第11章 支撑向量机 SVM
11-1 什么是支持向量机

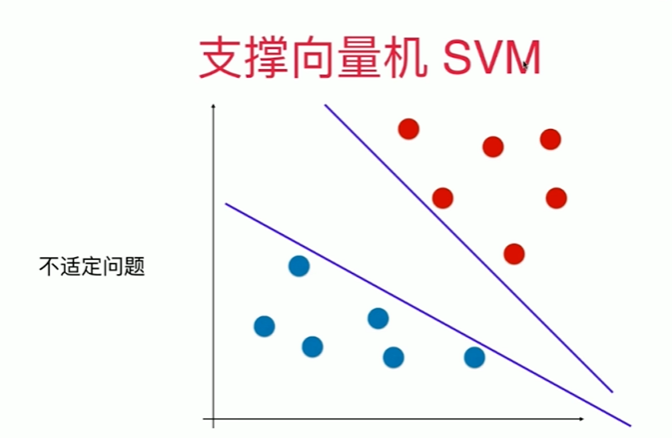
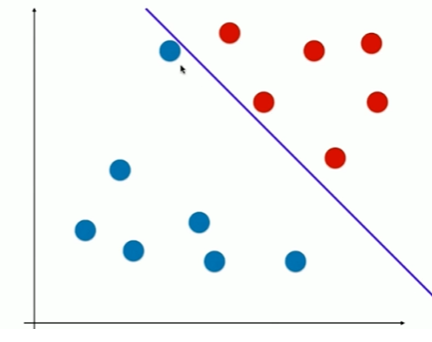
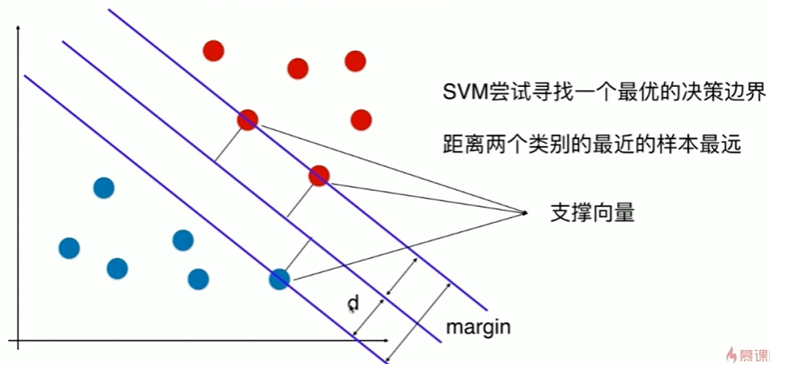

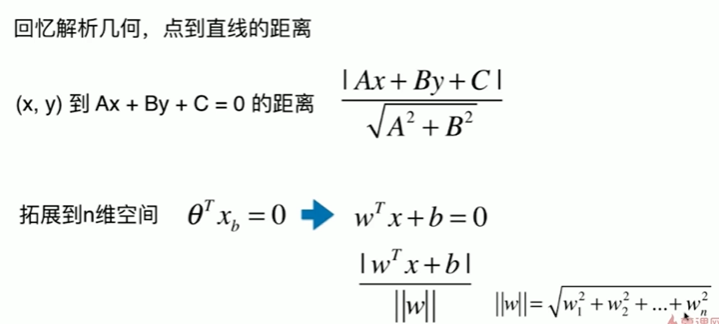
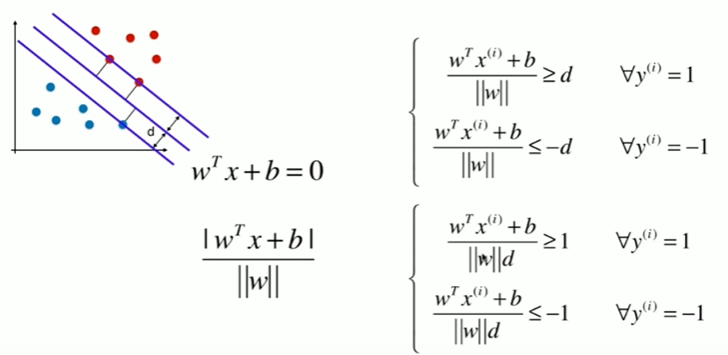
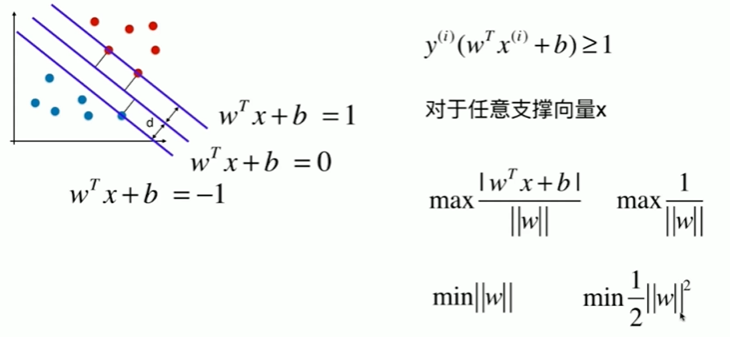
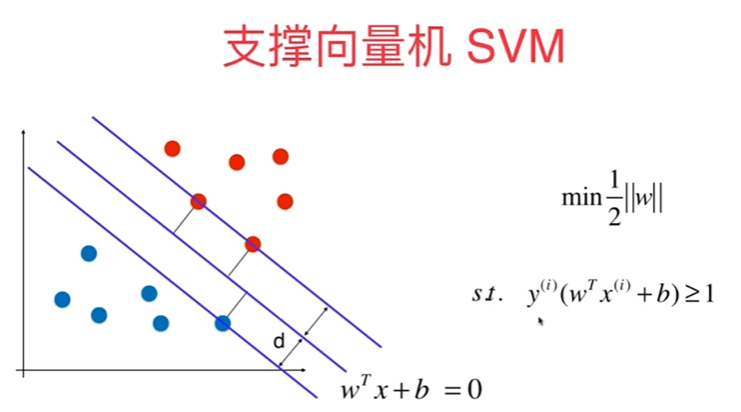
11-2 支持向量机的效用函数推导
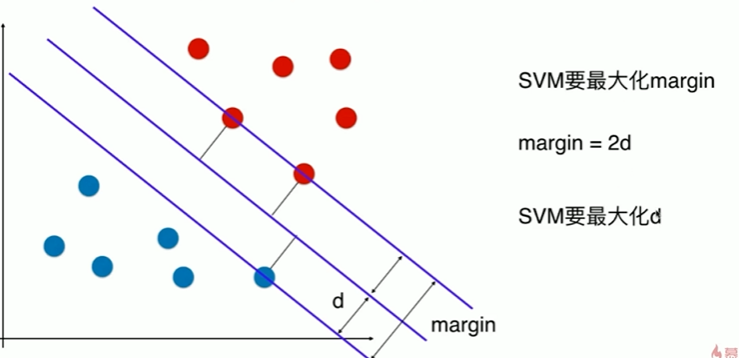
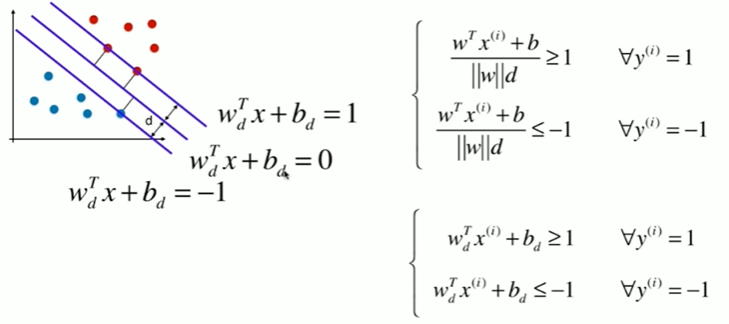
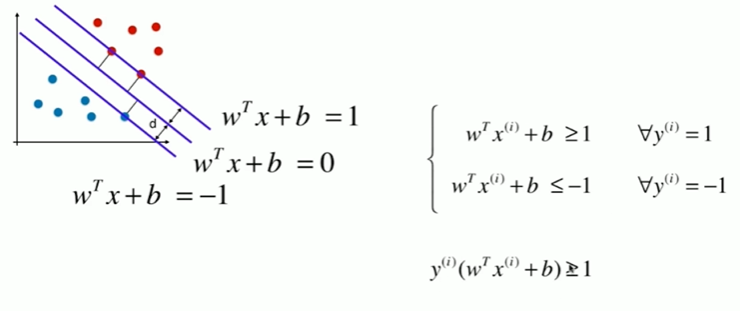

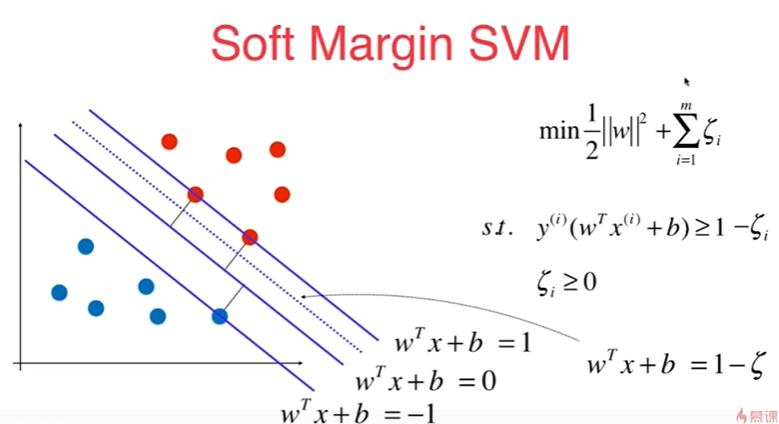
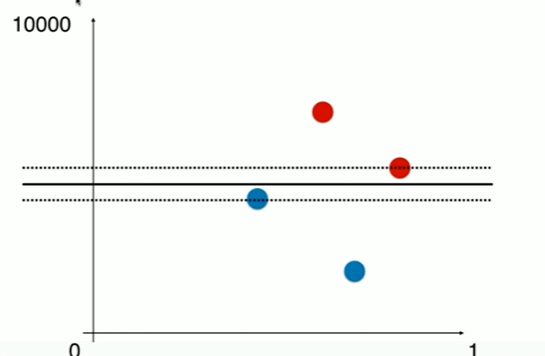
11-3 Soft Margin和SVM的正则化

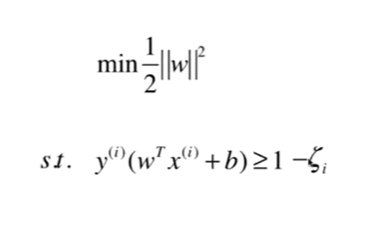
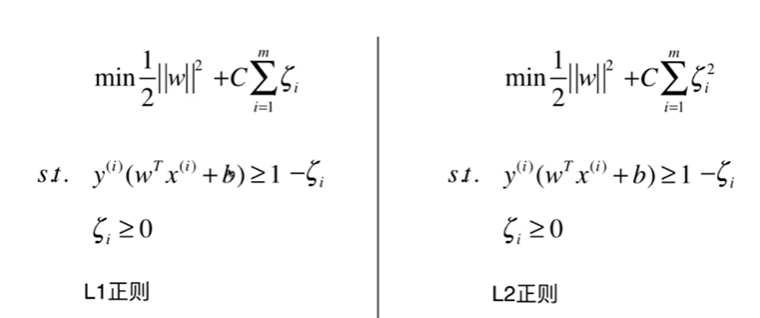
11-4 scikit-learn中的SVM
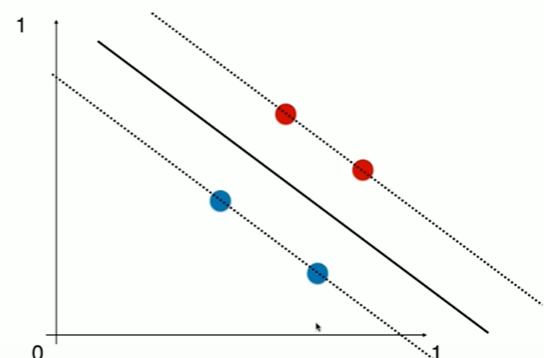
Notbook 示例
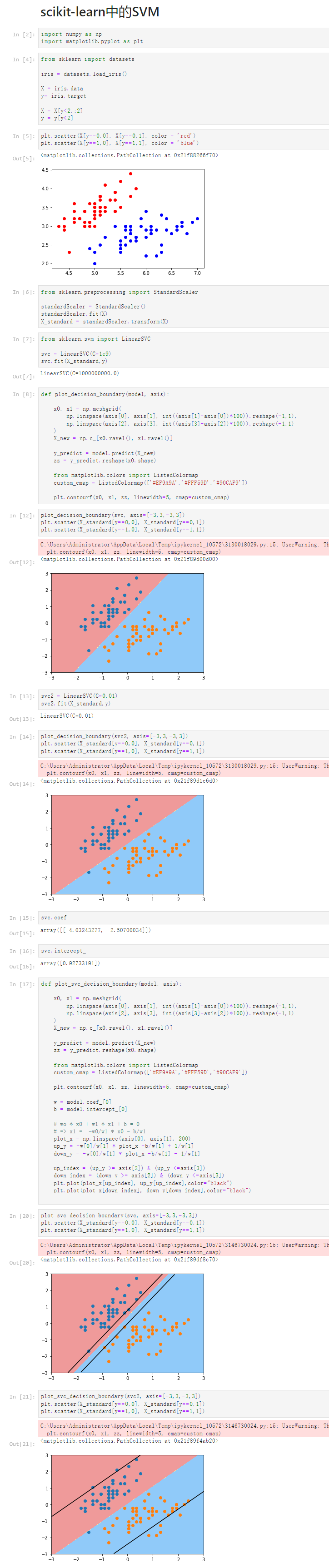
Notbook 源码
1 scikit-learn中的SVM 2 [2] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [4] 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 8 iris = datasets.load_iris() 9 10 X = iris.data 11 y= iris.target 12 13 X = X[y<2,:2] 14 y = y[y<2] 15 [5] 16 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1], color = 'red') 17 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1], color = 'blue') 18 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x21f88266f70> 19 20 [6] 21 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 22 23 standardScaler = StandardScaler() 24 standardScaler.fit(X) 25 X_standard = standardScaler.transform(X) 26 [7] 27 from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC 28 29 svc = LinearSVC(C=1e9) 30 svc.fit(X_standard,y) 31 LinearSVC(C=1000000000.0) 32 [8] 33 def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis): 34 35 x0, x1 = np.meshgrid( 36 np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1,1), 37 np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1,1) 38 ) 39 X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()] 40 41 y_predict = model.predict(X_new) 42 zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape) 43 44 from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap 45 custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9']) 46 47 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 48 [12] 49 plot_decision_boundary(svc, axis=[-3,3,-3,3]) 50 plt.scatter(X_standard[y==0,0], X_standard[y==0,1]) 51 plt.scatter(X_standard[y==1,0], X_standard[y==1,1]) 52 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_10572\3130018029.py:15: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth' 53 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 54 55 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x21f89d00d00> 56 57 [13] 58 svc2 = LinearSVC(C=0.01) 59 svc2.fit(X_standard,y) 60 LinearSVC(C=0.01) 61 [14] 62 plot_decision_boundary(svc2, axis=[-3,3,-3,3]) 63 plt.scatter(X_standard[y==0,0], X_standard[y==0,1]) 64 plt.scatter(X_standard[y==1,0], X_standard[y==1,1]) 65 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_10572\3130018029.py:15: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth' 66 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 67 68 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x21f89d1c6d0> 69 70 [15] 71 svc.coef_ 72 array([[ 4.03243277, -2.50700034]]) 73 [16] 74 svc.intercept_ 75 array([0.92733191]) 76 [17] 77 def plot_svc_decision_boundary(model, axis): 78 79 x0, x1 = np.meshgrid( 80 np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1,1), 81 np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1,1) 82 ) 83 X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()] 84 85 y_predict = model.predict(X_new) 86 zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape) 87 88 from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap 89 custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9']) 90 91 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 92 93 w = model.coef_[0] 94 b = model.intercept_[0] 95 96 # wo * x0 + w1 * x1 + b = 0 97 # => x1 = -w0/w1 * x0 - b/w1 98 plot_x = np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], 200) 99 up_y = -w[0]/w[1] * plot_x -b/w[1] + 1/w[1] 100 down_y = -w[0]/w[1] * plot_x -b/w[1] - 1/w[1] 101 102 up_index = (up_y >= axis[2]) & (up_y <=axis[3]) 103 down_index = (down_y >= axis[2]) & (down_y <=axis[3]) 104 plt.plot(plot_x[up_index], up_y[up_index],color="black") 105 plt.plot(plot_x[down_index], down_y[down_index],color="black") 106 107 [20] 108 plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc, axis=[-3,3,-3,3]) 109 plt.scatter(X_standard[y==0,0], X_standard[y==0,1]) 110 plt.scatter(X_standard[y==1,0], X_standard[y==1,1]) 111 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_10572\3146730024.py:15: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth' 112 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 113 114 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x21f89df8c70> 115 116 [21] 117 plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc2, axis=[-3,3,-3,3]) 118 plt.scatter(X_standard[y==0,0], X_standard[y==0,1]) 119 plt.scatter(X_standard[y==1,0], X_standard[y==1,1]) 120 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_10572\3146730024.py:15: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth' 121 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 122 123 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x21f89f4ab20>
11-5 SVM中使用多项式特征
Notbook 示例
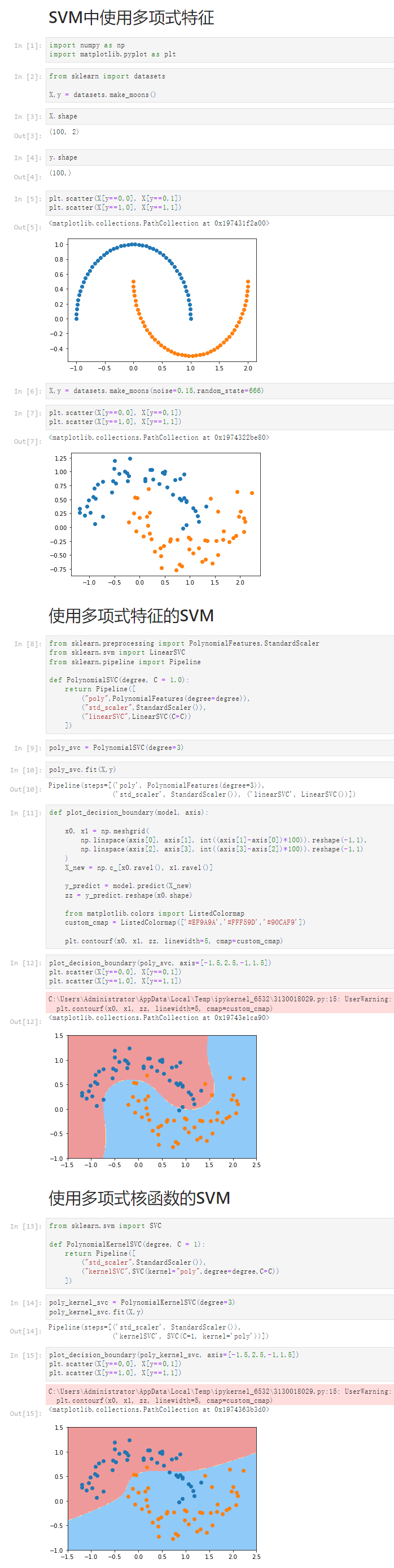
Notbook 源码
1 SVM中使用多项式特征 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 8 X,y = datasets.make_moons() 9 [3] 10 X.shape 11 (100, 2) 12 [4] 13 y.shape 14 (100,) 15 [5] 16 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 17 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 18 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x197431f2a00> 19 20 [6] 21 X,y = datasets.make_moons(noise=0.15,random_state=666) 22 [7] 23 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 24 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 25 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1974322be80> 26 27 使用多项式特征的SVM 28 [8] 29 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures,StandardScaler 30 