Codeforces Round #735 (Div. 2) A-E题解
A. Cherry
题意: 给你一个序列,定义\(f(l,r)\) = \(\max(al,al+1,....,ar)\) * \(\min(al,al+1,......,ar)\),对于所有pair的(l,r),找出这个f的最大值.
思路: 可以这样思考,如果对于一个较大的值\(a_i\),对于包他的区间有一个比它小的\(a_k\) ,且,\(k > i + 1 ,k < i - 1\),那么要求一个最大值,可以直接求这个较大值和他相邻的元素的乘积.于是我们可以直接通过枚举这个长度为2的每个子串,每次取\(max\)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
ll a[maxn];
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i<= n;i ++) cin >> a[i];
ll mx = 0;
for(int i = 2;i <= n;i ++){
mx = max(mx,a[i] * a[i- 1]);
}
cout << mx << endl;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
while(n --) solve();
}
B. Cobb
题意
给定一个数列定义\(f(i,j) = i * j - k*(a_i|a_j)\),然后找到对于所有的\(pair(i,j)\)中找到最大的\(发(i,j)\),\(k < \min(n,100)\)
思路
可以很明显的注意到,由于k的范围比较小,i*j的权重在i和j的取值都比较大的时候,ai和aj对整体的影响比较小.所以我们可以直接枚举整个数列中靠后的\(min(200,n)\)的这些元素,来取最大值,为什么选200?因为k最大取100,我们最多枚举200个就可以保证答案的正确性.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
ll a[maxn];
void solve(){
int n,k;
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) cin >> a[i];
int m = max(1,n - 200);
ll ans = -1e12;
for(int i = n;i >= m;i --){
for(int j = i - 1;j >= m;j --){
ans = max(ans,i * 1ll * j - k * (a[i]|a[j]));
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t --) solve();
}
C. Mikasa
题意
定义\(mex(a_0,......,a_n)\)为整个数列中没有出现过的最小的非负整数,现给你一个n,m,让你求\(mex(n\oplus0,n\oplus1,....,n\oplus m)\).
思路
我们知道\(a\oplus b = c,a\oplus c = b\),即,则我们可以通过n和m来确定这个\(x(那个mex值)\),那么我们可以通过找n和m+1的异或结果,来找x,对于每一位,如果n的这一位,和m+1的这一位,都是1的话,为了x最小,那么这一位就取0,如果都是0,那么x也取0,如果n的这一位是1,m+1的这一位是0,那x就必须取0,这时x的这一位取了1,那么m这一位本来是0,变为了1,比m+1还大了,那么这时候就退出,当前x为最小的x.
/*
* @Description: stay hungry ,stay foolish
* @Descripttion: Calm and analyze
* @Author: Aklice
* @Date: 2021-07-14 22:48:48
* @LastEditors: Aklice
* @LastEditTime: 2021-08-08 14:29:26
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0)
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
/*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*/
void solve(){
int n,m;
cin >> n >> m;
m ++;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 31;i >= 0;i --){
//cout << i << ' ';
int a = (n >> i)&1;
int b = (m >> i)&1;
if(!a && b){
ans += (1 << i);
}
else if(a && !b){
break;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
D. Diane
题意
用26个小写字母构造一个长度为n的字符串,这个字符串的所有的相同的子串数一定得是奇数.
思路
我们发现用一个n和n+2的由相同的字符组成的串,n为奇数,其两者的子串满足条件,但是不能挨着
/*
* @Description: stay hungry ,stay foolish
* @Descripttion: Calm and analyze
* @Author: Aklice
* @Date: 2021-07-14 22:48:48
* @LastEditors: Aklice
* @LastEditTime: 2021-08-08 14:34:45
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0)
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
/*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*/
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
if(n <= 26){
char beg = 'a';
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++){
cout << char(beg + i - 1);
}
cout << endl;
}
else{
if(n&1){
int x = n/2;
int y = n - x;
x --;y--;
while(x--)cout<<'a';
cout<<"bc";
while(y--)cout<<'a';
}
else{
int x = n/2;
int y = n - x - 1;
while(x --)cout<<'a';
cout<<'b';
while(y --)cout<<'a';
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
E. You
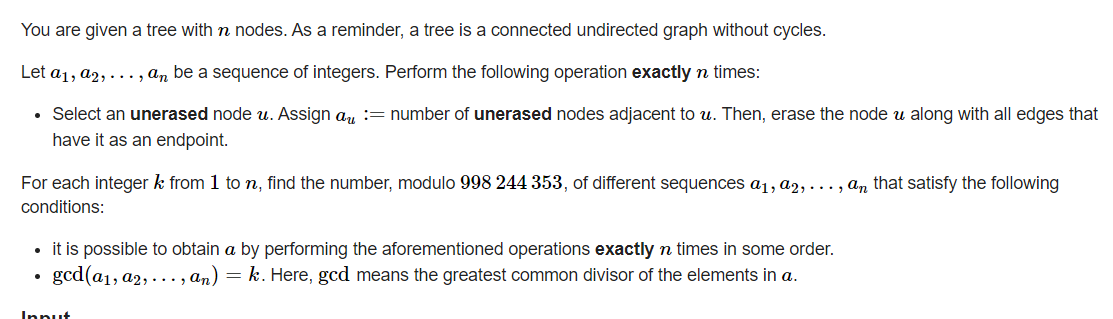
题意
给定一颗树,找出每一次满足k的\(a_i\)的序列
思路
每一次删边都会对一个点的大小做贡献,那么\(\sum(a_1,......,a_n) = n - 1\),同时每个\(a_imod k ==0\),那么\(n-1modk==0\),于是,我们要可以直接枚举n-1的因子.然后做dfs,对于每一个fa和son,如果\(a[son]modk==0\)那么这个边就加到a[fa]上,如果,加给a[son]或者不加都不能使其modk0,那么可以直接退出.特别的对于k0时,所有的情况等于这条边給两个端点哪上加的问题,则\(num[k] = 2^(n-1))\)
/*
* @Description: stay hungry ,stay foolish
* @Descripttion: Calm and analyze
* @Author: Aklice
* @Date: 2021-07-06 19:11:03
* @LastEditors: Aklice
* @LastEditTime: 2021-08-11 16:32:45
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int mod = 998244353;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
vector<int>G[maxn];
ll num[maxn];
int cnt[maxn];
int flag = 0;
ll qpow(ll a,ll b){
ll res = 1;
while(b){
if(b&1) res *= a;
res %= mod;
a *= a;
a %= mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res % mod;
}
void dfs(int u,int fa,int div){
if(flag) return ;
for(auto v : G[u]){
cnt[u] %= div;
if(v == fa) continue;
dfs(v,u,div);
}
if(cnt[u]%div == 0) cnt[fa]++;
else{
if(fa >= 1) cnt[u] ++;
if(cnt[u] % div != 0) flag = 1;
}
if(flag) return ;
}
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i < n;i ++){
int u,v;
cin >> u >> v;
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
num[1] = qpow(2,n - 1);
for(int i = 2;i <= n;i ++){
if((n - 1)%i == 0){
flag = 0;
dfs(1,-1,i);
num[i] = flag^1;
memset(cnt,0,sizeof cnt);
}
}
for(int i = n;i >=1;i --){
for(int j = 2;i * j <= n;j ++){
num[i] -= num[j*i];
}
}
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) {
cout << (num[i] + mod)%mod;
cout << ' ';
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++){
num[i] = 0;
G[i].clear();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t --) solve();
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号