2025杭电多校第一场 树上lcm、子序列、传送门个人题解
传送门
dijkstra
题目

思路
这题很明显是一个最短路问题,但是其中的限制条件比较特殊,每个边都有自己的颜色,在更新当前节点的时候需要考虑上一个节点的信息。
我们开的结构体\(edge\)存边时要记录其颜色\(c\);
给每个节点都开一个\(set\)用于储存到达这个节点路径最短的边都有哪些颜色;
开数组\(vis[N]\)用于跑dijkstra,\(dp[N]\)记录最短路
struct edge {
vector<pair<ll, ll>>e;//c,next
}a[N];
set<int>last[N];
int vis[N], dp[N];
设当前节点为\(u\),需要更新的节点为\(next\),\(u \xrightarrow{id}next\)所连的边的颜色为\(id\)
- 若\(last[next].count(id)\),由于dijkstra只会让\(next\)入队一次,说明\(next\)在之前被更新为最短路的时候已经算上了变换颜色的额外路径,当前的\(id\)在计算路径的时候就不需要加上路径了
- 若\(!\,last[next].count(id)\),说明\(next\)更新的最短路中不包含颜色\(id\),此时计算路径的时候就需要加上变换颜色的额外开销了
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define rep(i,a,b) for(ll i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define per(i,a,b) for(ll i=(a);i>=(b);i--)
#define see(stl) for(auto &ele:stl)cout<<ele<<"\n"; cout<<'\n';
#define endl '\n';
const ll inf = 1e9;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
struct edge {
vector<pair<ll, ll>>e;//c,next
}a[N];
set<int>last[N];
int vis[N], dp[N];
void dj(int s) {
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>>dq;
dp[s] = 0;
dq.push({ 0,s });
while (!dq.empty()) {
int u = dq.top().second;
dq.pop();
if (vis[u])continue;
vis[u] = 1;
for (auto& son : a[u].e) {
int id = son.first, next = son.second;
if (last[next].count(id)) {
if (dp[next] == dp[u]) {
if (!vis[next])dq.push({ dp[next],next });
}
else if (dp[next] > dp[u]) {
dp[next] = dp[u];
last[next].clear();
last[next].insert(id);
if (!vis[next])dq.push({ dp[next],next });
}
}
else {
if (dp[next] == dp[u] + 1) {
last[next].insert(id);
if (!vis[next])dq.push({ dp[next],next });
}
else if (dp[next] > dp[u] + 1) {
dp[next] = dp[u] + 1;
last[next].clear();
last[next].insert(id);
if (!vis[next])dq.push({ dp[next],next });
}
}
}
}
}
void eachT() {
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
rep(i, 1, n)dp[i] = inf, vis[i] = 0, last[i].clear(), a[i].e.clear();
rep(i, 1, m) {
int u, v, c; cin >> u >> v >> c;
a[u].e.push_back({ c,v });
a[v].e.push_back({ c,u });
}
dj(1);
cout << dp[n] << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)eachT();
return 0;
}
子序列
贪心
题目
思路
来自小组成员phaethon90
本题的关键在于“排列”二字,由此可以知道\(1\sim n\)均出现且只出现一次。