from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC 31 from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline 32 33 def PolynomialSVC(degree, C = 1.0): 34 return Pipeline([ 35 ("poly",PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree)), 36 ("std_scaler",StandardScaler()), 37 ("linearSVC",LinearSVC(C=C)) 38 ]) 39 [9] 40 poly_svc = PolynomialSVC(degree=3) 41 [10] 42 poly_svc.fit(X,y) 43 Pipeline(steps=[('poly', PolynomialFeatures(degree=3)), 44 ('std_scaler', StandardScaler()), ('linearSVC', LinearSVC())]) 45 [11] 46 def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis): 47 48 x0, x1 = np.meshgrid( 49 np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1,1), 50 np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1,1) 51 ) 52 X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()] 53 54 y_predict = model.predict(X_new) 55 zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape) 56 57 from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap 58 custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9']) 59 60 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 61 [12] 62 plot_decision_boundary(poly_svc, axis=[-1.5,2.5,-1,1.5]) 63 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 64 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 65 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_6532\3130018029.py:15: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth' 66 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 67 68 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x19743e1ca90> 69 70 使用多项式核函数的SVM 71 [13] 72 from sklearn.svm import SVC 73 74 def PolynomialKernelSVC(degree, C = 1): 75 return Pipeline([ 76 ("std_scaler",StandardScaler()), 77 ("kernelSVC",SVC(kernel="poly",degree=degree,C=C)) 78 ]) 79 [14] 80 poly_kernel_svc = PolynomialKernelSVC(degree=3) 81 poly_kernel_svc.fit(X,y) 82 Pipeline(steps=[('std_scaler', StandardScaler()), 83 ('kernelSVC', SVC(C=1, kernel='poly'))]) 84 [15] 85 plot_decision_boundary(poly_kernel_svc, axis=[-1.5,2.5,-1,1.5]) 86 