JDK源码笔记-LinkedList
1、概述
LinkedList ,基于节点实现的双向链表的 List ,每个节点都指向前一个和后一个节点从而形成链表。
相比 ArrayList 来说,我们日常开发使用 LinkedList 相对比较少
2、类图
LinkedList 实现的接口、继承的抽象类,如下图所示:
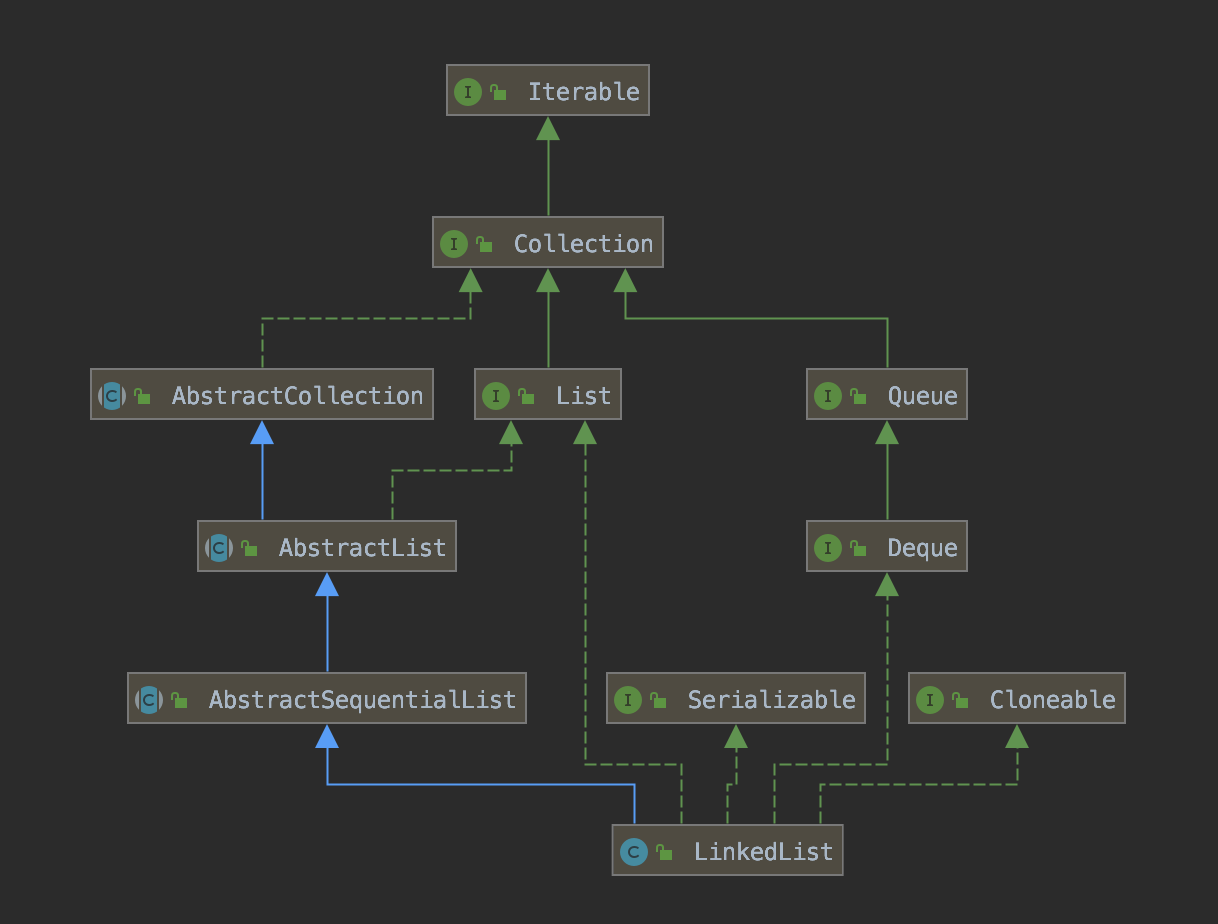
如下 3 个接口是 ArrayList 一致的:
如下 1 个接口是少于 ArrayList 的:
java.util.RandomAccess接口,LinkedList 不同于 ArrayList 的很大一点,不支持随机访问。
如下 1 个接口是多于 ArrayList 的:
-
java.util.Deque接口,提供双端队列的功能,LinkedList 支持快速的在头尾添加元素和读取元素,所以很容易实现该特性。
继承了 java.util.AbstractSequentialList 抽象类,它是 AbstractList 的子类,实现了只能连续访问“数据存储”(例如说链表)的 #get(int index)、#add(int index, E element) 等等随机操作的方法
3、属性
LinkedList 一共有 3 个属性。如下图所示:
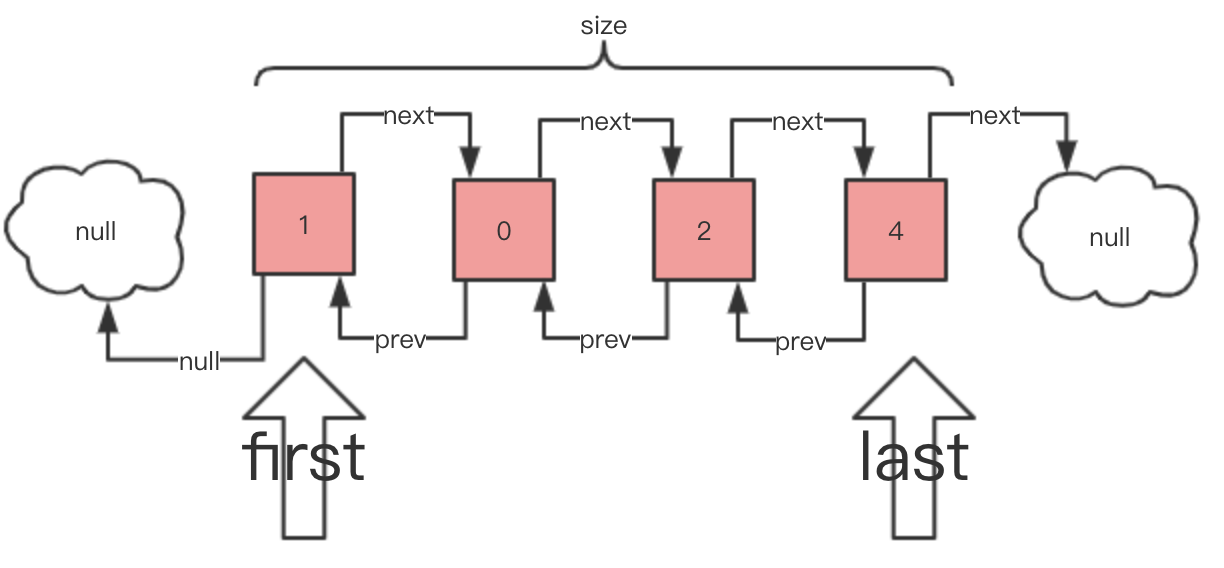
- 通过 Node 节点指向前后节点,从而形成双向链表。
first和last属性:链表的头尾指针。- 在初始时候,
first和last指向null,因为此时暂时没有 Node 节点。 - 在添加完首个节点后,创建对应的 Node 节点
node1,前后指向null。此时,first和last指向该 Node 节点。 - 继续添加一个节点后,创建对应的 Node 节点
node2,其prev = node1和next = null,而node1的prev = null和next = node2。此时,first保持不变,指向node1,last发生改变,指向node2。
- 在初始时候,
size属性:链表的节点数量。通过它进行计数,避免每次需要 List 大小时,需要从头到尾的遍历。
/** * 链表大小 */ transient int size = 0; /** * 头节点 * * Pointer to first node. */ transient Node<E> first; /** * 尾节点 * * Pointer to last node. */ transient Node<E> last; /** * 节点 * * @param <E> 元素泛型 */ private static class Node<E> { /** * 元素 */ E item; /** * 前一个节点 */ Node<E> next; /** * 后一个节点 */ Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
4、提供的方法
(1)构造方法
LinkedList 一共有两个构造方法,我们分别来看看
public LinkedList() { } public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); // 添加 c 到链表中 addAll(c); }
相比 ArrayList 来说,因为没有容量一说,所以不需要提供 #ArrayList(int initialCapacity) 这样的构造方法。
(2)添加单个元素
#add(E e) 方法,顺序添加单个元素到链表。代码如下:
public boolean add(E e) { //添加到末尾 linkLast(e); return true; } void linkLast(E e) { //记录原last节点 final Node<E> l = last; //创建新节点 // l 是newNode前一个节点 // e 是节点元素 //null 是newNode的下一个节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //last指向新节点 last = newNode; //如果 l 为空,则first节点也为空,那么first指向新节点 if (l == null) first = newNode; //如果 l 不为空,则first节点也不为空,那么last指向新节点 else l.next = newNode; //链表长度+1 size++; //操作数+1 modCount++; }
#add(int index, E element) 方法,插入单个元素到指定位置
public void add(int index, E element) { //校验是否超出范围 checkPositionIndex(index); //如果index = size,就是插入到尾部 if (index == size) //实际上就是add linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); } void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; //拿到原节点的前节点 final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; //创建新节点 //新节点的前节点指向原节点的前节点 //新节点的后节点指向原节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); //原节点的前节点指向新节点 succ.prev = newNode; //如果前节点为空 if (pred == null) //first指向新节点 first = newNode; else //否则前节点的后节点指向新节点 pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
#node(int index) 方法,获得第 index 个 Node 节点
Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); //size >> 1 位运算 结果大概为size的一半 //如果index在前半部分,正序遍历,获取第index的节点 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { //在后半部分,就倒序遍历,获取第index的节点 Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
#linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) 方法,添加元素 e 到 succ 节点的前面,与linkLast逻辑基本相同
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
因为 LinkedList 实现了 Deque 接口,所以它实现了 #addFirst(E e) 和 #addLast(E e) 方法,分别添加元素到链表的头尾
public void addFirst(E e) { linkFirst(e); } public boolean offerFirst(E e) { addFirst(e); // 调用上面的方法 return true; } public void addLast(E e) { linkLast(e); } public boolean offerLast(E e) { addLast(e); // 调用上面的方法 return true; }
linkLast方法就不多说了,下面是#linkFirst(E e) 方法,添加元素到队头
private void linkFirst(E e) { //记录first节点 final Node<E> f = first; //创建新节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); //first指向新节点 first = newNode; //如果first节点为空,则last节点也为空,那么last也指向新节点 if (f == null) last = newNode; else //原first节点的前节点指向新节点 f.prev = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
整体来说,添加单个元素,分为三个方法:
- 添加到队头
- 添加到队尾
- 添加到中间
(3)添加多个元素
#addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 方法,批量添加多个元素
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { checkPositionIndex(index); //要添加的数组 Object[] a = c.toArray(); //要添加数组的长度 int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; //新建两个节点,之后操作 Node<E> pred, succ; //如果index==size,那么就相当于在队尾添加,则succ=null,pred=las //如果index不等于size,那么就相当于在中间添加,则succ为index位置的节点,pred为index的前节点 if (index == size) { succ = null; pred = last; } else { succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } for (Object o : a) { //创建新节点 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); //判断pred是否为null,如果为null,那么pred也为null,那么first指向新节点 //如果不为null,index位置的前一个节点指向新节点 if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; //pred指向新节点 pred = newNode; } //如果succ为null,那么last也为null,则last指向pred //不为null,那么pred的next指向后节点,后节点的prev指向前节点 if (succ == null) { last = pred; } else { pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; modCount++; return true; }
(4)移除单个元素
#remove(int index) 方法,移除指定位置的元素,并返回该位置的原元素
public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); //调用node方法获得第index位置的节点,然后删除 return unlink(node(index)); } E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; //拿到x的元素 final E element = x.item; //拿到x的后节点 final Node<E> next = x.next; //拿到x的前节点 final Node<E> prev = x.prev; //如果x的前节点为null,那么将first指向x的后节点,可以理解为移除队头元素 //不为null,那么将x的前节点的next指向x的后节点,并将x的prev置null if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } //和前节点部分同里,只不过后节点为null时,为移除队尾元素 if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
#remove(Object o) 方法,移除首个为 o 的元素,并返回是否移除到
