第13章 集成学习和随机森林
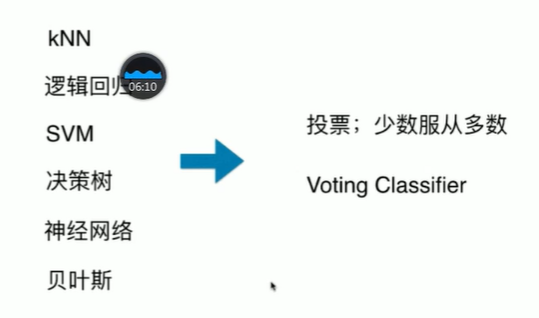
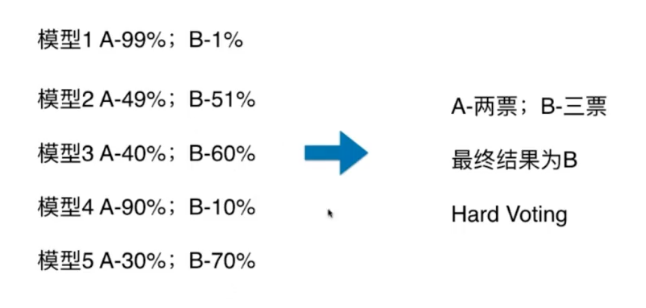
13-1什么是集成学习


Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
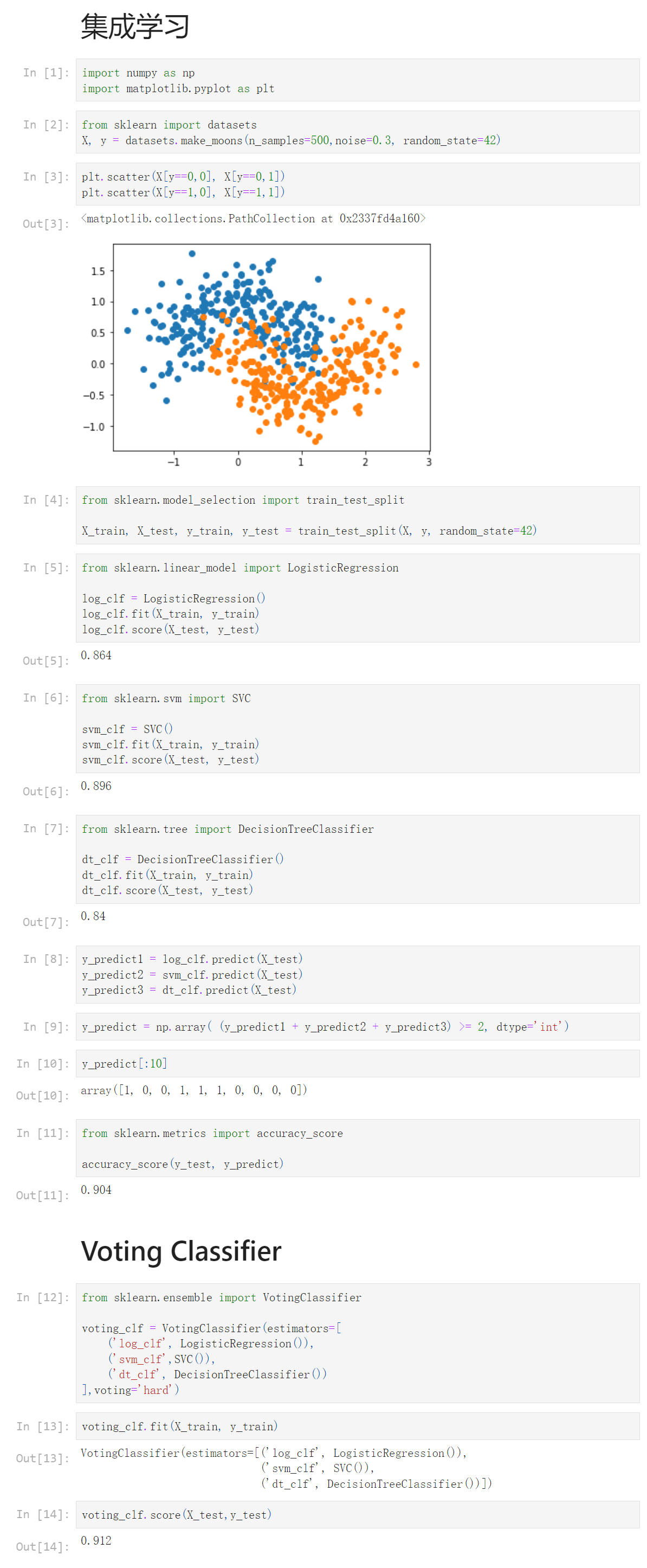
1 集成学习 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 X, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500,noise=0.3, random_state=42) 8 [3] 9 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 10 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 11 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x2337fd4a160> 12 13 [4] 14 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 15 16 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42) 17 [5] 18 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 19 20 log_clf = LogisticRegression() 21 log_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) 22 log_clf.score(X_test, y_test) 23 0.864 24 [6] 25 from sklearn.svm import SVC 26 27 svm_clf = SVC() 28 svm_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) 29 svm_clf.score(X_test, y_test) 30 0.896 31 [7] 32 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier 33 34 dt_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier() 35 dt_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) 36 dt_clf.score(X_test, y_test) 37 0.84 38 [8] 39 y_predict1 = log_clf.predict(X_test) 40 y_predict2 = svm_clf.predict(X_test) 