Java -多线程
跟着这个教学视频的代码演示过程
狂神的B站视频链接
多线程
从Thread类继承,直接使用继承自Thread类的子类TestThread的对象创建线程
//创建线程方式: 继承Thread类, 覆写run()方法,调用start启动线程
class TestThread extends Thread{
TestThread(){
super();
}
@Override
public void run(){
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
System.out.println("学习多线程: " + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread testThread = new TestThread();
testThread.start();//开启线程testThread,与主线程抢占输出
/*
使该线程开始执行; Java虚拟机调用这个线程的run方法。
结果是两个线程并发运行:当前线程(从调用start方法返回)和另一个线程(执行其run方法)。
多次启动一个线程是不合法的。 特别是,线程一旦完成执行就可能不会重新启动。
* */
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
System.out.println("Main: " + (i+100));
}
testThread.run();//
}
}
新创建的子线程与主线程交替执行
从Thread类继承,以TestThread2对象做参数创建Thread类的对象代理创建子线程,与前一种功能一致
class TestThread2 extends Thread{
TestThread2(){
super();
}
@Override
public void run(){
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
System.out.println("多线程: " + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread2 testThread2 = new TestThread2();
//不直接使用testThread2,而是新建一个Thread类型对象作为testThread2的代理,依然满足创建子线程功能
Thread thread = new Thread(testThread2);
thread.start();
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
System.out.println("Main: " + (i+100));
}
}
}
实现Runnable接口,具有多线程能力 启动线程: 传入目标对象+Thread对象.start()
class TestThread3 implements Runnable{
/* 实现Runnable接口,具有多线程能力
启动线程: 传入目标对象+Thread对象.start()
* */
private String name;
TestThread3(String name){
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println(name + "多线程: " + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread3 t1 = new TestThread3("IDEA: ");
TestThread3 t2 = new TestThread3("java: ");
