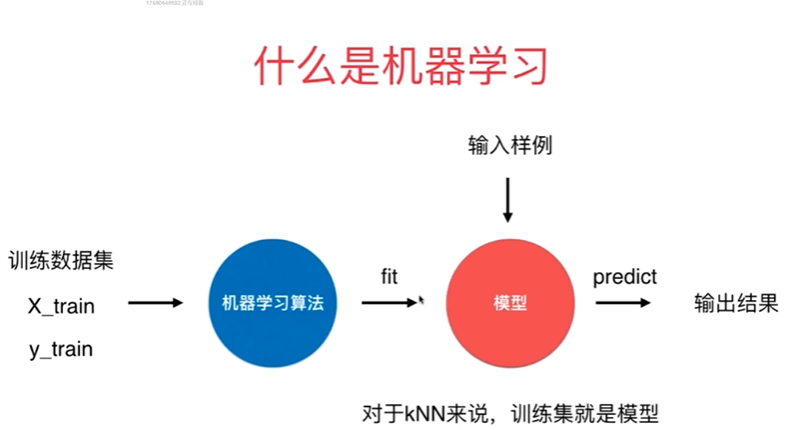
第4章上 最基础的分类算法-k近邻算法 kNN
4-1 k近邻算法基础

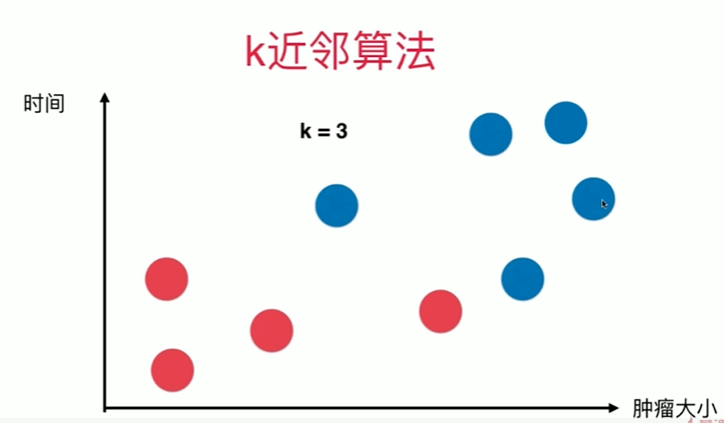
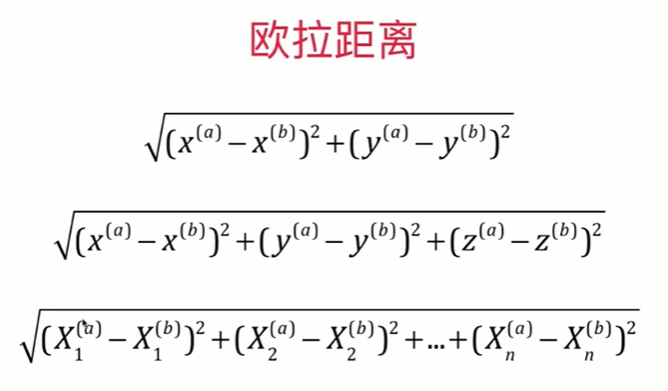
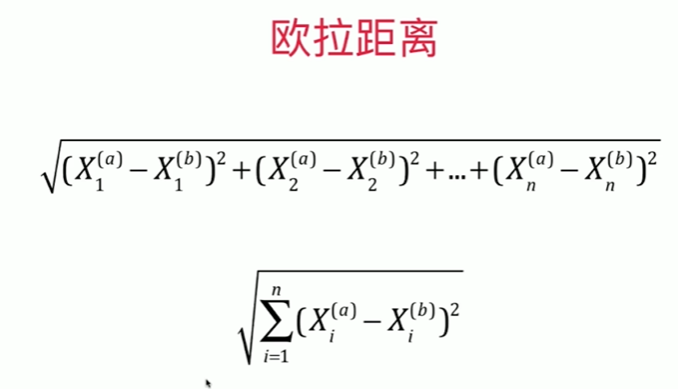
Notbook 示例
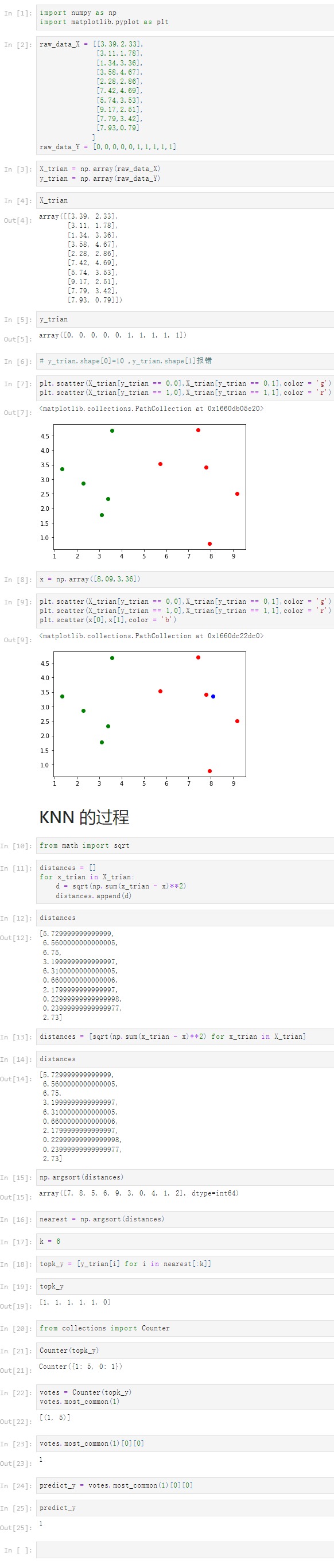
Notbook 源代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[2]
raw_data_X = [[3.39,2.33],
[3.11,1.78],
[1.34,3.36],
[3.58,4.67],
[2.28,2.86],
[7.42,4.69],
[5.74,3.53],
[9.17,2.51],
[7.79,3.42],
[7.93,0.79]
]
raw_data_Y = [0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1]
[3]
X_trian = np.array(raw_data_X)
y_trian = np.array(raw_data_Y)
[4]
X_trian
array([[3.39, 2.33],
[3.11, 1.78],
[1.34, 3.36],
[3.58, 4.67],
[2.28, 2.86],
[7.42, 4.69],
[5.74, 3.53],
[9.17, 2.51],
[7.79, 3.42],
[7.93, 0.79]])
[5]
y_trian
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
[6]
# y_trian.shape[0]=10 ,y_trian.shape[1]报错
[7]
plt.scatter(X_trian[y_trian == 0,0],X_trian[y_trian == 0,1],color = 'g')
plt.scatter(X_trian[y_trian == 1,0],X_trian[y_trian == 1,1],color = 'r')
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1660db05e20>
[8]
x = np.array([8.09,3.36])
[9]
plt.scatter(X_trian[y_trian == 0,0],X_trian[y_trian == 0,1],color = 'g')
plt.scatter(X_trian[y_trian == 1,0],X_trian[y_trian == 1,1],color = 'r')
plt.scatter(x[0],x[1],color = 'b')
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x1660dc22dc0>
KNN 的过程
[10]
from math import sqrt
[11]
distances = []
for x_trian in X_trian:
d = sqrt(np.sum(x_trian - x)**2)
distances.append(d)
[12]
distances
[5.729999999999999,
6.5600000000000005,
6.75,
3.1999999999999997,
6.3100000000000005,
0.6600000000000006,
2.1799999999999997,
0.22999999999999998,
0.23999999999999977,
2.73]
[13]
distances = [sqrt(np.sum(x_trian - x)**2) for x_trian in X_trian]
[14]
distances
[5.729999999999999,
6.5600000000000005,
6.75,
3.1999999999999997,
6.3100000000000005,
0.6600000000000006,
2.1799999999999997,
0.22999999999999998,
0.23999999999999977,
2.73]
[15]
np.argsort(distances)
array([7, 8, 5, 6, 9, 3, 0, 4, 1, 2], dtype=int64)
[16]
nearest = np.argsort(distances)
[17]
k = 6
[18]
topk_y = [y_trian[i] for i in nearest[:k]]
[19]
topk_y
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]
[20]
from collections import Counter
[21]
Counter(topk_y)
Counter({1: 5, 0: 1})
[22]
votes = Counter(topk_y)
votes.most_common(1)
[(1, 5)]
[23]
votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
1
[24]
predict_y = votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
[25]
predict_y
1
4-2 scikit-learn中的机器学习算法封装
Notbook 示例
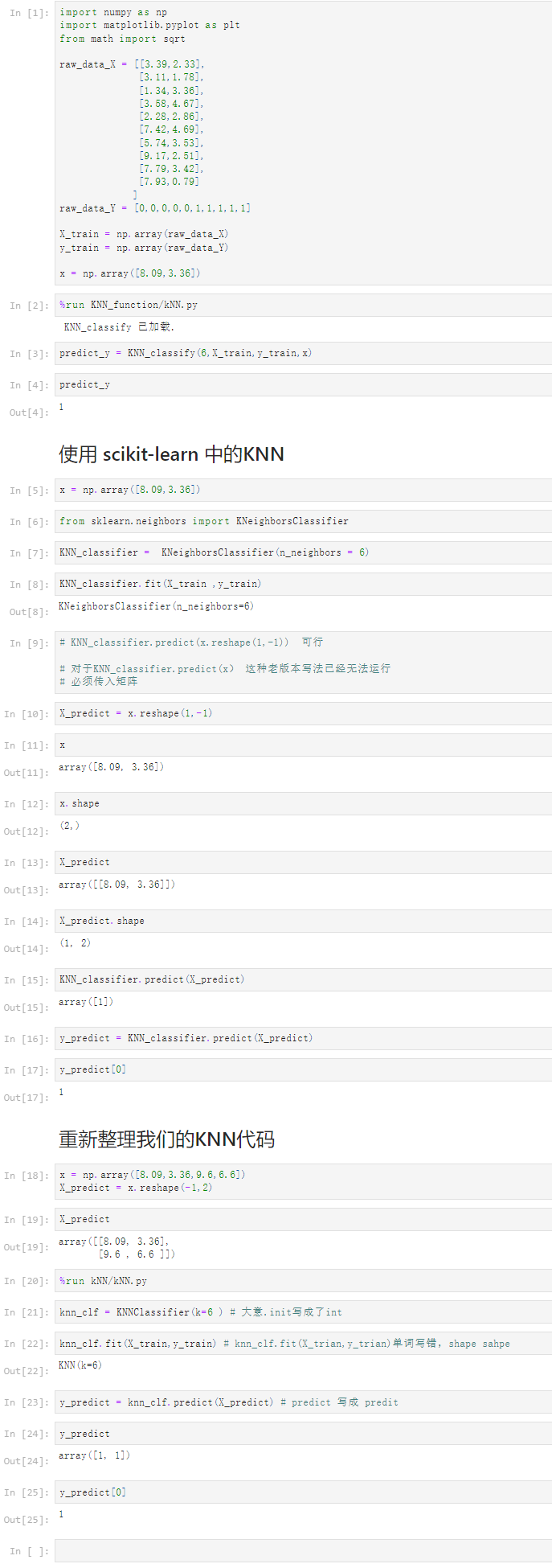
notbook 源码
