2025杭电多校第三场 三带一、性质不同的数字、核心共振 个人题解
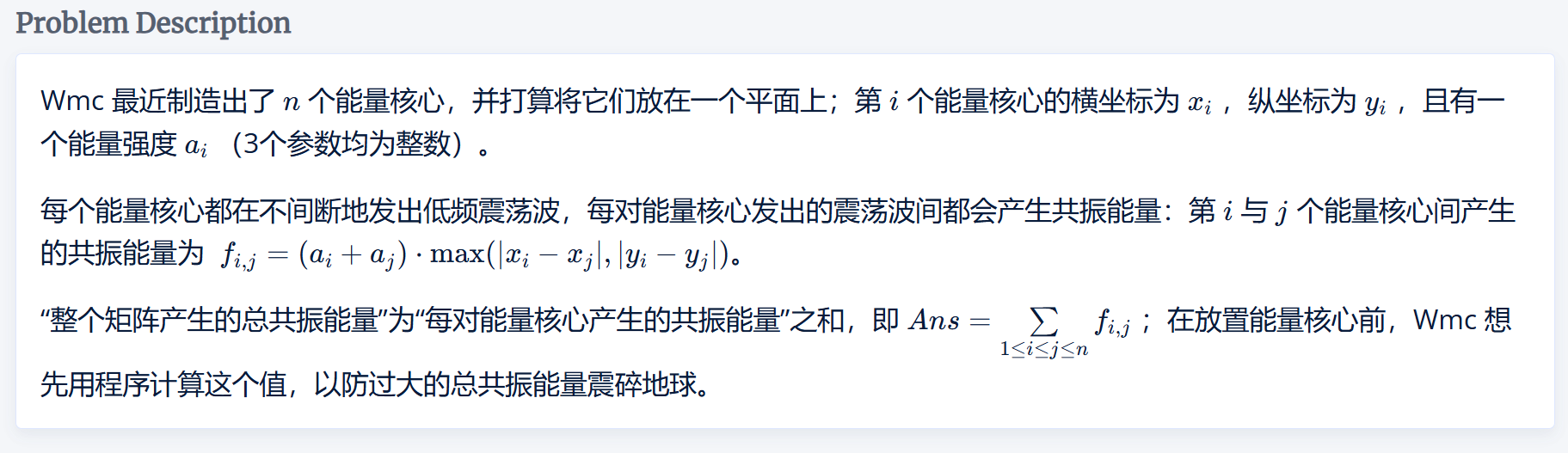
核心共振
前缀和 #数学 #曼哈顿距离 #切比雪夫距离
题目
思路
切比雪夫距离可以和曼哈顿距离互相转化!!
直接上数学推导!
先化简题目要求的式子:
将切比雪夫距离转化成曼哈顿距离:
将所求式子转化成前缀和:
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i <= (b); i++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i >= (b); i--)
#define mid ((l+r)>>1)
#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
const int mod=1e9+7;
int n;
const int N=2e5+5;
vector<pair<ll,ll>> u,v;
ll upre[N],vpre[N],inv2;
ll qpow(ll a, ll b){
ll res = 1;
while (b){
if (b & 1)
res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void solve() {
cin>>n;
u.clear(),v.clear();
u.reserve(n+1),v.reserve(n+1);
u.push_back({0,0}),v.push_back({0,0});
rep(i,1,n){
int x,y,a;cin>>x>>y>>a;
u.push_back({x+y,a}),v.push_back({x-y,a});
}
sort(u.begin()+1,u.end()),sort(v.begin()+1,v.end());
rep(i,1,n){
upre[i]=(u[i].first+upre[i-1])%mod;
vpre[i]=(v[i].first+vpre[i-1])%mod;
}
ll ans=0;
rep(i,1,n){
ll mul=(((2*i-1-n)*u[i].first+mod)%mod+upre[n]-upre[i]-upre[i-1]+2*mod)%mod;
ans+=(u[i].second*mul)%mod;
ans%=mod;
mul=(((2*i-1-n)*v[i].first+mod)%mod+vpre[n]-vpre[i]-vpre[i-1]+2*mod)%mod;
ans+=(v[i].second*mul)%mod;
ans%=mod;
}
ans=(ans*inv2)%mod;
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
inv2=qpow(2,mod-2);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
性质不同的数字
哈希 #扫描线 #差分
题目