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 87 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 88 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_6532\3130018029.py:15: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth' 89 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 90 91 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1974363b3d0>
11-6 核函数

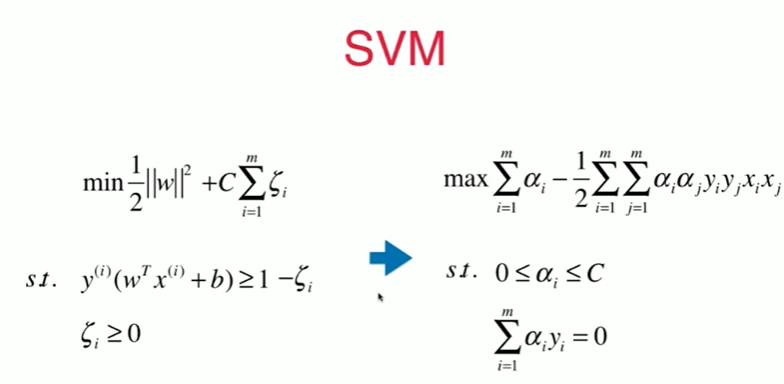
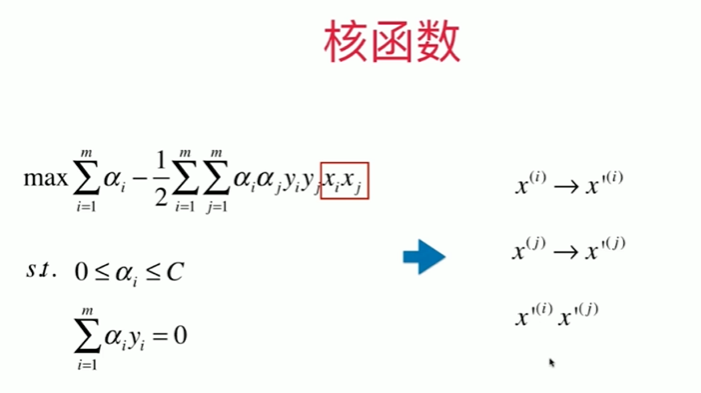
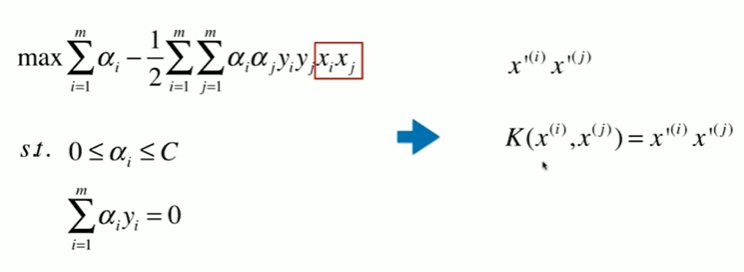
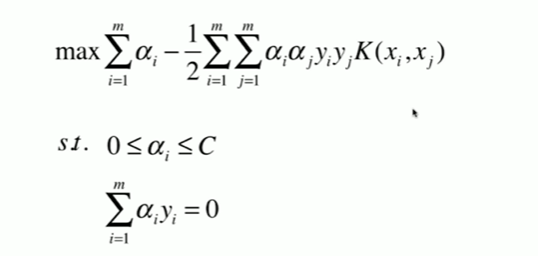

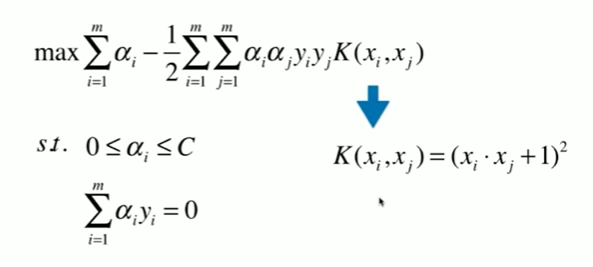
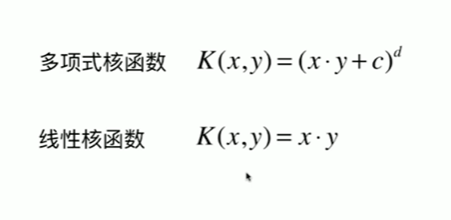
11-7 高斯核函数



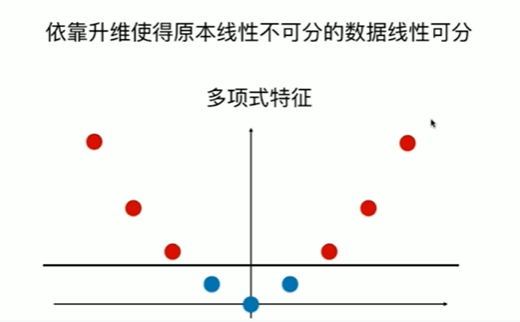
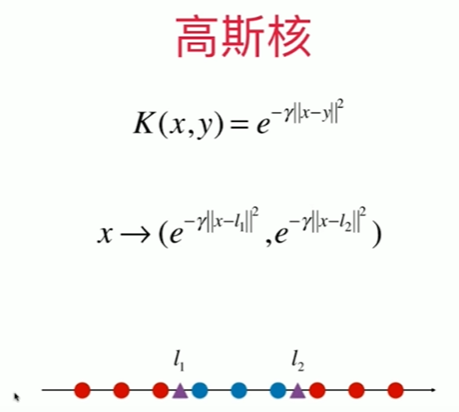
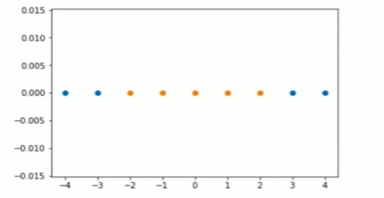
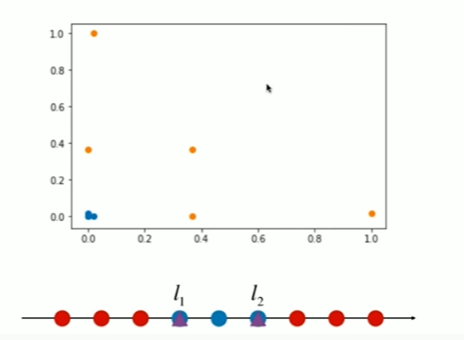
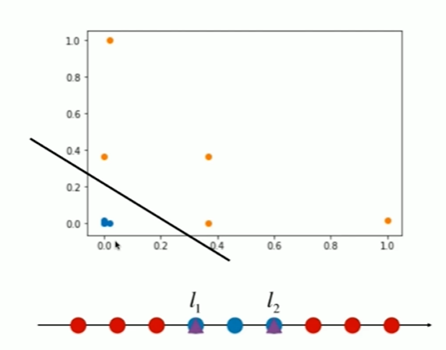

Notbook 示例
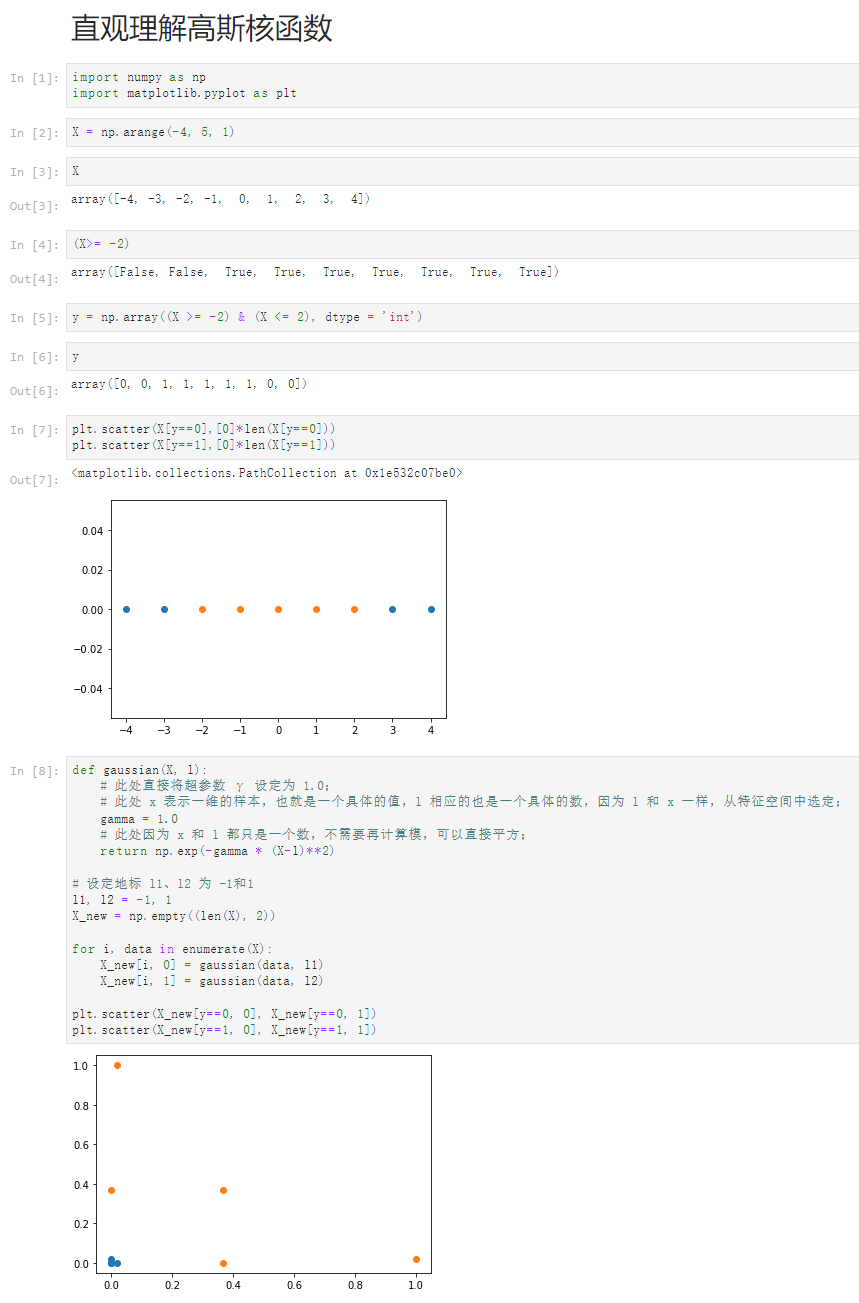
Notbook 源码
1 直观理解高斯核函数 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 X = np.arange(-4, 5, 1) 7 [3] 8 X 9 array([-4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) 10 [4] 11 (X>= -2) 12 array([False, False, True, True, True, True, True, True, True]) 13 [5] 14 y = np.array((X >= -2) & (X <= 2), dtype = 'int') 15 [6] 16 y 17 array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]) 18 [7] 19 plt.scatter(X[y==0],[0]*len(X[y==0])) 20 plt.scatter(X[y==1],[0]*len(X[y==1])) 21 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1e532c07be0> 22 23 [8] 24 def gaussian(X, l): 25 # 此处直接将超参数 γ 设定为 1.0; 26 # 此处 x 表示一维的样本,也就是一个具体的值,l 相应的也是一个具体的数,因为 l 和 x 一样,从特征空间中选定; 27 gamma = 1.0 28 # 此处因为 x 和 l 都只是一个数,不需要再计算模,可以直接平方; 29 return np.exp(-gamma * (X-l)**2) 30 31 # 设定地标 l1、l2 为 -1和1 32 l1, l2 = -1, 1 33 X_new = np.empty((len(X), 2)) 34 35 for i, data in enumerate(X): 36 X_new[i, 0] = gaussian(data, l1) 37 X_new[i, 1] = gaussian(data, l2) 38 39 plt.scatter(X_new[y==0, 0], X_new[y==0, 1]) 40 plt.scatter(X_new[y==1, 0], X_new[y==1, 1])
11-8 scikit-learn中的高斯核函数

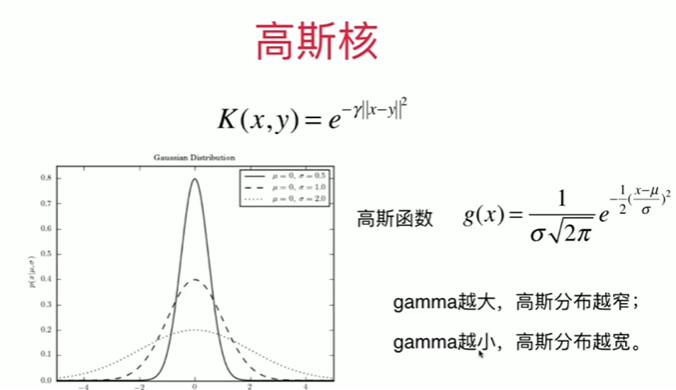
Notbook 示例
