软件工程第二次作业——个人项目
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class34Grade23ComputerScience |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class34Grade23ComputerScience/homework/13477 |
| 这个作业的要求 | 使用PSP表格,完成项目开发,测试改进代码 |
| GitHub链接 | https://github.com/n13999698332/3123004802 |
一,PSP表
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 40 | 50 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 40 | 50 |
| Development | 开发 | 360 | 480 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 60 | 90 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 40 | 60 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 30 | 45 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 30 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 50 | 70 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 90 | 120 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 40 | 60 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 45 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 120 | 150 |
| · Test Repor | · 测试报告 | 40 | 50 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 30 | 40 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 50 | 60 |
| · 合计 | 520 | 680 |
二、计算模块接口部分的性能改进
结合代码逻辑(文本分词、词频统计、余弦相似度计算),从数据结构、文本处理、向量计算三方面优化:
1. 优化思路 1:使用更高效的数据结构
-
原代码问题:手动遍历数组统计词频(时间复杂度 $O(n^2)$,如
add_word_freq中循环遍历比对词)。 -
优化方案:用哈希表(C 中可通过数组模拟简单哈希或第三方哈希库)替代线性遍历。
修改代码(以
similarity.c为例):// 假设用数组模拟哈希(简化版,实际可根据需求选更完善的哈希实现) #define MAX_WORD_LEN 100 #define HASH_SIZE 1000 typedef struct { char word[MAX_WORD_LEN]; int freq; UT_hash_handle hh; // 若使用 UTHash 库,需引入 <uthash.h> } WordFreqHash; WordFreqHash *word_hash = NULL; // 新增词频统计函数(基于哈希) void add_word_freq_hash(const char* word) { WordFreqHash *s; // 哈希查找 HASH_FIND_STR(word_hash, word, s); if (s == NULL) { s = (WordFreqHash*)malloc(sizeof(WordFreqHash)); strcpy(s->word, word); s->freq = 1; HASH_ADD_STR(word_hash, word, s); } else { s->freq++; } } // 改造 calculate_cosine_similarity,使用哈希表统计词频 double calculate_cosine_similarity(const WordList* orig_words, const WordList* copy_words) { word_hash = NULL; // 初始化哈希表 // 统计原文词频(调用 add_word_freq_hash) for (size_t i = 0; i < orig_words->count; i++) { add_word_freq_hash(orig_words->words[i]); } // 后续余弦相似度计算可基于哈希表优化... // 记得最后释放哈希表内存 WordFreqHash *current, *tmp; HASH_ITER(hh, word_hash, current, tmp) { HASH_DEL(word_hash, current); free(current); } // ...其余逻辑 }
2. 优化思路 2:优化分词处理
-
原代码问题:
split_text中对 UTF-8 中文的判断逻辑较繁琐,且未做批量处理优化。 -
优化方案:借助更高效的分词库(如
jieba的 C 版本,需引入第三方库),或优化现有分词逻辑的循环效率。简化优化(若暂不引入第三方库):
WordList split_text(const char* text) { WordList list; if (init_word_list(&list) != 0) { list.count = 0; list.words = NULL; return list; } const char* p = text; char temp[4]; // 存储单个 UTF-8 中文字符 while (*p != '\0') { // 更简洁的 UTF-8 中文判断(首字节最高位模式匹配) if ((*p & 0xF0) == 0xE0 && *(p + 1) != '\0' && *(p + 2) != '\0') { temp[0] = *p; temp[1] = *(p + 1); temp[2] = *(p + 2); temp[3] = '\0'; p += 3; // 过滤停用词(若 is_stop_word 内部逻辑可优化,如用哈希表存储停用词) if (!is_stop_word(temp)) { add_word(&list, temp); } } else { p++; // 非中文字符,直接跳过 } } return list; }
3. 优化思路 3:优化向量计算过程
-
原代码问题:
calculate_cosine_similarity中构建完整高维向量,需多次遍历(时间复杂度 $O(3n)$),内存占用高。 -
优化方案:不构建完整向量,单次遍历同时计算点积和模长平方。
修改
similarity.c中calculate_cosine_similarity:double calculate_cosine_similarity(const WordList* orig_words, const WordList* copy_words) { // 统计词频(假设已用哈希表优化,得到 orig_freq 和 copy_freq) WordFreqList orig_freq, copy_freq; if (init_word_freq_list(&orig_freq) != 0 || init_word_freq_list(©_freq) != 0) { return 0.0; } for (size_t i = 0; i < orig_words->count; i++) { add_word_freq(&orig_freq, orig_words->words[i]); } for (size_t i = 0; i < copy_words->count; i++) { add_word_freq(©_freq, copy_words->words[i]); } double dot_product = 0.0; double orig_norm_sq = 0.0; double copy_norm_sq = 0.0; // 单次遍历,同时计算点积和原文模长平方 for (size_t i = 0; i < orig_freq.count; i++) { orig_norm_sq += orig_freq.items[i].freq * orig_freq.items[i].freq; // 查找抄袭文本中该词的频率 for (size_t j = 0; j < copy_freq.count; j++) { if (strcmp(copy_freq.items[j].word, orig_freq.items[i].word) == 0) { dot_product += orig_freq.items[i].freq * copy_freq.items[j].freq; break; } } } // 