简单逆向Java程序
前置
来源
这个程序是我同学编写的一个学生分数管理系统,我将对这个已经编译的程序进行测试、逆向,找出其中的问题,并进行改进。
运行环境
- macOS 15.4
- IntelliJ IDEA 2024.2.3
- OpenJDK 23.0.2
- TomCat 11.0.4
- Safari 15.4
运行结果
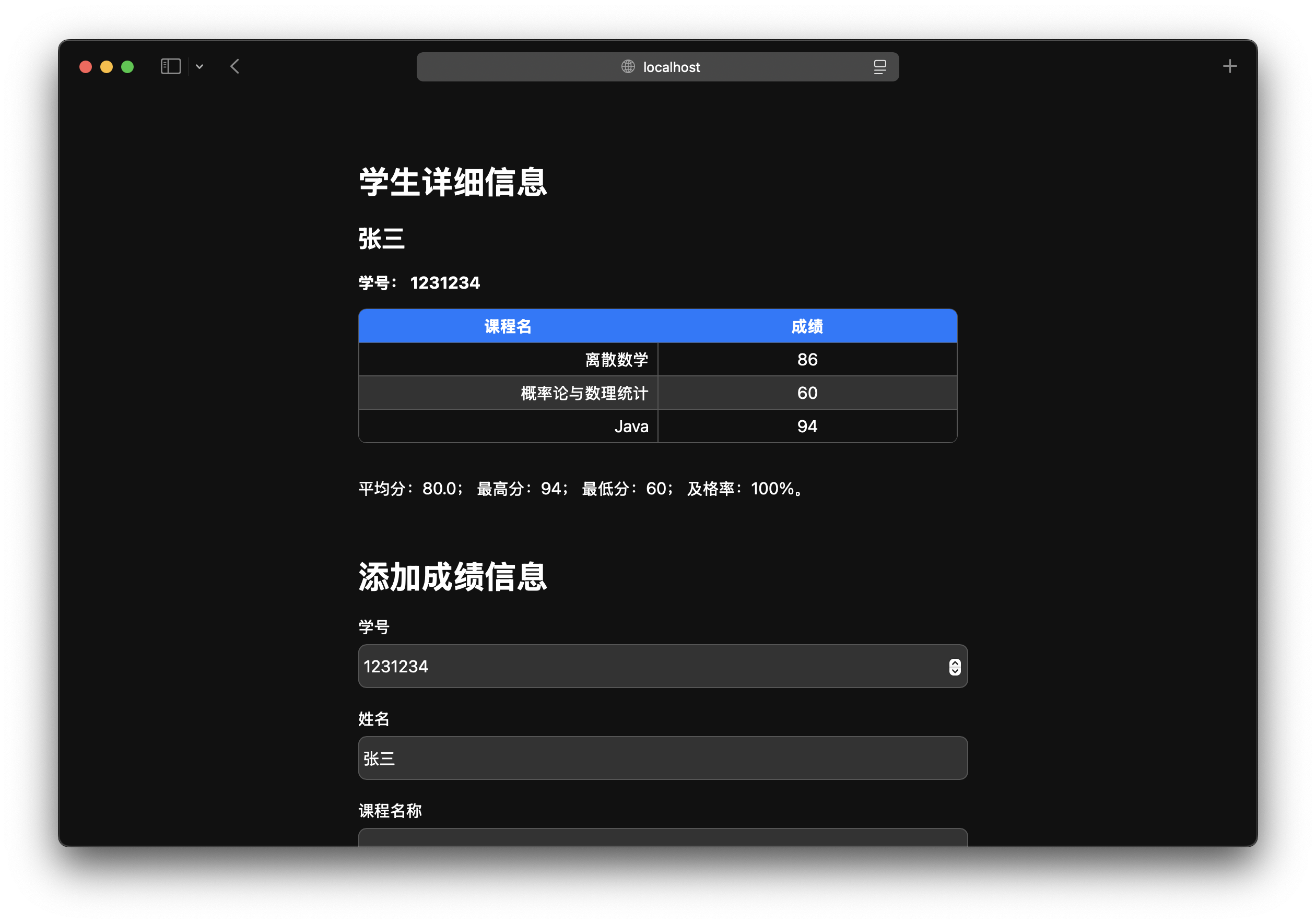
主要问题
在使用了这个程序之后,我发现了以下几个问题:
- 缺少绩点计算;
- 添加学生时,没有对学号进行唯一性检查;
- 添加成绩时,没有对成绩进行唯一性检查。
接下来,我将对这些问题进行改进。
逆向
朋友不够好心,没有提供源码,所以我只能通过逆向的方式来找出问题。
得益于IntelliJ IDEA内置的FernFlower,我能迅速的逆向Java Class,于是很快就破解出了这个项目的代码。
Score.class
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package com.example.javadzy;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Score implements Serializable {
private String course;
private int grade;
public Score(String course, int grade) {
this.course = course;
this.grade = grade;
}
public String getCourse() {
return this.course;
}
public void setCourse(String course) {
this.course = course;
}
public int getGrade() {
return this.grade;
}
public void setGrade(int grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
}
Student.class
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package com.example.javadzy;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private ArrayList<Score> scores;
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.scores = new ArrayList();
}
public Student(String name, ArrayList<Score> scores) {
this.name = name;
this.scores = scores;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public ArrayList<Score> getScores() {
return this.scores;
}
public void addScore(Score score) {
this.scores.add(score);
}
public int getSize() {
return this.scores.size();
}
public class Statistics {
public float average = 0.0F;
public int max = 0;
public int min = 100;
public float passRate = 0.0F;