1 [1] 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from math import sqrt 5 6 raw_data_X = [[3.39,2.33], 7 [3.11,1.78], 8 [1.34,3.36], 9 [3.58,4.67], 10 [2.28,2.86], 11 [7.42,4.69], 12 [5.74,3.53], 13 [9.17,2.51], 14 [7.79,3.42], 15 [7.93,0.79] 16 ] 17 raw_data_Y = [0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1] 18 19 X_train = np.array(raw_data_X) 20 y_train = np.array(raw_data_Y) 21 22 x = np.array([8.09,3.36]) 23 [2] 24 %run KNN_function/kNN.py 25 KNN_classify 已加载. 26 27 [3] 28 predict_y = KNN_classify(6,X_train,y_train,x) 29 [4] 30 predict_y 31 1 32 使用 scikit-learn 中的KNN 33 [5] 34 x = np.array([8.09,3.36]) 35 [6] 36 from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier 37 [7] 38 KNN_classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 6) 39 [8] 40 KNN_classifier.fit(X_train ,y_train) 41 KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=6) 42 [9] 43 # KNN_classifier.predict(x.reshape(1,-1)) 可行 44 45 # 对于KNN_classifier.predict(x) 这种老版本写法已经无法运行 46 # 必须传入矩阵 47 [10] 48 X_predict = x.reshape(1,-1) 49 [11] 50 x 51 array([8.09, 3.36]) 52 [12] 53 x.shape 54 (2,) 55 [13] 56 X_predict 57 array([[8.09, 3.36]]) 58 [14] 59 X_predict.shape 60 (1, 2) 61 [15] 62 KNN_classifier.predict(X_predict) 63 array([1]) 64 [16] 65 y_predict = KNN_classifier.predict(X_predict) 66 [17] 67 y_predict[0] 68 1 69 重新整理我们的KNN代码 70 [18] 71 x = np.array([8.09,3.36,9.6,6.6]) 72 X_predict = x.reshape(-1,2) 73 [19] 74 X_predict 75 array([[8.09, 3.36], 76 [9.6 , 6.6 ]]) 77 [20] 78 %run kNN/kNN.py 79 [21] 80 knn_clf = KNNClassifier(k=6 ) # 大意.init写成了int 81 [22] 82 knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) # knn_clf.fit(X_trian,y_trian)单词写错,shape sahpe 83 KNN(k=6) 84 [23] 85 y_predict = knn_clf.predict(X_predict) # predict 写成 predit 86 [24] 87 y_predict 88 array([1, 1]) 89 [25] 90 y_predict[0] 91 1
4-3 训练数据集,测试数据集
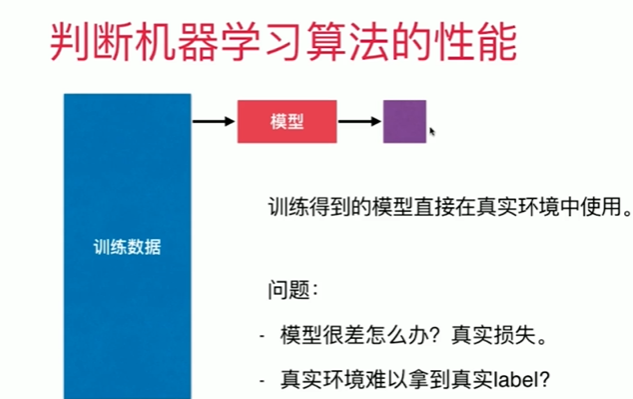
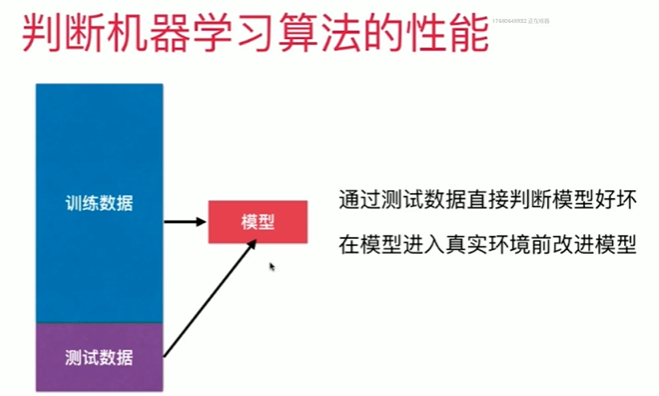

Notbook 示例
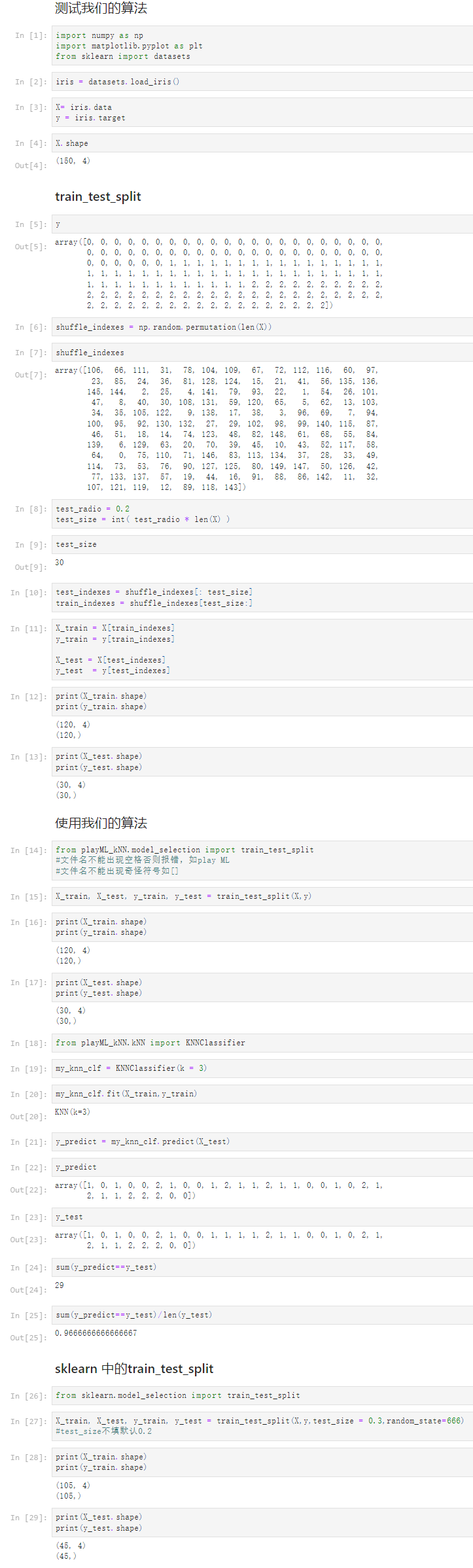
Notbook 源码
1 测试我们的算法 2 [1] 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 from sklearn import datasets 6 [2] 7 iris = datasets.load_iris() 8 [3] 9 X= iris.data 10 y = iris.target 11 [4] 12 X.shape 13 (150, 4) 14 train_test_split 15 [5] 16 y 17 array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 18 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 19 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 20 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 21 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 22 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 23 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]) 24 [6] 25 shuffle_indexes = np.random.permutation(len(X)) 26 [7] 27 shuffle_indexes 28 array([106, 66, 111, 31, 78, 104, 