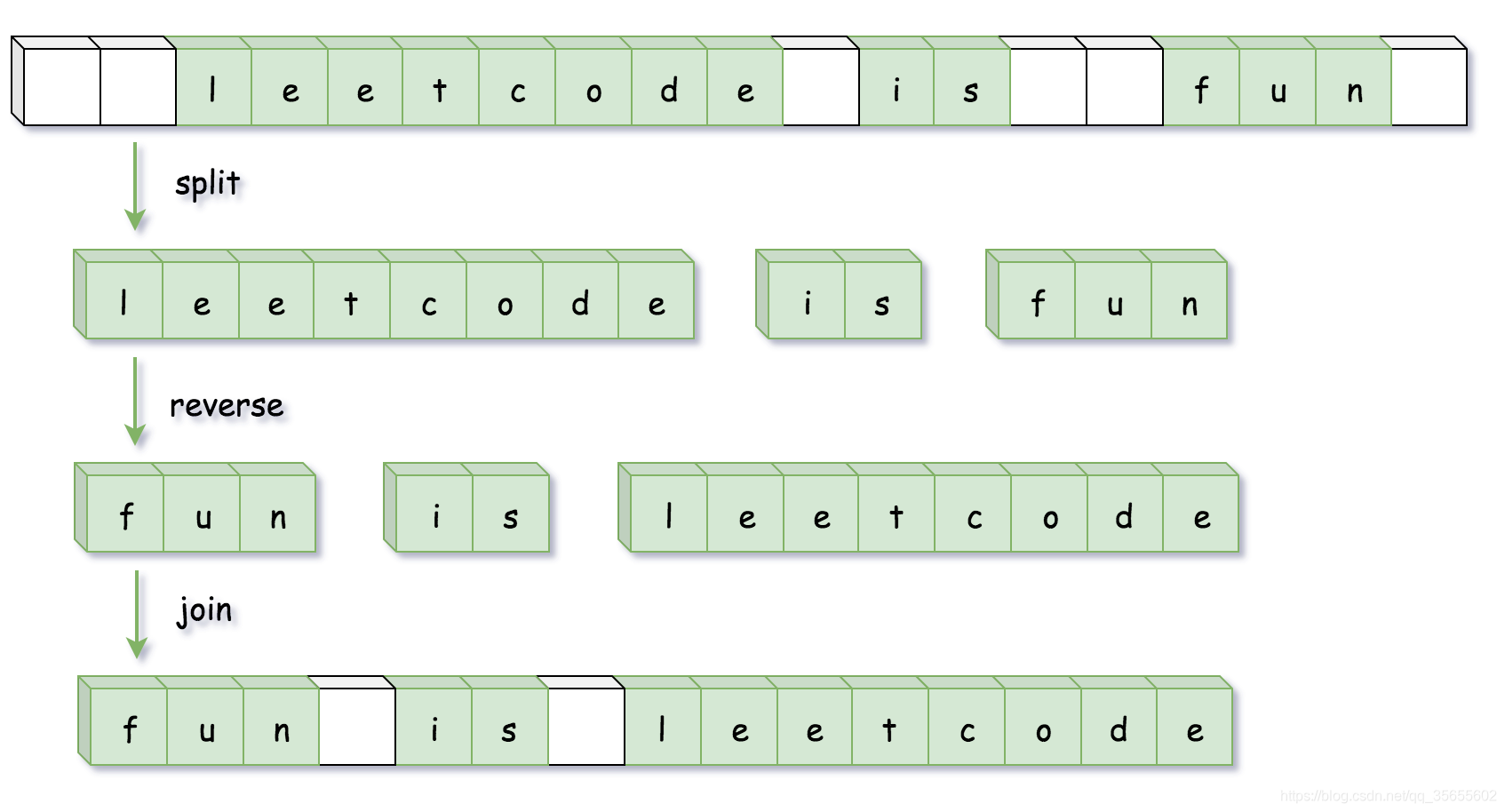
方法一:利用java语言特性(内置API函数完成操作)
- 使用 split (拆分)将字符串按空格分割成字符串数组;
- 使用 reverse (翻转)将字符串数组进行反转;
- 使用 join(连接) 方法将字符串数组拼成一个字符串。
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
// 除去开头和末尾的空白字符
s = s.trim();
// 正则匹配连续的空白字符作为分隔符分割
List<String> wordList = Arrays.asList(s.split("\\s+"));
Collections.reverse(wordList);
return String.join(" ", wordList);
}
}
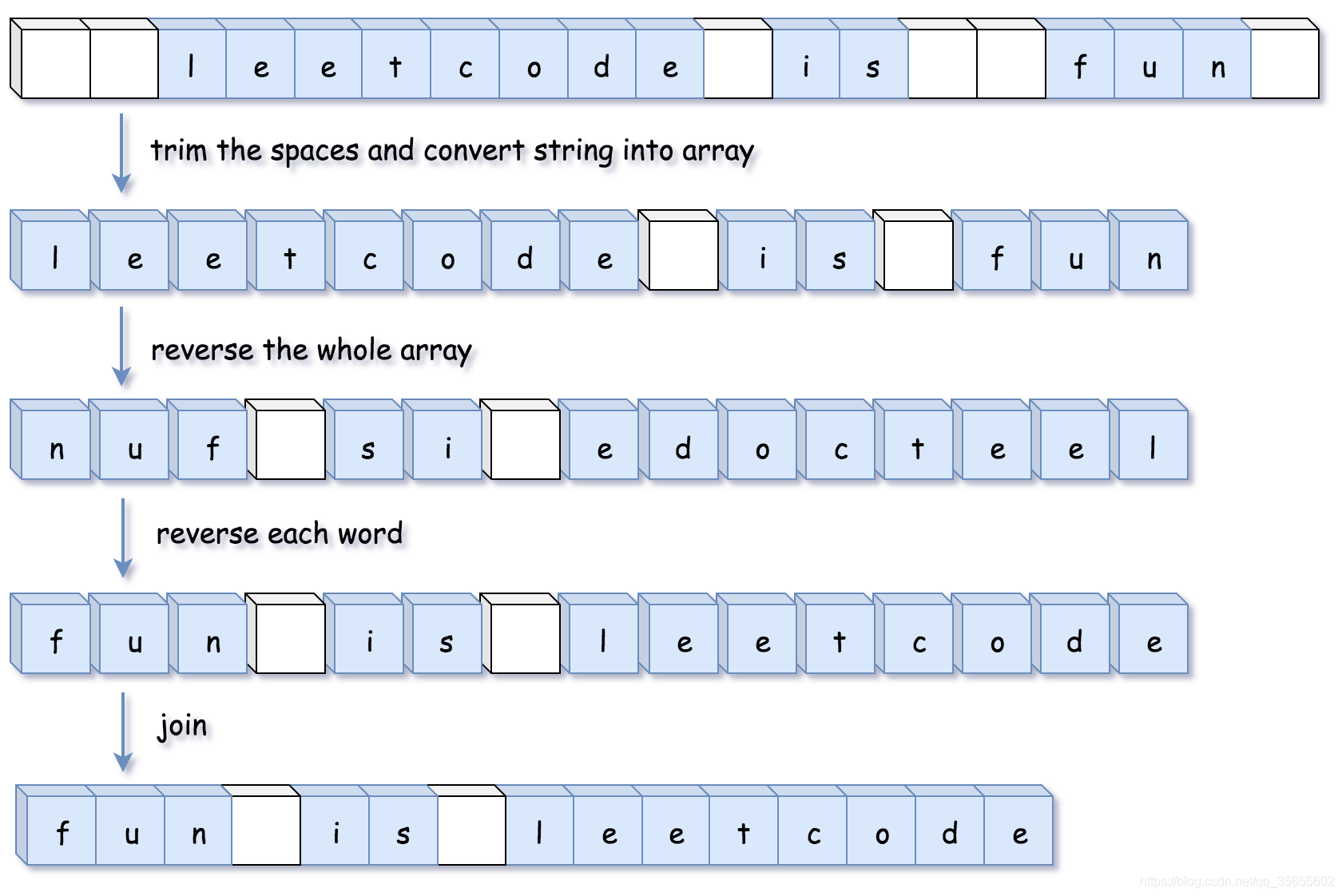
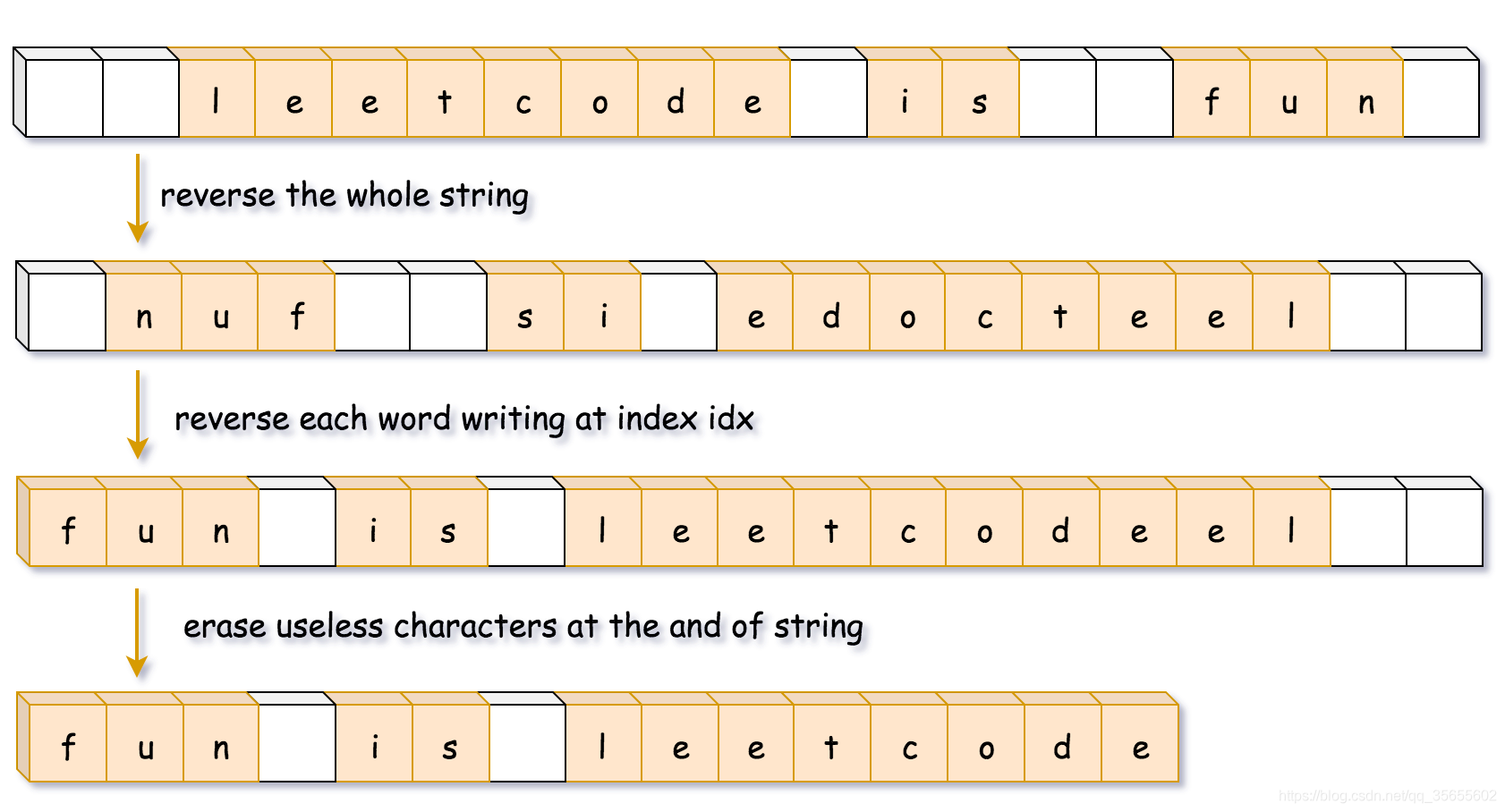
方法二:
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
StringBuilder sb = trimSpaces(s);
// 翻转字符串
reverse(sb, 0, sb.length() - 1);
// 翻转每个单词
reverseEachWord(sb);
return sb.toString();
}
public StringBuilder trimSpaces(String s) {
int left = 0, right = s.length() - 1;
// 去掉字符串开头的空白字符
while (left <= right && s.charAt(left) == ' ') {
++left;
}
// 去掉字符串末尾的空白字符
