第8章上 多项式回归与模型泛化
8-1 什么是多项式回归
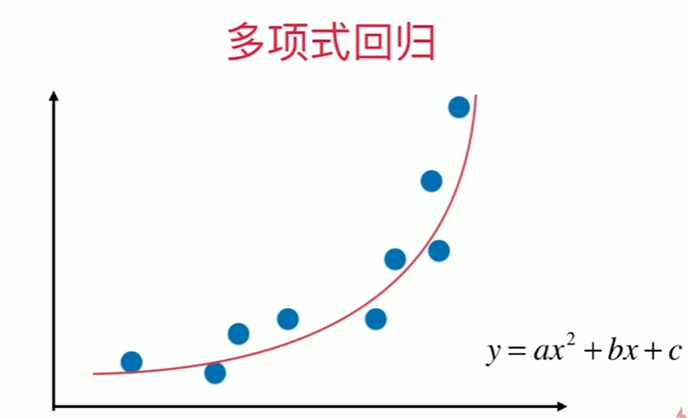
Notbook 示例
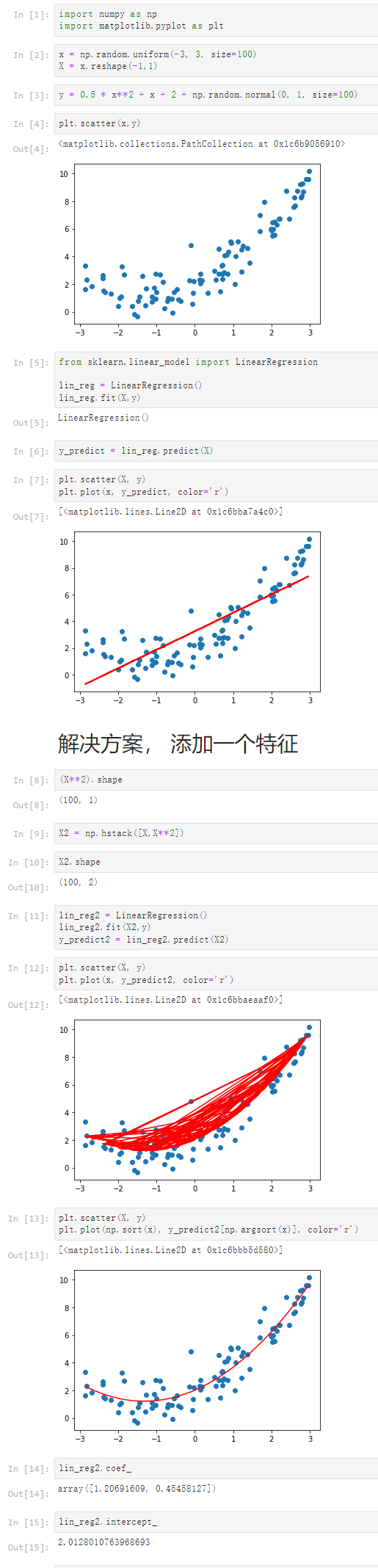
Notbook 源码
1 [1] 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 [2] 5 x = np.random.uniform(-3, 3, size=100) 6 X = x.reshape(-1,1) 7 [3] 8 y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, size=100) 9 [4] 10 plt.scatter(x,y) 11 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1c6b9056910> 12 13 [5] 14 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 15 16 lin_reg = LinearRegression() 17 lin_reg.fit(X,y) 18 LinearRegression() 19 [6] 20 y_predict = lin_reg.predict(X) 21 [7] 22 plt.scatter(X, y) 23 plt.plot(x, y_predict, color='r') 24 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1c6bba7a4c0>] 25 26 解决方案, 添加一个特征 27 [8] 28 (X**2).shape 29 (100, 1) 30 [9] 31 X2 = np.hstack([X,X**2]) 32 [10] 33 X2.shape 34 (100, 2) 35 [11] 36 lin_reg2 = LinearRegression() 37 lin_reg2.fit(X2,y) 38 y_predict2 = lin_reg2.predict(X2) 39 [12] 40 plt.scatter(X, y) 41 plt.plot(x, y_predict2, color='r') 42 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1c6bbaeaaf0>] 43 44 [13] 45 plt.scatter(X, y) 46 plt.plot(np.sort(x), y_predict2[np.argsort(x)], color='r') 47 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1c6bbb5d580>] 48 49 [14] 50 lin_reg2.coef_ 51 array([1.20691609, 0.45458127]) 52 [15] 53 lin_reg2.intercept_ 54 2.0128010763968693
8-2 scikit-learn中的多项式回归于pipeline
Notbook 示例
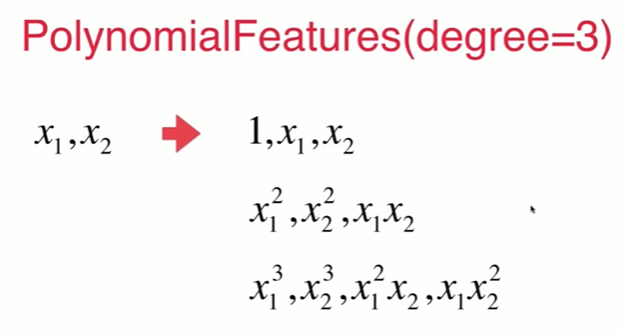
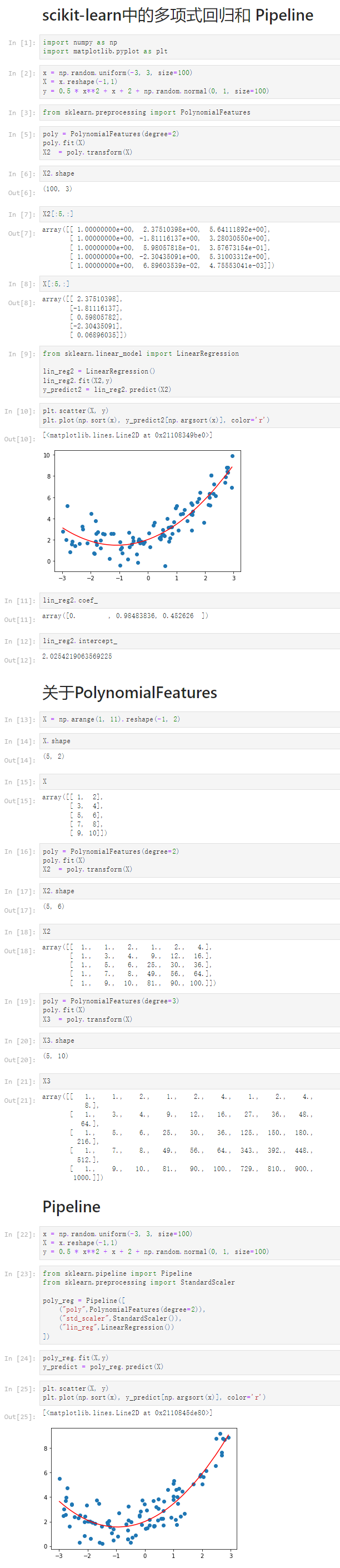
Notbook 源码
1 scikit-learn中的多项式回归和 Pipeline 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 x = np.random.uniform(-3, 3, size=100) 7 X = x.reshape(-1,1) 8 y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, size=100) 9 [3] 10 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures 11 [5] 12 poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2) 13 poly.fit(X) 14 X2 = poly.transform(X) 15 [6] 16 X2.shape 17 (100, 3) 18 [7] 19 X2[:5,:] 20 array([[ 1.00000000e+00, 2.37510398e+00, 5.64111892e+00], 21 [ 1.00000000e+00, -1.81116137e+00, 3.28030550e+00], 22 [ 1.00000000e+00, 5.98057818e-01, 3.57673154e-01], 23 [ 1.00000000e+00, -2.30435091e+00, 5.31003312e+00], 24 [ 1.00000000e+00, 6.89603539e-02, 4.75553041e-03]]) 25 [8] 26 X[:5,:] 27 array([[ 2.37510398], 28 [-1.81116137], 29 [ 0.59805782], 30 [-2.30435091], 31 [ 0.06896035]]) 32 [9] 33 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 34 35 lin_reg2 = LinearRegression() 36 lin_reg2.fit(X2,y) 37 y_predict2 = lin_reg2.predict(X2) 38 [10] 39 plt.scatter(X, y) 40 plt.plot(np.sort(x), y_predict2[np.argsort(x)], color='r') 41 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x21108349be0>] 42 43 [11] 44 lin_reg2.coef_ 45 array([0. , 0.98483836, 0.452626 ]) 46 [12] 47 lin_reg2.intercept_ 48 2.0254219063569225 49 关于PolynomialFeatures 50 [13] 51 X = np.arange(1, 11).reshape(-1, 2) 52 [14] 53 X.shape 54 (5, 2) 55 [15] 56 X 57 array([[ 1, 2], 58 [ 3, 4], 59 [ 5, 6], 60 [ 7, 8], 61 [ 9, 10]]) 62 [16] 63 poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2) 64 poly.fit(X) 65 X2 = poly.transform(X) 66 [17] 67 X2.shape 68 (5, 6) 69 [18] 70 X2 71 array([[ 1., 1., 2., 1., 2., 4.], 72 [ 1., 3., 4., 9., 12., 16.], 73 [ 1., 5., 6., 25., 30., 36.], 74 [ 1., 7., 8., 49., 56., 64.], 75 [ 1., 9., 10., 81., 90., 100.]]) 76 [19] 77 poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3) 78 poly.fit(X) 79 X3 = poly.transform(X) 80 [20] 81 X3.shape 82 (5, 10) 83 [21] 84 X3 85 array([[ 1., 1., 2., 1., 2., 4., 1., 2., 4., 86 8.], 87 [ 1., 3., 4., 9., 12., 16., 27., 36., 48., 88 64.], 89 [ 1., 5., 6., 25., 30., 36., 125., 150., 180., 90 216.], 91 [ 1., 7., 8., 49., 56., 64., 343., 392., 448., 92 512.], 93 [ 1., 9., 10., 81., 90., 100., 729., 810., 900., 94 1000.]]) 