若给定子序列的两个端点\([l,r]\),中间则最多有\(min\{ a[l],a[r] \}-1\)个数满足条件,此时只要知道有多少个小于\(min\{ a[l],a[r] \}\)的数不在\([l,r]\)中国,利用差值即可\(O(1)\)算出最大长度
用双指针\(l,r\)数组的两端遍历:
由于长度上限与\(min\{ a[l],a[r] \}\)有关,因此每次都移动所指的值较小的那个指针,直到遇到比原端点更大的值(小值对答案的更新没有贡献)
注意到此时区间外的点的值均小于现在两个指针所指的值,于是可以\(O(1)\)算出子序列的最大长度并更新答案
最后需要注意一下特判\(n==1\)的情形
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i <= (b); i++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i >= (b); i--)
//#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
#define double long double
const int N=2e6+5;
int a[N];
void solve() {
int n;cin>>n;
rep(i,1,n)cin>>a[i];
if(n==1){cout<<1<<'\n';return;}
int cnt=-1,l=1,r=n,ans=0;
while(l<r){
ans=max(ans,min(a[l],a[r])-(++cnt)+1);
if(a[l]<a[r])l++;
else r--;
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) solve();
return 0;
}
树上LCM
树上dp dp 子集合dp
思路
fishergo大佬在赛时用莫比乌斯反演过了本题,但本蒟蒻到现在还没学明白
由\(lcm\)的性质,我们很容易推出结论:
- 设节点\(u\)的值为\(a[u]\),若\(lcm(a[u],x)>x\),则点\(u\)必定不能再路径中
- 所有能够到达的点的值必定是\(x\)的因数
将\(x\)质因数分解为\(q_{1}^{p_{1}}q_{2}^{p_{2}}\dots q_{k}^{p_{k}}\),由于\(x\leq 1e7\),则\(k\leq 7\)
此时所有合法的点的值\(a[u]\)都可以表示为\(q_{1}^{u_{1}}q_{2}^{u_{2}}\dots q_{k}^{u_{k}}\),只有在\(u_{i}==p_{i}\)的时候,\(u\)才算作对\(lcm\)贡献了因数\(q_{i}^{p_{i}}\)(如\(x=2^3·3^2\),\(a[u]=2^3\)时对\(lcm\)的\(2^3\)因数有贡献,\(a[v]=2^2·3\)时对\(lcm\)没有任何贡献)
由于每个质因数的幂次这个整体\(q_{i}^{p_{i}}\)要么有贡献要么没有贡献,因此可以对\(q_{1}^{p_{1}}q_{2}^{p_{2}}\dots q_{k}^{p_{k}}\)状态压缩为位数为\(k\)的二进制数,\(1\)代表有这个因数整体,\(0\)代表没有(如\(x=2^3·3^2·5^4\),\(a[u]=2^3·5^4\)压缩后为\(101(2)\) )
因此我们将所有的\(a[u]\)状态压缩,合法的就将压缩后的十进制数存为\(state\),不合法的存为\(-1\)
接下来进行树上dp:
状态含义:
\(f[u][state]\)表示以节点\(u\)为根的子树中,以\(u\)为端点的路径的\(lcm\)状态压缩后为\(state\)的路径数
\(dp_{u}[state]\)表示当前状态下,\(u\)已经处理完的子树中,以\(u\)为端点的路径的\(lcm\)状态压缩后为\(state\)的超集的路径数
超集:若\(i|j=i\),则称\(j\)为\(i\)的子集,\(i\)为\(j\)的超集
状态转移:
预处理超集和:
树上dp:
其中\(one\)代表二进制表示为全1的数
预处理超集和的过程可以参考文章:高维前缀和
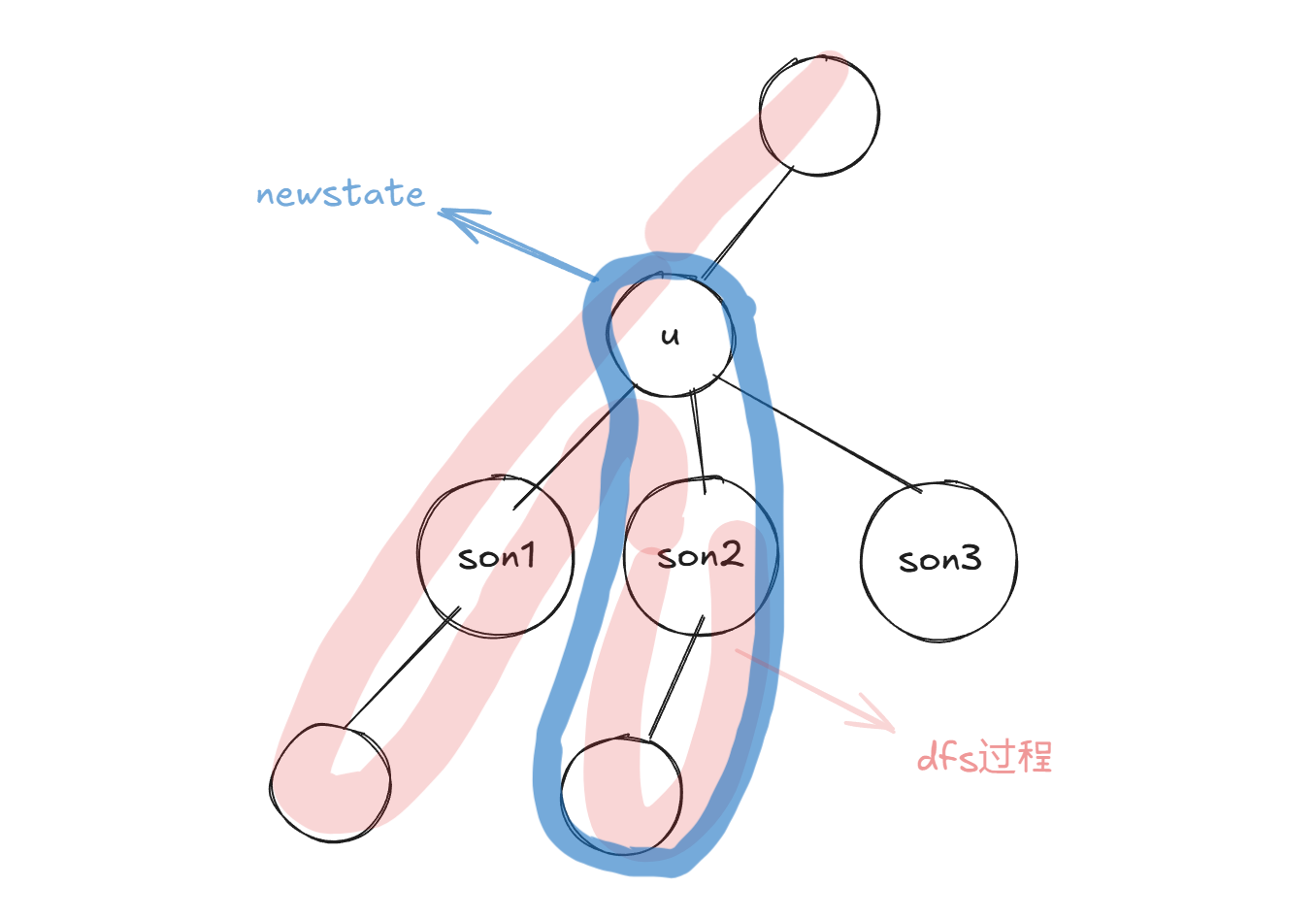
在dfs回溯的过程进行树上dp
遍历从\(son\)中传回来的所有状态压缩的数\(i\),与当前点\(u\)的状态压缩数\(a[i].state\)作或运算,可得\(son\)所在子树中某条状态为\(i\)的路径多加上\(u\)点后的新状态\(newstate=i\ |\ a[u].state\)
现在的目标便是在已处理的子树(图中红色部分)中找到一些包含节点\(u\)的路径,使得这些路径和蓝色路径拼接起来后的\(lcm\)为\(x\),即这两部分的状态在或运算后为\(one\)
因此找出\(newstate\)的补集\(newstate \wedge one\),其超集与\(state\)或运算后必然是\(one\)
蓝色部分的路径个数为\(f[son][i]\),红色部分的路径个数为\(dp[\ state \wedge one\ ]\),二者相乘即可算出对答案的贡献
最后,\(a[u].state\)本身就是\(one\)的情况需要特判