public Statistics(final Student this$0) {
int sum = 0;
int passCount = 0;
Iterator var4 = this$0.scores.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Score score = (Score)var4.next();
sum += score.getGrade();
if (score.getGrade() > this.max) {
this.max = score.getGrade();
}
if (score.getGrade() < this.min) {
this.min = score.getGrade();
}
if (score.getGrade() >= 60) {
++passCount;
}
}
if (!this$0.scores.isEmpty()) {
this.average = (float)sum / (float)this$0.scores.size();
this.passRate = (float)passCount / (float)this$0.scores.size();
}
}
}
}
StudentDataHandler.class
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package com.example.javadzy;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class StudentDataHandler {
private static StudentDataHandler instance = null;
private TreeMap<Integer, Student> students;
private final File file = new File(System.getProperty("user.home"), "/.cache/data.dat");
private void readData() {
System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
try {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(this.file));
try {
this.students = (TreeMap)ois.readObject();
} catch (Throwable var5) {
try {
ois.close();
} catch (Throwable var4) {
var5.addSuppressed(var4);
}
throw var5;
}
ois.close();
} catch (Exception var6) {
Exception e = var6;
this.students = new TreeMap();
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void writeData() {
try {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(this.file));
try {
oos.writeObject(this.students);
} catch (Throwable var5) {
try {
oos.close();
} catch (Throwable var4) {
var5.addSuppressed(var4);
}
throw var5;
}
oos.close();
} catch (Exception var6) {