41 y_predict3 = dt_clf.predict(X_test) 42 [9] 43 y_predict = np.array( (y_predict1 + y_predict2 + y_predict3) >= 2, dtype='int') 44 [10] 45 y_predict[:10] 46 array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]) 47 [11] 48 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score 49 50 accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict) 51 0.904 52 Voting Classifier 53 [12] 54 from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier 55 56 voting_clf = VotingClassifier(estimators=[ 57 ('log_clf', LogisticRegression()), 58 ('svm_clf',SVC()), 59 ('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier()) 60 ],voting='hard') 61 [13] 62 voting_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) 63 VotingClassifier(estimators=[('log_clf', LogisticRegression()), 64 ('svm_clf', SVC()), 65 ('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier())]) 66 [14] 67 voting_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 68 0.912
13-2 SoftVoting Classifier

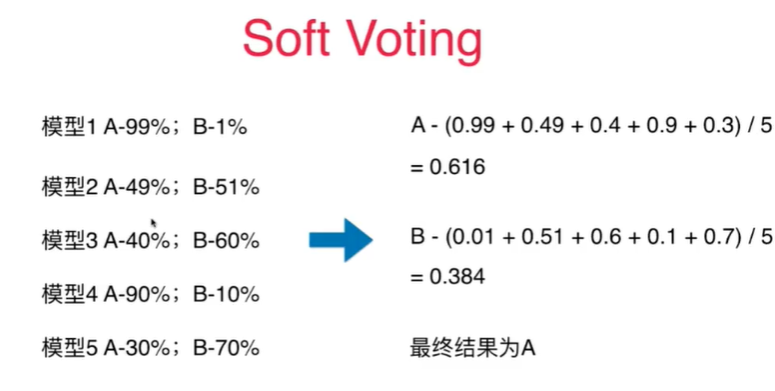

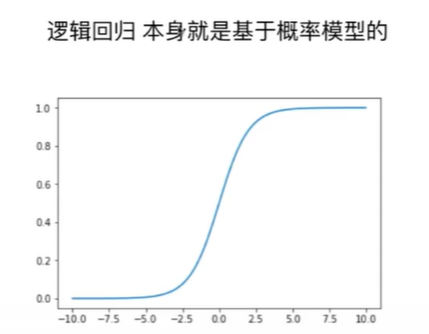
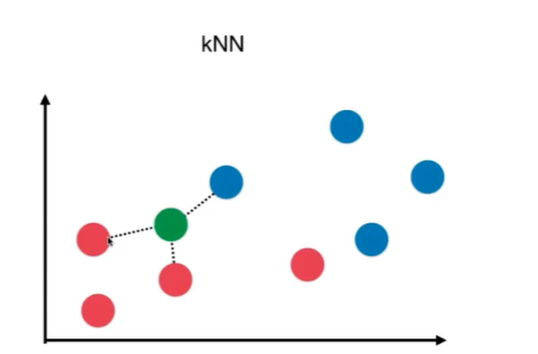
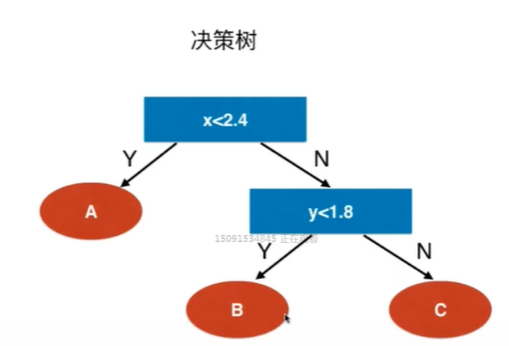

Notbook 示例
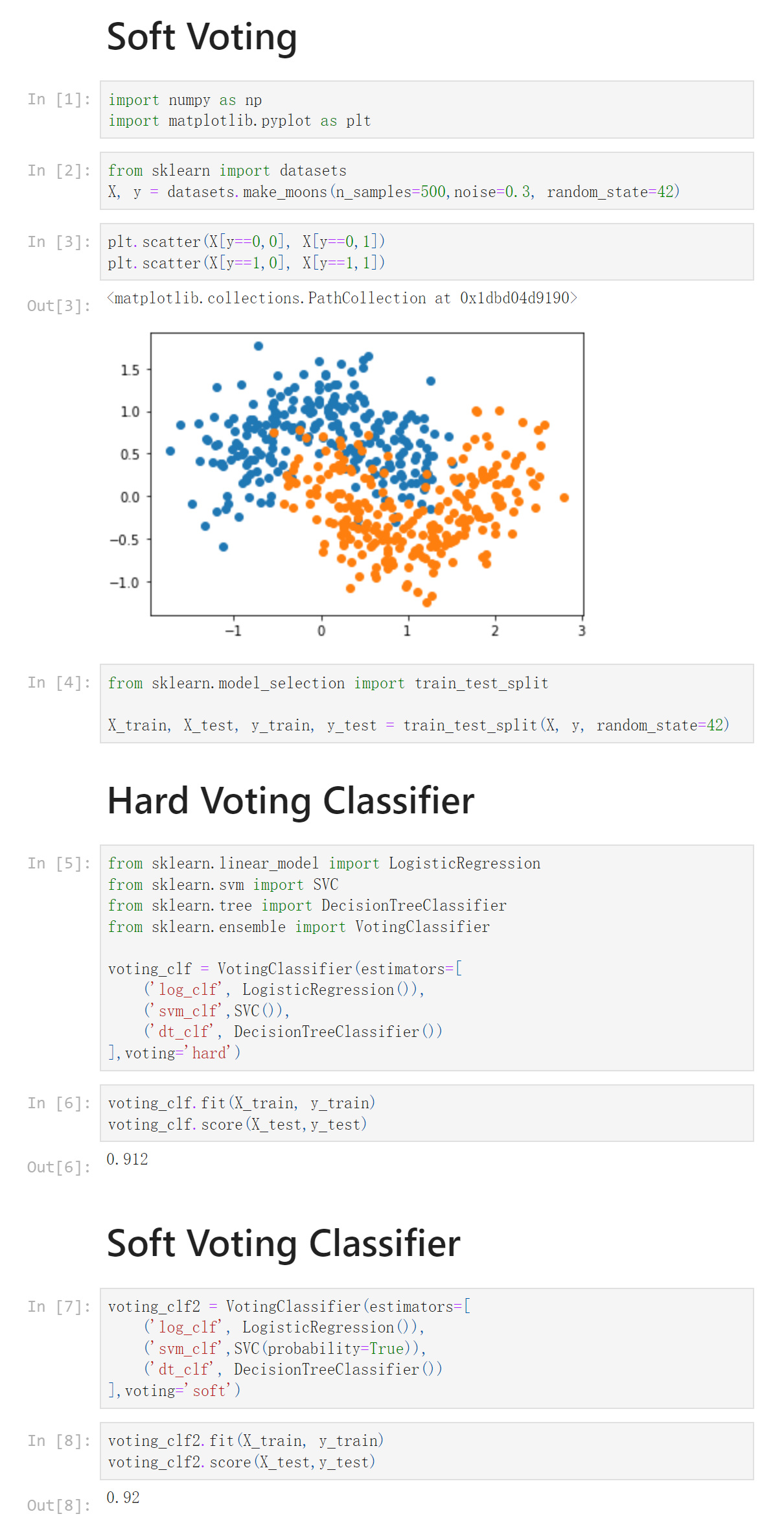
Notbook 源码