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i <= (b); i++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i >= (b); i--)
#define mid ((l+r)>>1)
#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
vector<ll>prime, vis;
void sieve(ll len) {
vis.assign(len + 1, 0);
prime.push_back(0);
rep(i, 2, len) {
if (!vis[i])prime.push_back(i);
for (ll j = 1; i * prime[j] <= len && j < prime.size(); j++) {
vis[prime[j] * i] = 1;
if (i % prime[j] == 0)break;
}
}
}
vector<int>cnt, fac;
int len,one;
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
if (b == 0)return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
ll lcm(ll a, ll b) {
return a * b / gcd(a, b);
}
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n, x;
struct node {
vector<int>e;
int val, state;
}a[N];
vector<ll>f[N];
ll ans;
int get(int y) {
if (lcm(x, y) != x)return -1;
int val = 0, j = 0;
rep(i, 0, len - 1) {
int cur = 0;
while (y % fac[i] == 0) {
y /= fac[i];
cur++;
}
if (cur == cnt[i])val |= (1 << j);
j++;
}
return val;
}
void dfs(int u, int fa) {
int val = a[u].val;
a[u].state = get(val);
f[u].resize(one+1,0);
for (auto& son : a[u].e) {
if (son == fa)continue;
dfs(son, u);
}
if (a[u].state == -1)return;
f[u][a[u].state] = 1;
for (auto& son : a[u].e) {
if (son == fa)continue;
vector<ll>dp = f[u];
rep(j, 0, len - 1) {
rep(i, 0, one) {
if (!(i >>j & 1))dp[i] += dp[i ^ (1 << j)];
}
}
rep(i, 0, one) {//f[son][i]
int state = i | a[u].state;
ans += dp[state ^ one] * f[son][i];
f[u][state] += f[son][i];
}
}
if (a[u].state == one)ans++;
}
void init() {
ans = 0;
rep(i, 1, n)a[i].e.clear(), a[i].state = 0,f[i].clear();
cnt.assign(10, 0), fac.assign(10, 0);
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> x;
init();
int pos = 0, tmp = x;
rep(i, 1, prime.size() - 1) {
if (prime[i] > x)break;
if (tmp % prime[i] == 0) {
fac[pos] = prime[i];
while (tmp % prime[i] == 0) {
tmp /= prime[i];
cnt[pos]++;
}
pos++;
}
}
len = pos; one = ((1 << (len)) - 1);
rep(i, 1, n - 1) {
int u, v; cin >> u >> v;
a[u].e.push_back(v);
a[v].e.push_back(u);
}
rep(i, 1, n)cin >> a[i].val;
dfs(1, 0);
cout << ans;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
sieve(1e7);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号