public boolean remove(Object o) { //元素为null时,遍历链表,找到null的元素,删除 //不为null时,遍历链表,找的和o元素相等的节点,删除 if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
#removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) 和 #removeLastOccurrence(Object o) 方法,分别实现移除链表首个节点和最后节点
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { // 移除首个 return remove(o); } public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) { if (o == null) { // o 为 null 的情况 // 倒序遍历,找到 null 的元素后,进行移除 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { // 倒序遍历,找到等于 o 的元素后,进行移除 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
#remove() 方法,移除链表首个节点
public E remove() { return removeFirst(); } public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; //链表为空时,抛出异常 if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); //移除链表首个节点 return unlinkFirst(f); } private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { // assert f == first && f != null; //拿到首个节点元素 final E element = f.item; //拿到首个节点指向的后节点 final Node<E> next = f.next; //元素置null,后节点指向置null f.item = null; f.next = null; // help GC //first指向首个节点指向的后节点 first = next; //如果后节点为null,那么整个链表时null的,那么last也为null //不为空的话,后节点的前节点指向置空 if (next == null) last = null; else next.prev = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
#removeLast() 方法,移除链表最后一个节点,和#removeFirst()方法思路是差不多的
public E removeLast() { final Node<E> l = last; // 如果链表为空,则抛出 NoSuchElementException 移除 if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); // 移除链表的最后一个元素 return unlinkLast(l); } private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { // assert l == last && l != null; final E element = l.item; // 获得 f 的上一个节点 final Node<E> prev = l.prev; // 设置 l 的 item 为 null ,帮助 GC l.item = null; // 设置 l 的 prev 为 null ,帮助 GC l.prev = null; // help GC // 修改 last 指向 prev last = prev; // 修改 prev 节点的 next 指向 null if (prev == null) // 如果链表只有一个元素,说明被移除后,队列就是空的,则 first 设置为 null first = null; else prev.next = null; // 链表大小减一 size--; // 增加数组修改次数 modCount++; return element; }
#poll() 和 # pop()方法,移除链表的头或尾,差异点在于链表为空时候,不会抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常
public E poll() { // 移除头 final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } public E pop() { return removeFirst(); } // LinkedList.java 实现 Deque 接口 public E pollFirst() { // 移除头 final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } public E pollLast() { // 移除尾 final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l); }
(5)移除多个元素
#removeAll(Collection<?> c) 方法,批量移除指定的多个元素
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); boolean modified = false; // 获得迭代器 Iterator<?> it = iterator(); // 通过迭代器遍历 while (it.hasNext()) { // 如果 c 中存在该元素,则进行移除 if (c.contains(it.next())) { it.remove(); modified = true; // 标记修改 } } return modified; }