1 Soft Voting 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 X, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500,noise=0.3, random_state=42) 8 [3] 9 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 10 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 11 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1dbd04d9190> 12 13 [4] 14 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 15 16 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42) 17 Hard Voting Classifier 18 [5] 19 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 20 from sklearn.svm import SVC 21 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier 22 from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier 23 24 voting_clf = VotingClassifier(estimators=[ 25 ('log_clf', LogisticRegression()), 26 ('svm_clf',SVC()), 27 ('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier()) 28 ],voting='hard') 29 [6] 30 voting_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) 31 voting_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 32 0.912 33 Soft Voting Classifier 34 [7] 35 voting_clf2 = VotingClassifier(estimators=[ 36 ('log_clf', LogisticRegression()), 37 ('svm_clf',SVC(probability=True)), 38 ('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier()) 39 ],voting='soft') 40 [8] 41 voting_clf2.fit(X_train, y_train) 42 voting_clf2.score(X_test,y_test) 43 0.92
13-3 Bagging和Pasting






Notbook 示例
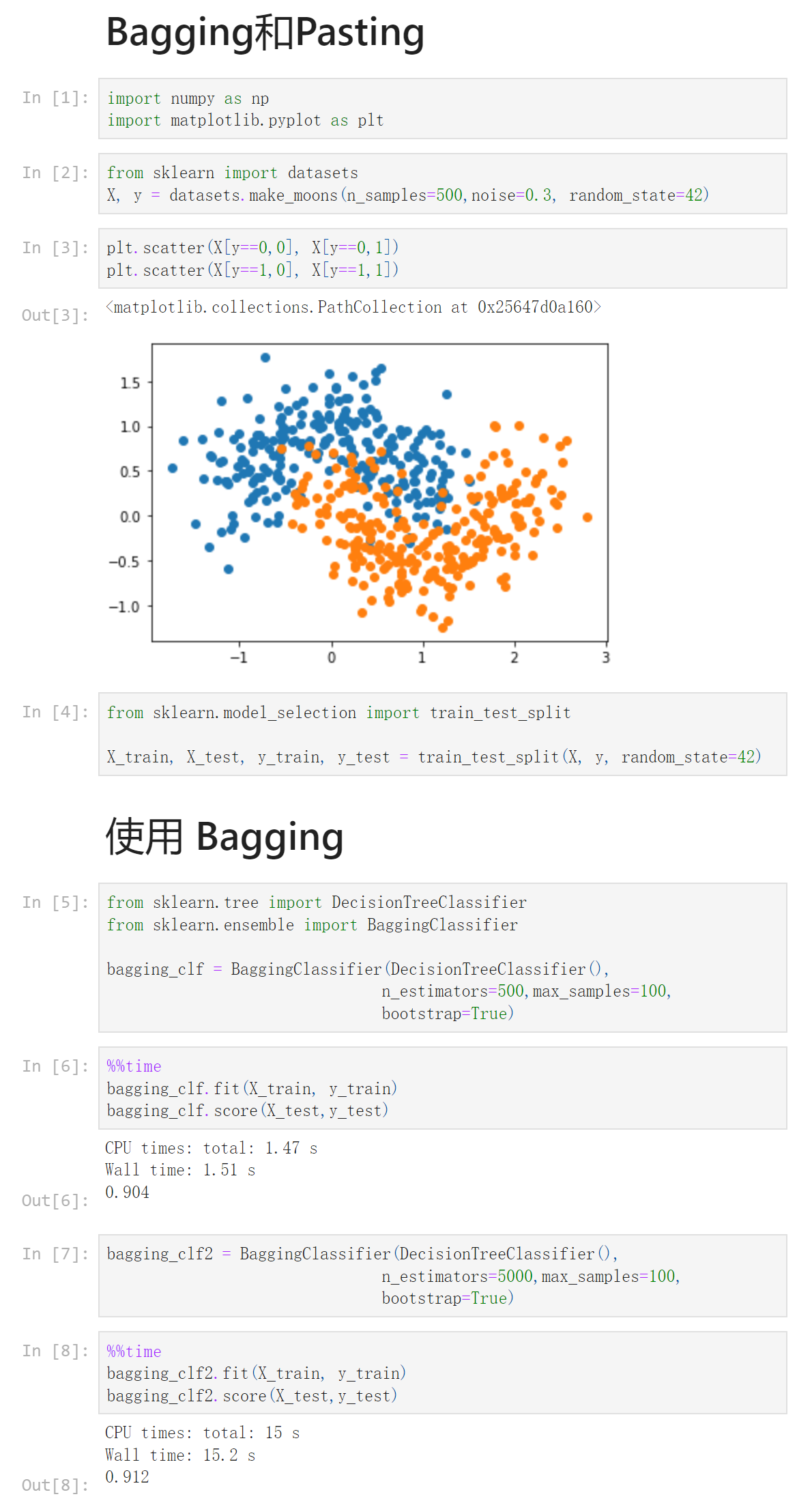
Notbook 源码