109, 67, 72, 112, 116, 60, 97, 29 23, 85, 24, 36, 81, 128, 124, 15, 21, 41, 56, 135, 136, 30 145, 144, 2, 25, 4, 141, 79, 93, 22, 1, 54, 26, 101, 31 47, 8, 40, 30, 108, 131, 59, 120, 65, 5, 62, 13, 103, 32 34, 35, 105, 122, 9, 138, 17, 38, 3, 96, 69, 7, 94, 33 100, 95, 92, 130, 132, 27, 29, 102, 98, 99, 140, 115, 87, 34 46, 51, 18, 14, 74, 123, 48, 82, 148, 61, 68, 55, 84, 35 139, 6, 129, 63, 20, 70, 39, 45, 10, 43, 52, 117, 58, 36 64, 0, 75, 110, 71, 146, 83, 113, 134, 37, 28, 33, 49, 37 114, 73, 53, 76, 90, 127, 125, 80, 149, 147, 50, 126, 42, 38 77, 133, 137, 57, 19, 44, 16, 91, 88, 86, 142, 11, 32, 39 107, 121, 119, 12, 89, 118, 143]) 40 [8] 41 test_radio = 0.2 42 test_size = int( test_radio * len(X) ) 43 [9] 44 test_size 45 30 46 [10] 47 test_indexes = shuffle_indexes[: test_size] 48 train_indexes = shuffle_indexes[test_size:] 49 [11] 50 X_train = X[train_indexes] 51 y_train = y[train_indexes] 52 53 X_test = X[test_indexes] 54 y_test = y[test_indexes] 55 [12] 56 print(X_train.shape) 57 print(y_train.shape) 58 (120, 4) 59 (120,) 60 61 [13] 62 print(X_test.shape) 63 print(y_test.shape) 64 (30, 4) 65 (30,) 66 67 使用我们的算法 68 [14] 69 from playML_kNN.model_selection import train_test_split 70 #文件名不能出现空格否则报错,如play ML 71 #文件名不能出现奇怪符号如[] 72 [15] 73 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y) 74 [16] 75 print(X_train.shape) 76 print(y_train.shape) 77 (120, 4) 78 (120,) 79 80 [17] 81 print(X_test.shape) 82 print(y_test.shape) 83 (30, 4) 84 (30,) 85 86 [18] 87 from playML_kNN.kNN import KNNClassifier 88 [19] 89 my_knn_clf = KNNClassifier(k = 3) 90 [20] 91 my_knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) 92 KNN(k=3) 93 [21] 94 y_predict = my_knn_clf.predict(X_test) 95 [22] 96 y_predict 97 array([1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 98 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0]) 99 [23] 100 y_test 101 array([1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 102 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0]) 103 [24] 104 sum(y_predict==y_test) 105 29 106 [25] 107 sum(y_predict==y_test)/len(y_test) 108 0.9666666666666667 109 sklearn 中的train_test_split 110 [26] 111 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 112 [27] 113 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.3,random_state=666) 114 #test_size不填默认0.2 115 [28] 116 print(X_train.shape) 117 print(y_train.shape) 118 (105, 4) 119 (105,) 120 121 [29] 122 print(X_test.shape) 123 print(y_test.shape) 124 (45, 4) 125 (45,)
4-4 分类准确度
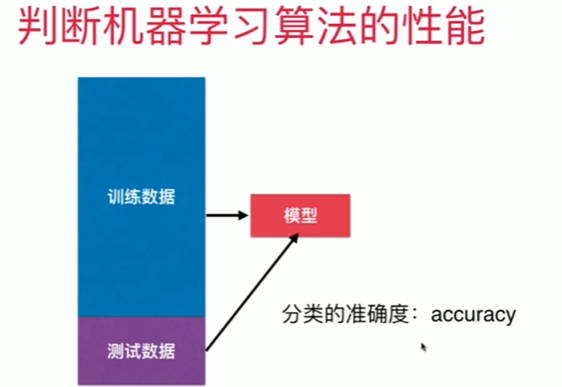
Notbook 示例
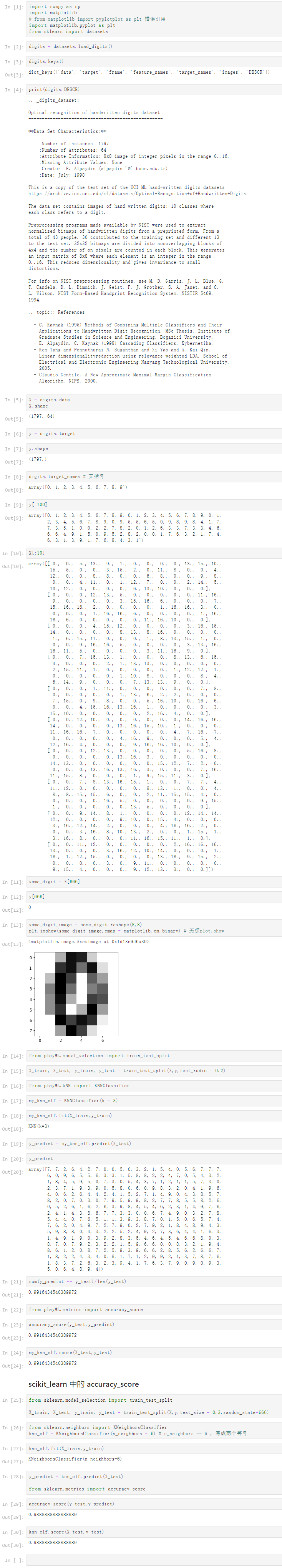
Notbook 源码