#retainAll(Collection<?> c) 方法,求 LinkedList 和指定多个元素的交集。简单来说,恰好和 #removeAll(Collection<?> c) 相反,移除不在 c 中的元素
// AbstractCollection.java public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); boolean modified = false; // 获得迭代器 Iterator<E> it = iterator(); // 通过迭代器遍历 while (it.hasNext()) { // <X> 如果 c 中不存在该元素,则进行移除 if (!c.contains(it.next())) { it.remove(); modified = true; } } return modified; }
(6)查找单个元素
#indexOf(Object o) 方法,查找首个为指定元素的位置
public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) {//如果o为null //循环遍历 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index;//找到返回 index++; } } else {//如果o不为null //循环遍历 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index;//找到返回 index++; } } return -1; }
而 #contains(Object o) 方法,就是基于该方法实现
public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; }
有时我们需要查找最后一个为指定元素的位置,所以会使用到 #lastIndexOf(Object o) 方法
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { int index = size; if (o == null) { // 如果 o 为 null 的情况 // 倒序遍历,如果 item 为 null 的节点,进行返回 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (x.item == null) return index; // 找到 } } else { // 如果 o 非 null 的情况 // 倒序遍历,如果 item 为 o 的节点,进行返回 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; // 找到 } } // 未找到 return -1; }
(7)获得指定位置的元素
#get(int index) 方法,获得指定位置的元素
public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); // 基于 node(int index) 方法实现 return node(index).item; }
因为 LinkedList 实现了 Deque 接口,所以它实现了 #peekFirst() 和 #peekLast() 方法,分别获得元素到链表的头尾
public E peekFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; } public E peekLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : l.item; }
因为 LinkedList 实现了 Queue 接口,所以它实现了 #peek() 和 #element() 方法,分别获得元素到链表的头
public E peek() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; } public E element() { // 如果链表为空识,抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常 return getFirst(); } public E getFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) // 如果链表为空识,抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常 throw new NoSuchElementException(); return f.item; }
(8)获取指定位置的元素
#set(int index, E element) 方法,设置指定位置的元素
public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); //获取index的节点 Node<E> x = node(index); E oldVal = x.item; //设置index节点的元素 x.item = element; return oldVal; }
(9)转换为数组
#toArray() 方法,将 ArrayList 转换成 [] 数组
public Object[] toArray() { //相同长度的新数组 Object[] result = new Object[size]; int i = 0; //循环设置数组中对应位置的值 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) result[i++] = x.item; return result; }
实际场景下,我们可能想要指定 T 泛型的数组,那么我们就需要使用到 #toArray(T[] a) 方法