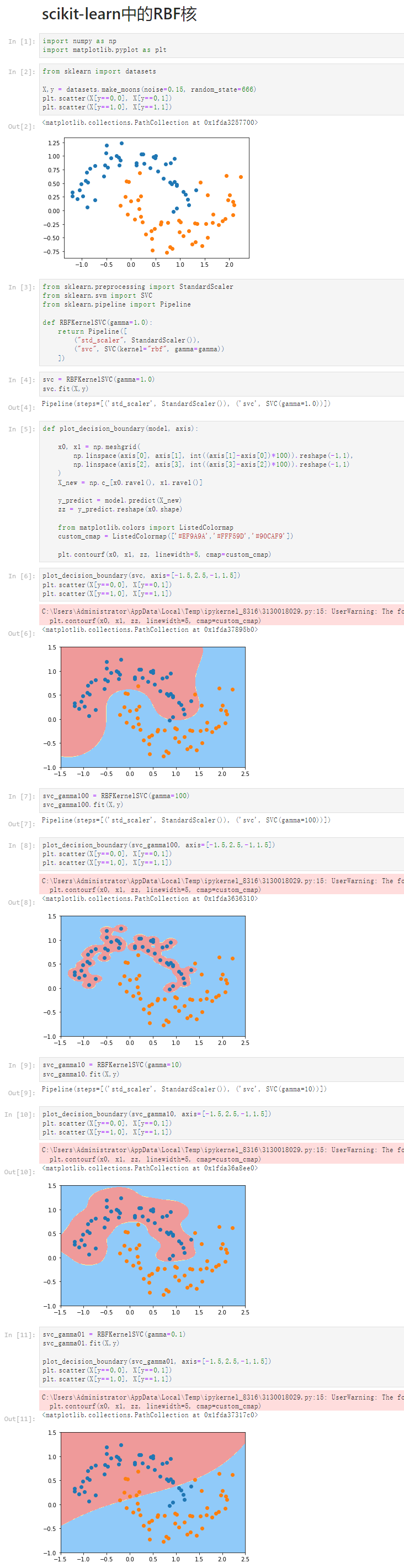
Notbook 源码
1 scikit-learn中的RBF核 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 8 X,y = datasets.make_moons(noise=0.15, random_state=666) 9 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 10 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 11 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1fda3257700> 12 13 [3] 14 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 15 from sklearn.svm import SVC 16 from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline 17 18 def RBFKernelSVC(gamma=1.0): 19 return Pipeline([ 20 ("std_scaler", StandardScaler()), 21 ("svc", SVC(kernel="rbf", gamma=gamma)) 22 ]) 23 [4] 24 svc = RBFKernelSVC(gamma=1.0) 25 svc.fit(X,y) 26 Pipeline(steps=[('std_scaler', StandardScaler()), ('svc', SVC(gamma=1.0))]) 27 [5] 28 def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis): 29 30 x0, x1 = np.meshgrid( 31 np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1,1), 32 np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1,1) 33 ) 34 X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()] 35 36 y_predict = model.predict(X_new) 37 zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape) 38 39 from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap 40 custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9']) 41 42 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 43 [6] 44 plot_decision_boundary(svc, axis=[-1.5,2.5,-1,1.5]) 45 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 46 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 47 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_8316\3130018029.py:15: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth' 48 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 49 50 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1fda37895b0> 51 52 [7] 53 svc_gamma100 = RBFKernelSVC(gamma=100) 54 svc_gamma100.fit(X,y) 55 Pipeline(steps=[('std_scaler', StandardScaler()), ('svc', SVC(gamma=100))]) 56 [8] 57 plot_decision_boundary(svc_gamma100, axis=[-1.5,2.5,-1,1.5]) 