95 Pipeline 96 [22] 97 x = np.random.uniform(-3, 3, size=100) 98 X = x.reshape(-1,1) 99 y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, size=100) 100 [23] 101 from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline 102 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 103 104 poly_reg = Pipeline([ 105 ("poly",PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)), 106 ("std_scaler",StandardScaler()), 107 ("lin_reg",LinearRegression()) 108 ]) 109 [24] 110 poly_reg.fit(X,y) 111 y_predict = poly_reg.predict(X) 112 [25] 113 plt.scatter(X, y) 114 plt.plot(np.sort(x), y_predict[np.argsort(x)], color='r') 115 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x2110845de80>]
8-3 过拟合与欠拟合
Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
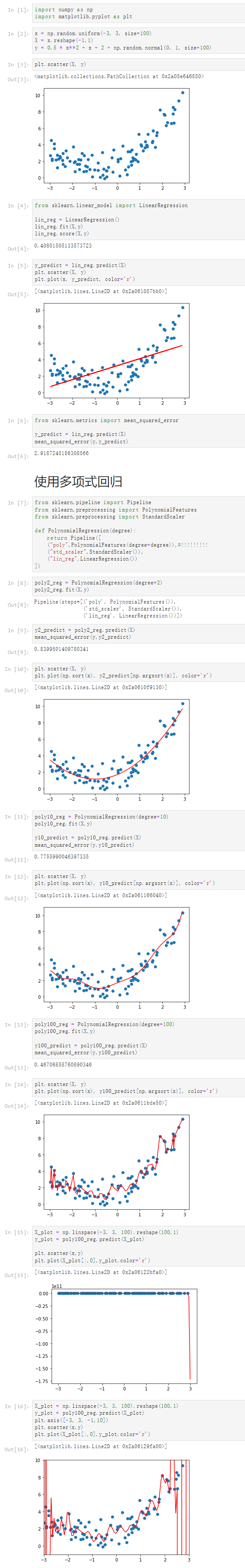
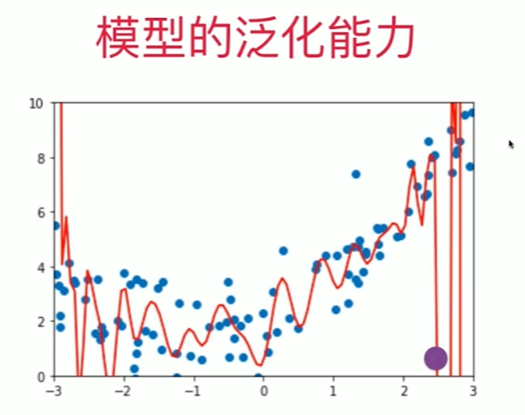
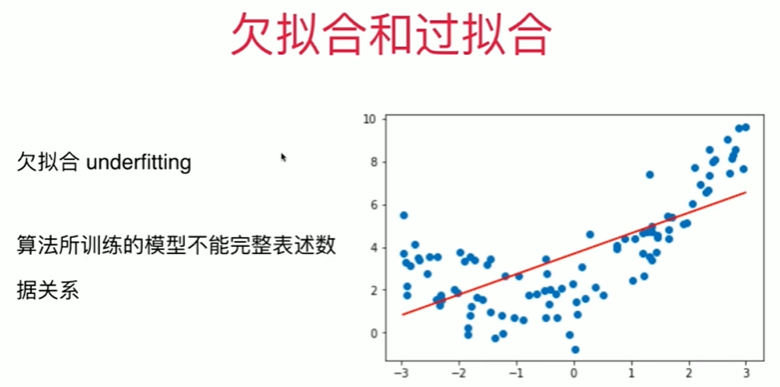
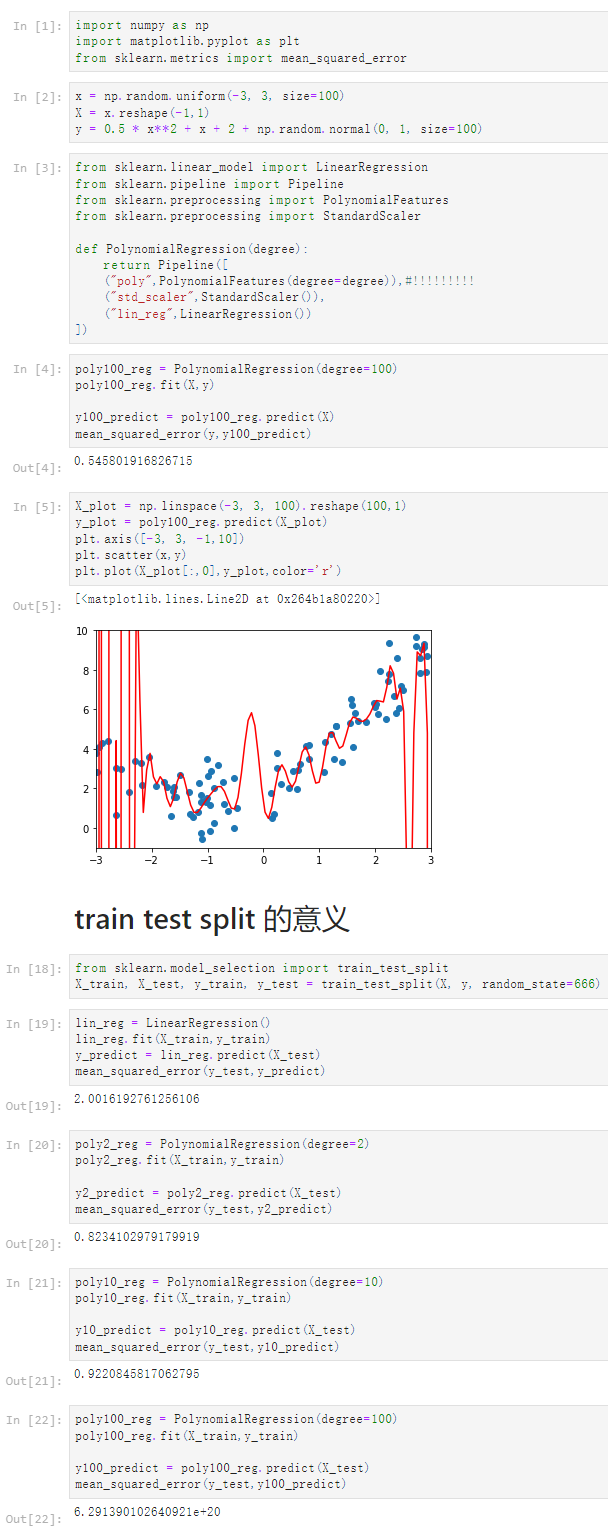
1 [1] 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 [2] 5 x = np.random.uniform(-3, 3, size=100) 6 X = x.reshape(-1,1) 7 y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, size=100) 8 [3] 9 plt.scatter(X, y) 10 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x2a05e646850> 11 12 [4] 13 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 14 15 lin_reg = LinearRegression() 16 lin_reg.fit(X,y) 17 lin_reg.score(X,y) 18 0.40801505133573723 19 [5] 20 y_predict = lin_reg.predict(X) 21 plt.scatter(X, y) 22 plt.plot(x, y_predict, color='r') 23 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x2a061057bb0>] 24 25 [6] 26 from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error 27 28 y_predict = lin_reg.predict(X) 29 mean_squared_error(y,y_predict) 