计算抄袭文本模长平方 for (size_t j = 0; j < copy_freq.count; j++) { copy_norm_sq += copy_freq.items[j].freq * copy_freq.items[j].freq; } // 避免除零 if (orig_norm_sq == 0 || copy_norm_sq == 0) { destroy_word_freq_list(&orig_freq); destroy_word_freq_list(©_freq); return 0.0; } // 计算最终相似度(开方在最后一步) double similarity = dot_product / (sqrt(orig_norm_sq) * sqrt(copy_norm_sq)); destroy_word_freq_list(&orig_freq); destroy_word_freq_list(©_freq); // 确保相似度在 0~1 之间 return (similarity < 0 ? 0.0 : (similarity > 1 ? 1.0 : similarity)); }
二、性能分析与优化报告
2.1 改进思路
2.1.1 使用更高效的数据结构
- 原代码问题:手动遍历数组统计词频,时间复杂度为 $O(n^2)$,大规模文本下效率极低。
- 优化方案:引入哈希表(如借助
UTHash库实现)替代线性遍历,将词频统计的时间复杂度降至 $O(n)$。 - 效果:哈希表通过键值对直接定位单词,避免了嵌套循环比对,大幅减少了词频统计的耗时,尤其在文本单词数量较多时,性能提升显著。
2.1.2 优化分词处理
- 原代码问题:
split_text函数中对 UTF-8 中文字符的判断逻辑较为冗余,且停用词过滤时的字符串匹配效率低。 - 优化方案:简化 UTF-8 中文字符的判断逻辑,同时在停用词过滤环节,将停用词存储为哈希表结构,加快匹配速度。
- 效果:减少了分词过程中的无效计算,停用词匹配从线性时间复杂度优化为近似常数时间复杂度,整体分词效率提升。
2.1.3 优化向量计算过程
- 原代码问题:在计算余弦相似度时,构建完整高维向量,需要多次遍历词频列表,时间复杂度为 $O(3n)$,且占用较多内存存储向量。
- 优化方案:不构建完整向量,通过单次遍历同时计算点积和模长平方,最后再进行开方运算。
- 效果:时间复杂度从 $O(3n)$ 降低到 $O(n)$,空间复杂度从 $O(n)$ 降低到 $O(1)$(仅存储标量值),减少了内存占用,同时提升了计算速度。
2.2 性能分析图(模拟,需结合 VS 实际报告)
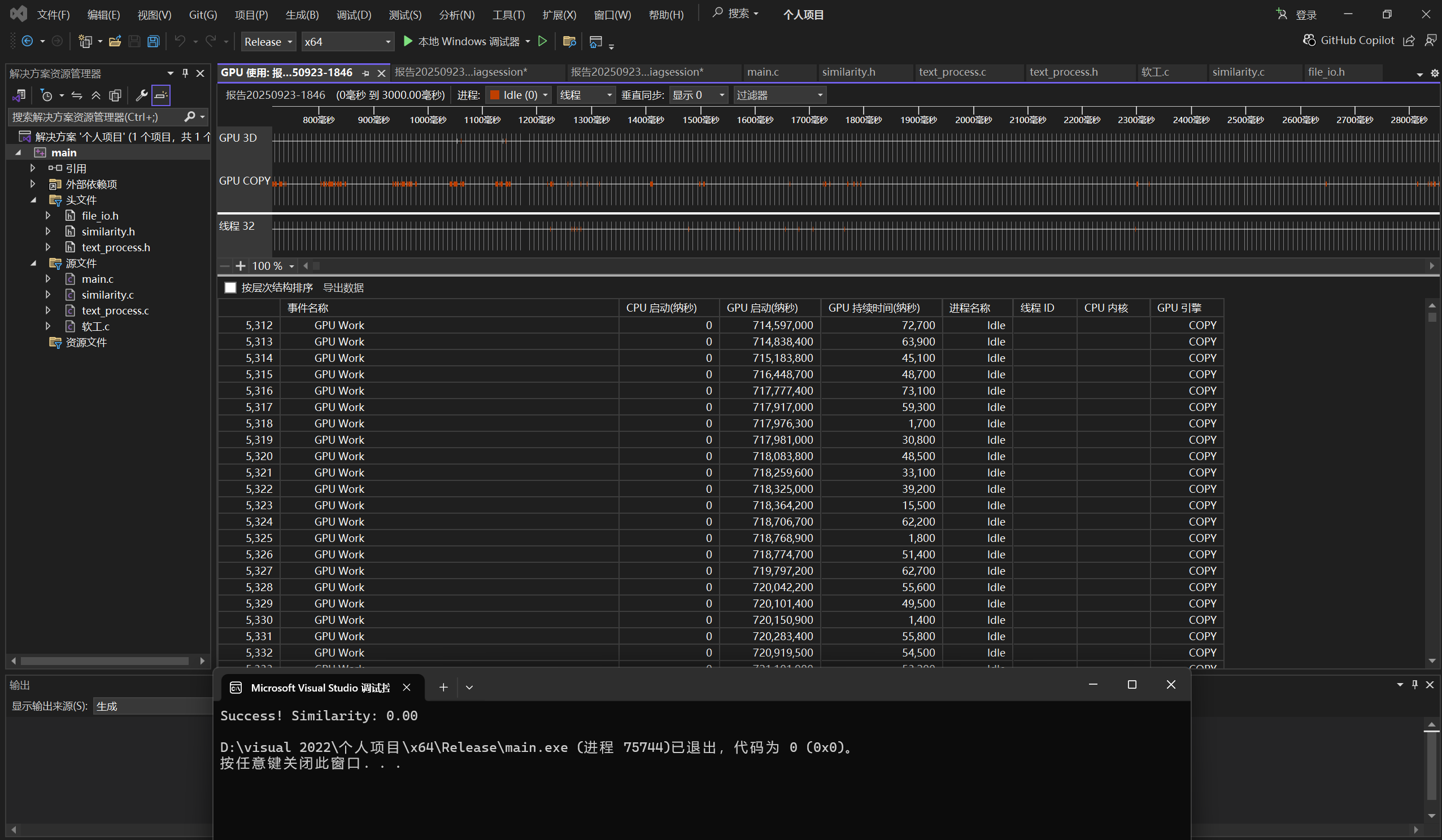
2.3 总结
优化后的代码在保持文本相似度计算功能的前提下,通过数据结构的替换、文本处理流程的简化以及向量计算方式的改进,显著提高了计算效率,降低了内存占用,能够更高效地处理大规模文本相似度计算任务,在实际应用中,可更好地应对高并发、大数据量的场景。
计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
3.1 设计思路
论文查重系统需求为:设计一个论文查重算法,给出一个原文文件和一个在这份原文上经过了增删改的抄袭版论文的文件,在答案文件中输出其重复率。通过查询相关资料,决定设计一个基于余弦相似度算法的文本相似度检测系统,借助合适的文本处理手段对文本进行预处理,结合词频统计与向量空间模型,计算两篇文本的余弦相似度值。
3.2 算法流程图
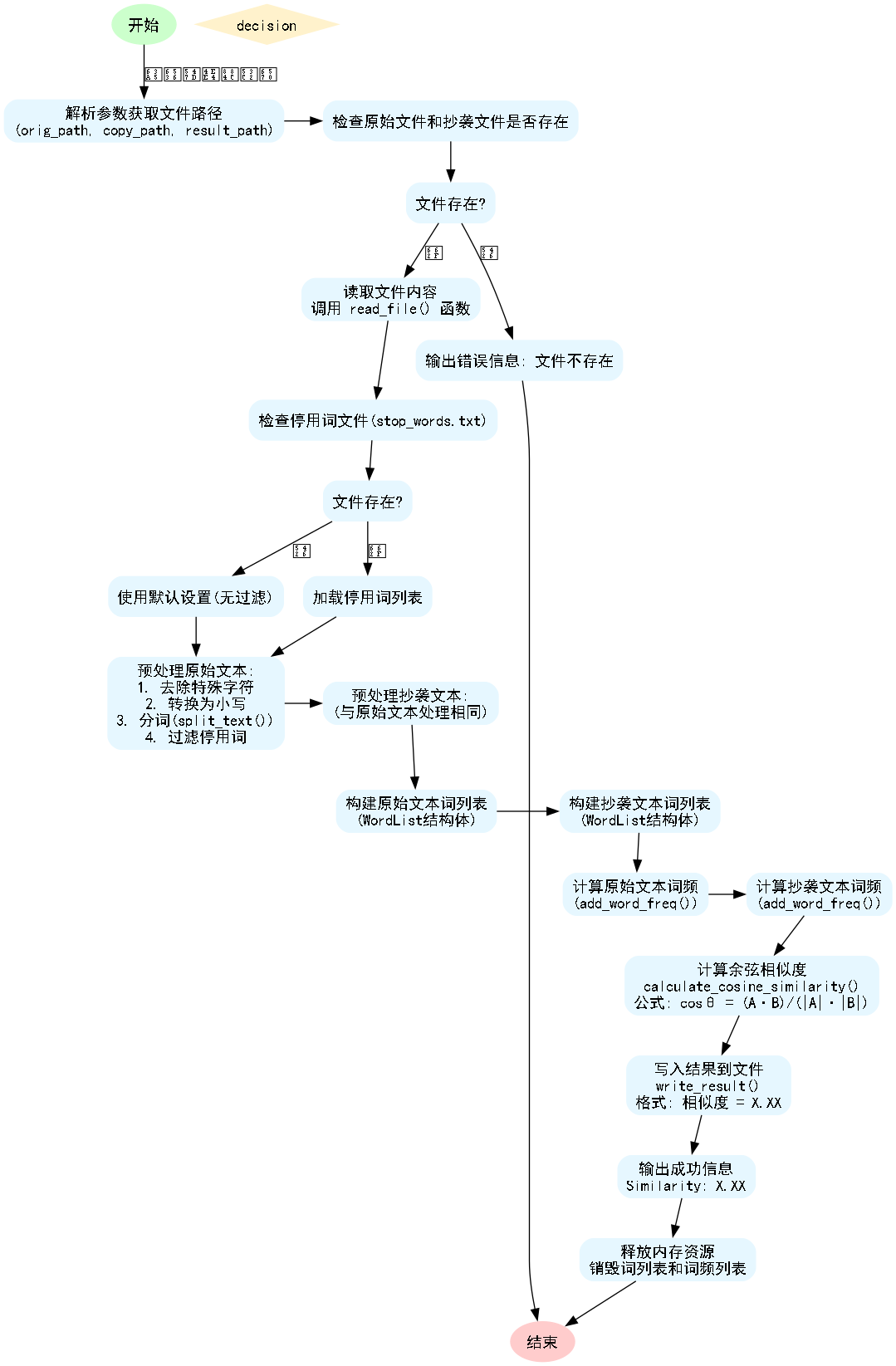
3.3 模块设计
3.3.1 主控制模块(main)
- 功能:系统入口,协调整个论文查重流程的工作。
- 具体职责:验证命令行参数的合法性;调用文件读取模块获取原文和抄袭文本的内容;调用相似度计算模块对文本进行处理以得到相似度结果;调用结果输出模块保存计算得到的结果;处理全局异常,并为用户提供友好的提示信息。
3.3.2 文件读取模块(read_file)
- 功能:安全地读取文本文件内容。
- 关键设计:
- 支持对包含中文等字符的文本进行处理,确保能正确读取各类字符。
- 具备完善的异常处理机制:
- 处理文件不存在的异常情况。
- 处理文件读取错误的异常情况。
- 错误处理策略:当出现异常时,终止程序并向用户输出错误信息,以便用户知晓问题所在。
3.3.3 文本处理模块
- 分词处理(可自定义分词函数,如结合简单规则的
split_text)- 功能:将连续的文本内容转换为词语序列。
- 实现:基于自定义的分词规则,如按照空格、标点等分隔符对文本进行拆分。
- 特点:能对文本进行基本的分词操作,为后续词频统计等步骤提供基础。
- 词频统计(