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { //如果传入数组长度比size小,直接复制一个数组返回 if (a.length < size) a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance( a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); int i = 0; Object[] result = a; //循环遍历赋值 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) result[i++] = x.item; //如果传入的数组长度大于size,那么将size位置置null if (a.length > size) a[size] = null; return a; }
(10)求哈希值
#hashCode() 方法,求 LinkedList 的哈希值
public int hashCode() { int hashCode = 1; // 遍历,求哈希 for (E e : this) hashCode = 31*hashCode + (e==null ? 0 : e.hashCode()); return hashCode; }
(11)判断相等
#equals(Object o) 方法,判断是否相等
public boolean equals(Object o) { // 如果 o 就是自己,直接返回 true if (o == this) return true; // 如果不为 List 类型,直接返回 false if (!(o instanceof List)) return false; // 创建迭代器,顺序遍历比对 ListIterator<E> e1 = listIterator(); ListIterator<?> e2 = ((List<?>) o).listIterator(); while (e1.hasNext() && e2.hasNext()) { E o1 = e1.next(); Object o2 = e2.next(); if (!(o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2))) // 如果不相等,返回 false return false; } // 如果有迭代器没有遍历完,说明两者长度不等,所以就不相等;否则,就相等了 return !(e1.hasNext() || e2.hasNext()); }
(12)清空链表
public void clear() { // Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but: // - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit // more than one generation // - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { //拿到x的后节点 Node<E> next = x.next; //将前后节点指向和元素全部置空 x.item = null; x.next = null; x.prev = null; //x指向x的后节点 x = next; } first = last = null; size = 0; modCount++; }
(13)克隆
#clone() 方法,克隆 LinkedList 对象
public Object clone() { //调用父类clone方法 LinkedList<E> clone = superClone(); // Put clone into "virgin" state //将clone重置为初始状态,此处注意,first、last等都是重新初始化的,不与前LinkedList共享 clone.first = clone.last = null; clone.size = 0; clone.modCount = 0; // Initialize clone with our elements //循环遍历添加节点 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) clone.add(x.item); return clone; }
(14)创建子数组
#subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) 方法,创建 ArrayList 的子数组
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size()); // 根据判断 RandomAccess 接口,判断是否支持随机访问 return (this instanceof RandomAccess ? new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex) : new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex)); }
- 该方法,是通过父类 AbstractList 来实现的。
- 根据判断 RandomAccess 接口,判断是否支持随机访问,从而创建 RandomAccessSubList 或 SubList 对象
(15)创建Iterator迭代器
#iterator() 方法,创建迭代器
public Iterator<E> iterator() { return listIterator(); } // AbstractList.java public ListIterator<E> listIterator() { return listIterator(0); } // AbstractSequentialList.java public abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index);
- 该方法,是通过父类 AbstractSequentialList 来实现的。
- 整个调用过程是,
iterator() => listIterator() => listIterator(int index)的顺序,就是我们在代码里贴进去的顺序。最终呢,是调用 LinkedList 对#listIterator(int index)的实现