30 2.9187245186308566 31 使用多项式回归 32 [7] 33 from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline 34 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures 35 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 36 37 def PolynomialRegression(degree): 38 return Pipeline([ 39 ("poly",PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree)),#!!!!!!!!! 40 ("std_scaler",StandardScaler()), 41 ("lin_reg",LinearRegression()) 42 ]) 43 [8] 44 poly2_reg = PolynomialRegression(degree=2) 45 poly2_reg.fit(X,y) 46 Pipeline(steps=[('poly', PolynomialFeatures()), 47 ('std_scaler', StandardScaler()), 48 ('lin_reg', LinearRegression())]) 49 [9] 50 y2_predict = poly2_reg.predict(X) 51 mean_squared_error(y,y2_predict) 52 0.8399501409780341 53 [10] 54 plt.scatter(X, y) 55 plt.plot(np.sort(x), y2_predict[np.argsort(x)], color='r') 56 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x2a0610f9130>] 57 58 [11] 59 poly10_reg = PolynomialRegression(degree=10) 60 poly10_reg.fit(X,y) 61 62 y10_predict = poly10_reg.predict(X) 63 mean_squared_error(y,y10_predict) 64 0.7755990046397335 65 [12] 66 plt.scatter(X, y) 67 plt.plot(np.sort(x), y10_predict[np.argsort(x)], color='r') 68 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x2a061166040>] 69 70 [13] 71 poly100_reg = PolynomialRegression(degree=100) 72 poly100_reg.fit(X,y) 73 74 y100_predict = poly100_reg.predict(X) 75 mean_squared_error(y,y100_predict) 76 0.46706858760890346 77 [14] 78 plt.scatter(X, y) 79 plt.plot(np.sort(x), y100_predict[np.argsort(x)], color='r') 80 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x2a0611bde50>] 81 82 [15] 83 X_plot = np.linspace(-3, 3, 100).reshape(100,1) 84 y_plot = poly100_reg.predict(X_plot) 85 86 plt.scatter(x,y) 87 plt.plot(X_plot[:,0],y_plot,color='r') 88 