58 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 59 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 60 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_8316\3130018029.py:15: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth' 61 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 62 63 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1fda3636310> 64 65 [9] 66 svc_gamma10 = RBFKernelSVC(gamma=10) 67 svc_gamma10.fit(X,y) 68 Pipeline(steps=[('std_scaler', StandardScaler()), ('svc', SVC(gamma=10))]) 69 [10] 70 plot_decision_boundary(svc_gamma10, axis=[-1.5,2.5,-1,1.5]) 71 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 72 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 73 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_8316\3130018029.py:15: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth' 74 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 75 76 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1fda36a8ee0> 77 78 [11] 79 svc_gamma01 = RBFKernelSVC(gamma=0.1) 80 svc_gamma01.fit(X,y) 81 82 plot_decision_boundary(svc_gamma01, axis=[-1.5,2.5,-1,1.5]) 83 plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1]) 84 plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1]) 85 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_8316\3130018029.py:15: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth' 86 plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) 87 88 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1fda37317c0>
11-9 SVM思路解决回归问题
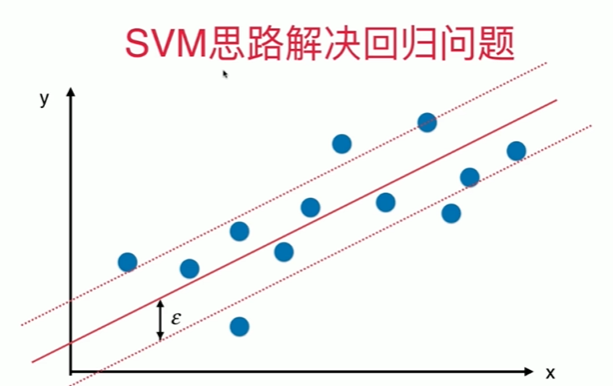
Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
1 SVM 思路解决回归问题 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 8 boston = datasets.load_boston() 9 X = boston.data 10 y = boston.target 11 F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\deprecation.py:87: FutureWarning: Function load_boston is deprecated; `load_boston` is deprecated in 1.0 and will be removed in 1.2. 