new Thread(t1).start();
new Thread(t2).start();
}
}
多个线程操作同一个资源的情况下,数据发生紊乱
class TestThread4 implements Runnable{
//多个线程操作同一个资源的情况下,数据发生紊乱
int ticketNums = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
if(ticketNums <= 0) {
break;
}
//模拟延时
try{
Thread.sleep(200);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+
"拿到了第" + ticketNums-- + "票");
//currentThread():返回对当前正在执行的线程对象的引用
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread4 testThread4 = new TestThread4();
new Thread(testThread4,"学生").start();
//分配一个新的Thread对象。 此构造函数与Thread (null, target, name)具有相同的效果。
//参数:
//target – 在该线程启动时调用其run方法的对象。
//如果为null ,则调用此线程的 run 方法。
//name – 新线程的名称
new Thread(testThread4,"老师").start();
new Thread(testThread4,"黄牛党").start();
}
}
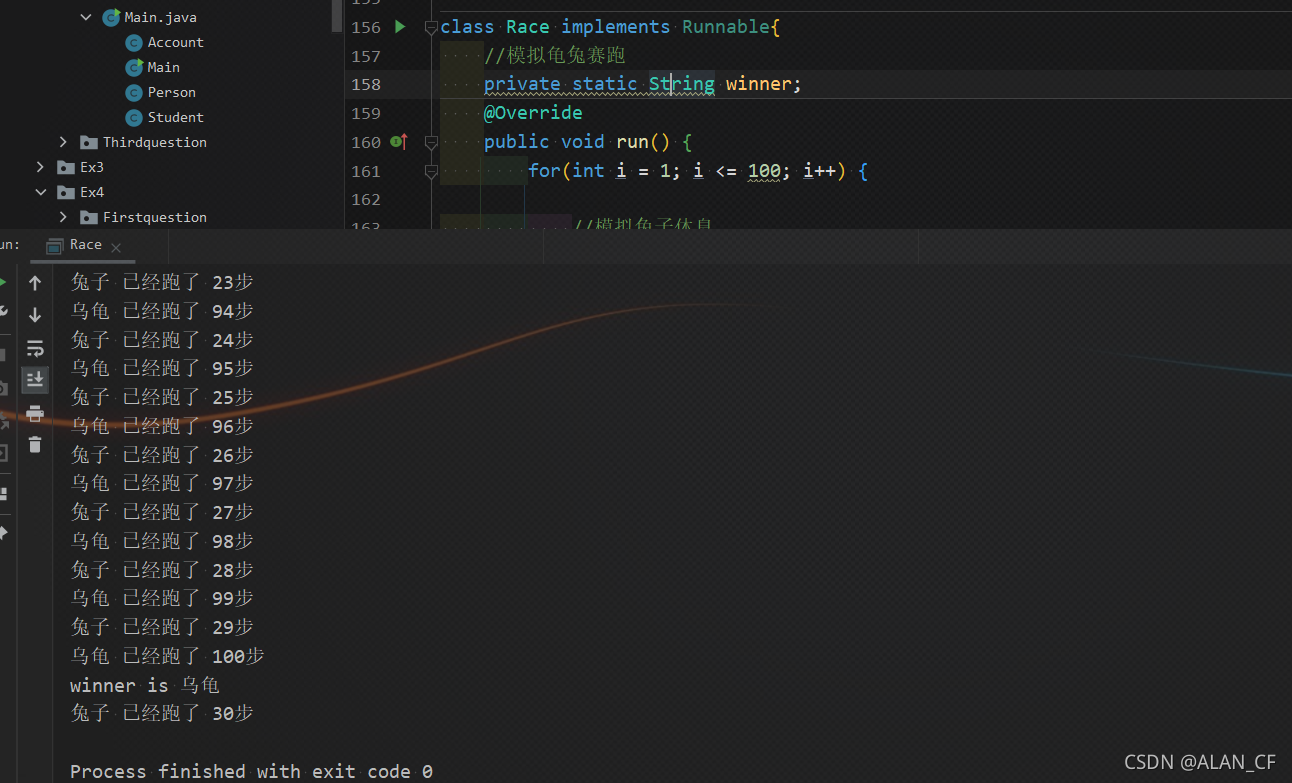
两个线程模拟龟兔赛跑
class Race implements Runnable{
//模拟龟兔赛跑