Exception e = var6;
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private StudentDataHandler() {
this.readData();
}
public static synchronized StudentDataHandler getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new StudentDataHandler();
}
return instance;
}
public void addStudent(int id, String name) throws StudentDataException {
Student student = new Student(name);
if (!this.students.containsKey(id)) {
this.students.put(id, student);
this.writeData();
} else {
throw new StudentDataException("学号已存在");
}
}
public void addScore(int id, String course, int grade) throws StudentDataException {
if (this.students.containsKey(id)) {
Student student = (Student)this.students.get(id);
student.addScore(new Score(course, grade));
this.writeData();
} else {
throw new StudentDataException("学号不存在");
}
}
public void removeStudent(int id) throws StudentDataException {
if (this.students.containsKey(id)) {
this.students.remove(id);
this.writeData();
} else {
throw new StudentDataException("学号不存在");
}
}
public TreeMap<Integer, Student> getStudents() {
return this.students;
}
public Student getStudent(int id) {
return (Student)this.students.get(id);
}
}
JSP文件无需逆向,因为它们不会被编译,这里就不贴出来了。
改进
补全绩点计算
观察到Student.class中的Statistics子类,我决定在这里添加绩点计算。
首先添加了一个gpa方法,用于计算绩点。随后在Statistics构造函数中的循环调用这个方法,以此便可以计算出平均绩点。
Student.class
public class Statistics {
public float average;
public int max;
public int min;
public float passRate;
public float gpa;
public Statistics() {
this.average = 0;
this.max = 0;
this.min = 100;
this.passRate = 0;
this.gpa = 0;
int sum = 0;
int passCount = 0;
double gpaSum = 0;
for (Score score : scores) {
sum += score.getGrade();
gpaSum += gpa(score.getGrade());
