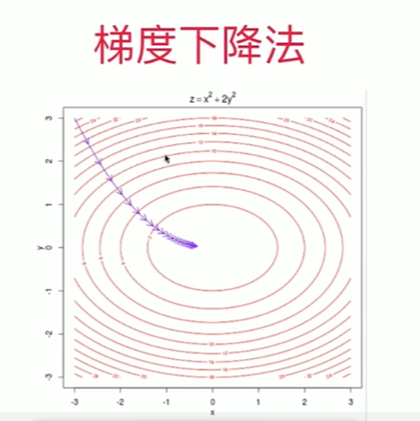
第6章 梯度下降法
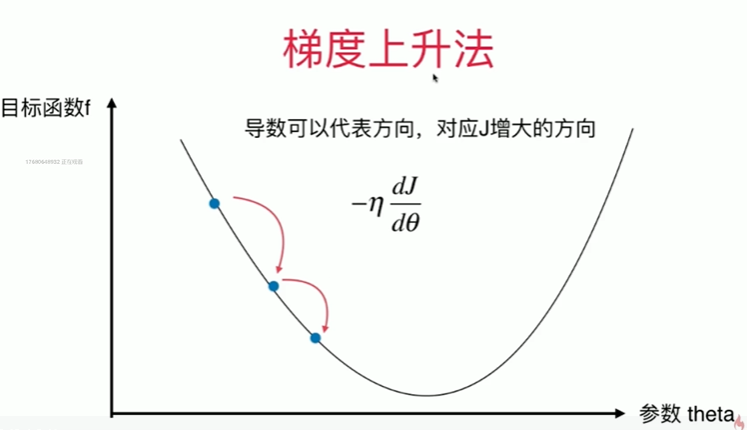
6-1 什么是梯度下降法

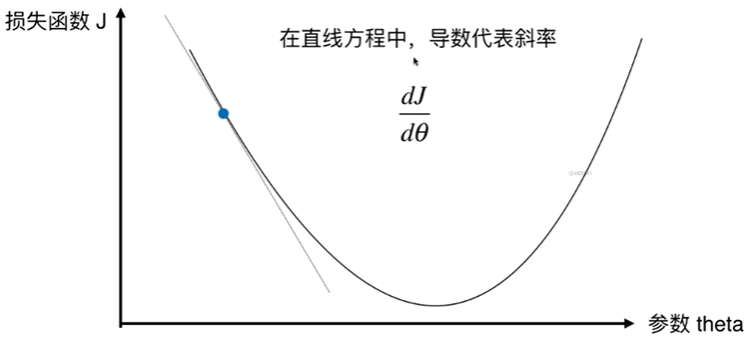
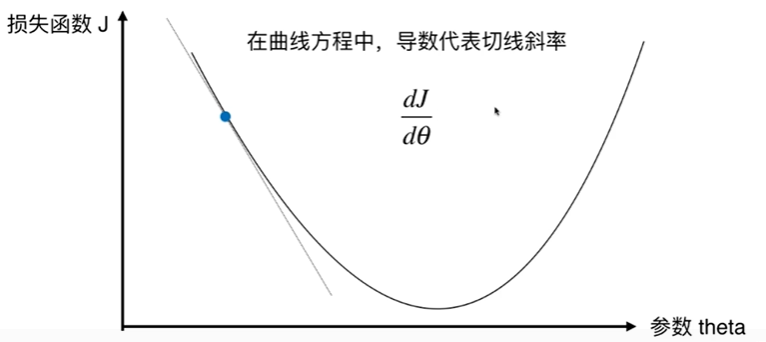
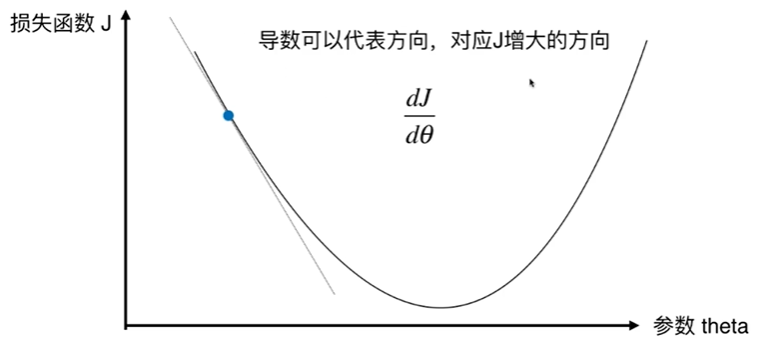
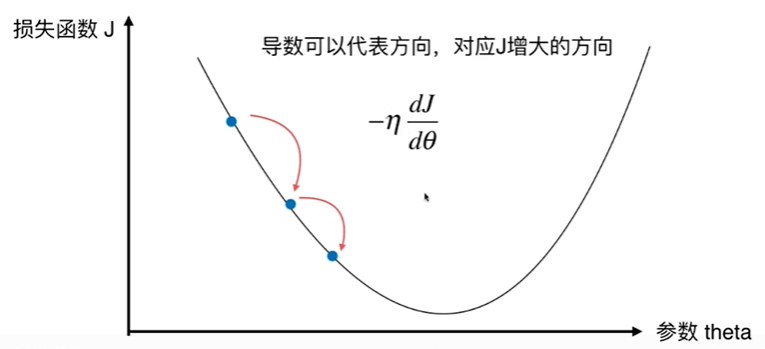
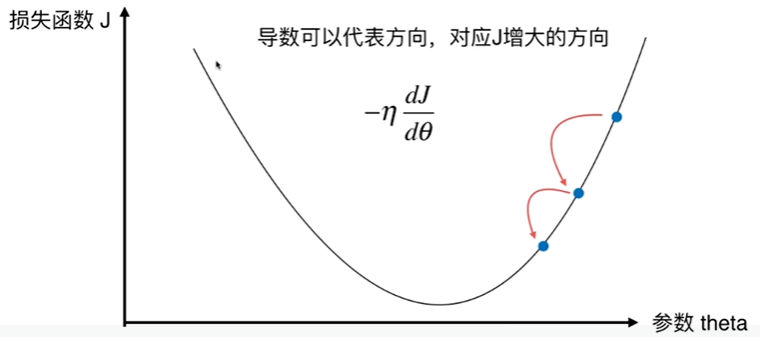

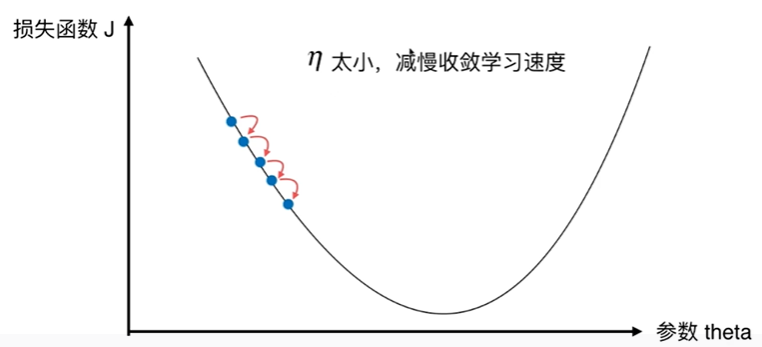
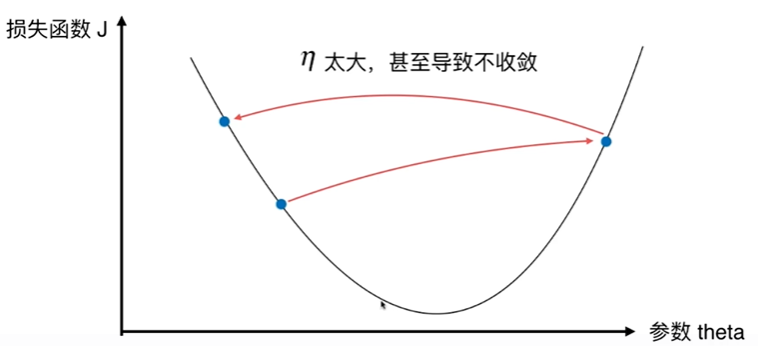


6-2 模拟实现梯度下降法
Notbook 示例
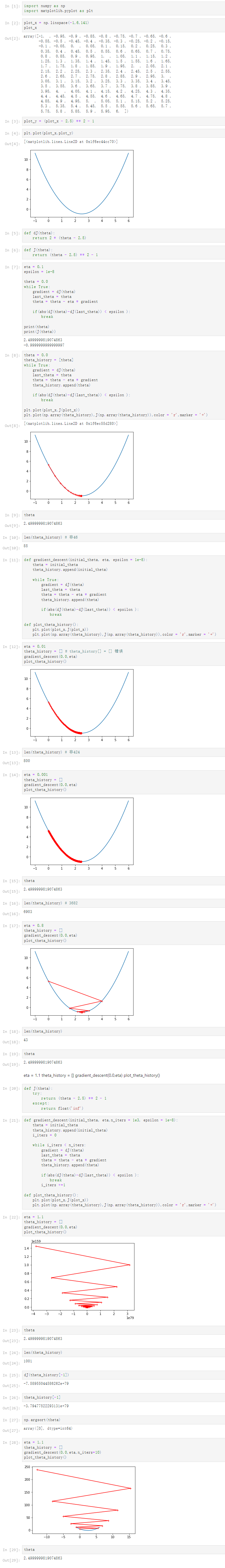
Notbook 源码
1 [1] 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 [2] 5 plot_x = np.linspace(-1,6,141) 6 plot_x 7 array([-1. , -0.95, -0.9 , -0.85, -0.8 , -0.75, -0.7 , -0.65, -0.6 , 8 -0.55, -0.5 , -0.45, -0.4 , -0.35, -0.3 , -0.25, -0.2 , -0.15, 9 -0.1 , -0.05, 0. , 0.05, 0.1 , 0.15, 0.2 , 0.25, 0.3 , 10 0.35, 0.4 , 0.45, 0.5 , 0.55, 0.6 , 0.65, 0.7 , 0.75, 11 0.8 , 0.85, 0.9 , 0.95, 1. , 1.05, 1.1 , 1.15, 1.2 , 12 1.25, 1.3 , 1.35, 1.4 , 1.45, 1.5 , 1.55, 1.6 , 1.65, 13 1.7 , 1.75, 1.8 , 1.85, 1.9 , 1.95, 2. , 2.05, 2.1 , 14 2.15, 2.2 , 2.25, 2.3 , 2.35, 2.4 , 2.45, 2.5 , 2.55, 15 2.6 , 2.65, 2.7 , 2.75, 2.8 , 2.85, 2.9 , 2.95, 3. , 16 3.05, 3.1 , 3.15, 3.2 , 3.25, 3.3 , 3.35, 3.4 , 3.45, 17 3.5 , 3.55, 3.6 , 3.65, 3.7 , 3.75, 3.8 , 3.85, 3.9 , 18 3.95, 4. , 4.05, 4.1 , 4.15, 4.2 , 4.25, 4.3 , 4.35, 19 4.4 , 4.45, 4.5 , 4.55, 4.6 , 4.65, 4.7 , 4.75, 4.8 , 20 4.85, 4.9 , 4.95, 5. , 5.05, 5.1 , 5.15, 5.2 , 5.25, 21 5.3 , 5.35, 5.4 , 5.45, 5.5 , 5.55, 5.6 , 5.65, 5.7 , 22 5.75, 5.8 , 5.85, 5.9 , 5.95, 6. ]) 23 [3] 24 plot_y = (plot_x - 2.5) ** 2 - 1 25 [4] 26 plt.plot(plot_x,plot_y) 27 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1f6ec44cc70>] 28 29 [5] 30 def dJ(theta): 31 return 2 * (theta - 2.5) 32 [6] 33 def J(theta): 34 return (theta - 2.5) ** 2 - 1 35 [7] 36 eta = 0.1 37 epsilon = 1e-8 38 39 theta = 0.0 40 while True: 41 gradient = dJ(theta) 42 last_theta = theta 43 theta = theta - eta * gradient 44 45 if(abs(dJ(theta)-dJ(last_theta)) < epsilon ): 46 break 47 48 print(theta) 49 print(J(theta)) 50 2.4999999819074863 51 -0.9999999999999997 52 53 [8] 54 theta = 0.0 55 theta_history = [theta] 56 while True: 57 gradient = dJ(theta) 58 last_theta = theta 59 theta = theta - eta * gradient 60 theta_history.append(theta) 61 62 if(abs(dJ(theta)-dJ(last_theta)) < epsilon ): 63 break 64 65 plt.plot(plot_x,J(plot_x)) 66 plt.plot(np.array(theta_history),J(np.array(theta_history)),color = 'r',marker = '+') 67 [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1f6ec55d280>] 68 69 [9] 70 theta 71 2.4999999819074863 72 [10] 73 len(theta_history) # 非46 74 85 75 [11] 76 def gradient_descent(initial_theta, eta, epsilon = 1e-8): 77 theta = initial_theta 78 theta_history.append(initial_theta) 79 80 while True: 81 gradient = dJ(theta) 82 last_theta = theta 83 theta = theta - eta * gradient 84 theta_history.append(theta) 