private static String winner;
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
//模拟兔子休息
if(Thread.currentThread().getName()=="兔子" && i%10==0){
try{
Thread.sleep(1);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " 已经跑了 " + i + "步");
boolean flag = isGameOver(i);
if(flag){
break;
}
}
}
private boolean isGameOver(int steps) {
if(winner != null) {
return true;
} else {
if(steps == 100) {
winner = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("winner is " + winner);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Race race = new Race();
new Thread(race,"兔子").start();
new Thread(race,"乌龟").start();
}
}
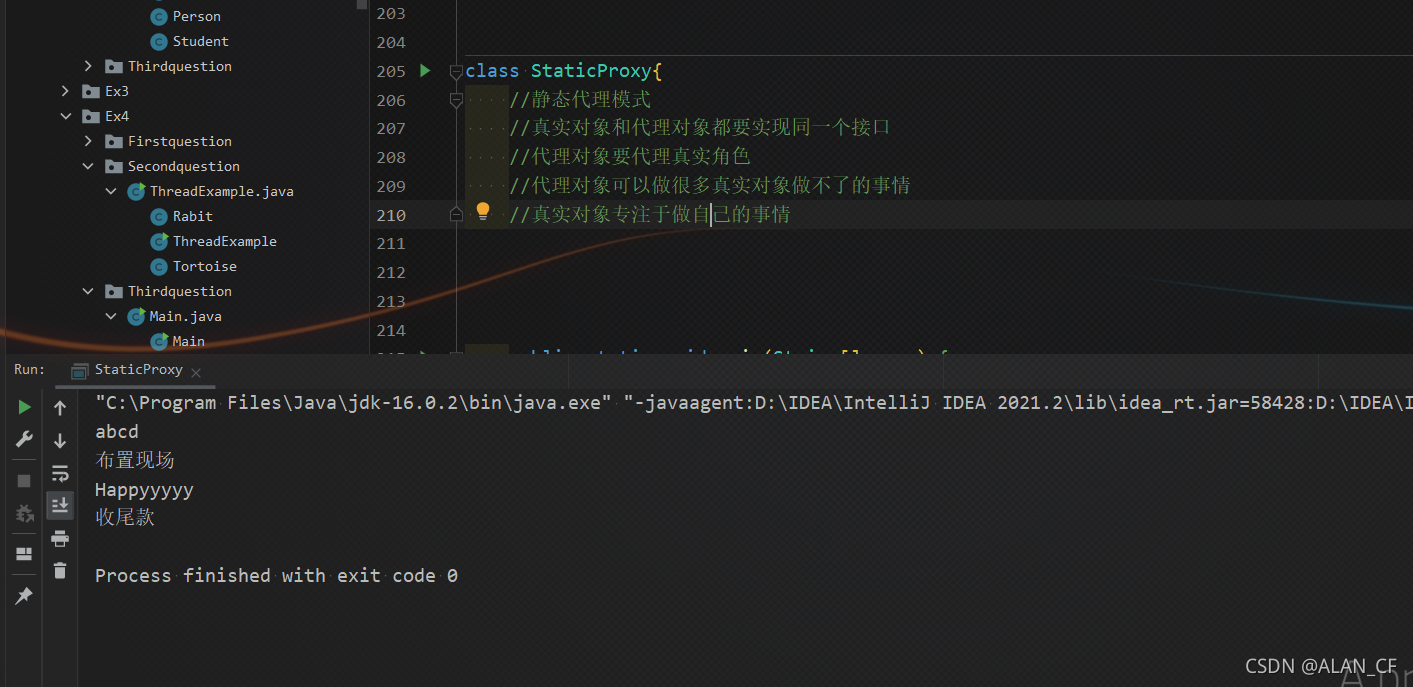
静态代理
class StaticProxy{
//静态代理模式
//真实对象和代理对象都要实现同一个接口
//代理对象要代理真实角色
//代理对象可以做很多真实对象做不了的事情
//真实对象专注于做自己的事情
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()-> System.out.println("abcd")).start();