if (score.getGrade() > max) {
max = score.getGrade();
}
if (score.getGrade() < min) {
min = score.getGrade();
}
if (score.getGrade() >= 60) {
passCount++;
}
}
if (!scores.isEmpty()) {
average = (float) sum / scores.size();
passRate = (float) passCount / scores.size();
gpa = (float) gpaSum / scores.size();
}
}
public double gpa(float score) {
if (score >= 90) {
return 4;
} else if (score >= 85) {
return 3.7;
} else if (score >= 82) {
return 3.3;
} else if (score >= 78) {
return 3;
} else if (score >= 75) {
return 2.7;
} else if (score >= 72) {
return 2.3;
} else if (score >= 68) {
return 2;
} else if (score >= 64) {
return 1.5;
} else if (score >= 60) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
我还调整了studentDetail.jsp,以便以正确的格式显示绩点。
studentDetail.jsp
<p>
平均绩点:<%= String.format("%.00f",stats.gpa) %>。
平均分:<%= String.format("%.00f",stats.average) %>;
最高分:<%= stats.max %>;
最低分:<%= stats.min %>;
及格率:<%= String.format("%.0f%%",stats.passRate * 100) %>。
</p>
补全唯一性检查
观察StudentDataHandler.class,发现添加学生addStudent和添加成绩addScore两个方法实际都进行了对学号进行唯一性检查。
在检查到重复学号后,抛出了StudentDataException异常,这两个方法所抛出的异常实际上也被JSP处理了,但是并没有显示。
addStudent.jsp
<%
if (request.getMethod().equalsIgnoreCase("POST")) {
int id = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("id"));
String name = request.getParameter("name");
try {
StudentDataHandler.getInstance().addStudent(id, name);
} catch (StudentDataException e) {
out.println("<p>已有重复学生</p>");
} finally {
out.println("<p>学生已添加成功!</p>");
}
response.sendRedirect("index.jsp");
}
%>
studentDetail.jsp
<%
if (request.getMethod().equalsIgnoreCase("POST")) {
int id2 = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("id2"));