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x2a06122bfa0>] 89 90 [16] 91 X_plot = np.linspace(-3, 3, 100).reshape(100,1) 92 y_plot = poly100_reg.predict(X_plot) 93 plt.axis([-3, 3, -1,10]) 94 plt.scatter(x,y) 95 plt.plot(X_plot[:,0],y_plot,color='r') 96 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x2a06129fa00>]
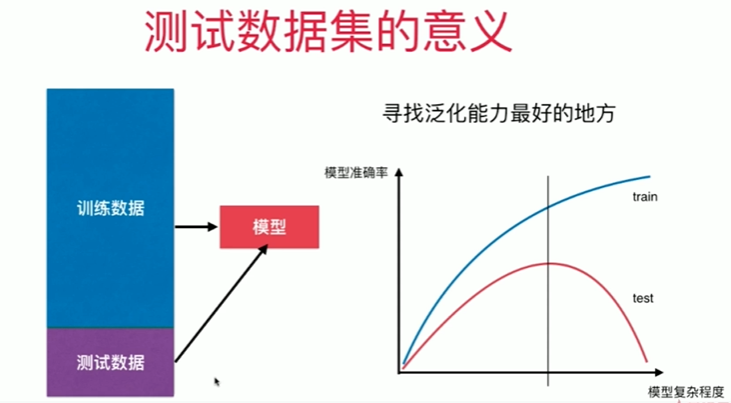
8-4 为什么要训练数据集与测试数据集

Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
1 [1] 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error 5 [2] 6 x = np.random.uniform(-3, 3, size=100) 7 X = x.reshape(-1,1) 8 y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, size=100) 9 [3] 10 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 11 from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline 12 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures 13 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 14 15 def PolynomialRegression(degree): 16 return Pipeline([ 17 ("poly",PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree)),#!!!!!!!!! 18 ("std_scaler",StandardScaler()), 19 ("lin_reg",LinearRegression()) 20 ]) 21 [4] 22 poly100_reg = PolynomialRegression(degree=100) 23 poly100_reg.fit(X,y) 24 25 y100_predict = poly100_reg.predict(X) 26 mean_squared_error(y,y100_predict) 27 0.545801916826715 28 [5] 29 X_plot = np.linspace(-3, 3, 100).reshape(100,1) 30 y_plot = poly100_reg.predict(X_plot) 31 plt.axis([-3, 3, -1,10]) 32 plt.scatter(x,y) 33 plt.plot(X_plot[:,0],y_plot,color='r') 34 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x264b1a80220>] 35 36 train test split 的意义 37 [18] 38 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 39 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=666) 40 [19] 41 lin_reg = LinearRegression() 42 lin_reg.fit(X_train,y_train) 43 y_predict = lin_reg.predict(X_test) 44 mean_squared_error(y_test,y_predict) 