new WeddingCompany(new You()).happyMarry();
// WeddingCompany weddingCompany = new WeddingCompany(new You());
//weddingCompany.happyMarry();
}
}
interface Marry{
void happyMarry();
}
//真实类
class You implements Marry{
@Override
public void happyMarry() {
System.out.println("Happyyyyy");
}
}
//代理类
class WeddingCompany implements Marry{
private Marry target;
public WeddingCompany(Marry target){
//将真实对象传入
this.target = target;
}
private void after() {
System.out.println("收尾款");
}
private void before() {
System.out.println("布置现场");
}
@Override
public void happyMarry() {
before();
this.target.happyMarry();//真实对象执行
after();
}
}
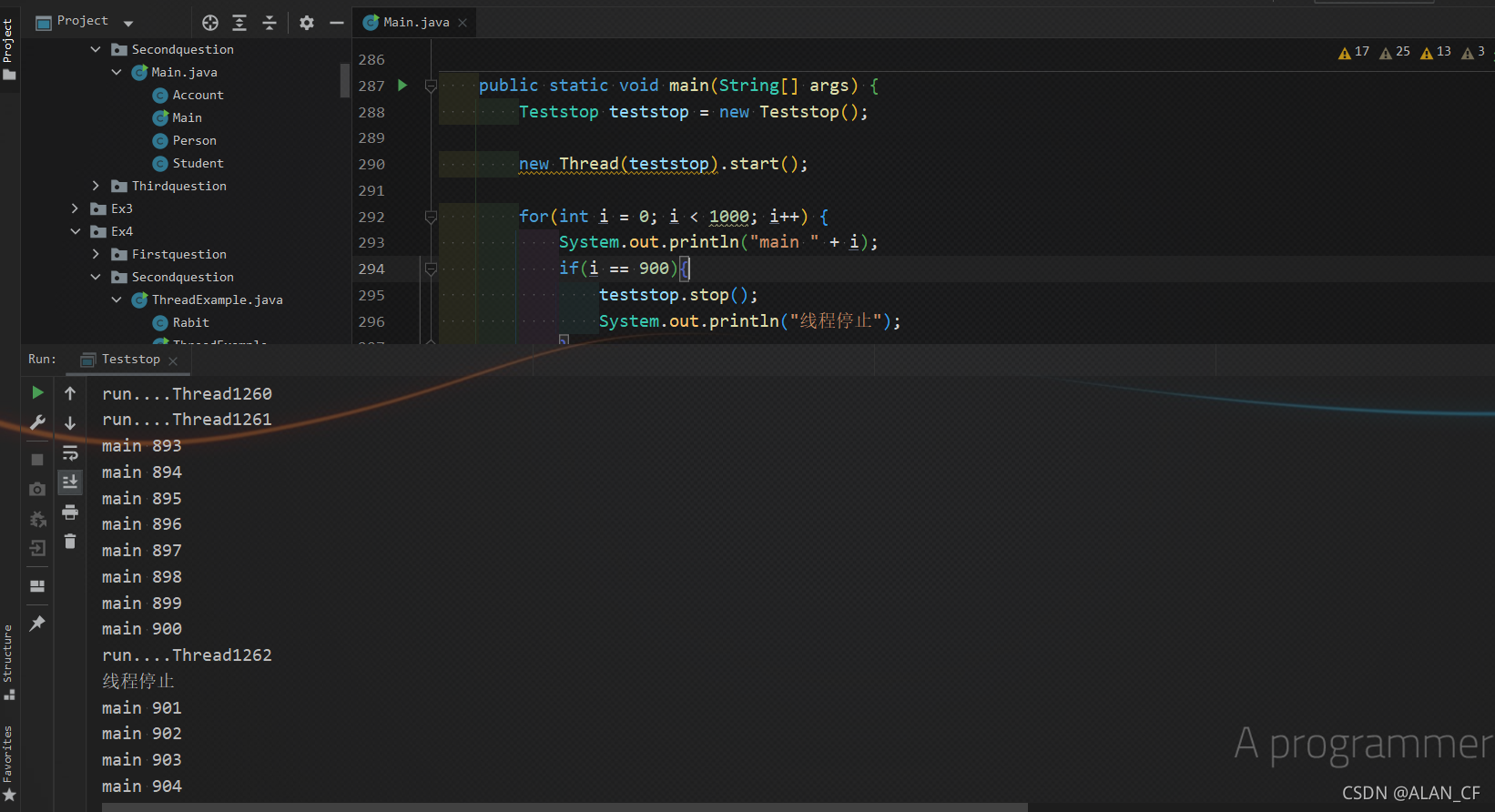
设置标志位让线程停止
//1、建议线程正常停止,利用次数,不建议死循环
//2、建议使用标志位,设置一个标志位
//3、不要使用stop等弃用方法
class Teststop implements Runnable{
//线程停止