12 13 The Boston housing prices dataset has an ethical problem. You can refer to 14 the documentation of this function for further details. 15 16 The scikit-learn maintainers therefore strongly discourage the use of this 17 dataset unless the purpose of the code is to study and educate about 18 ethical issues in data science and machine learning. 19 20 In this special case, you can fetch the dataset from the original 21 source:: 22 23 import pandas as pd 24 import numpy as np 25 26 27 data_url = "http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/boston" 28 raw_df = pd.read_csv(data_url, sep="\s+", skiprows=22, header=None) 29 data = np.hstack([raw_df.values[::2, :], raw_df.values[1::2, :2]]) 30 target = raw_df.values[1::2, 2] 31 32 Alternative datasets include the California housing dataset (i.e. 33 :func:`~sklearn.datasets.fetch_california_housing`) and the Ames housing 34 dataset. You can load the datasets as follows:: 35 36 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing 37 housing = fetch_california_housing() 38 39 for the California housing dataset and:: 40 41 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml 42 housing = fetch_openml(name="house_prices", as_frame=True) 43 44 for the Ames housing dataset. 45 46 warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning) 47 48 [3] 49 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 50 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=666) 51 [4] 52 from sklearn.svm import LinearSVR 53 from sklearn.svm import SVR 54 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 55 from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline 56 57 def StandardLinearSVR(epsilon=0.1): 58 return Pipeline([ 59 ("std_scaler", StandardScaler()), 60 ("linearSVR",LinearSVR(epsilon=epsilon)) 61 ]) 62 [5] 63 svr = StandardLinearSVR() 64 svr.fit(X_train, y_train) 65 Pipeline(steps=[('std_scaler', StandardScaler()), 66 ('linearSVR', LinearSVR(epsilon=0.1))]) 67 [6] 68 svr.score(X_test,y_test) 69 0.6356218812016852








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号