String course = request.getParameter("course");
int scoreValue = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("score"));
try {
handler.addScore(id2, course, scoreValue);
out.println("<p>成绩已添加成功!</p>");
} catch (StudentDataException e) {
out.println("<p>添加失败: " + e.getMessage() + "</p>");
}
// Redirect to the same page with the id parameter
response.sendRedirect("studentDetail.jsp?id=" + id2);
}
%>
这是为什么呢?因为两个方法在打印出相应的错误后,随后立即被引导到其他页面,所以错误信息并没有被显示出来。
于是,我决定把在显示错误后,将页面引导到错误页面。
addStudent.jsp
<%
if (request.getMethod().equalsIgnoreCase("POST")) {
int id = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("id"));
String name = request.getParameter("name");
boolean success = true;
String errorMessage = "";
try {
StudentDataHandler.getInstance().addStudent(id, name);
} catch (StudentDataException e) {
success = false;
errorMessage = e.getMessage();
}
if (success) {
response.sendRedirect("index.jsp");
} else {
response.sendRedirect("error.jsp?message=\"" + URLEncoder.encode(errorMessage, StandardCharsets.UTF_8) + "\"");
}
}
%>
studentDetail.jsp
<%
if (request.getMethod().equalsIgnoreCase("POST")) {
int id2 = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("id2"));
String course = request.getParameter("course");
int scoreValue = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("score"));
boolean success = true;
String errorMessage = "";
try {
handler.addScore(id2, course, scoreValue);
} catch (StudentDataException e) {
success = false;
errorMessage = e.getMessage();
}
if (success) {
response.sendRedirect("studentDetail.jsp?id=" + id2);
} else {
response.sendRedirect("error.jsp?message=\"" + URLEncoder.encode(errorMessage, StandardCharsets.UTF_8) + "\"");