1 Bagging和Pasting 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 X, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500,noise=0.3, random_state=42) 8 [3] 9 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 10 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 11 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x25647d0a160> 12 13 [4] 14 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 15 16 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42) 17 使用 Bagging 18 [5] 19 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier 20 from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier 21 22 bagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(), 23 n_estimators=500,max_samples=100, 24 bootstrap=True) 25 [6] 26 %%time 27 bagging_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) 28 bagging_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 29 CPU times: total: 1.47 s 30 Wall time: 1.51 s 31 32 0.904 33 [7] 34 bagging_clf2 = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(), 35 n_estimators=5000,max_samples=100, 36 bootstrap=True) 37 [8] 38 %%time 39 bagging_clf2.fit(X_train, y_train) 40 bagging_clf2.score(X_test,y_test) 41 CPU times: total: 15 s 42 Wall time: 15.2 s 43 44 0.912
13-4 oob(Out-of-Bag)和关于Bagging的更多讨论




Notbook 示例

Notbook 源码
1 obb 和更多Bagging相关 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 X, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500,noise=0.3, random_state=42) 8 [3] 9 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 10 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 11 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x26a0b87a280> 12 13 使用obb 14 [4] 15 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier 16 from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier 17 18 bagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(), 19 n_estimators=500,max_samples=100, 20 bootstrap=True, oob_score=True) 21 22 bagging_clf.fit(X,y) 23 bagging_clf.oob_score_ 24 0.92 25 n_jobs 26 [5] 27 %%time 28 bagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(), 29 n_estimators=500,max_samples=100, 30 bootstrap=True, oob_score=True ) 31 32 bagging_clf.fit(X,y) 33 bagging_clf.oob_score_ 34 CPU times: total: 1.77 s 35 Wall time: 1.81 s 36 37 0.918 38 [6] 39 %%time 40 bagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(), 41 n_estimators=500,max_samples=100, 42 bootstrap=True, oob_score=True, 43 n_jobs =-1 ) 44 45 bagging_clf.fit(X,y) 46 bagging_clf.oob_score_ 47 CPU times: total: 453 ms 48 Wall time: 6.93 s 49 50 0.918 51 bootstrap_features 52 [7] 53 %%time 54 random_subspaces_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(), 55 n_estimators=500,max_samples=500, 56 