45 2.0016192761256106 46 [20] 47 poly2_reg = PolynomialRegression(degree=2) 48 poly2_reg.fit(X_train,y_train) 49 50 y2_predict = poly2_reg.predict(X_test) 51 mean_squared_error(y_test,y2_predict) 52 0.8234102979179919 53 [21] 54 poly10_reg = PolynomialRegression(degree=10) 55 poly10_reg.fit(X_train,y_train) 56 57 y10_predict = poly10_reg.predict(X_test) 58 mean_squared_error(y_test,y10_predict) 59 0.9220845817062795 60 [22] 61 poly100_reg = PolynomialRegression(degree=100) 62 poly100_reg.fit(X_train,y_train) 63 64 y100_predict = poly100_reg.predict(X_test) 65 mean_squared_error(y_test,y100_predict) 66 6.291390102640921e+20
8-5 学习曲线

Notbook 示例
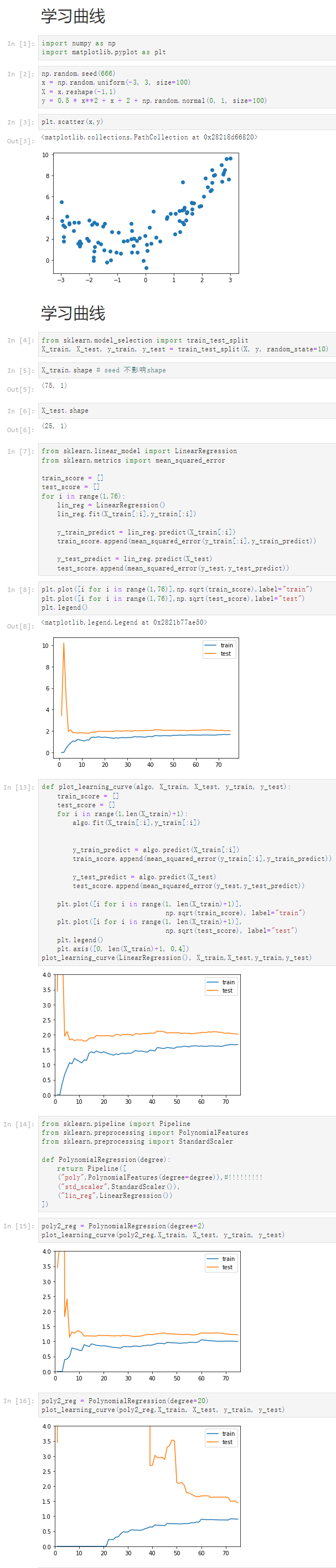
Notbook 源码
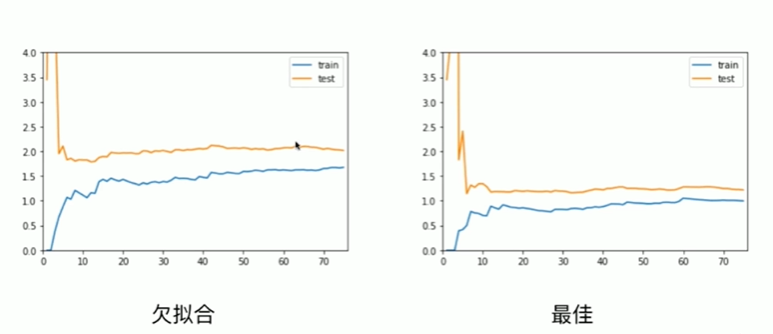
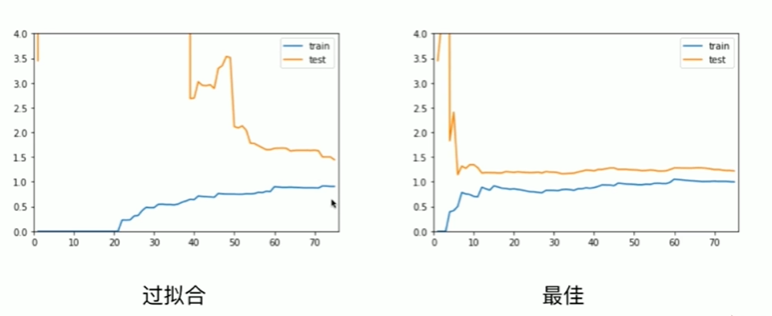
1 学习曲线 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 np.random.seed(666) 7 x = np.random.uniform(-3, 3, size=100) 8 X = x.reshape(-1,1) 9 y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, size=100) 10 [3] 11 plt.scatter(x,y) 12 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x28218d66820> 13 14 学习曲线 15 [4] 16 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 17 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=10) 18 [5] 19 X_train.shape # seed 不影响shape 20 (75, 1) 21 [6] 22 X_test.shape 23 (25, 1) 24 [7] 25 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 26 from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error 27 28 train_score = [] 29 test_score = [] 30 for i in range(1,76): 31 lin_reg = LinearRegression() 32 lin_reg.fit(X_train[:i],y_train[:i]) 33 34 y_train_predict = lin_reg.predict(X_train[:i]) 35 train_score.append(mean_squared_error(y_train[:i],y_train_predict)) 36 37 y_test_predict = lin_reg.predict(X_test) 38 test_score.append(mean_squared_error(y_test,y_test_predict)) 