1 [1] 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib 4 # from matplotlib import pyplotplot as plt 错误引用 5 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 6 from sklearn import datasets 7 [2] 8 digits = datasets.load_digits() 9 [3] 10 digits.keys() 11 dict_keys(['data', 'target', 'frame', 'feature_names', 'target_names', 'images', 'DESCR']) 12 [4] 13 print(digits.DESCR) 14 .. _digits_dataset: 15 16 Optical recognition of handwritten digits dataset 17 -------------------------------------------------- 18 19 **Data Set Characteristics:** 20 21 :Number of Instances: 1797 22 :Number of Attributes: 64 23 :Attribute Information: 8x8 image of integer pixels in the range 0..16. 24 :Missing Attribute Values: None 25 :Creator: E. Alpaydin (alpaydin '@' boun.edu.tr) 26 :Date: July; 1998 27 28 This is a copy of the test set of the UCI ML hand-written digits datasets 29 https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Optical+Recognition+of+Handwritten+Digits 30 31 The data set contains images of hand-written digits: 10 classes where 32 each class refers to a digit. 33 34 Preprocessing programs made available by NIST were used to extract 35 normalized bitmaps of handwritten digits from a preprinted form. From a 36 total of 43 people, 30 contributed to the training set and different 13 37 to the test set. 32x32 bitmaps are divided into nonoverlapping blocks of 38 4x4 and the number of on pixels are counted in each block. This generates 39 an input matrix of 8x8 where each element is an integer in the range 40 0..16. This reduces dimensionality and gives invariance to small 41 distortions. 42 43 For info on NIST preprocessing routines, see M. D. Garris, J. L. Blue, G. 44 T. Candela, D. L. Dimmick, J. Geist, P. J. Grother, S. A. Janet, and C. 45 L. Wilson, NIST Form-Based Handprint Recognition System, NISTIR 5469, 46 1994. 47 48 .. topic:: References 49 50 - C. Kaynak (1995) Methods of Combining Multiple Classifiers and Their 51 Applications to Handwritten Digit Recognition, MSc Thesis, Institute of 52 Graduate Studies in Science and Engineering, Bogazici University. 53 - E. Alpaydin, C. Kaynak (1998) Cascading Classifiers, Kybernetika. 54 - Ken Tang and Ponnuthurai N. Suganthan and Xi Yao and A. Kai Qin. 55 Linear dimensionalityreduction using relevance weighted LDA. School of 56 Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang Technological University. 57 2005. 58 - Claudio Gentile. A New Approximate Maximal Margin Classification 59 Algorithm. NIPS. 2000. 