85 86 if(abs(dJ(theta)-dJ(last_theta)) < epsilon ): 87 break 88 89 def plot_theta_history(): 90 plt.plot(plot_x,J(plot_x)) 91 plt.plot(np.array(theta_history),J(np.array(theta_history)),color = 'r',marker = '+') 92 [12] 93 eta = 0.01 94 theta_history = [] # theta_history[] = [] 错误 95 gradient_descent(0.0,eta) 96 plot_theta_history() 97 98 [13] 99 len(theta_history) # 非424 100 800 101 [14] 102 eta = 0.001 103 theta_history = [] 104 gradient_descent(0.0,eta) 105 plot_theta_history() 106 107 [15] 108 theta 109 2.4999999819074863 110 [16] 111 len(theta_history) # 3682 112 6903 113 [17] 114 eta = 0.8 115 theta_history = [] 116 gradient_descent(0.0,eta) 117 plot_theta_history() 118 119 [18] 120 len(theta_history) 121 43 122 [19] 123 theta 124 2.4999999819074863 125 eta = 1.1 theta_history = [] gradient_descent(0.0,eta) plot_theta_history() 126 127 [20] 128 def J(theta): 129 try: 130 return (theta - 2.5) ** 2 - 1 131 except: 132 return float('inf') 133 [21] 134 def gradient_descent(initial_theta, eta,n_iters = 1e3, epsilon = 1e-8): 135 theta = initial_theta 136 theta_history.append(initial_theta) 137 i_iters = 0 138 139 while i_iters < n_iters: 140 gradient = dJ(theta) 141 last_theta = theta 142 theta = theta - eta * gradient 143 theta_history.append(theta) 144 145 if(abs(dJ(theta)-dJ(last_theta)) < epsilon ): 146 break 147 i_iters +=1 148 149 def plot_theta_history(): 150 plt.plot(plot_x,J(plot_x)) 151 plt.plot(np.array(theta_history),J(np.array(theta_history)),color = 'r',marker = '+') 152 [22] 153 eta = 1.1 154 theta_history = [] 155 gradient_descent(0.0,eta) 156 plot_theta_history() 157 158 [23] 159 theta 160 2.4999999819074863 161 [24] 162 len(theta_history) 163 1001 164 [25] 165 dJ(theta_history[-1]) 166 -7.58955044586262e+79 167 [26] 168 theta_history[-1] 169 -3.79477522293131e+79 170 [27] 171 np.argsort(theta) 172 array([0], dtype=int64) 173 [28] 174 eta = 1.1 175 theta_history = [] 176 gradient_descent(0.0,eta,n_iters=10) 177 plot_theta_history() 178 179 [29] 180 theta 181 2.4999999819074863
6-3 线性回归中的梯度下降法
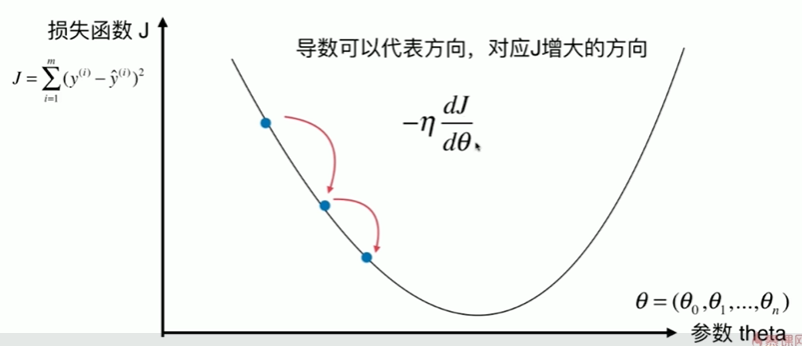
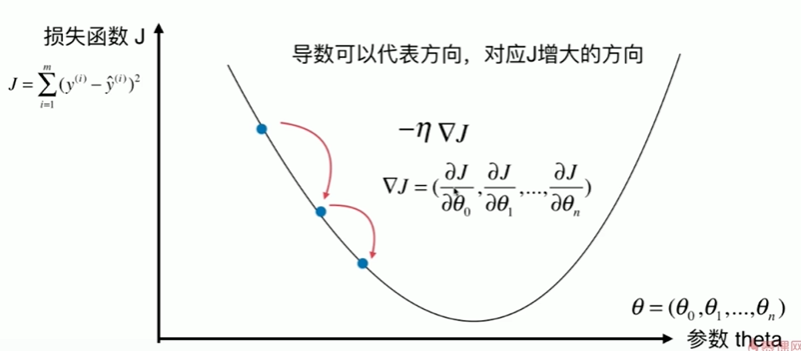
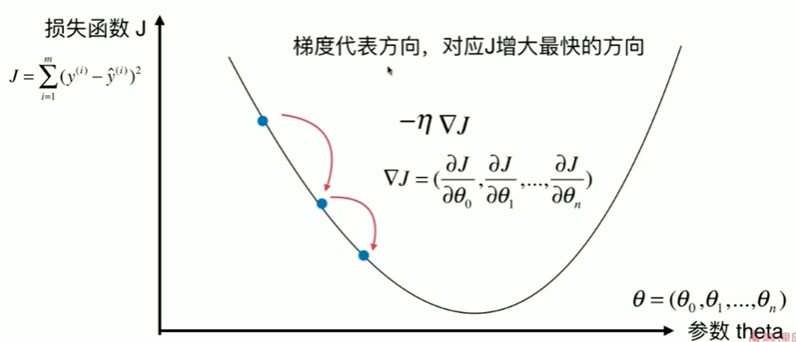


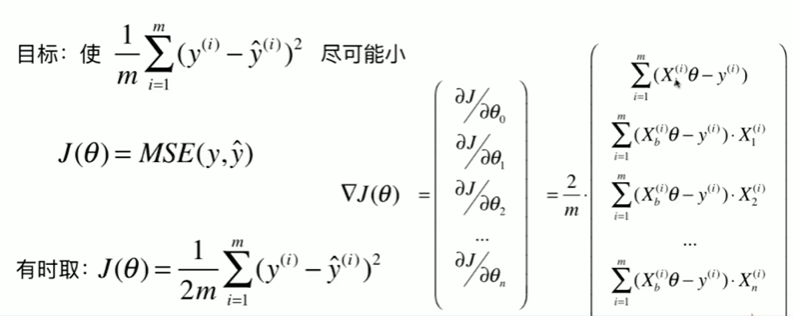
6-4 实现线性回归中的梯度下降法
Notbook 示例

Notbook 源码
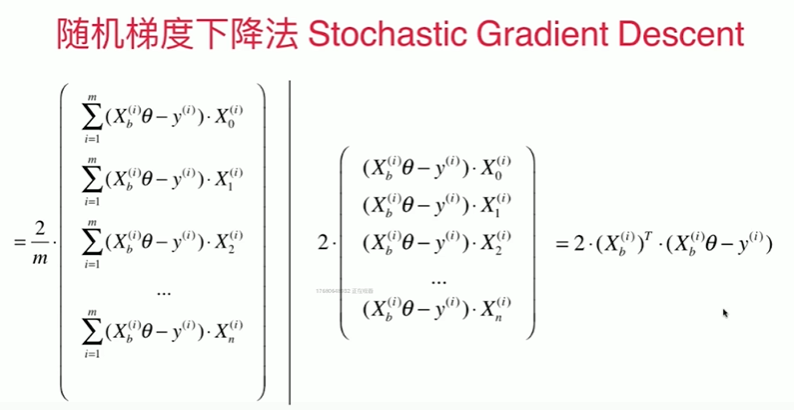
1 在线性回归模型中实现梯度下降法 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 np.random.seed(666) 7 x = 2 * np.random.random(size = 100) 8 y = x * 3.0 + 4.0 + np.random.normal(size = 100) 9 [3] 10 X = x.reshape(-1,1) 11 [4] 12 X.shape 13 (100, 1) 14 [5] 15 y.shape 16 (100,) 17 [6] 18 plt.scatter(X,y) 19 <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1e197c4cf70> 20 21 使用梯度下降法训练 22 %E6%A2%AF%E5%BA%A6%E4%B8%8B%E9%99%8D.png 23 24 [7] 25 def J(theta, X_b, y): 26 try: 27 return np.sum( ( y - X_b.dot(theta) ) ** 2 ) / len(X_b) 