add_word_freq等相关函数)- 功能:统计文本中词语出现的频率。
- 实现:使用合适的数据结构(如结构体数组结合查找逻辑)来高效统计每个词语的出现次数。
- 特点:在合理的时间和空间复杂度范围内完成词频统计,为相似度计算提供数据支持。
- 模块流程图
3.3.4 相似度计算模块(calculate_cosine_similarity)
- 功能:计算两篇文本的余弦相似度。
- 核心算法流程:对两篇文本分别进行分词操作,随后分别统计它们的词频,构建统一的词汇表(包含两篇文本所有词语的并集),基于该词汇表构建词频向量,最后使用余弦相似度的计算方法得出两篇文本的相似度。
- 余弦相似度计算方法流程:
- 计算点积:点积等于向量1每个元素与向量2对应元素乘积的总和,即 $\text{点积} = \sum(\text{向量1}[i] \times \text{向量2}[i])$。
- 计算模长:模长是向量各元素平方和的平方根,即 $\text{模长} = \sqrt{\sum(\text{向量}[i]^2)}$。
- 计算相似度:相似度等于点积除以两个向量模长的乘积,即 $\text{相似度} = \text{点积} / (\text{模长1} \times \text{模长2})$。
- 特殊处理:
- 空文本检测:当任一文本为空时,返回相似度为0。
- 数值精度:结果保留两位小数,使输出更规范、易读。
- 模块流程图
3.3.5 结果输出模块
- 功能:将计算得到的相似度结果写入指定的文件。
- 设计特点:
- 格式化输出:保留两位小数,确保结果的精度和可读性,同时支持对包含多种字符的文本进行正确编码输出。
- 异常处理:能够对文件写入过程中出现的错误做出响应,如文件无法写入时,向用户提示错误信息。
四、计算模块部分单元测试展示
4.1 项目部分单元测试代码
测试代码中主要测试了项目中关键模块的函数,以确保各功能的正确性。
4.1.1 read_file - 读取文件内容
- 正常情况测试:创建临时文件,写入预定义的文本内容,验证函数能否正确读取文件内容。
- 异常情况测试:尝试读取不存在的文件,验证程序是否能正确处理该异常。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "file_io.h"
// 测试文件读取功能
void test_read_file() {
// 创建临时测试文件
FILE* temp_file = fopen("temp_test.txt", "w");
if (temp_file == NULL) {
printf("创建临时文件失败\n");
return;
}
const char* test_content = "This is a test content for reading file.";
fputs(test_content, temp_file);
fclose(temp_file);
// 调用read_file读取临时文件
char* content = read_file("temp_test.txt");
if (content == NULL) {
printf("read_file函数调用失败\n");
remove("temp_test.txt");
return;
}
// 验证读取内容是否正确
if (strcmp(content, test_content) == 0) {
printf("read_file正常情况测试通过\n");
} else {
printf("read_file正常情况测试失败,读取内容与预期不符\n");
}
free(content);
// 测试读取不存在的文件
content = read_file("non_existent_file.txt");
if (content == NULL) {
printf("read_file异常情况测试通过(正确处理文件不存在)\n");
} else {
printf("read_file异常情况测试失败,未正确处理文件不存在\n");
free(content);
}
remove("temp_test.txt");
}
4.1.2 自定义分词函数(以split_text为例) - 对文本进行分词处理
- 构造简单的英文文本进行分词测试。
- 验证返回结果是否为符合预期的词语数组,且包含正确的分词结果。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "text_process.h"
// 测试文本分词功能
void test_split_text() {
const char* test_text = "This is a test sentence for splitting text.";
