论文解读(PAWS)《Semi-Supervised Learning of Visual Features by Non-Parametrically Predicting View Assignments with Support Samples》
论文信息
论文标题:Semi-Supervised Learning of Visual Features by Non-Parametrically Predicting View Assignments with Support Samples
论文作者:Mahmoud Assran, Mathilde Caron, Ishan Misra, Piotr Bojanowski, Armand Joulin, Nicolas Ballas
论文来源:NeurIPS 2021
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
视屏讲解:click
1 介绍
提出问题:充分利用无标注目标;
解决办法:对无标注数据使用一种可信的伪标签策略;
2 方法
2.1 整体框架
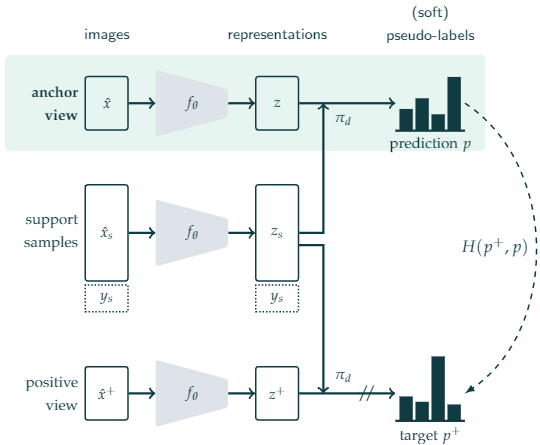
2.2 问题定义
We consider a large dataset of unlabeled images $\mathcal{D}= \left(\mathrm{x}_{i}\right)_{i \in[1, N]}$ and a small support dataset of annotated images $\mathcal{S}=\left(\mathbf{x}_{s i}, y_{i}\right)_{i \in[1, M]}$ , with $M \ll N $.Our goal is to learn image representations by leveraging both $\mathcal{D}$ and $\mathcal{S}$ during pretraining. After pre-training with $\mathcal{D}$ and $\mathcal{S}$ , we fine-tune the learned representations using only the labeled set $\mathcal{S}$ .
2.3 相似度分类器
公式:
$\pi_{d}\left(z_{i}, \mathbf{z}_{\mathcal{S}}\right)=\sum_{\left(z_{s_{j}}, y_{j}\right) \in \mathbf{z}_{\mathcal{S}}}\left(\frac{d\left(z_{i}, z_{s j}\right)}{\sum_{z_{s k} \in \mathbf{z}_{\mathcal{S}}} d\left(z_{i}, z_{s k}\right)}\right) y_{j}$
Note:Soft Nearest Neighbours strategy
其中:
$d(a, b) =\exp \left( \frac{a^{T} b}{\|a\|\|b\| \tau} \right)$
简化:
$p_{i}:=\pi_{d}\left(z_{i}, \mathbf{z}_{\mathcal{S}}\right)=\sigma_{\tau}\left(z_{i} \mathbf{z}_{\mathcal{S}}^{\top}\right) \mathbf{y}_{\mathcal{S}}$
锐化:
$\left[\rho\left(p_{i}\right)\right]_{k}:=\frac{\left[p_{i}\right]_{k}^{1 / T}}{\sum_{j=1}^{K}\left[p_{i}\right]_{j}^{1 / T}}, \quad k=1, \ldots, K$
Note:锐化目标会鼓励网络产生自信的预测,避免模型崩溃问题。
代码:

def snn(query, supports, labels):
"""
:param query: torch.Size([2048, 128])
:param supports: torch.Size([1280, 128])
:param labels: torch.Size([1280, 10]) 经过了标签平滑
:return:
"""
""" Soft Nearest Neighbours similarity classifier """
# Step 1: normalize embeddings
query = torch.nn.functional.normalize(query)
supports = torch.nn.functional.normalize(supports)
# Step 2: gather embeddings from all workers
supports = AllGather.apply(supports)
# Step 3: compute similarlity between local embeddings
return softmax(query @ supports.T / tau) @ labels
labels
tensor([[0.9100, 0.0100, 0.0100, ..., 0.0100, 0.0100, 0.0100],
[0.0100, 0.9100, 0.0100, ..., 0.0100, 0.0100, 0.0100],
[0.0100, 0.0100, 0.9100, ..., 0.0100, 0.0100, 0.0100],
...,
[0.0100, 0.0100, 0.0100, ..., 0.9100, 0.0100, 0.0100],
[0.0100, 0.0100, 0.0100, ..., 0.0100, 0.9100, 0.0100],
[0.0100, 0.0100, 0.0100, ..., 0.0100, 0.0100, 0.9100]],
device='cuda:0')