60 61 62 [5] 63 X = digits.data 64 X.shape 65 (1797, 64) 66 [6] 67 y = digits.target 68 [7] 69 y.shape 70 (1797,) 71 [8] 72 digits.target_names # 无括号 73 array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) 74 [9] 75 y[:100] 76 array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 77 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, 9, 5, 5, 6, 5, 0, 9, 8, 9, 8, 4, 1, 7, 78 7, 3, 5, 1, 0, 0, 2, 2, 7, 8, 2, 0, 1, 2, 6, 3, 3, 7, 3, 3, 4, 6, 79 6, 6, 4, 9, 1, 5, 0, 9, 5, 2, 8, 2, 0, 0, 1, 7, 6, 3, 2, 1, 7, 4, 80 6, 3, 1, 3, 9, 1, 7, 6, 8, 4, 3, 1]) 81 [10] 82 X[:10] 83 array([[ 0., 0., 5., 13., 9., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 13., 15., 10., 84 15., 5., 0., 0., 3., 15., 2., 0., 11., 8., 0., 0., 4., 85 12., 0., 0., 8., 8., 0., 0., 5., 8., 0., 0., 9., 8., 86 0., 0., 4., 11., 0., 1., 12., 7., 0., 0., 2., 14., 5., 87 10., 12., 0., 0., 0., 0., 6., 13., 10., 0., 0., 0.], 88 [ 0., 0., 0., 12., 13., 5., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 11., 16., 89 9., 0., 0., 0., 0., 3., 15., 16., 6., 0., 0., 0., 7., 90 15., 16., 16., 2., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 16., 16., 3., 0., 91 0., 0., 0., 1., 16., 16., 6., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 16., 92 16., 6., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 11., 16., 10., 0., 0.], 93 [ 0., 0., 0., 4., 15., 12., 0., 0., 0., 0., 3., 16., 15., 94 14., 0., 0., 0., 0., 8., 13., 8., 16., 0., 0., 0., 0., 95 1., 6., 15., 11., 0., 0., 0., 1., 8., 13., 15., 1., 0., 96 0., 0., 9., 16., 16., 5., 0., 0., 0., 0., 3., 13., 16., 97 16., 11., 5., 0., 0., 0., 0., 3., 11., 16., 9., 0.], 98 [ 0., 0., 7., 15., 13., 1., 0., 0., 0., 8., 13., 6., 15., 99 4., 0., 0., 0., 2., 1., 13., 13., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 100 2., 15., 11., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 12., 12., 1., 101 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 10., 8., 0., 0., 0., 8., 4., 102 5., 14., 9., 0., 0., 0., 7., 13., 13., 9., 0., 0.], 103 [ 0., 0., 0., 1., 11., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 7., 8., 104 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 13., 6., 2., 2., 0., 0., 0., 105 7., 15., 0., 9., 8., 0., 0., 5., 16., 10., 0., 16., 6., 106 0., 0., 4., 15., 16., 13., 16., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 3., 107 15., 10., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 2., 16., 4., 0., 0.], 108 [ 0., 0., 12., 10., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 14., 16., 16., 109 14., 0., 0., 0., 0., 13., 16., 15., 10., 1., 0., 0., 0., 110 11., 16., 16., 7., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 4., 7., 16., 7., 111 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 4., 16., 9., 0., 0., 0., 5., 4., 112 12., 16., 4., 0., 0., 0., 9., 16., 16., 10., 0., 0.], 113 [ 0., 0., 0., 12., 13., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 