思路
将每个线段编号,观察数轴上的位置\(pos\),\(pos\)这个位置上所有覆盖的线段所构成的集合记为其状态,比如在\(pos=3\)的位置上有编号为\(\{ 1,3,4 \}\)的三条线段覆盖,\(pos=3\)的状态即为\(\{ 1,3,4 \}\)。
题目所求即整个数轴上有多少种不同的状态。
我们可以对每条线段进行随机编号,这样可以保证后续哈希的过程产生碰撞的概率极小。
在输入线段\([l,r]\)的时候在\(l\)与\(r+1\)位置打上差分标记
随后以哈希值\(hash\)作为扫描线一路还原过去,开一个哈希表\(unordered\_map<ll,bool>cnt\)记录不同状态数
最后输出状态总数\(cnt.size()\)即可
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i <= (b); i++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i >= (b); i--)
#define mid ((l+r)>>1)
#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
const int N=2e5+5;
const ll mod=1145141919810;
unordered_map<ll,bool>cnt;
unordered_map<ll,bool>vis;
struct line{
vector<ll>l,r;
};
map<int,line>mp;
mt19937 rng(chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
void solve() {
cnt.clear();mp.clear();vis.clear();
int n;cin>>n;
rep(i,1,n){
int l,r;cin>>l>>r;
ll idx=rng();
while(vis[idx])idx=rng();
vis[idx]=1;
mp[l].l.push_back(idx);
mp[r+1].r.push_back(idx);
}
if(n==0){cout<<1<<'\n';return;}
ll hash=0;
for(auto&lin:mp){
for(auto&ele:lin.second.l){
hash=(hash+ele)%mod;
}
for(auto&ele:lin.second.r){
ele%=mod;
hash=(hash-ele+mod)%mod;
}
cnt[hash];
}
cout<<cnt.size()<<'\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
// initrd();
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
三带一
二分 #数学
题目

思路
求最大值,考虑二分答案,判断当前答案是否合法。
对于数字\(i\),设配对成功了\(b_{i}\)个\(3\),剩余\(c_{i}=a_{i}-3\times b_{i}\)
则有\(3\times b_{i}\leq a_{i}\quad b_{i}\leq \left\lfloor \frac{a_{i}}{3} \right\rfloor\)
设\(A=\sum a_{i},ans=\sum b_{i},C=\sum c_{i}=A-3\times ans\)
每二分确定一个\(ans\),\(b_{i}\)都由多条不等式确定:
因此对于所有的\(ans\),只需要满足任意\(i\)都有
即为一种合法答案。
为何不等式\(b_{i}+c_{i}\leq C\)为合法的充要条件?
以\(n=3\)时的情况为例:
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i <= (b); i++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i >= (b); i--)
#define mid ((l+r)>>1)
#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
int a[14],A;
bool check(int ans){
int down=0;
rep(i,1,13){
int val=(int)(ceil((1.0)*(a[i]-A+3*ans)/2));
if(a[i]/3<val)return 0;
if(val<0)val=0;
down+=val;
}
if(ans<down)return 0;
return 1;
}
void solve() {
A=0;
int up=0;
rep(i,1,13)cin>>a[i],A+=a[i],up+=a[i]/3;
int l=0,r=min(A/4,up)+1;
while(l+1<r){
if(check(mid)){
l=mid;
}else{
r=mid;
}
}
cout<<l<<'\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)solve();
return 0;
}
类题:王国——迁移
二分 #数学
题目

思路
求最小值,考虑二分答案判断合理性
二分确定一个答案\(ans\),则每个城市能接受的人数\(d_{i}=\left\lfloor \frac{ans}{c_{i}} \right\rfloor\)
设\(D=\sum d_{i},B=\sum b_{i}\),则对于所有的\(i\),有不等式:
原理与上题相同
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i <= (b); i++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i >= (b); i--)
#define mid ((l+r)>>1)
#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
const int N=1e6+5;
ll a[N],b[N],c[N],d[N],B,n,D;
bool check(ll ans){
rep(i,1,n){
d[i]=ans/c[i];
D+=d[i];
}
if(D<B)return 0;
rep(i,1,n){
if(b[i]+d[a[i]]>D)return 0;
}
return 1;
}
void solve() {
B=0;
cin>>n;
rep(i,1,n)cin>>a[i];
rep(i,1,n)cin>>b[i],B+=b[i];
rep(i,1,n)cin>>c[i];
ll l=0,r=1e12;
while(l+1<r){
D=0;
if(check(mid))r=mid;
else l=mid;
}
cout<<r<<'\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)solve();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号