28 except: 29 return float('inf') 30 [8] 31 def dJ(theta, X_b, y): 32 res = np.empty(len(theta)) 33 res[0] = np.sum( X_b.dot(theta) - y ) 34 for i in range(1,len(theta)): 35 res[i] = (X_b.dot(theta) - y).dot(X_b[:,i]) 36 return res * 2 / len(theta) 37 [9] 38 def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta,n_iters = 1e5, epsilon = 1e-8): 39 theta = initial_theta 40 # theta_history.append(initial_theta) 41 i_iters = 0 42 43 while i_iters < n_iters: 44 gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y) 45 last_theta = theta 46 theta = theta - eta * gradient 47 # theta_history.append(theta) 48 49 if(abs(J(theta, X_b, y)-J(last_theta,X_b,y)) < epsilon ): 50 break 51 i_iters +=1 52 53 return theta 54 55 [10] 56 X_b = np.hstack( [ np.ones((len(X),1)) ,X ] ) 57 initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1]) 58 59 eta = 0.001 # 仅仅在 eta,n_iters = 1e5, eta = 0.0001 时得到正确数值 60 theta = gradient_descent(X_b,y,initial_theta,eta) 61 [11] 62 theta 63 array([4.02271672, 3.006001 ]) 64 [12] 65 X_b.shape[0] 66 100 67 封装我们的线性回归算法 68 [14] 69 from playML.LinearRegression import LinearRegression 70 [15] 71 lin_reg = LinearRegression() 72 lin_reg.fit_gd(X,y) 73 LinearRegression() 74 [16] 75 lin_reg.coef_ 76 array([3.0111697]) 77 [18] 78 lin_reg.interception_ # 为什么没加ion 79 4.01658859640915
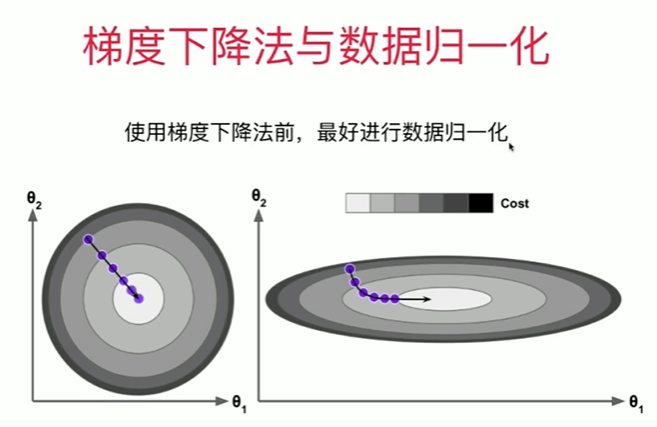
6-5 梯度下降的向量化和数据标准化
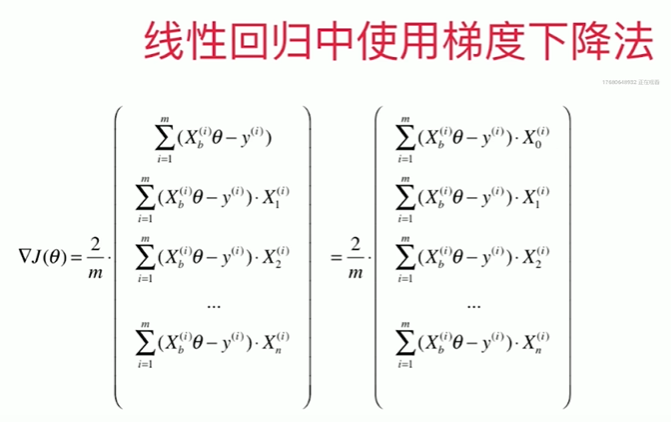
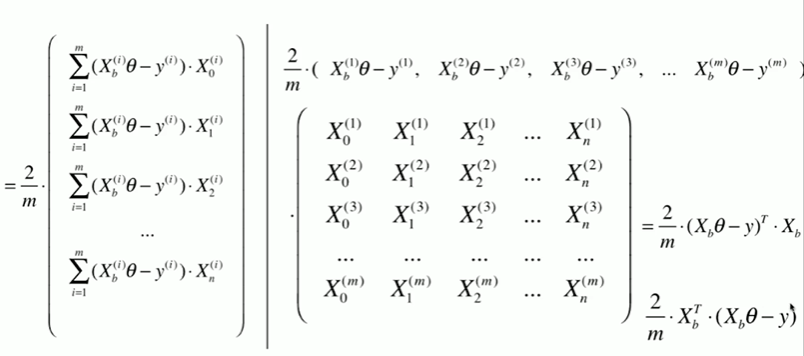
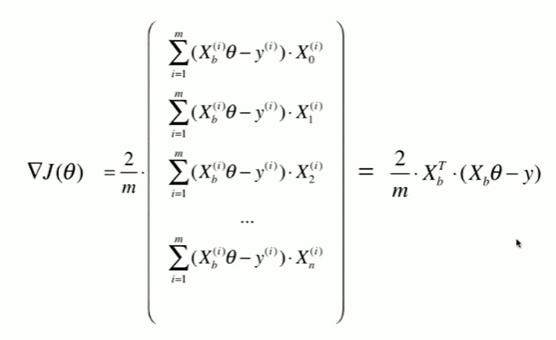
Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
1 梯度下降法的向量化 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 from sklearn import datasets 5 [2] 6 boston = datasets.load_boston() 7 X = boston.data 8 y = boston.target 9 10 11 X = X[ y < 50.0] 12 y = y[ y < 50.0] 13 F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\deprecation.py:87: FutureWarning: Function load_boston is deprecated; `load_boston` is deprecated in 1.0 and will be removed in 1.2. 14 15 The Boston housing prices dataset has an ethical problem. You can refer to 16 the documentation of this function for further details. 17 18 The scikit-learn maintainers therefore strongly discourage the use of this 19 dataset unless the purpose of the code is to study and educate about 20 ethical issues in data science and machine learning. 21 22 In this special case, you can fetch the dataset from the original 23 source:: 24 25 import pandas as pd 26 import numpy as np 27 28 29 data_url = "http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/boston" 30 raw_df = pd.read_csv(data_url, sep="\s+", skiprows=22, header=None) 31 data = np.hstack([raw_df.values[::2, :], raw_df.values[1::2, :2]]) 32 target = raw_df.values[1::2, 2] 33 34 Alternative datasets include the California housing dataset (i.e. 35 :func:`~sklearn.datasets.fetch_california_housing`) and the Ames housing 36 dataset. You can load the datasets as follows:: 37 38 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing 39 housing = fetch_california_housing() 40 41 for the California housing dataset and:: 42 43 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml 44 housing = fetch_openml(name="house_prices", as_frame=True) 45 46 for the Ames housing dataset. 