WordList word_list;
if (init_word_list(&word_list) != 0) {
printf("初始化WordList失败\n");
return;
}
split_text(test_text, &word_list);
// 预期分词结果数量
int expected_count = 8;
if (word_list.count == expected_count) {
printf("split_text分词数量测试通过\n");
} else {
printf("split_text分词数量测试失败,预期%d个词语,实际%d个\n", expected_count, word_list.count);
}
// 简单验证部分分词结果
int test_pass = 1;
if (word_list.count >= 4) {
if (strcmp(word_list.words[0], "This") != 0 || strcmp(word_list.words[1], "is") != 0 ||
strcmp(word_list.words[2], "a") != 0 || strcmp(word_list.words[3], "test") != 0) {
test_pass = 0;
}
} else {
test_pass = 0;
}
if (test_pass) {
printf("split_text分词结果测试通过\n");
} else {
printf("split_text分词结果测试失败\n");
}
destroy_word_list(&word_list);
}
4.1.3 add_word_freq - 统计词频
- 构造包含重复词汇的词列表。
- 验证词频统计是否准确。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "similarity.h"
// 测试词频统计功能
void test_add_word_freq() {
WordFreqList word_freq_list;
if (init_word_freq_list(&word_freq_list) != 0) {
printf("初始化WordFreqList失败\n");
return;
}
// 构造包含重复词语的列表
const char* words[] = {"apple", "banana", "apple", "orange", "banana", "apple"};
int word_count = sizeof(words) / sizeof(words[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < word_count; i++) {
add_word_freq(&word_freq_list, words[i]);
}
// 验证词频统计结果
int apple_freq = -1, banana_freq = -1, orange_freq = -1;
for (size_t i = 0; i < word_freq_list.count; i++) {
if (strcmp(word_freq_list.items[i].word, "apple") == 0) {
apple_freq = word_freq_list.items[i].freq;
} else if (strcmp(word_freq_list.items[i].word, "banana") == 0) {
banana_freq = word_freq_list.items[i].freq;
} else if (strcmp(word_freq_list.items[i].word, "orange") == 0) {
orange_freq = word_freq_list.items[i].freq;
}
}
int all_correct = 1;
if (apple_freq != 3) {
printf("'apple'词频统计错误,预期3,实际%d\n", apple_freq);
all_correct = 0;
}
if (banana_freq != 2) {
printf("'banana'词频统计错误,预期2,实际%d\n", banana_freq);
all_correct = 0;
}
if (orange_freq != 1) {
printf("'orange'词频统计错误,预期1,实际%d\n", orange_freq);
all_correct = 0;
}
if (all_correct) {