//1、设置一个标志位
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while(flag){
System.out.println("run....Thread" + i++);
}
}
//2、设置一个公开的方法停止线程,转换标志位
public void stop(){
this.flag = false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Teststop teststop = new Teststop();
new Thread(teststop).start();
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("main " + i);
if(i == 900){
teststop.stop();
System.out.println("线程停止");
}
}
}
}
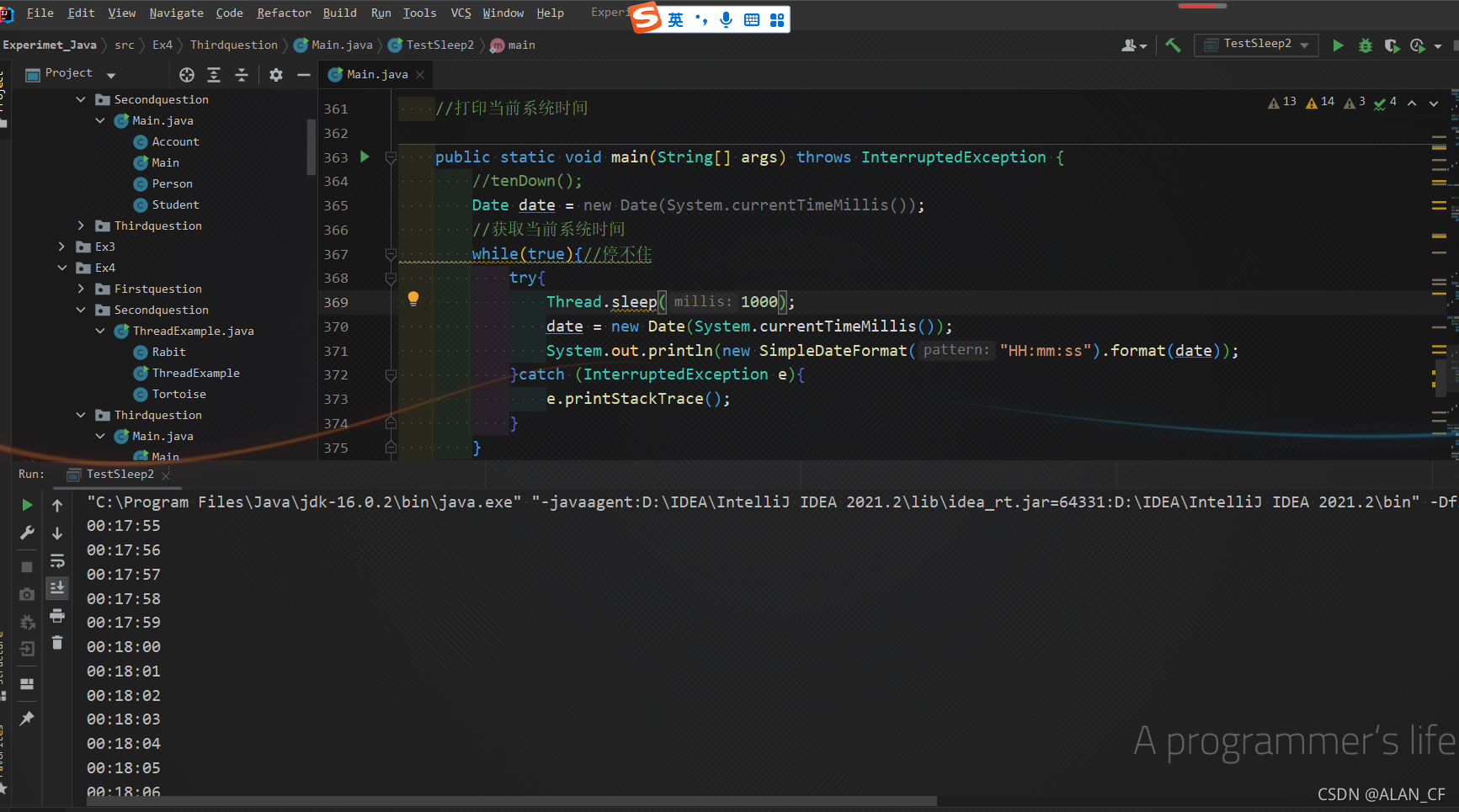
模拟倒计时、打印当前系统时间
class TestSleep2 {
//模拟倒计时
public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException{
int num = 10;
while(true){
Thread.sleep(1000);
//1000毫秒==1秒
System.out.println(num--);
if(num<=0){
break;
}
}
}
//打印当前系统时间
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//tenDown();
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