47 48 warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning) 49 50 [3] 51 from playML.model_selection import train_test_split 52 53 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, seed=222) 54 [4] 55 from playML.LinearRegression import LinearRegression 56 57 lin_reg1 = LinearRegression() 58 %time lin_reg1.fit_normal(X_train,y_train) 59 lin_reg1.score(X_test,y_test) 60 CPU times: total: 0 ns 61 Wall time: 770 ms 62 63 0.8129794056212779 64 [5] 65 lin_reg2 = LinearRegression() 66 lin_reg2.fit_gd(X_train,y_train) 67 C:\Users\Administrator\PycharmProjects\pythonProject\anaconda\第4章 最基础的分类算法-k近邻算法\playML\LinearRegression.py:33: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in square 68 return np.sum((y - X_b.dot(theta)) ** 2) / len(X_b) 69 C:\Users\Administrator\PycharmProjects\pythonProject\anaconda\第4章 最基础的分类算法-k近邻算法\playML\LinearRegression.py:57: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in double_scalars 70 if (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon): 71 C:\Users\Administrator\PycharmProjects\pythonProject\anaconda\第4章 最基础的分类算法-k近邻算法\playML\LinearRegression.py:54: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in subtract 72 theta = theta - eta * gradient 73 74 LinearRegression() 75 [6] 76 lin_reg2.coef_ 77 array([nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan]) 78 [7] 79 X_train[:10,:] 80 array([[1.42362e+01, 0.00000e+00, 1.81000e+01, 0.00000e+00, 6.93000e-01, 81 6.34300e+00, 1.00000e+02, 1.57410e+00, 2.40000e+01, 6.66000e+02, 82 2.02000e+01, 3.96900e+02, 2.03200e+01], 83 [3.67822e+00, 0.00000e+00, 1.81000e+01, 0.00000e+00, 7.70000e-01, 84 5.36200e+00, 9.62000e+01, 2.10360e+00, 2.40000e+01, 6.66000e+02, 85 2.02000e+01, 3.80790e+02, 1.01900e+01], 86 [1.04690e-01, 4.00000e+01, 6.41000e+00, 1.00000e+00, 4.47000e-01, 87 7.26700e+00, 4.90000e+01, 4.78720e+00, 4.00000e+00, 2.54000e+02, 88 1.76000e+01, 3.89250e+02, 6.05000e+00], 89 [1.15172e+00, 0.00000e+00, 8.14000e+00, 0.00000e+00, 5.38000e-01, 90 5.70100e+00, 9.50000e+01, 3.78720e+00, 4.00000e+00, 3.07000e+02, 91 2.10000e+01, 3.58770e+02, 1.83500e+01], 92 [6.58800e-02, 0.00000e+00, 2.46000e+00, 0.00000e+00, 4.88000e-01, 93 7.76500e+00, 8.33000e+01, 2.74100e+00, 3.00000e+00, 1.93000e+02, 94 1.78000e+01, 3.95560e+02, 7.56000e+00], 95 [2.49800e-02, 0.00000e+00, 1.89000e+00, 0.00000e+00, 5.18000e-01, 96 6.54000e+00, 5.97000e+01, 6.26690e+00, 1.00000e+00, 4.22000e+02, 97 1.59000e+01, 