bootstrap=True, oob_score=True, 57 n_jobs =-1 , 58 max_features=1, bootstrap_features=True) 59 60 random_subspaces_clf.fit(X,y) 61 random_subspaces_clf.oob_score_ 62 CPU times: total: 438 ms 63 Wall time: 1.38 s 64 65 0.82 66 [8] 67 %%time 68 random_patches_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(), 69 n_estimators=500,max_samples=100, 70 bootstrap=True, oob_score=True, 71 n_jobs =-1 , 72 max_features=1, bootstrap_features=True) 73 74 random_patches_clf.fit(X,y) 75 random_patches_clf.oob_score_ 76 CPU times: total: 469 ms 77 Wall time: 1.31 s 78 79 0.856
13-5 随机森林和Extra-Trees


Notbook 示例
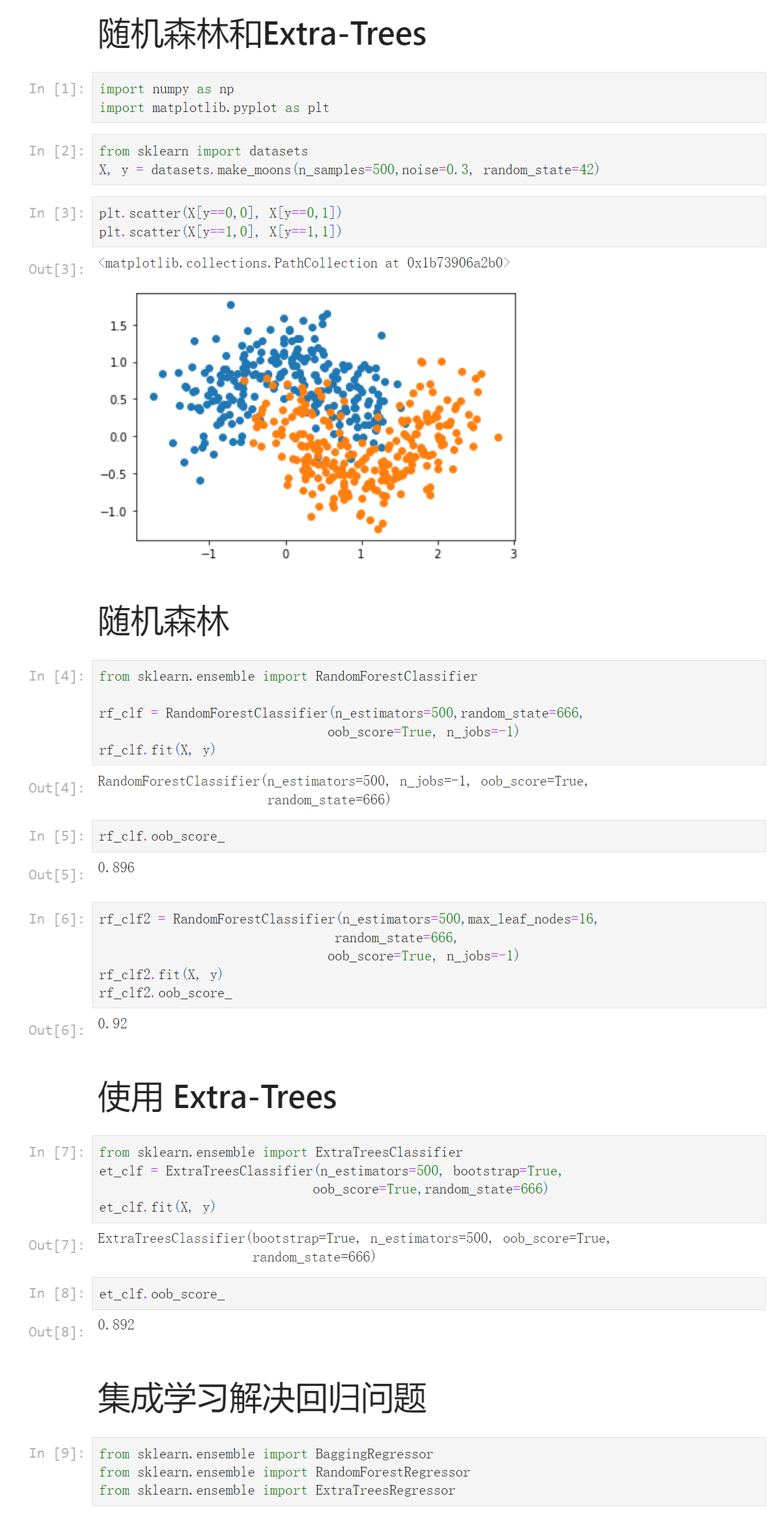
Notbook 源码
1 随机森林和Extra-Trees 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 X, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500,noise=0.3, random_state=42) 8 [3] 9 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 10 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 11 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1b73906a2b0> 12 13 随机森林 14 [4] 15 from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier 16 17 rf_clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500,random_state=666, 18 oob_score=True, n_jobs=-1) 19 rf_clf.fit(X, y) 20 RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500, n_jobs=-1, oob_score=True, 21 random_state=666) 22 [5] 23 rf_clf.oob_score_ 24 