//获取当前系统时间
while(true){//停不住
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(date));
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
yeild方法
//礼让不一定成功。看CPU心情
class TestYield implements Runnable{
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestYield testYield = new TestYield();
new Thread(testYield,"A").start();
new Thread(testYield,"B").start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +"开始执行");
Thread.yield();//礼让
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "结束执行");
}
}
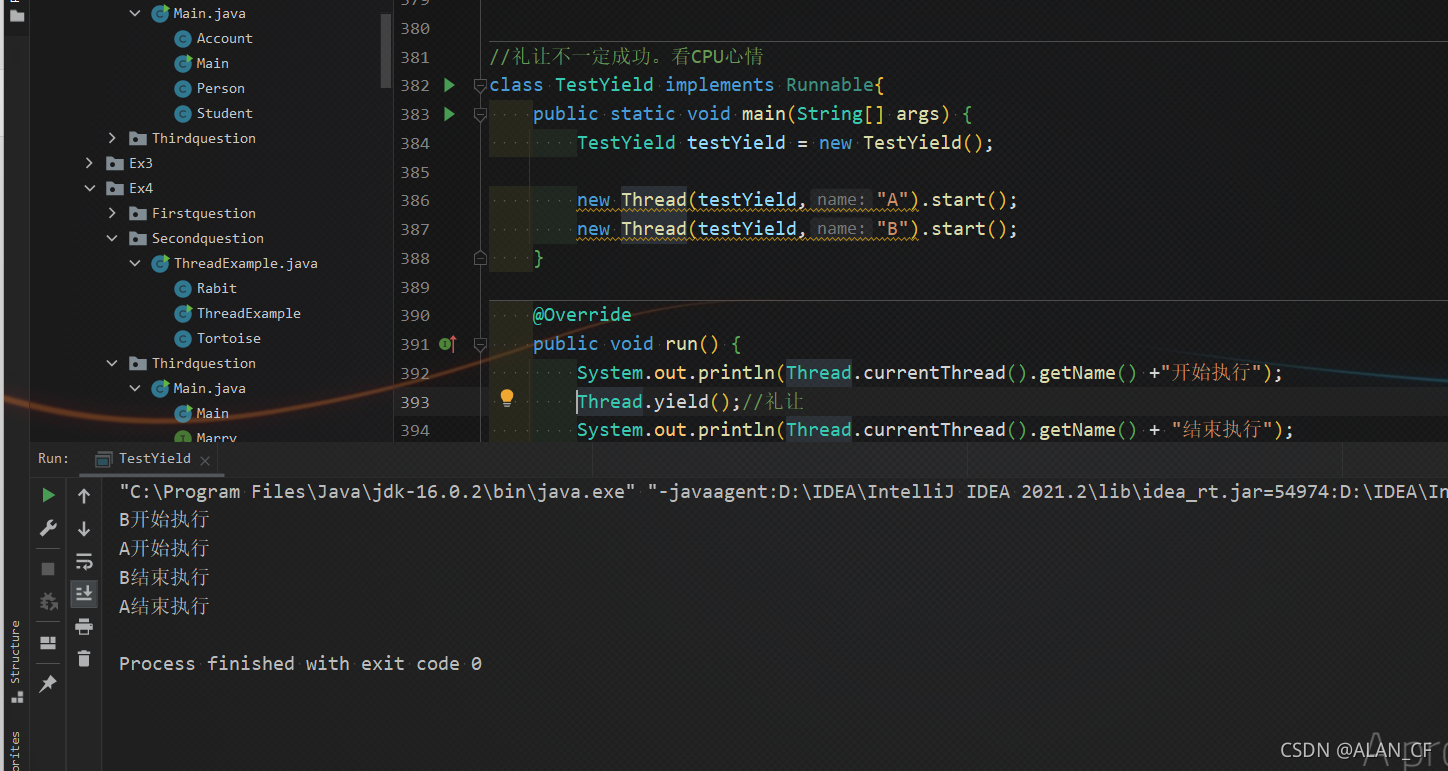
join插队方法
class TestJoin implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("线程VIP coming" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TestJoin testJoin = new TestJoin();
Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin);
//thread 做 testJoin 的代理