3.89960e+02, 8.65000e+00], 98 [7.75223e+00, 0.00000e+00, 1.81000e+01, 0.00000e+00, 7.13000e-01, 99 6.30100e+00, 8.37000e+01, 2.78310e+00, 2.40000e+01, 6.66000e+02, 100 2.02000e+01, 2.72210e+02, 1.62300e+01], 101 [9.88430e-01, 0.00000e+00, 8.14000e+00, 0.00000e+00, 5.38000e-01, 102 5.81300e+00, 1.00000e+02, 4.09520e+00, 4.00000e+00, 3.07000e+02, 103 2.10000e+01, 3.94540e+02, 1.98800e+01], 104 [1.14320e-01, 0.00000e+00, 8.56000e+00, 0.00000e+00, 5.20000e-01, 105 6.78100e+00, 7.13000e+01, 2.85610e+00, 5.00000e+00, 3.84000e+02, 106 2.09000e+01, 3.95580e+02, 7.67000e+00], 107 [5.69175e+00, 0.00000e+00, 1.81000e+01, 0.00000e+00, 5.83000e-01, 108 6.11400e+00, 7.98000e+01, 3.54590e+00, 2.40000e+01, 6.66000e+02, 109 2.02000e+01, 3.92680e+02, 1.49800e+01]]) 110 [8] 111 lin_reg2.fit_gd(X_train,y_train,eta = 0.000001) 112 LinearRegression() 113 [9] 114 lin_reg2.score(X_test,y_test) 115 0.5183037995455362 116 [10] 117 %time lin_reg2.fit_gd(X_train,y_train,eta = 0.0000031001,n_iters=1e12) 118 CPU times: total: 14.9 s 119 Wall time: 8.04 s 120 121 LinearRegression() 122 [11] 123 lin_reg2.score(X_test,y_test) 124 0.6180704373142486 125 使用梯度下降法前进行数据归一化 126 [12] 127 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 128 [13] 129 standardScaler = StandardScaler() 130 standardScaler.fit(X_train) 131 StandardScaler() 132 [14] 133 X_train_standard = standardScaler.transform(X_train) 134 [15] 135 lin_reg3 = LinearRegression() 136 %time lin_reg3.fit_gd(X_train_standard,y_train) 137 CPU times: total: 5.5 s 138 Wall time: 2.82 s 139 140 LinearRegression() 141 [16] 142 X_test_standard = standardScaler.transform(X_test) 143 [17] 144 lin_reg3.score(X_test_standard,y_test) 145 0.8130040900692703 146 梯度下降法的优势 147 [18] 148 m = 2000 149 n = 5000 150 151 big_X = np.random.normal(size=(m,n)) 152 true_theta = np.random.uniform(0.0,100.0,size=n+1) 153 big_y = big_X.dot(true_theta[1:]) + true_theta[0] + np.random.normal(0.0,10.0,size = m) 154 [19] 155 big_reg1 = LinearRegression() 156 %time big_reg1.fit_normal(big_X,big_y) 157 CPU times: total: 1min 19s 158 Wall time: 46.6 s 159 160 LinearRegression() 161 [29] 162 big_reg2 = LinearRegression() 163 %time big_reg2.fit_gd(big_X,big_y,eta=0.1,n_iters=1e3) 164 # CPU times: total: 8min 8s 原因是eta=0.001,n_iters = 1e4 165 # Wall time: 5min 41s 所以与具体模型关系甚大 166 CPU times: total: 5.75 s 167 Wall time: 3.29 s 168 169 LinearRegression() 170 [30] 171 big_reg2.coef_ 172 array([14.82820315, 43.97009426, 6.49921157, ..., 7.31030043, 173 51.42885153, 20.76248914]) 174 [31] 175 big_reg2.interception_ 176 102.55282983264055
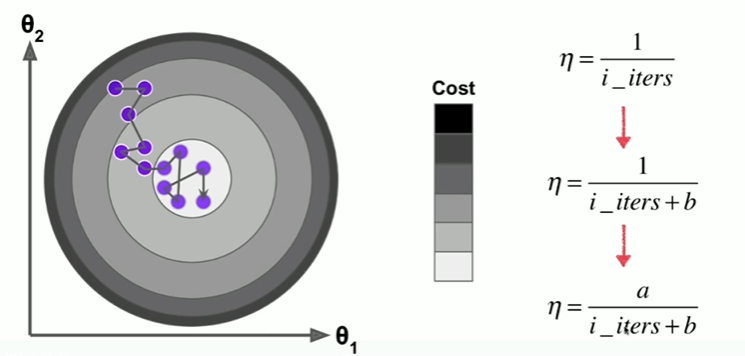
6-6 随机梯度下降法

Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
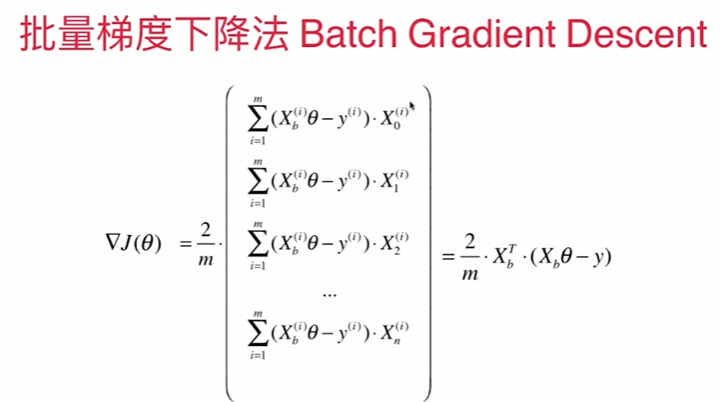