while (left <= right && s.charAt(right) == ' ') {
--right;
}
// 将字符串间多余的空白字符去除
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (left <= right) {
char c = s.charAt(left);
if (c != ' ') {
sb.append(c);
} else if (sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1) != ' ') {
sb.append(c);
}
++left;
}
return sb;
}
public void reverse(StringBuilder sb, int left, int right) {
while (left < right) {
char tmp = sb.charAt(left);
sb.setCharAt(left++, sb.charAt(right));
sb.setCharAt(right--, tmp);
}
}
public void reverseEachWord(StringBuilder sb) {
int n = sb.length();
int start = 0, end = 0;
while (start < n) {
// 循环至单词的末尾
while (end < n && sb.charAt(end) != ' ') {
++end;
}
// 翻转单词
reverse(sb, start, end - 1);
// 更新start,去找下一个单词
start = end + 1;
++end;
}
}
}
方法三: (双端队列)
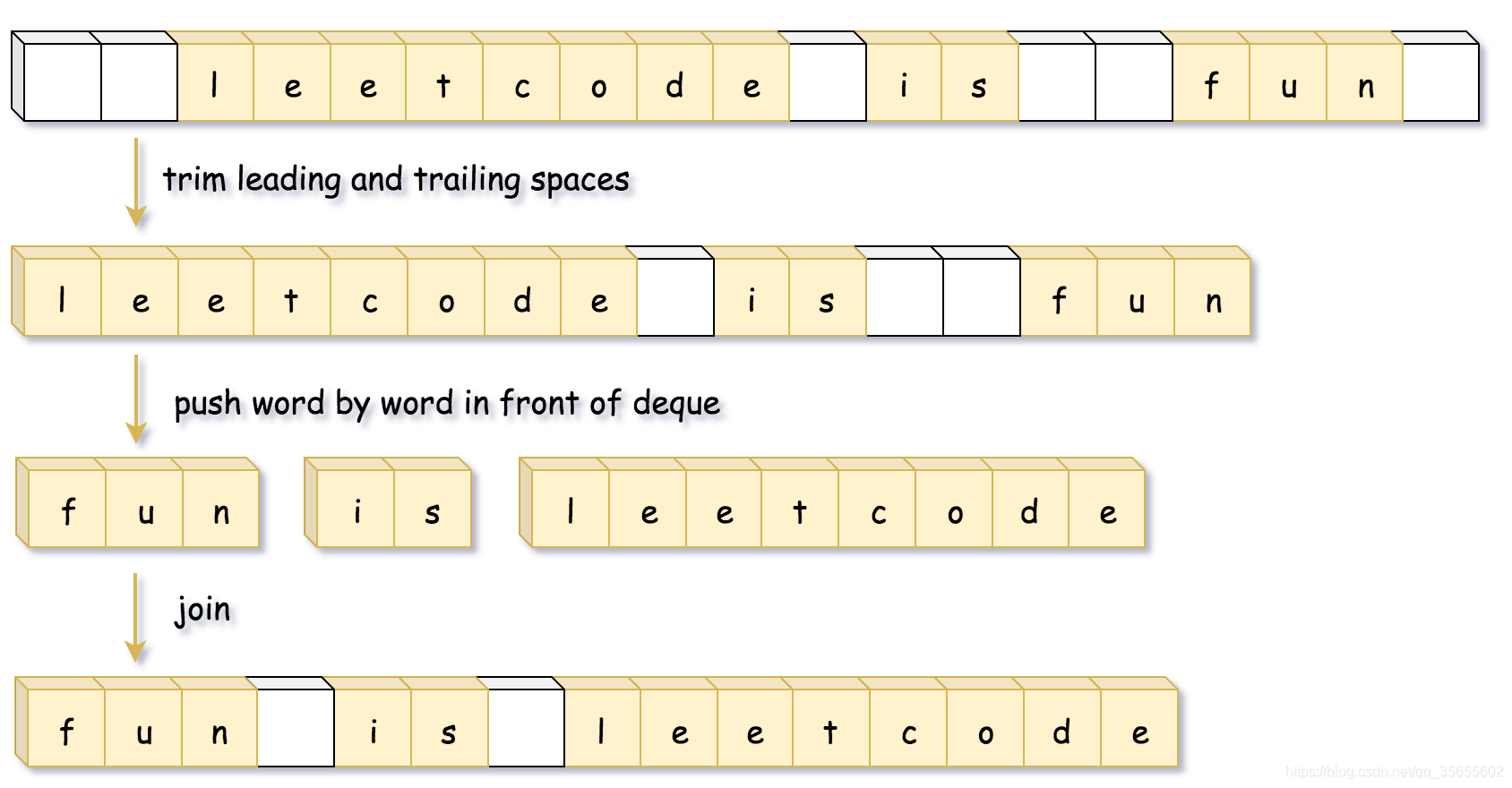