thread.start();
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("main: "+ i);
//main显示200以后被插队
if(i==200){
thread.join();
}
}
}
}
main跑到200之前,交错交替进行
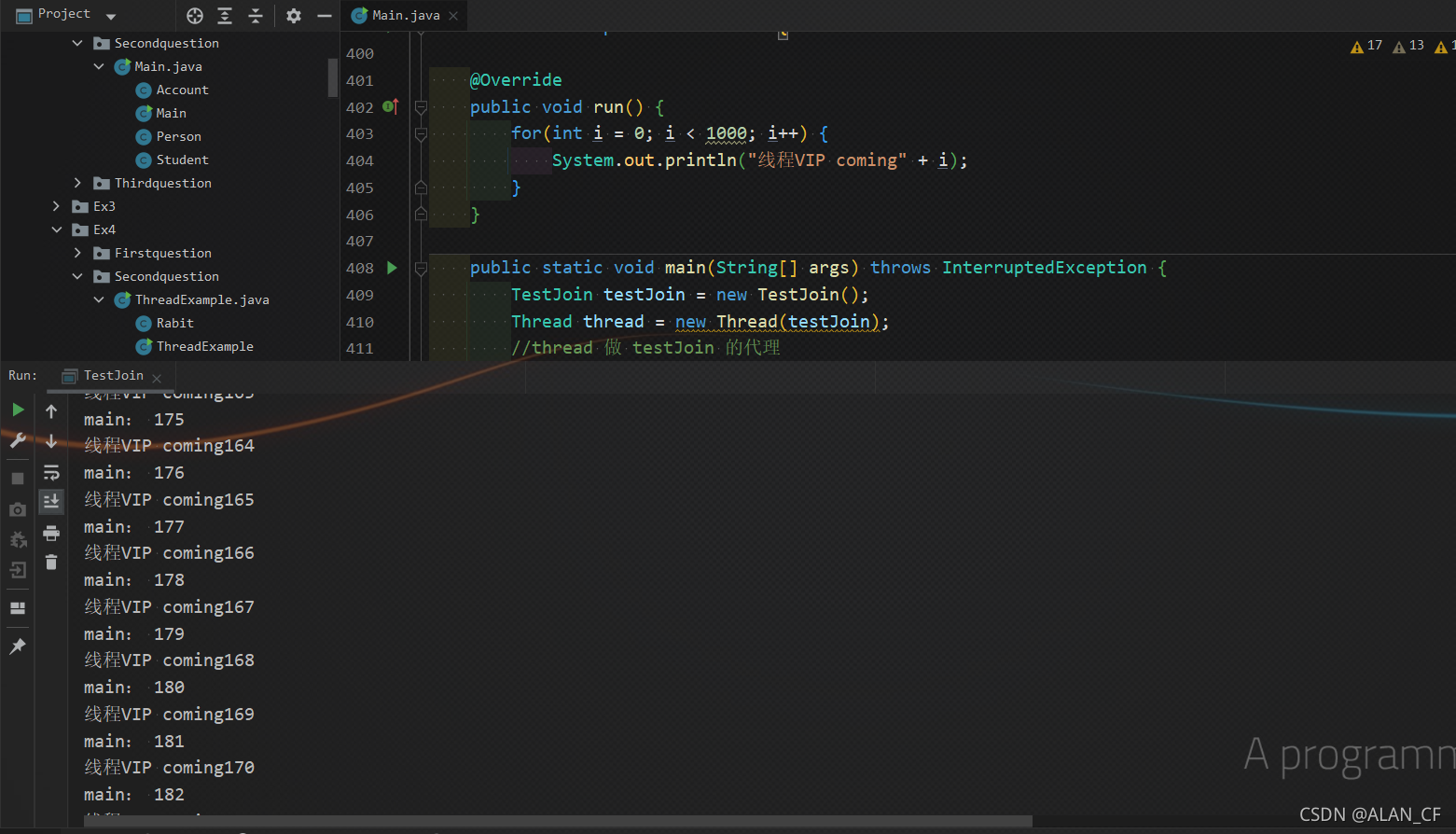
main200,开始,join方法强行让thread方法插队,只执行它一个线程
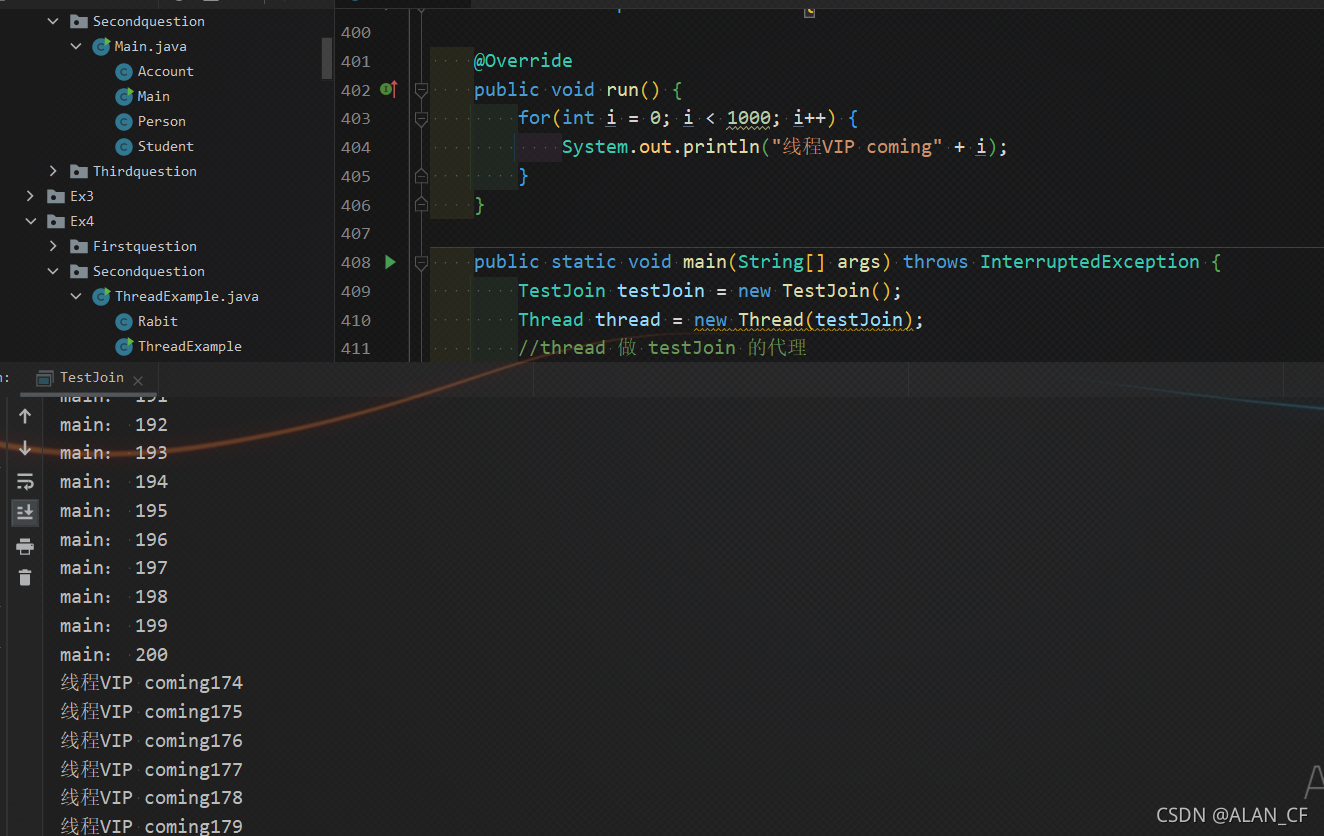
当thread线程执行全部完了以后,再开始执行主线程
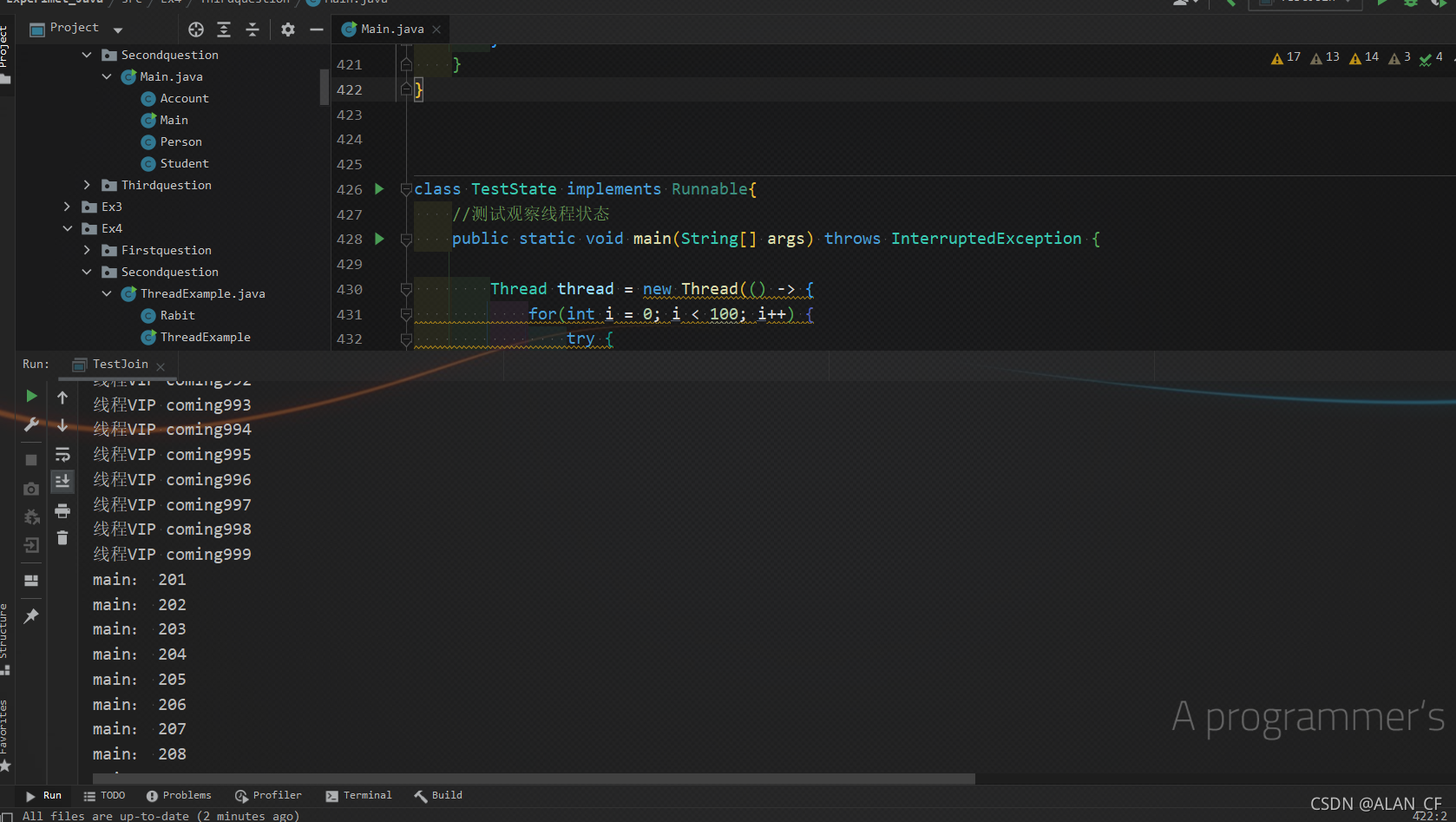
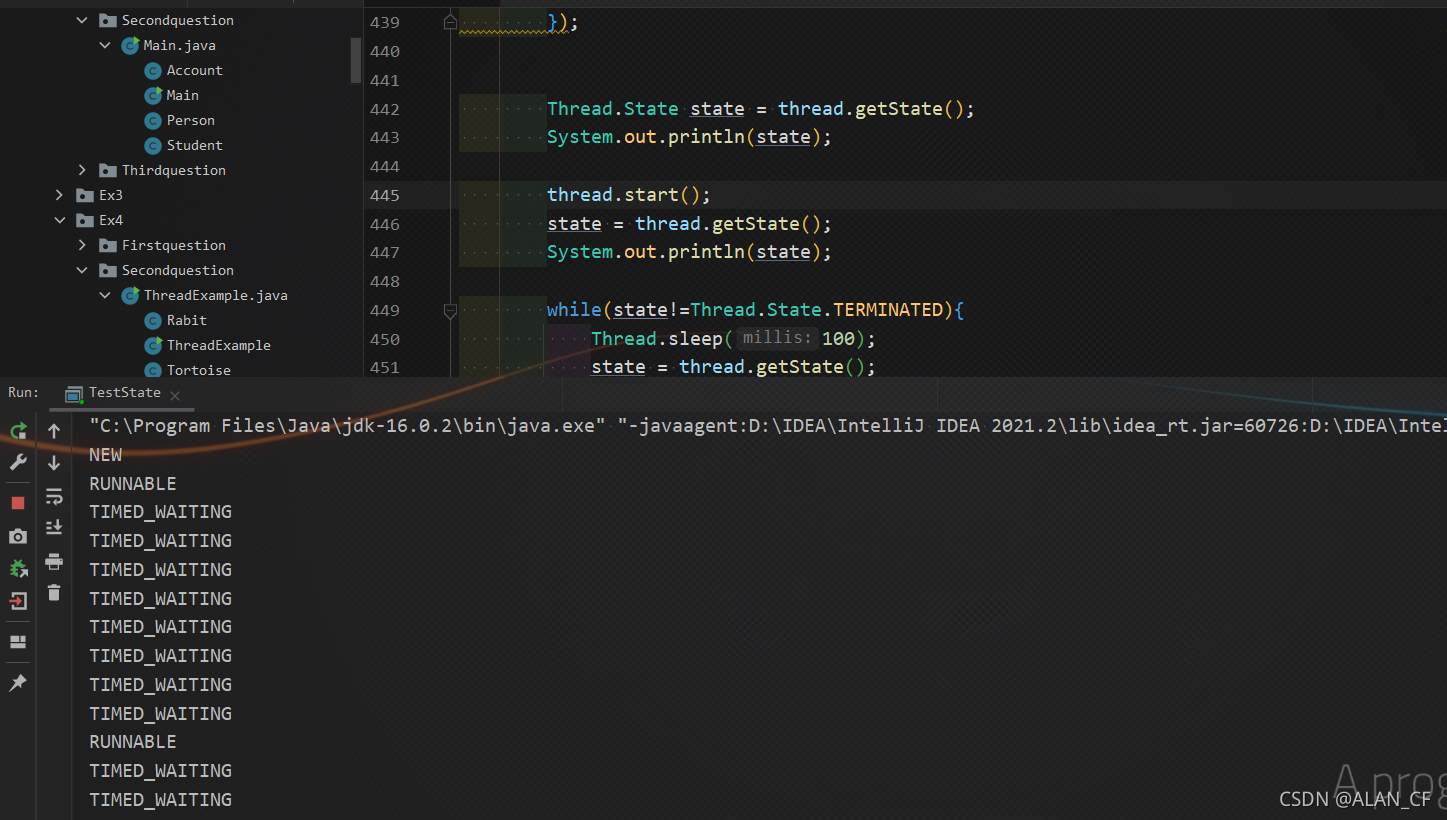
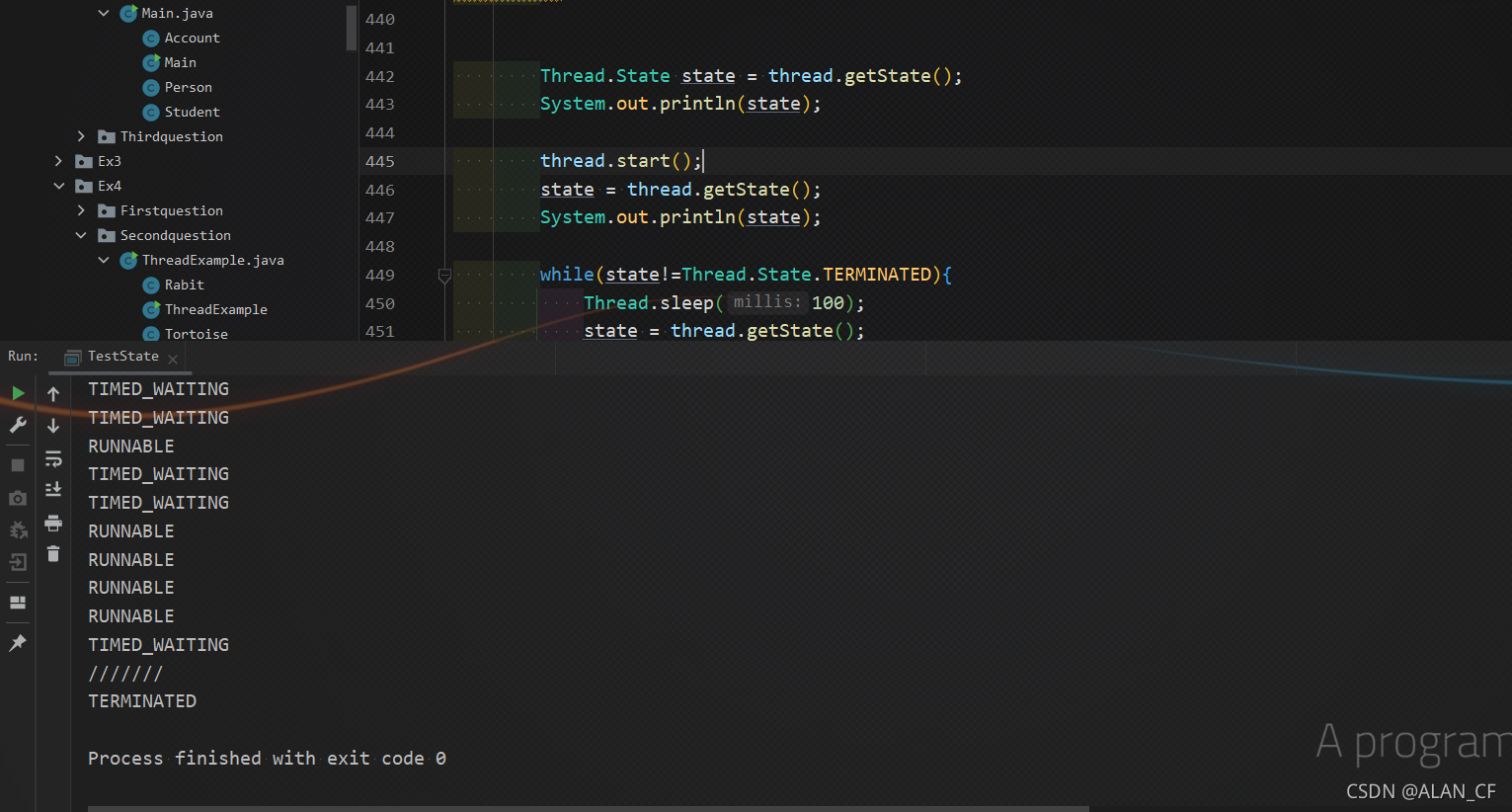
观察线程状态
class TestState implements Runnable{
//测试观察线程状态
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("///");
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
thread.start();
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
while(state!=Thread.State.TERMINATED){
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
//更新线程状态
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号