1 随机梯度下降法 2 3 [1] 4 import numpy as np 5 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 6 [2] 7 m = 100000 8 9 x = np.random.normal(size = m) 10 X = x.reshape(-1,1) 11 12 y = 4.0*x + 3. + np.random.normal(0,3,size=m) 13 [3] 14 y.shape 15 (100000,) 16 [4] 17 def J(theta, X_b, y): 18 try: 19 return np.sum( ( y - X_b.dot(theta) ) ** 2 ) / len(y) 20 except: 21 return float('inf') 22 23 def dJ(theta, X_b, y): 24 return X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y) * 2 / len(y) 25 26 def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters = 1e5, epsilon = 1e-8): 27 theta = initial_theta 28 i_iters = 0 29 30 while i_iters < n_iters: 31 gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y) 32 last_theta = theta 33 theta = theta - eta * gradient 34 35 if(abs(J(theta, X_b, y)-J(last_theta,X_b,y)) < epsilon ): 36 break 37 i_iters +=1 38 39 return theta 40 [5] 41 %%time 42 X_b = np.hstack( [ np.ones((len(X),1)) ,X ] ) 43 initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1]) 44 eta = 0.01 # 仅仅在 eta,n_iters = 1e5, eta = 0.0001 时得到正确数值 45 theta = gradient_descent(X_b,y,initial_theta,eta) 46 CPU times: total: 1.81 s 47 Wall time: 946 ms 48 49 [6] 50 theta 51 array([2.97998979, 3.99960807]) 52 随机梯度下降法 53 [7] 54 def dJ_sgd(theta, X_b_i, y_i): 55 return X_b_i.T.dot(X_b_i.dot(theta) - y_i) * 2 56 [8] 57 def sgd(X_b, y, initial_theta, n_iters): 58 59 t0 = 5 60 t1 = 50 61 62 def learning_rate(t): 63 return t0 / (t + t1) 64 65 theta = initial_theta 66 for cur_iter in range(n_iters): 67 rand_i = np.random.randint(len(X_b)) 68 gradient = dJ_sgd(theta, X_b[rand_i],y[rand_i]) 69 theta = theta - learning_rate(cur_iter) * gradient 70 return theta 71 [9] 72 %%time 73 X_b = np.hstack( [ np.ones((len(X),1)) ,X ] ) 74 initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1]) 75 theta = sgd(X_b, y, initial_theta, n_iters=len(X_b//3)) 76 CPU times: total: 1.84 s 77 Wall time: 1.79 s 78 79 [10] 80 theta 81 array([2.99897113, 4.02392746])
6-7 scikit-learn中的随机梯度下降法
Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
1 使用我们自己的SGD 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 m = 100000 7 8 x = np.random.normal(size = m) 9 X = x.reshape(-1,1) 10 11 y = 4.0*x + 3. + np.random.normal(0,3,size=m) 12 [3] 13 from playML.LinearRegression import LinearRegression 14 15 lin_reg = LinearRegression() 16 lin_reg.fit_sgd(X, y, n_iters=2) 17 LinearRegression() 18 [4] 19 lin_reg._theta 20 array([3.01202028, 3.97799884]) 21 [5] 22 lin_reg.coef_ 23 array([3.97799884]) 24 [6] 25 lin_reg.interception_ 26 3.012020275313304 27 真实使用我们自己的SGD 28 [7] 29 from sklearn import datasets 30 31 boston = datasets.load_boston() 32 X = boston.data 33 y = boston.target 34 35 36 X = X[ y < 50.0] 37 y = y[ y < 50.0] 38 F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\deprecation.py:87: FutureWarning: Function load_boston is deprecated; `load_boston` is deprecated in 1.0 and will be removed in 1.2. 