0.896 25 [6] 26 rf_clf2 = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500,max_leaf_nodes=16, 27 random_state=666, 28 oob_score=True, n_jobs=-1) 29 rf_clf2.fit(X, y) 30 rf_clf2.oob_score_ 31 0.92 32 使用 Extra-Trees 33 [7] 34 from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier 35 et_clf = ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=500, bootstrap=True, 36 oob_score=True,random_state=666) 37 et_clf.fit(X, y) 38 ExtraTreesClassifier(bootstrap=True, n_estimators=500, oob_score=True, 39 random_state=666) 40 [8] 41 et_clf.oob_score_ 42 0.892 43 集成学习解决回归问题 44 [9] 45 from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingRegressor 46 from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor 47 from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesRegressor
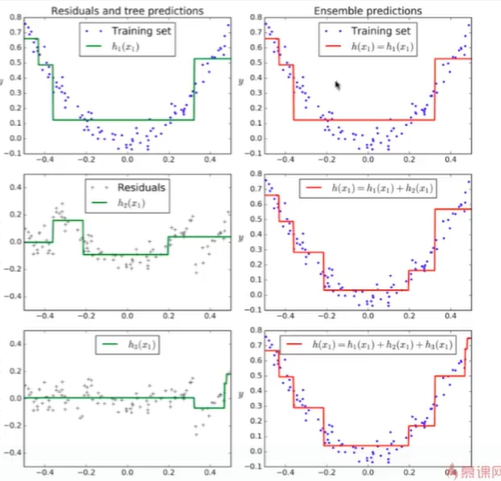
13-6 Ada Boosting和Gradient Boosting

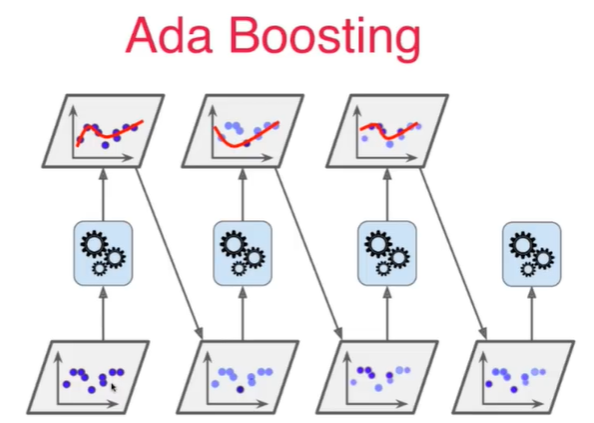

Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
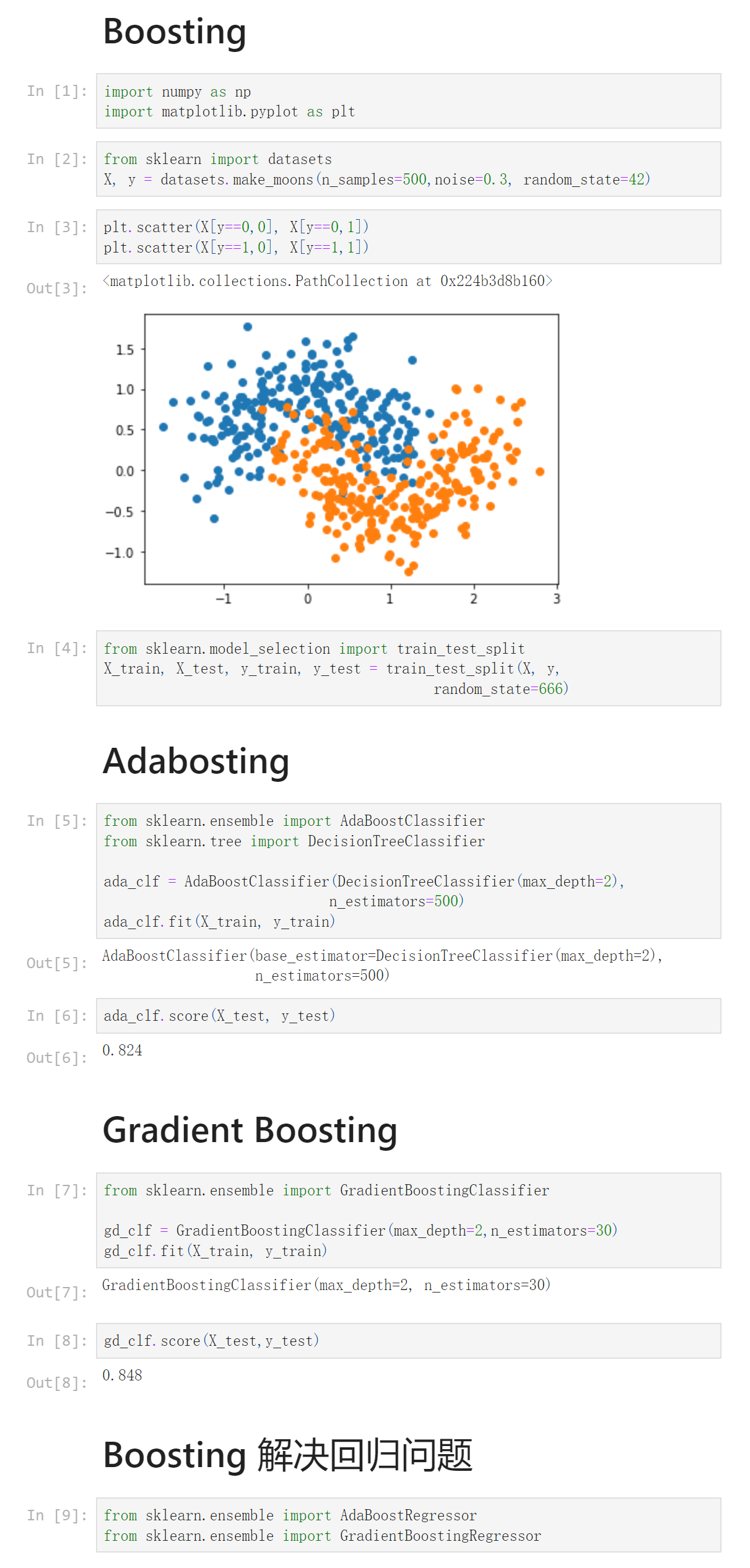
1 Boosting 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 X, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500,noise=0.3, random_state=42) 8 [3] 9 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 10 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 11 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x224b3d8b160> 12 13 [4] 14 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 15 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, 16 random_state=666) 17 Adabosting 18 [5] 19 from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier 20 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier 21 22 ada_clf = AdaBoostClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2), 23 n_estimators=500) 24 ada_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) 25 AdaBoostClassifier(base_estimator=DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2), 26 n_estimators=500) 27 [6] 28 ada_clf.score(X_test, y_test) 29 0.824 30 Gradient Boosting 31 [7] 32 from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier 33 34 gd_clf = GradientBoostingClassifier(max_depth=2,n_estimators=30) 35 gd_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) 36 GradientBoostingClassifier(max_depth=2, n_estimators=30) 37 [8] 38 gd_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 39 0.848 40 Boosting 解决回归问题 41 [9] 42 from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostRegressor 43 from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor
13-7 Stacking
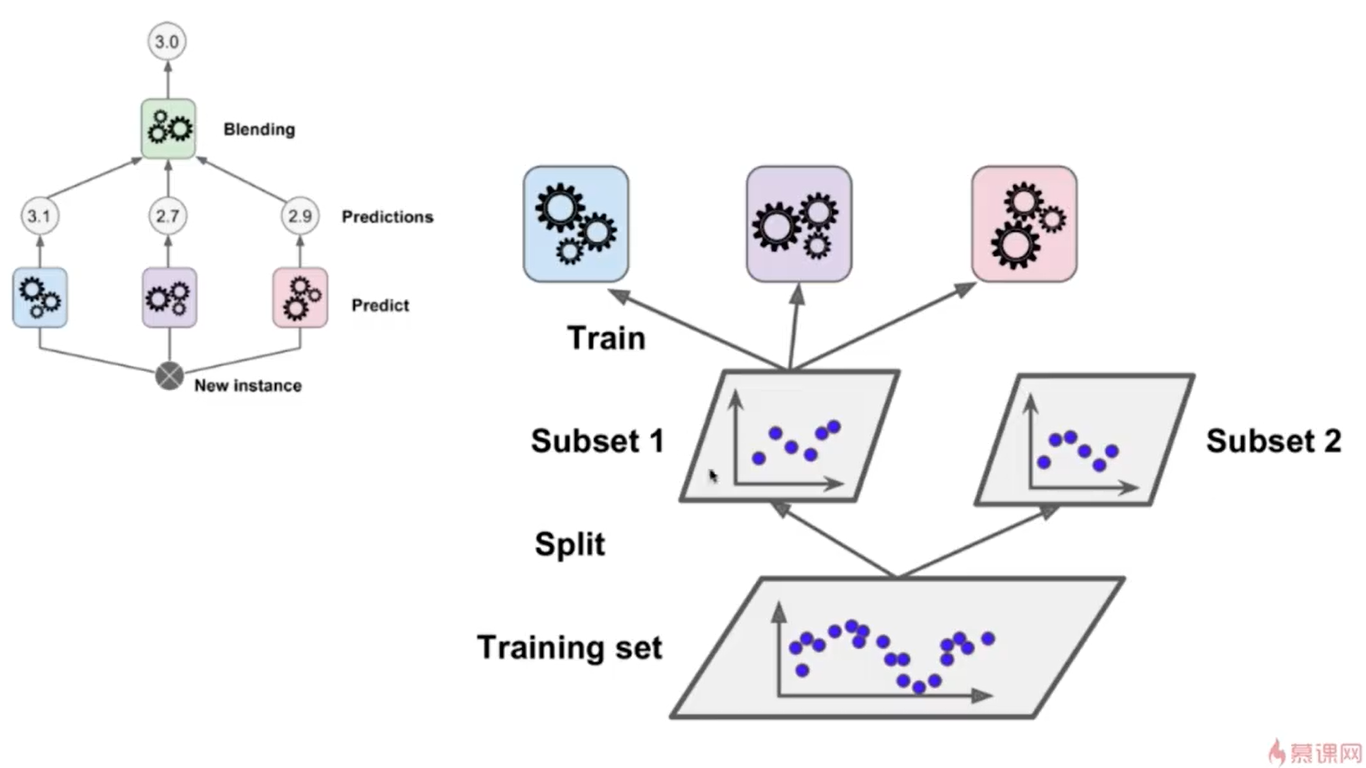
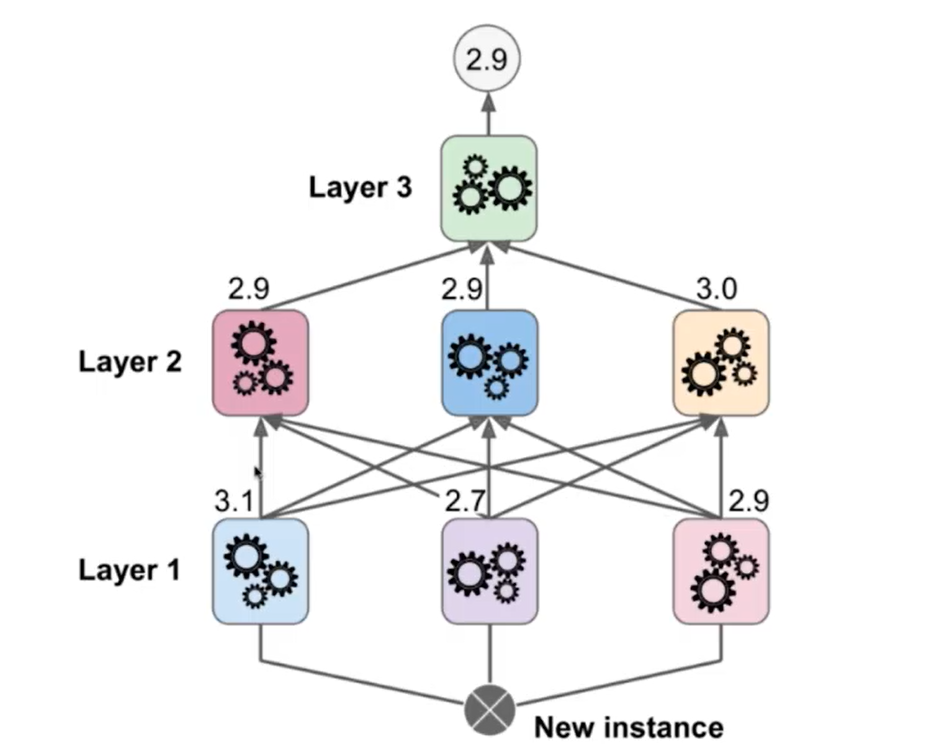
第14章 更多机器学习算法
14-1 scikit-learan 文档的学习
网址:www.scikit-learn.org






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号