def sharpen(p):
#T = 0.25
sharp_p = p**(1./T)
sharp_p /= torch.sum(sharp_p, dim=1, keepdim=True) #Size([512, 10])
return sharp_p
2.4 训练目标
总目标:
$\frac{1}{2 n} \sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(H\left(\rho\left(p_{i}^{+}\right), p_{i}\right)+H\left(\rho\left(p_{i}\right), p_{i}^{+}\right)\right)-H(\bar{p})$
ME-MAX 正则化项:$H(\bar{p})$
其中:
$\bar{p}:=\frac{1}{2 n} \sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(\rho\left(p_{i}\right)+\right. \left.\rho\left(p_{i}^{+}\right)\right) $ 表示所有未标记表示的锐化预测的平均值;
该正则化项在鼓励个体预测有信心的同时,鼓励平均预测接近均匀分布。ME-MAX 正则化项之前已在判别式无监督聚类社区中用于平衡学习的聚类大小[35]。

def init_paws_loss(
multicrop=6,
tau=0.1,
T=0.25,
me_max=True
):
"""
Make semi-supervised PAWS loss
:param multicrop: number of small multi-crop views
:param tau: cosine similarity temperature
:param T: target sharpenning temperature
:param me_max: whether to perform me-max regularization
"""
softmax = torch.nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def sharpen(p):
sharp_p = p**(1./T)
sharp_p /= torch.sum(sharp_p, dim=1, keepdim=True)
return sharp_p
def snn(query, supports, labels):
""" Soft Nearest Neighbours similarity classifier """
# Step 1: normalize embeddings
query = torch.nn.functional.normalize(query)
supports = torch.nn.functional.normalize(supports)
# Step 2: gather embeddings from all workers
supports = AllGather.apply(supports)
# Step 3: compute similarlity between local embeddings
return softmax(query @ supports.T / tau) @ labels
def loss(
anchor_views,
anchor_supports,
anchor_support_labels,
target_views,
target_supports,
target_support_labels,
sharpen=sharpen,
snn=snn
):
# -- NOTE: num views of each unlabeled instance = 2+multicrop
batch_size = len(anchor_views) // (2+multicrop)
# Step 1: compute anchor predictions
probs = snn(anchor_views, anchor_supports, anchor_support_labels)
# Step 2: compute targets for anchor predictions
with torch.no_grad():
targets = snn(target_views, target_supports, target_support_labels)
targets = sharpen(targets)
if multicrop > 0:
mc_target = 0.5*(targets[:batch_size]+targets[batch_size:])
targets = torch.cat([targets, *[mc_target for _ in range(multicrop)]], dim=0)
targets[targets < 1e-4] *= 0 # numerical stability
# Step 3: compute cross-entropy loss H(targets, queries)
loss = torch.mean(torch.sum(torch.log(probs**(-targets)), dim=1))
# Step 4: compute me-max regularizer
rloss = 0.
if me_max:
avg_probs = AllReduce.apply(torch.mean(sharpen(probs), dim=0))
rloss -= torch.sum(torch.log(avg_probs**(-avg_probs)))
return loss, rloss
return loss

loss = torch.mean(torch.sum(torch.log(probs**(-targets)), dim=1)) # probs、targets = torch.Size([2048, 10])

# Example of target with class indices
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3, dtype=torch.long).random_(5)
output = loss(input, target)
output.backward()
# Example of target with class probabilities
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3, 5).softmax(dim=1)
output = loss(input, target)
output.backward()

avg_probs = torch.mean(sharpen(probs), dim=0)
rloss -= torch.sum(torch.log(avg_probs**(-avg_probs)))
3 总结
略
因上求缘,果上努力~~~~ 作者:别关注我了,私信我吧,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/BlairGrowing/p/17325013.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号