}
}
%>
error.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>错误</title>
<link href="main.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>出错了!</h1>
<p>错误信息: <%= request.getParameter("message") %></p>
<div class="button-container">
<a href="index.jsp" class="button">返回首页</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
但是这里又出现了一个大问题:Student类中的scores存储的是一个ArrayList<Score>,而想在ArrayList中查找是否有重复的Score对象,
最差时间复杂度是O(n),这显然是不合理的。
所以我决定重构scores的数据结构,将ArrayList<Score>改为HashMap<String, Integer>,以此来提高查找效率,同时也方便了唯一性检查。
Student.class
package com.example.javadzy;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name; // 姓名
private HashMap<String, Integer> scores;
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.scores = new HashMap<>();
}
public Student(String name, HashMap<String, Integer> scores) {
this.name = name;
this.scores = scores;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HashMap<String, Integer> getScores() {
return scores;
}
public void addScore(String course, Integer score) throws StudentDataException {
if (scores.containsKey(course)) {
throw new StudentDataException("课程名重复");
}
this.scores.put(course, score);
}
public int getSize() {
return scores.size();
}
public class Statistics {
public float average;
public int max;
public int min;
public float passRate;
public float gpa;
public Statistics() {
this.average = 0;
this.max = 0;
this.min = 100;
this.passRate = 0;
this.gpa = 0;
int sum = 0;
int passCount = 0;
double gpaSum = 0;
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> kvpair : scores.entrySet()) {
sum += kvpair.getValue();
gpaSum += gpa(kvpair.getValue());
if (kvpair.getValue() > max) {