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
int left = 0, right = s.length() - 1;
// 去掉字符串开头的空白字符
while (left <= right && s.charAt(left) == ' ') {
++left;
}
// 去掉字符串末尾的空白字符
while (left <= right && s.charAt(right) == ' ') {
--right;
}
Deque<String> d = new ArrayDeque<String>();
StringBuilder word = new StringBuilder();
while (left <= right) {
char c = s.charAt(left);
if ((word.length() != 0) && (c == ' ')) {
// 将单词 push 到队列的头部
d.offerFirst(word.toString());
word.setLength(0);
} else if (c != ' ') {
word.append(c);
}
++left;
}
d.offerFirst(word.toString());
return String.join(" ", d);
}
}
557. 反转字符串中的单词 III
给定一个字符串,你需要反转字符串中每个单词的字符顺序,同时仍保留空格和单词的初始顺序。
示例:
输入:“Let’s take LeetCode contest”
输出:“s’teL ekat edoCteeL tsetnoc”
提示:
在字符串中,每个单词由单个空格分隔,并且字符串中不会有任何额外的空格。
思路:
开辟一个新字符串。然后从头到尾遍历原字符串,直到找到空格为止,此时找到了一个单词,并能得到单词的起止位置。随后,根据单词的起止位置,可以将该单词逆序放到新字符串当中。如此循环多次,直到遍历完原字符串,就能得到翻转后的结果。
