集合-复习篇
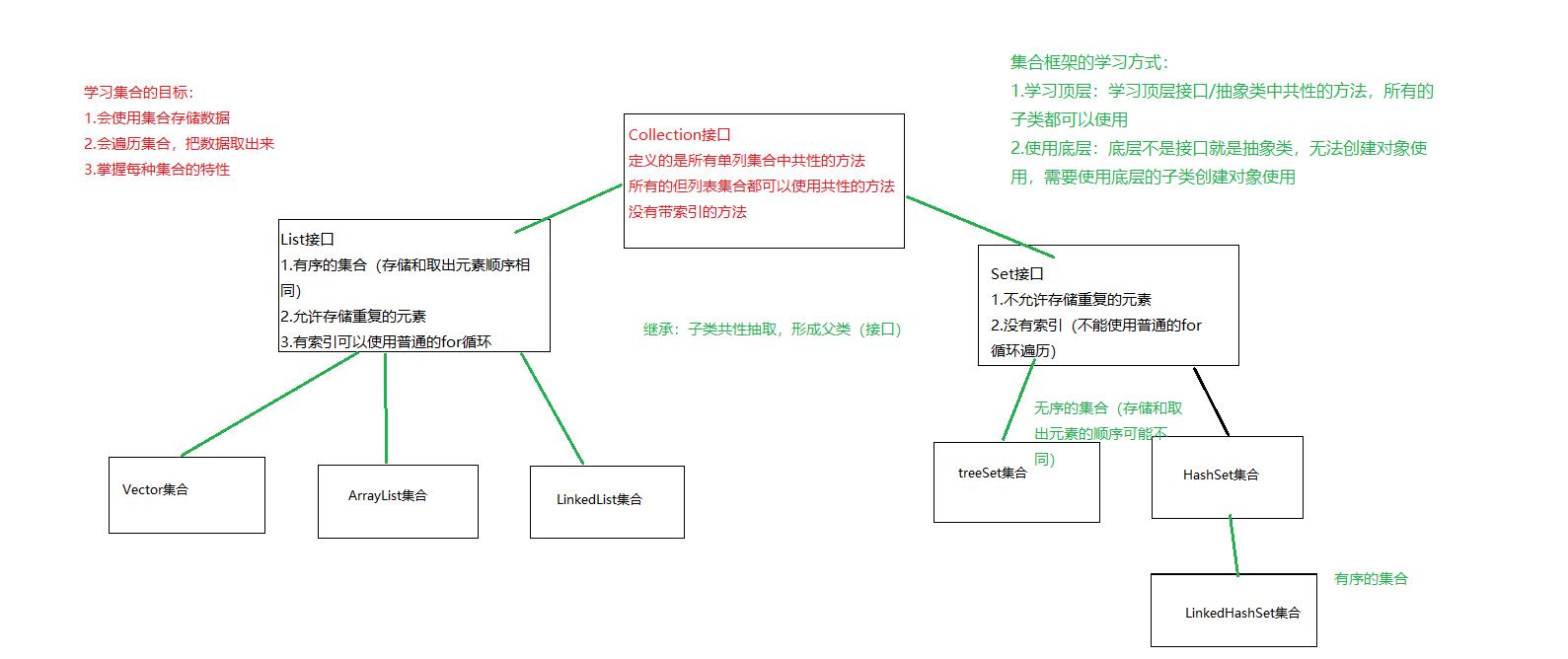
集合学习计划图
Collection集合常用功能
Collection是所有单列集合最顶层的接口,里面定义了所有单列集合的共性方法
1.public boolean add(E e) 添加元素
2.public boolean remove(E e) 删除元素
3.public boolean contains(E e) 是否包含
4.public boolean isEmpty() 是否为空
5.public void clear() 清空所有元素
6.public int size() 返回元素个数
7.public Object[] toArray() 将集合中元素存入数组
代码测试:

/* java.util.Collection接口 所有单列集合的最顶层接口,里面定义了所有单列集合共性的方法 任意的单列集合都可以使用Collection中定义的方法 1.public boolean add(E e) 添加元素 2.public boolean remove(E e) 删除元素 3.public boolean contains(E e) 是否包含 4.public boolean isEmpty() 是否为空 5.public void clear() 清空所有元素 6.public int size() 返回元素个数 7.public Object[] toArray() 将集合中元素存入数组 */ public class Demo01Collection { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象,可以使用多态 Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>(); System.out.println(coll);//Collection重写了toString()方法 coll.add("张三"); coll.add("李四"); coll.add("王五"); Object[] objects = coll.toArray(); for(Object obj : objects){ System.out.println(obj); } /* 其他自行测试 */ } }
Collection迭代器
|
boolean |
hasNext() 如果仍有元素可以迭代,则返回 true。 |
|
next() |
代码测试:

/* java.util.Iterator接口:迭代器(对集合进行遍历) 有两个常用方法 boolean hasNext()如果仍有元素可以迭代,则返回true E next() 返回迭代的下一个元素。 Iterator迭代器是一个接口,无法直接使用,需要使用改接口的实现类对象,获取实现类的方式比较特殊 Collection接口中有一个方法,iterator(),这个方法返回的就是迭代器的实现类对象 Iterator<E> iterator() 返回在此 collection 的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。 迭代器使用步骤(重点): 1.使用集合中的方法iterator()获取迭代器的实现类对象,使用Iterator接口接收(多态) 2.使用Iterator接口中的方法hasNext判断还有没有下一个元素 3.使用Iterator接口中的方法next取出集合中的下一个元素 */ public class Demo01Iterator { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); arrayList.add("张三"); arrayList.add("李四"); arrayList.add("王五"); Iterator<String> iterator = arrayList.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ String s = iterator.next(); System.out.println(s); } } }
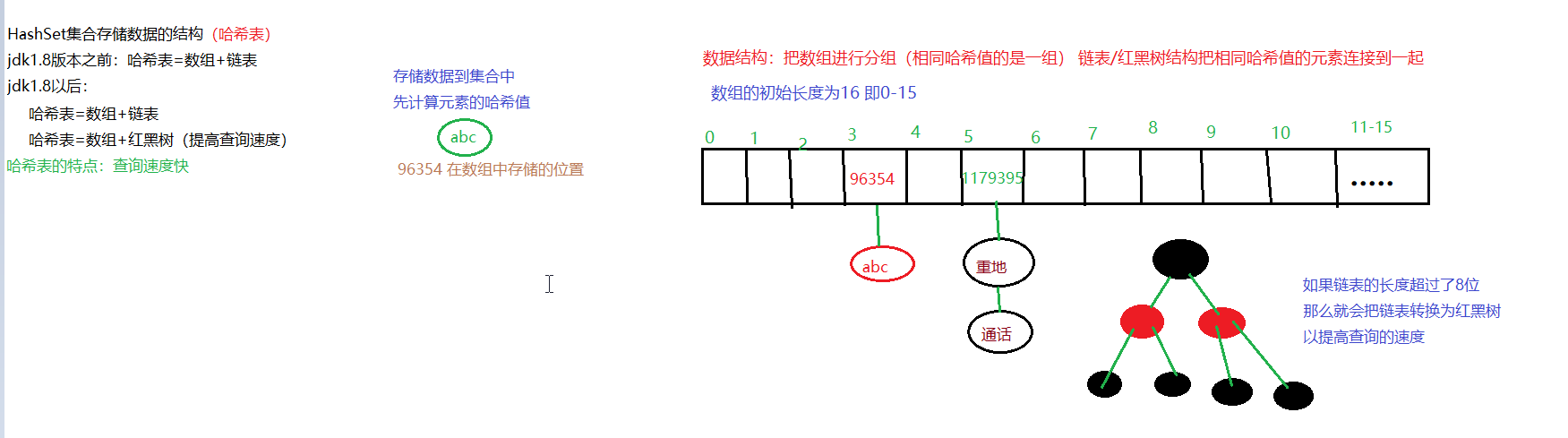
HashSet集合介绍
代码示例:

/* java.util.set接口 extends Collection接口 Set接口特点: 1.不允许存储重复元素 2.没有索引,没有带索引的方法,也不能使用普通的for循环遍历 增强for循环可以 java.util.HashSet集合 实现了 Set接口 HashSet特点: 1.不允许存储重复元素 2.没有索引,也没有带索引的方法,不能使用普通for循环 增强for循环可以 3.是一个无序的集合,存储元素和取出元素可能顺序不一致 4.底层是一个哈希表结构(查询的速度非常的快) */ public class Demo01Set { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>(); //添加元素 hashSet.add(1); hashSet.add(3); hashSet.add(2); hashSet.add(1); //迭代器遍历 Iterator<Integer> iterator = hashSet.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ Integer i = iterator.next(); System.out.println(i); } System.out.println("=============="); for(Integer i : hashSet){ System.out.println(i); } } }
哈希值

/* 哈希值:是一个十进制的整数,由系统随机给出(就是对象的地址值,是一个逻辑地址,是模拟出来的地址,并不是实际数据存储的地址) 在Object中有一个方法 可以获取哈希值 int hashCode() 返回该对象的哈希码值。 hashCode方法的源码: public native int hashCode(); native 代表该方法调用的是本地操作系统的方法 */ public class Demo01HashCode { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo01HashCode code = new Demo01HashCode(); int i = code.hashCode(); System.out.println(i); } }
HashSet存储结构
HashSet存储原理
代码示例:

/* Set集合不允许存储重复元素的原理 原理: 向hashSet存入元素时 会判读集合中是否存在该元素对应的hashCode 如果存在,则进一步判断,通过equals方法判断两个元素是否为同一个元素 如果是同一个元素,则不向集合中存储该元素 反之存储 反之存储 */ public class Demo02HashSetSaveString { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建HashSet集合对象 HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>(); String s1 = new String("abc"); String s2 = new String("abc"); hashSet.add(s1); hashSet.add(s2); hashSet.add("重地"); hashSet.add("通话"); System.out.println(hashSet);//[重地, 通话, abc] System.out.println(s1.hashCode());//96354 System.out.println("abc".hashCode());//96354 } }
Collections
java.util.Collections
此类完全由在 collection 上进行操作或返回 collection 的静态方法组成。它包含在 collection 上操作的多态算法,即“包装器”,包装器返回由指定 collection 支持的新 collection,以及少数其他内容。
|
static <T> boolean
|
addAll(List<?> list, T... elements) |
|
static void |
|
|
static <T > void
|
|
|
static <T> void
|
sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) |





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号