5., 16., 8., 114 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 13., 16., 3., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 115 14., 13., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 15., 12., 7., 2., 0., 116 0., 0., 0., 13., 16., 13., 16., 3., 0., 0., 0., 7., 16., 117 11., 15., 8., 0., 0., 0., 1., 9., 15., 11., 3., 0.], 118 [ 0., 0., 7., 8., 13., 16., 15., 1., 0., 0., 7., 7., 4., 119 11., 12., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 8., 13., 1., 0., 0., 4., 120 8., 8., 15., 15., 6., 0., 0., 2., 11., 15., 15., 4., 0., 121 0., 0., 0., 0., 16., 5., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 9., 15., 122 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 13., 5., 0., 0., 0., 0.], 123 [ 0., 0., 9., 14., 8., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 12., 14., 14., 124 12., 0., 0., 0., 0., 9., 10., 0., 15., 4., 0., 0., 0., 125 3., 16., 12., 14., 2., 0., 0., 0., 4., 16., 16., 2., 0., 126 0., 0., 3., 16., 8., 10., 13., 2., 0., 0., 1., 15., 1., 127 3., 16., 8., 0., 0., 0., 11., 16., 15., 11., 1., 0.], 128 [ 0., 0., 11., 12., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 2., 16., 16., 16., 129 13., 0., 0., 0., 3., 16., 12., 10., 14., 0., 0., 0., 1., 130 16., 1., 12., 15., 0., 0., 0., 0., 13., 16., 9., 15., 2., 131 0., 0., 0., 0., 3., 0., 9., 11., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 132 9., 15., 4., 0., 0., 0., 9., 12., 13., 3., 0., 0.]]) 133 [11] 134 some_digit = X[666] 135 [12] 136 y[666] 137 0 138 [13] 139 some_digit_image = some_digit.reshape(8,8) 140 plt.imshow(some_digit_image,cmap = matplotlib.cm.binary) # 无须plot.show 141 <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1d13c9d6a30> 142 143 [14] 144 from playML.model_selection import train_test_split 145 [15] 146 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_radio = 0.2) 147 [16] 148 from playML.kNN import KNNClassifier 149 [17] 150 my_knn_clf = KNNClassifier(k = 3) 151 [18] 152 my_knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) 153 KNN(k=3) 154 [19] 155 y_predict = my_knn_clf.predict(X_test) 156 [20] 157 y_predict 158 array([7, 7, 2, 6, 4, 2, 7, 0, 0, 5, 0, 3, 2, 1, 5, 4, 0, 5, 6, 7, 7, 7, 159 6, 0, 9, 6, 5, 5, 6, 3, 3, 1, 5, 8, 8, 2, 2, 4, 7, 0, 5, 4, 3, 2, 160 1, 8, 4, 5, 9, 5, 0, 7, 3, 0, 5, 4, 3, 7, 1, 2, 1, 1, 5, 7, 3, 0, 161 2, 3, 7, 1, 9, 3, 9, 0, 5, 8, 0, 6, 0, 9, 8, 3, 2, 0, 4, 1, 9, 6, 162 4, 0, 6, 2, 6, 4, 4, 2, 4, 1, 5, 2, 7, 1, 4, 9, 0, 4, 3, 8, 5, 7, 163 8, 2, 0, 7, 0, 3, 0, 7, 9, 5, 9, 9, 8, 2, 7, 7, 8, 5, 5, 8, 2, 6, 164 0, 5, 2, 6, 1, 6, 2, 6, 3, 9, 8, 4, 5, 4, 6, 2, 3, 1, 4, 9, 7, 6, 165 2, 4, 1, 4, 3, 8, 6, 7, 7, 3, 3, 0, 0, 6, 7, 4, 9, 0, 3, 2, 7, 8, 