39 40 The Boston housing prices dataset has an ethical problem. You can refer to 41 the documentation of this function for further details. 42 43 The scikit-learn maintainers therefore strongly discourage the use of this 44 dataset unless the purpose of the code is to study and educate about 45 ethical issues in data science and machine learning. 46 47 In this special case, you can fetch the dataset from the original 48 source:: 49 50 import pandas as pd 51 import numpy as np 52 53 54 data_url = "http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/boston" 55 raw_df = pd.read_csv(data_url, sep="\s+", skiprows=22, header=None) 56 data = np.hstack([raw_df.values[::2, :], raw_df.values[1::2, :2]]) 57 target = raw_df.values[1::2, 2] 58 59 Alternative datasets include the California housing dataset (i.e. 60 :func:`~sklearn.datasets.fetch_california_housing`) and the Ames housing 61 dataset. You can load the datasets as follows:: 62 63 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing 64 housing = fetch_california_housing() 65 66 for the California housing dataset and:: 67 68 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml 69 housing = fetch_openml(name="house_prices", as_frame=True) 70 71 for the Ames housing dataset. 72 73 warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning) 74 75 [8] 76 from playML.model_selection import train_test_split 77 78 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, seed=666) # 666 效果比 222 好很多 79 [9] 80 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 81 82 standardScaler = StandardScaler() 83 standardScaler.fit(X_train) 84 X_train_standard = standardScaler.transform(X_train) 85 X_test_standard = standardScaler.transform(X_test) 86 [10] 87 from playML.LinearRegression import LinearRegression 88 89 lin_reg2 = LinearRegression() 90 %time lin_reg2.fit_sgd(X_train_standard, y_train, n_iters=2) 91 lin_reg2.score(X_test_standard,y_test) 92 CPU times: total: 15.6 ms 93 Wall time: 8.98 ms 94 95 0.7911189802097699 96 [11] 97 %time lin_reg2.fit_sgd(X_train_standard, y_train, n_iters=50) 98 lin_reg2.score(X_test_standard,y_test) 99 CPU times: total: 219 ms 100 Wall time: 226 ms 101 102 0.8132588958621522 103 [13] 104 %time lin_reg2.fit_sgd(X_train_standard, y_train, n_iters=500) 105 lin_reg2.score(X_test_standard,y_test) 106 CPU times: total: 2.09 s 107 Wall time: 2.93 s 108 109 0.8129564757875579 110 scikit-learn 中的SGD 111 [14] 112 from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressor 113 [15] 114 sgd_reg = SGDRegressor() 115 %time sgd_reg.fit(X_train_standard,y_train) 116 sgd_reg.score(X_test_standard,y_test) 117 CPU times: total: 0 ns 118 Wall time: 116 ms 119 120 0.8129895569490898 121 [18] 122 sgd_reg = SGDRegressor(n_iter_no_change=100)# n_iter 报错 123 %time sgd_reg.fit(X_train_standard,y_train) 124 sgd_reg.score(X_test_standard,y_test) 125 CPU times: total: 15.6 ms 126 Wall time: 22.9 ms 127 128 0.8131520202077357