max = kvpair.getValue();
}
if (kvpair.getValue() < min) {
min = kvpair.getValue();
}
if (kvpair.getValue() >= 60) {
passCount++;
}
}
if (!scores.isEmpty()) {
average = (float) sum / scores.size();
passRate = (float) passCount / scores.size();
gpa = (float) gpaSum / scores.size();
}
}
public double gpa(float score) {
if (score >= 90) {
return 4;
} else if (score >= 85) {
return 3.7;
} else if (score >= 82) {
return 3.3;
} else if (score >= 78) {
return 3;
} else if (score >= 75) {
return 2.7;
} else if (score >= 72) {
return 2.3;
} else if (score >= 68) {
return 2;
} else if (score >= 64) {
return 1.5;
} else if (score >= 60) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
}
于是,Student中scores的唯一性检查就这样完成了。
重构结果
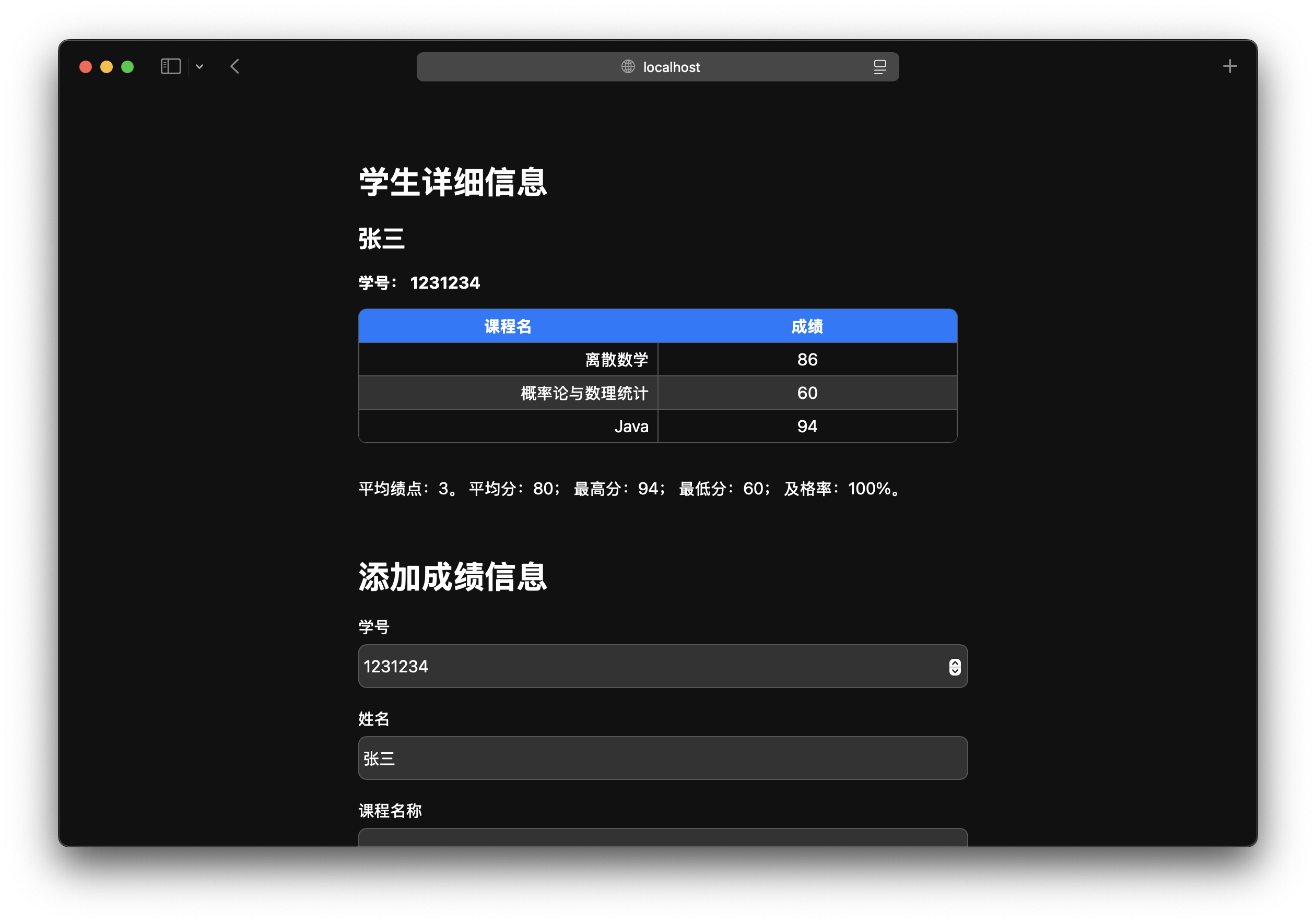
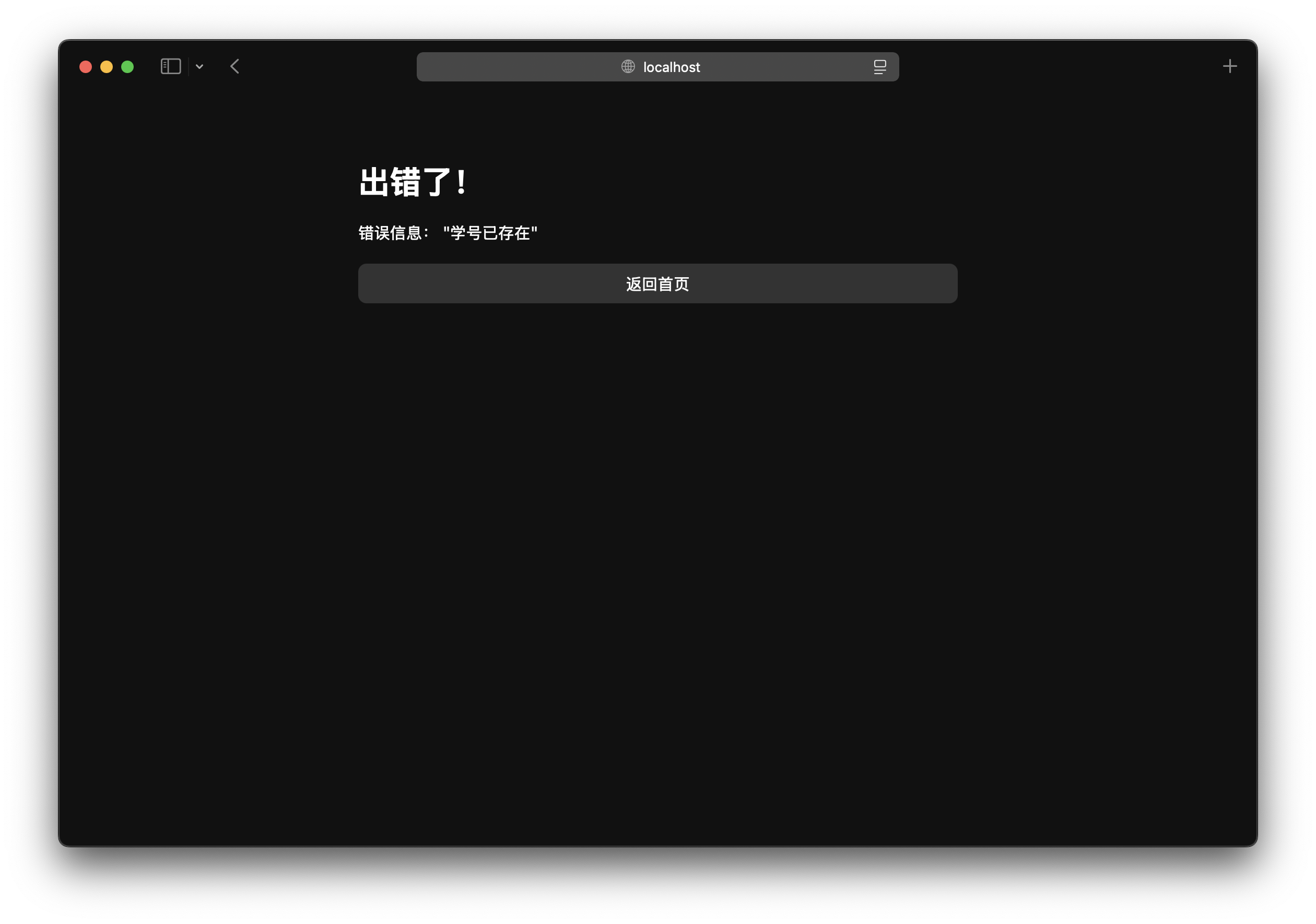
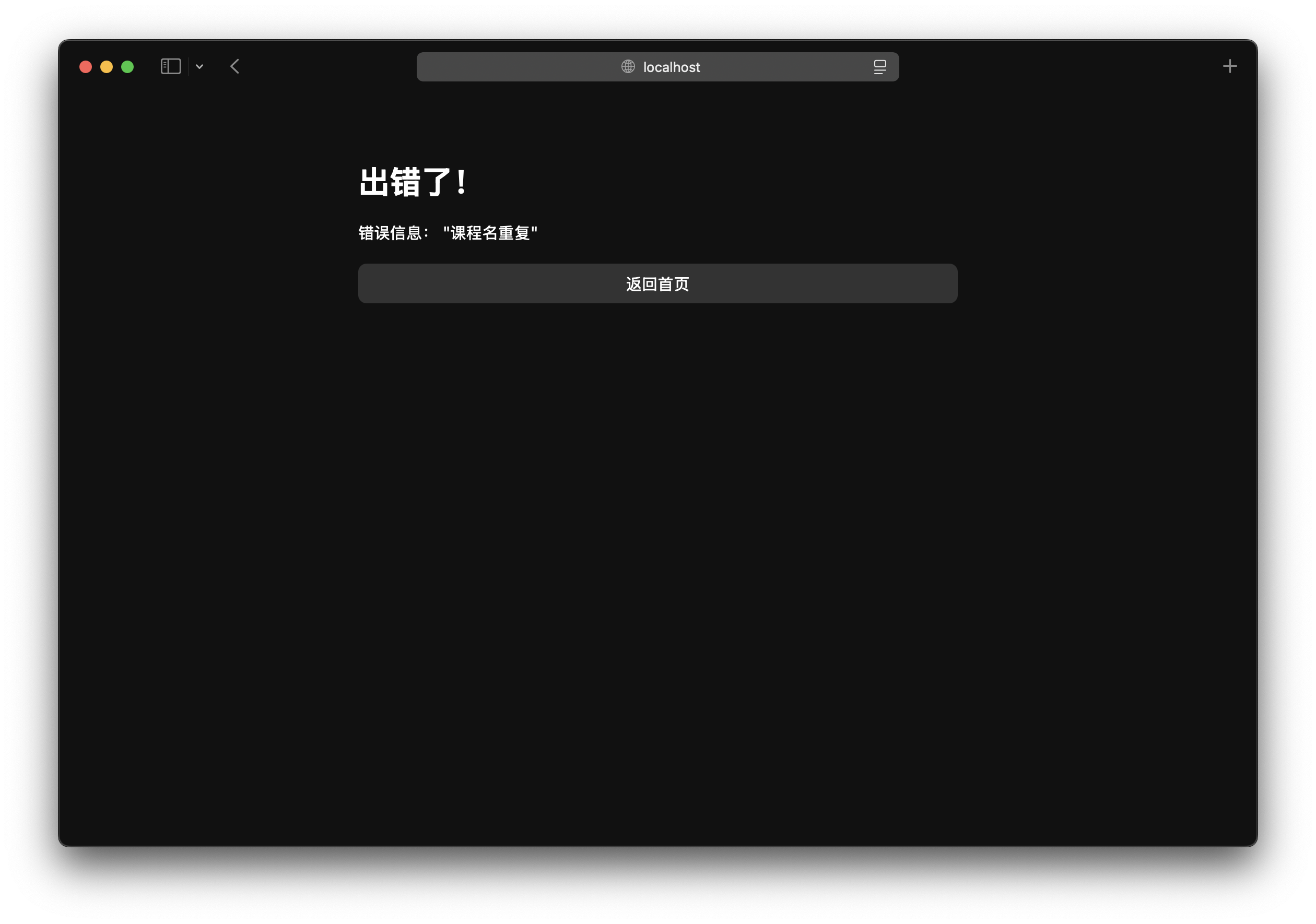
总结
在这次逆向工程和改进过程中,我遇到了以下几个难点和挑战:
难点
- 逆向工程:由于没有源码,我需要通过逆向工程工具(IntelliJ IDEA内置的FernFlower)来获取原始代码。这一过程虽然工具提供了很大帮助,但仍需要仔细分析和理解反编译后的代码;
- 数据结构重构:原始代码中使用
ArrayList<Score>存储成绩,查找重复成绩的效率较低。将其重构为HashMap<String, Integer>后,查找效率显著提高,但需要确保所有相关代码都进行了相应的修改;
异常处理和用户反馈:在添加学生和成绩时,原始代码虽然进行了唯一性检查,但异常信息没有正确反馈给用户。通过修改JSP页面,确保用户能够看到详细的错误信息; - 代码理解和重构:理解反编译后的代码逻辑,并进行合理的重构是一个耗时的过程。特别是将
ArrayList<Score>重构为HashMap<String, Integer>,需要确保所有相关逻辑都进行了相应的修改。
花时间比较久的部分
- 测试和验证:每次修改后,都需要进行充分的测试,确保新代码能够正确运行,并且没有引入新的问题。
我对逆向软件工程的一些思考
- 工具的重要性:逆向工程工具在理解和获取原始代码方面提供了极大的帮助,但仍需要开发者具备较强的代码分析和理解能力;
- 代码可维护性:在进行逆向工程和重构时,发现原始代码在某些方面缺乏可维护性,比方说数据结构选择不当、异常处理不完善。这提醒我们在编写代码时,应尽量考虑代码的可维护性和扩展性。
- 用户体验:在软件开发中,用户体验至关重要。通过改进异常处理和用户反馈机制,可以显著提升用户体验,减少用户在使用过程中的困惑和不便。
通过这次逆向工程和改进,我不仅解决了原始程序中的问题,还积累了宝贵的经验和思考,为今后的开发工作提供了有益的借鉴。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号