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
StringBuffer ret = new StringBuffer();
int length = s.length();
int i = 0;
while (i < length){
int start = i;
while (i < length && s.charAt(i) != ' '){
i++;
}
for (int p = start; p < i; p++) {
ret.append(s.charAt(start + i - 1 - p));
}
while (i < length && s.charAt(i) ==' '){
i++;
ret.append(' ');
}
}
return ret.toString();
}
}
917. 仅仅反转字母
给定一个字符串 S,返回 “反转后的” 字符串,其中不是字母的字符都保留在原地,而所有字母的位置发生反转。
示例 1:
输入:“ab-cd”
输出:“dc-ba”
示例 2:
输入:“a-bC-dEf-ghIj”
输出:“j-Ih-gfE-dCba”
示例 3:
输入:“Test1ng-Leet=code-Q!”
输出:“Qedo1ct-eeLg=ntse-T!”
提示:
S.length <= 100
33 <= S[i].ASCIIcode <= 122
S 中不包含 \ or "
方法一:字母栈
将 s 中的所有字母单独存入栈中,所以出栈等价于对字母反序操作。(或者,可以用数组存储字母并反序数组。)
然后,遍历 s 的所有字符,如果是字母我们就选择栈顶元素输出。
class Solution {
public String reverseOnlyLetters(String S) {
Stack<Character> letters = new Stack();
for (char c: S.toCharArray())
if (Character.isLetter(c))
letters.push(c);
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
for (char c: S.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isLetter(c))
ans.append(letters.pop());
else
ans.append(c);
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
方法二:反转指针
一个接一个输出 s 的所有字符。当遇到一个字母时,我们希望找到逆序遍历字符串的下一个字母。
所以我们这么做:维护一个指针 j 从后往前遍历字符串,当需要字母时就使用它。
class Solution {
public String reverseOnlyLetters(String S) {
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
int j = S.length() - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); ++i) {
if (Character.isLetter(S.charAt(i))) {
while (!Character.isLetter(S.charAt(j)))
j--;
ans.append(S.charAt(j--));
} else {
ans.append(S.charAt(i));
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号