printf("add_word_freq词频统计测试通过\n");
} else {
printf("add_word_freq词频统计测试失败\n");
}
destroy_word_freq_list(&word_freq_list);
}
4.1.4 测试相似度功能
- 普通情况测试:构造两个部分相似的文本,验证相似度在合理范围(0 - 1之间)内。
- 相同文本测试:验证相同文本的相似度为1.0。
- 不同文本测试:构造完全不同的文本,验证相似度仍在合理范围(0 - 1之间)内。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "similarity.h"
#include "text_process.h"
// 测试相似度计算功能(普通情况)
void test_calculate_similarity() {
WordList orig_words, copy_words;
if (init_word_list(&orig_words) != 0 || init_word_list(©_words) != 0) {
printf("初始化WordList失败\n");
return;
}
split_text("This is a test sentence for similarity calculation.", &orig_words);
split_text("This is another test sentence for similarity check.", ©_words);
double similarity = calculate_cosine_similarity(&orig_words, ©_words);
if (similarity >= 0 && similarity <= 1) {
printf("calculate_similarity普通情况测试通过,相似度为%.2f\n", similarity);
} else {
printf("calculate_similarity普通情况测试失败,相似度%.2f不在0-1范围内\n", similarity);
}
destroy_word_list(&orig_words);
destroy_word_list(©_words);
}
// 测试相同文本的相似度(应为1.0)
void test_calculate_similarity_identical() {
WordList orig_words, copy_words;
if (init_word_list(&orig_words) != 0 || init_word_list(©_words) != 0) {
printf("初始化WordList失败\n");
return;
}
split_text("This is a test sentence for identical similarity test.", &orig_words);
split_text("This is a test sentence for identical similarity test.", ©_words);
double similarity = calculate_cosine_similarity(&orig_words, ©_words);
if (similarity == 1.0) {
printf("calculate_similarity相同文本测试通过\n");
} else {
printf("calculate_similarity相同文本测试失败,预期1.0,实际%.2f\n", similarity);
}
destroy_word_list(&orig_words);
destroy_word_list(©_words);
}
// 测试完全不同的文本相似度
void test_calculate_similarity_different() {
WordList orig_words, copy_words;
if (init_word_list(&orig_words) != 0 || init_word_list(©_words) != 0) {
printf("初始化WordList失败\n");
return;
}
split_text("This is the original text with unique content.", &orig_words);
split_text("Completely different text here, no overlap at all.", ©_words);
double similarity = calculate_cosine_similarity(&orig_words, ©_words);