166 5, 4, 4, 0, 7, 6, 5, 1, 1, 3, 9, 3, 8, 7, 0, 1, 5, 0, 6, 5, 7, 4, 167 7, 6, 2, 0, 4, 9, 7, 2, 7, 9, 0, 2, 7, 9, 2, 1, 8, 4, 8, 9, 4, 3, 168 5, 9, 8, 8, 0, 4, 3, 2, 2, 5, 2, 4, 9, 2, 7, 3, 6, 4, 4, 1, 6, 3, 169 1, 4, 9, 1, 9, 0, 3, 9, 2, 8, 3, 5, 4, 6, 4, 5, 4, 6, 6, 8, 0, 3, 170 8, 7, 0, 7, 9, 2, 3, 2, 2, 1, 5, 9, 6, 6, 0, 0, 8, 3, 2, 1, 9, 4, 171 8, 6, 1, 2, 0, 8, 7, 2, 5, 9, 3, 9, 6, 6, 2, 8, 5, 6, 2, 6, 6, 7, 172 1, 8, 2, 2, 4, 3, 4, 0, 8, 1, 7, 1, 2, 9, 9, 2, 1, 3, 7, 8, 7, 6, 173 1, 8, 3, 7, 2, 6, 3, 2, 3, 9, 4, 1, 7, 6, 3, 7, 9, 0, 9, 0, 9, 3, 174 5, 0, 6, 4, 8, 9, 4]) 175 [21] 176 sum(y_predict == y_test)/len(y_test) 177 0.9916434540389972 178 [22] 179 from playML.metrics import accuracy_score 180 [23] 181 accuracy_score(y_test,y_predict) 182 0.9916434540389972 183 [24] 184 my_knn_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 185 0.9916434540389972 186 scikit_learn 中的 accuracy_score 187 [25] 188 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 189 190 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.3,random_state=666) 191 [26] 192 from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier 193 knn_clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 6) # n_neighbors == 6 ,写成两个等号 194 [27] 195 knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) 196 KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=6) 197 [28] 198 y_predict = knn_clf.predict(X_test) 199 200 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score 201 [29] 202 accuracy_score(y_test,y_predict) 203 0.9888888888888889 204 [30] 205 knn_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 206 0.9888888888888889
4-5 超参数


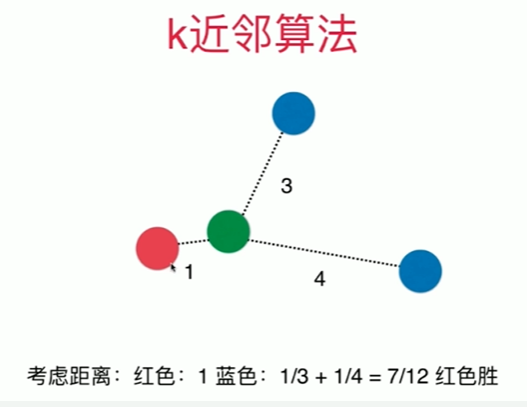
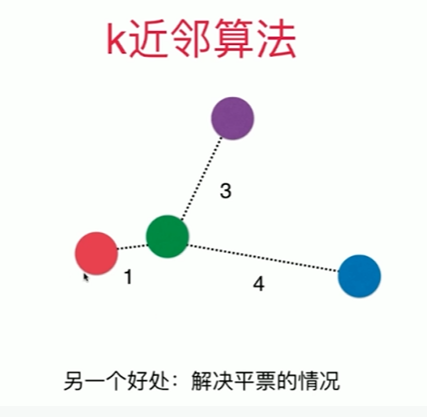


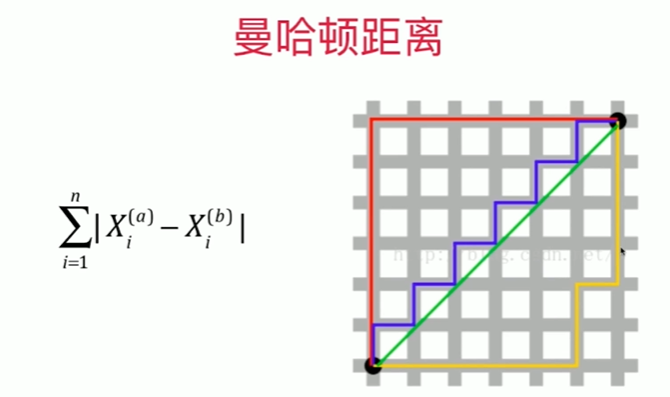
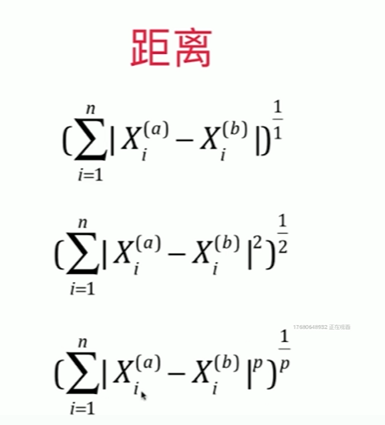

Notbook 示例
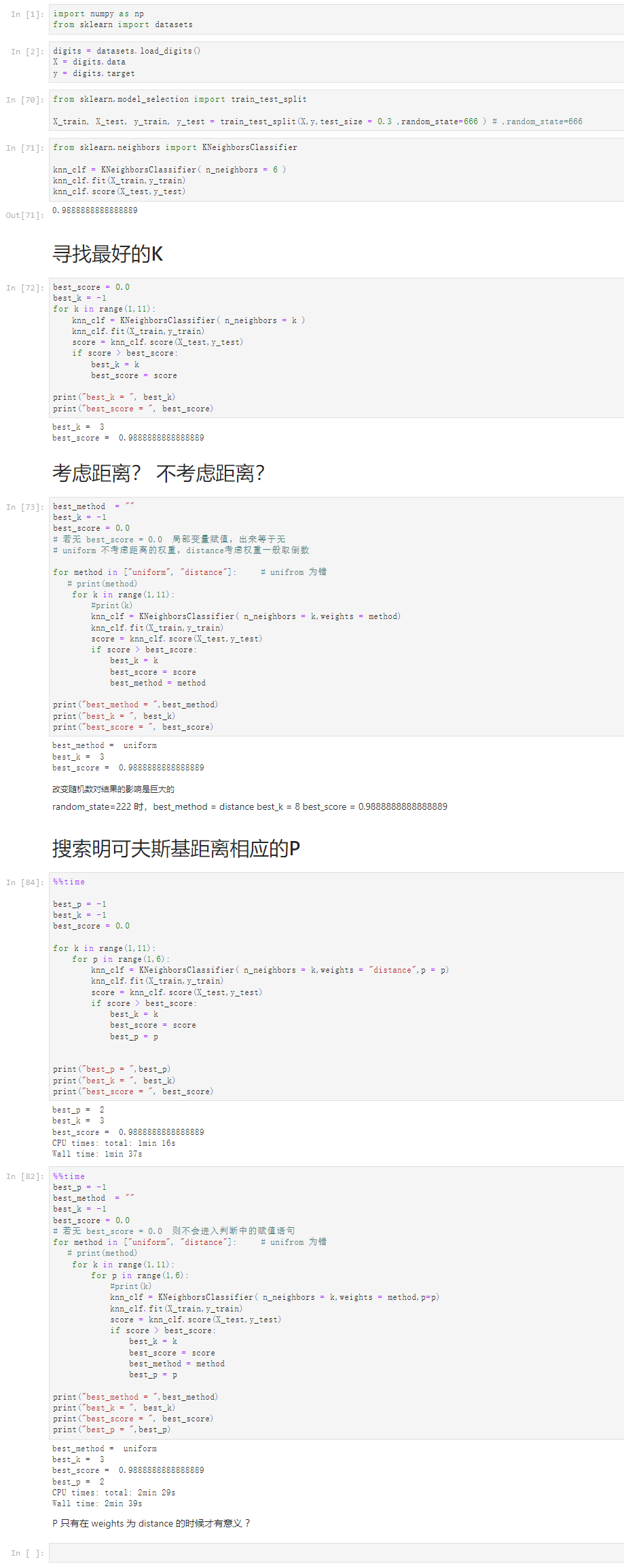
Notbook 源码
1 [1] 2 import numpy as np 3 from sklearn import datasets 4 [2] 5 digits = datasets.load_digits() 6 X = digits.data 7 y = digits.target 8 [70] 9 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 10 11 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.3 ,random_state=666 ) # ,random_state=666 12 [71] 13 from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier 14 15 knn_clf = KNeighborsClassifier( n_neighbors = 6 ) 16 knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) 17 knn_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 18 0.9888888888888889 19 寻找最好的K 20 [72] 21 best_score = 0.0 22 best_k = -1 23 for k in range(1,11): 24 knn_clf = KNeighborsClassifier( n_neighbors = k ) 25 knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) 26 score = knn_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 27 if score > best_score: 28 best_k = k 29 best_score = score 30 31 print("best_k = ", best_k) 32 print("best_score = ", best_score) 33 best_k = 3 34 best_score = 0.9888888888888889 35 36 考虑距离? 