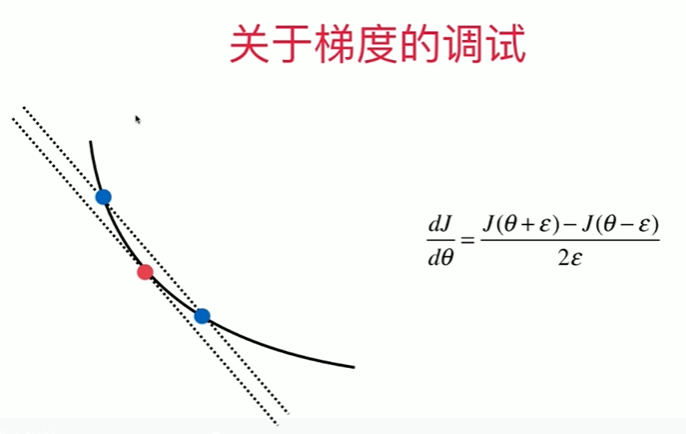
6-8 如何确定梯度计算的准确性 调试梯度下降法
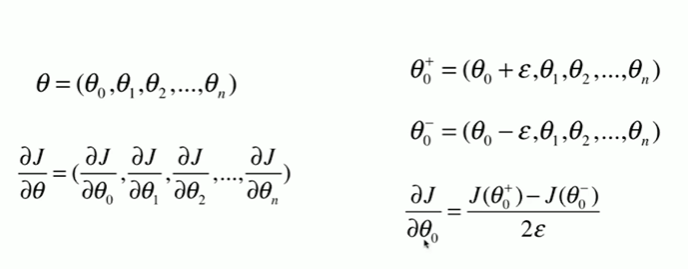
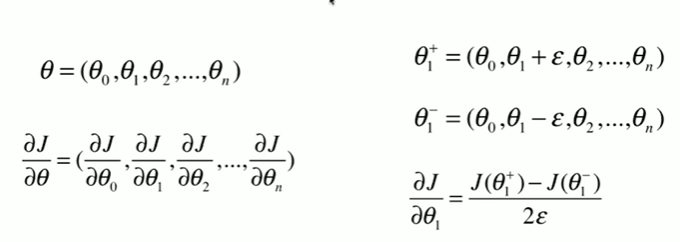
Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
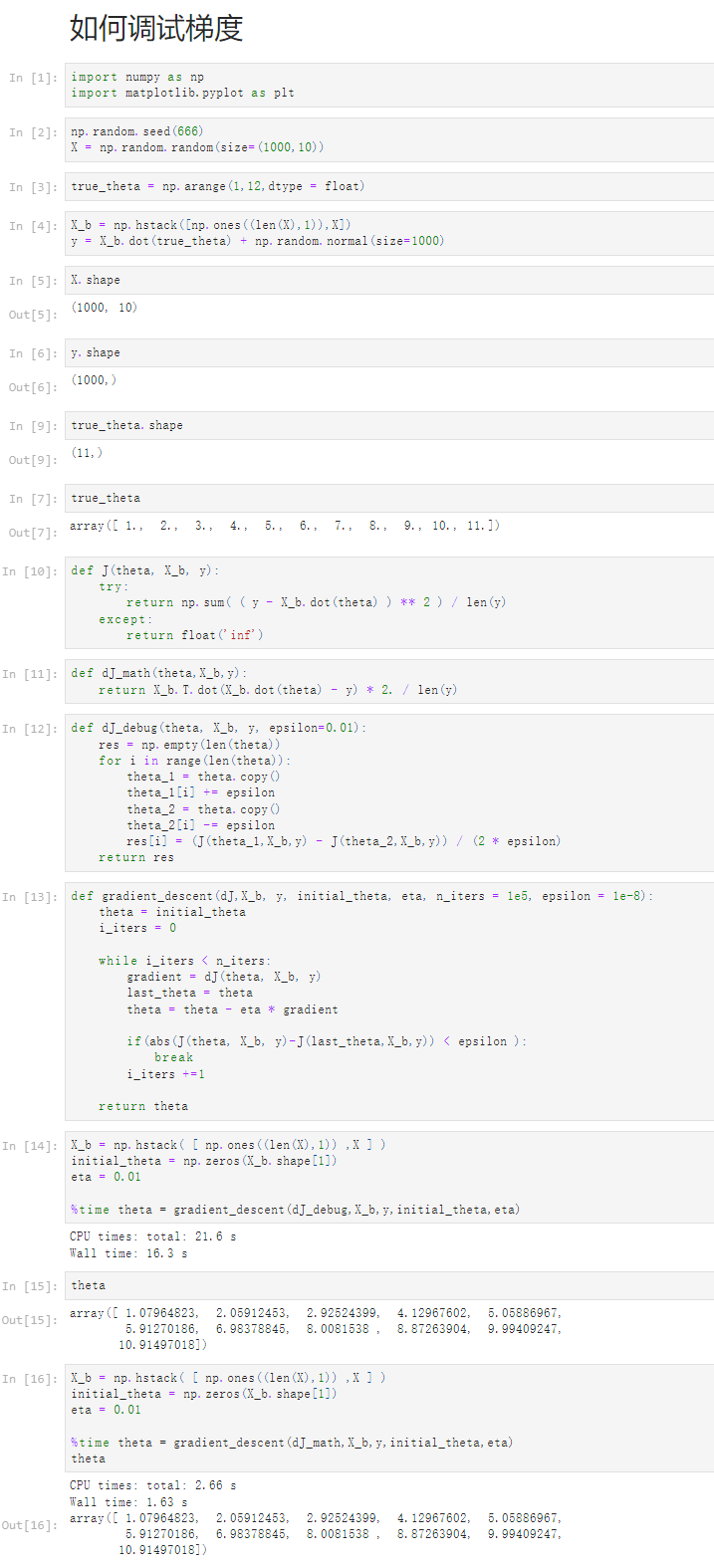
1 如何调试梯度 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 [2] 6 np.random.seed(666) 7 X = np.random.random(size=(1000,10)) 8 [3] 9 true_theta = np.arange(1,12,dtype = float) 10 [4] 11 X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X),1)),X]) 12 y = X_b.dot(true_theta) + np.random.normal(size=1000) 13 [5] 14 X.shape 15 (1000, 10) 16 [6] 17 y.shape 18 (1000,) 19 [9] 20 true_theta.shape 21 (11,) 22 [7] 23 true_theta 24 array([ 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11.]) 25 [10] 26 def J(theta, X_b, y): 27 try: 28 return np.sum( ( y - X_b.dot(theta) ) ** 2 ) / len(y) 29 except: 30 return float('inf') 31 [11] 32 def dJ_math(theta,X_b,y): 33 return X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y) * 2. / len(y) 34 [12] 35 def dJ_debug(theta, X_b, y, epsilon=0.01): 36 res = np.empty(len(theta)) 37 for i in range(len(theta)): 38 theta_1 = theta.copy() 39 theta_1[i] += epsilon 40 theta_2 = theta.copy() 41 theta_2[i] -= epsilon 42 res[i] = (J(theta_1,X_b,y) - J(theta_2,X_b,y)) / (2 * epsilon) 43 return res 44 [13] 45 def gradient_descent(dJ,X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters = 1e5, epsilon = 1e-8): 46 theta = initial_theta 47 i_iters = 0 48 49 while i_iters < n_iters: 50 gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y) 51 last_theta = theta 52 theta = theta - eta * gradient 53 54 if(abs(J(theta, X_b, y)-J(last_theta,X_b,y)) < epsilon ): 55 break 56 i_iters +=1 57 58 return theta 59 [14] 60 X_b = np.hstack( [ np.ones((len(X),1)) ,X ] ) 61 initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1]) 62 eta = 0.01 63 64 %time theta = gradient_descent(dJ_debug,X_b,y,initial_theta,eta) 65 CPU times: total: 21.6 s 66 Wall time: 16.3 s 67 68 [15] 69 theta 70 array([ 1.07964823, 2.05912453, 2.92524399, 4.12967602, 5.05886967, 71 5.91270186, 6.98378845, 8.0081538 , 8.87263904, 9.99409247, 72 10.91497018]) 73 [16] 74 X_b = np.hstack( [ np.ones((len(X),1)) ,X ] ) 75 initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1]) 76 eta = 0.01 77 78 %time theta = gradient_descent(dJ_math,X_b,y,initial_theta,eta) 79 theta 80 CPU times: total: 2.66 s 81 Wall time: 1.63 s 82 83 array([ 1.07964823, 2.05912453, 2.92524399, 4.12967602, 5.05886967, 84 5.91270186, 6.98378845, 8.0081538 , 8.87263904, 9.99409247, 85 10.91497018])
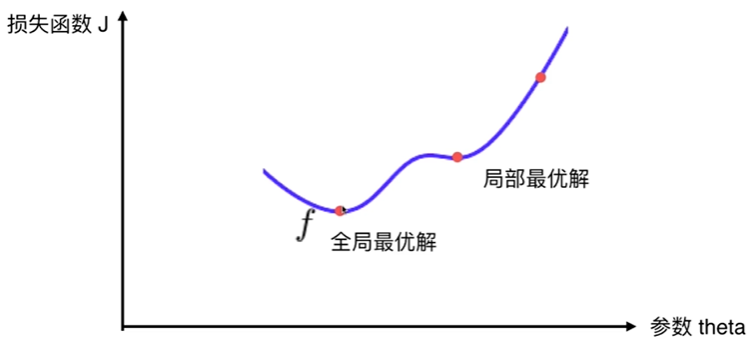
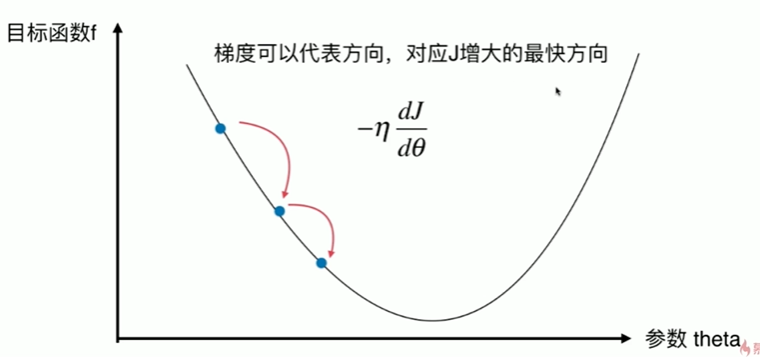
6-9 有关梯度下降法的更多深入讨论










 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号