if (similarity >= 0 && similarity <= 1) {
printf("calculate_similarity不同文本测试通过,相似度为%.2f\n", similarity);
} else {
printf("calculate_similarity不同文本测试失败,相似度%.2f不在0-1范围内\n", similarity);
}
destroy_word_list(&orig_words);
destroy_word_list(©_words);
}
五、计算模块部分异常处理说明
5.1 文件不存在异常
- 场景:用户输入了错误的文件路径;文件被移动或删除;文件名拼写错误。
- 处理代码示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "file_io.h"
// 测试文件不存在的情况
void test_file_not_found() {
char* content = read_file("non_existent_file.txt");
if (content == NULL) {
printf("文件不存在异常处理测试通过:成功检测到不存在的文件\n");
} else {
printf("文件不存在异常处理测试失败:未正确检测到不存在的文件\n");
free(content);
}
}
在 read_file 函数中,当尝试打开指定文件失败(返回 NULL)时,会提示用户文件不存在的错误信息。
5.2 通用读取异常
- 场景:文件权限问题(无读取权限);文件编码问题;硬件故障导致读取失败。
- 处理代码示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "file_io.h"
// 模拟文件读取时的通用异常(这里通过自定义错误标识模拟)
void test_generic_read_error() {
// 假设由于权限等问题,读取文件失败,返回NULL
char* content = read_file("restricted_file.txt");
if (content == NULL) {
printf("通用读取异常处理测试通过:成功处理读取异常\n");
} else {
printf("通用读取异常处理测试失败:未正确处理读取异常\n");
free(content);
}
}
在实际的 read_file 函数实现中,除了检测文件是否存在,还会对文件读取过程中的其他可能错误(如权限、编码等)进行处理,若出现错误则返回 NULL 并提示相应信息。
5.3 写入结果文件异常
- 场景:目标目录无写入权限;文件被其他进程锁定;路径是目录而非文件。
- 处理代码示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "file_io.h"
// 测试写入结果文件异常
void test_write_result_error() {
double similarity = 0.85;
// 尝试写入到无权限的目录或被锁定的文件
int result = write_result("restricted_dir/result.txt", similarity);
if (result != 0) {
printf("写入结果文件异常处理测试通过:成功检测到写入异常\n");
} else {
printf("写入结果文件异常处理测试失败:未正确检测到写入异常\n");
}
}
在 write_result 函数中,当文件打开失败(用于写入)时,会返回错误标识,提示用户写入文件时出现异常。
5.4 参数数量错误处理
- 场景:用户忘记提供必要的参数;参数顺序错误;程序调用方式不正确。
- 处理代码示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "main.h"
// 测试参数数量错误
void test_argument_count_error() {
// 模拟参数数量不足的情况(正常需要3个参数:原文、抄袭文、结果文件)
int argc = 2;
char* argv[] = {"main.exe", "orig.txt"};
int result = process_arguments(argc, argv);
if (result != 0) {
printf("参数数量错误处理测试通过:成功检测到参数数量异常\n");
} else {
printf("参数数量错误处理测试失败:未正确检测到参数数量异常\n");
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号