39 [8] 40 plt.plot([i for i in range(1,76)],np.sqrt(train_score),label="train") 41 plt.plot([i for i in range(1,76)],np.sqrt(test_score),label="test") 42 plt.legend() 43 <matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x2821b77ae50> 44 45 [13] 46 def plot_learning_curve(algo, X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test): 47 train_score = [] 48 test_score = [] 49 for i in range(1,len(X_train)+1): 50 algo.fit(X_train[:i],y_train[:i]) 51 52 53 y_train_predict = algo.predict(X_train[:i]) 54 train_score.append(mean_squared_error(y_train[:i],y_train_predict)) 55 56 y_test_predict = algo.predict(X_test) 57 test_score.append(mean_squared_error(y_test,y_test_predict)) 58 59 plt.plot([i for i in range(1, len(X_train)+1)], 60 np.sqrt(train_score), label="train") 61 plt.plot([i for i in range(1, len(X_train)+1)], 62 np.sqrt(test_score), label="test") 63 plt.legend() 64 plt.axis([0, len(X_train)+1, 0,4]) 65 plot_learning_curve(LinearRegression(), X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test) 66 67 [14] 68 from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline 69 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures 70 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 71 72 def PolynomialRegression(degree): 73 return Pipeline([ 74 ("poly",PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree)),#!!!!!!!!! 75 ("std_scaler",StandardScaler()), 76 ("lin_reg",LinearRegression()) 77 ]) 78 [15] 79 poly2_reg = PolynomialRegression(degree=2) 80 plot_learning_curve(poly2_reg,X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test) 81 82 [16] 83 poly2_reg = PolynomialRegression(degree=20) 84 plot_learning_curve(poly2_reg,X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test)







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号