不考虑距离? 37 [73] 38 best_method = "" 39 best_k = -1 40 best_score = 0.0 41 # 若无 best_score = 0.0 局部变量赋值,出来等于无 42 # uniform 不考虑距离的权重,distance考虑权重一般取倒数 43 44 for method in ["uniform", "distance"]: # unifrom 为错 45 # print(method) 46 for k in range(1,11): 47 #print(k) 48 knn_clf = KNeighborsClassifier( n_neighbors = k,weights = method) 49 knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) 50 score = knn_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 51 if score > best_score: 52 best_k = k 53 best_score = score 54 best_method = method 55 56 print("best_method = ",best_method) 57 print("best_k = ", best_k) 58 print("best_score = ", best_score) 59 60 best_method = uniform 61 best_k = 3 62 best_score = 0.9888888888888889 63 64 改变随机数对结果的影响是巨大的 65 random_state=222 时,best_method = distance best_k = 8 best_score = 0.9888888888888889 66 67 搜索明可夫斯基距离相应的P 68 [84] 69 %%time 70 71 best_p = -1 72 best_k = -1 73 best_score = 0.0 74 75 for k in range(1,11): 76 for p in range(1,6): 77 knn_clf = KNeighborsClassifier( n_neighbors = k,weights = "distance",p = p) 78 knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) 79 score = knn_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 80 if score > best_score: 81 best_k = k 82 best_score = score 83 best_p = p 84 85 86 print("best_p = ",best_p) 87 print("best_k = ", best_k) 88 print("best_score = ", best_score) 89 best_p = 2 90 best_k = 3 91 best_score = 0.9888888888888889 92 CPU times: total: 1min 16s 93 Wall time: 1min 37s 94 95 [82] 96 %%time 97 best_p = -1 98 best_method = "" 99 best_k = -1 100 best_score = 0.0 101 # 若无 best_score = 0.0 则不会进入判断中的赋值语句 102 for method in ["uniform", "distance"]: # unifrom 为错 103 # print(method) 104 for k in range(1,11): 105 for p in range(1,6): 106 #print(k) 107 knn_clf = KNeighborsClassifier( n_neighbors = k,weights = method,p=p) 108 knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) 109 score = knn_clf.score(X_test,y_test) 110 if score > best_score: 111 best_k = k 112 best_score = score 113 best_method = method 114 best_p = p 115 116 print("best_method = ",best_method) 117 print("best_k = ", best_k) 118 print("best_score = ", best_score) 119 print("best_p = ",best_p) 120 best_method = uniform 121 best_k = 3 122 best_score = 0.9888888888888889 123 best_p = 2 124 CPU times: total: 2min 29s 125 Wall time: 2min 39s 126 127 P 只有在 weights 为 distance 的时候才有意义 ?






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号