C 和 C++ 中的 void 指针之间的区别?
C 和 C++ 中的 void 指针之间的区别?
看以下例子;
voidp;
chars;
p=s;
s=p; //this is wrong ,should do s=(char*)p;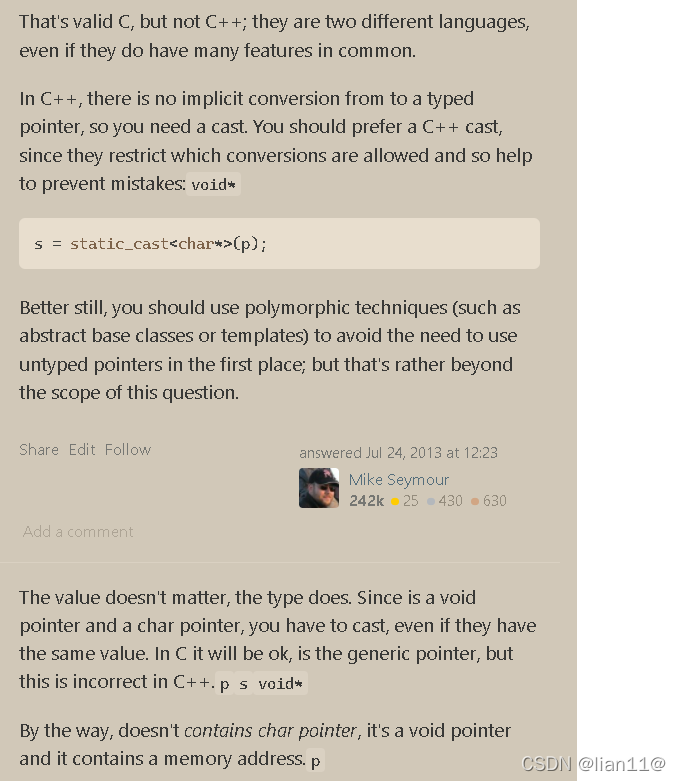
即是 s=p; //this is wrong ,should do s=(char*)p;
在 C++ 中,没有 从 到类型化指针的隐式转换,因此需要强制转换。您应该更喜欢C++转换,因为它们限制了允许的转换,因此有助于防止错误:void*
C 和 C++ 中的 void 指针之间的区别?
看以下例子;
voidp;
chars;
p=s;
s=p; //this is wrong ,should do s=(char*)p;
即是 s=p; //this is wrong ,should do s=(char*)p;
在 C++ 中,没有 从 到类型化指针的隐式转换,因此需要强制转换。您应该更喜欢C++转换,因为它们限制了允许的转换,因此有助于防止错误:void*