(16)创建LIstIterator迭代器
#listIterator(int index) 方法,创建 ListIterator 迭代器
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { checkPositionIndex(index); return new ListItr(index); }
因为 ListItr 的实现代码比较简单,我们就不逐个来看了,直接贴加了注释的代码
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> { /** * 最后返回的节点 */ private Node<E> lastReturned; /** * 下一个节点 */ private Node<E> next; /** * 下一个访问元素的位置,从下标 0 开始。 * * 主要用于 {@link #nextIndex()} 中,判断是否遍历结束 */ private int nextIndex; /** * 创建迭代器时,数组修改次数。 * * 在迭代过程中,如果数组发生了变化,会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。 */ private int expectedModCount = modCount; ListItr(int index) { // assert isPositionIndex(index); // 获得下一个节点 next = (index == size) ? null : node(index); // 下一个节点的位置 nextIndex = index; } public boolean hasNext() { return nextIndex < size; } public E next() { // 校验是否数组发生了变化 checkForComodification(); // 如果已经遍历到结尾,抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常 if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); // lastReturned 指向,记录最后访问节点 lastReturned = next; // next 指向,下一个节点 next = next.next; // 下一个节点的位置 + 1 nextIndex++; // 返回 lastReturned return lastReturned.item; } public boolean hasPrevious() { return nextIndex > 0; } public E previous() { // 校验是否数组发生了变化 checkForComodification(); // 如果已经遍历到结尾,抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常 if (!hasPrevious()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); // 修改 lastReturned 和 next 的指向。此时,lastReturned 和 next 是相等的。 lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev; // 下一个节点的位置 - 1 nextIndex--; // 返回 lastReturned return lastReturned.item; } public int nextIndex() { return nextIndex; } public int previousIndex() { return nextIndex - 1; } public void remove() { // 校验是否数组发生了变化 checkForComodification(); // 如果 lastReturned 为空,抛出 IllegalStateException 异常,因为无法移除了。 if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); // 获得 lastReturned 的下一个 Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next; // 移除 lastReturned 节点 unlink(lastReturned); // 此处,会分成两种情况 if (next == lastReturned) // 说明发生过调用 `#previous()` 方法的情况,next 指向下一个节点,而 nextIndex 是无需更改的 next = lastNext; else nextIndex--; // nextIndex 减一。 // 设置 lastReturned 为空 lastReturned = null; // 增加数组修改次数 expectedModCount++; } public void set(E e) { // 如果 lastReturned 为空,抛出 IllegalStateException 异常,因为无法修改了。 if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); // 校验是否数组发生了变化 checkForComodification(); // 修改 lastReturned 的 item 为 e lastReturned.item = e; } public void add(E e) { // 校验是否数组发生了变化 checkForComodification(); // 设置 lastReturned 为空 lastReturned = null; // 此处,会分成两种情况 if (next == null) // 如果 next 已经遍历到尾,则 e 作为新的尾节点,进行插入。算是性能优化 linkLast(e); else // 插入到 next 的前面 linkBefore(e, next); // nextIndex 加一。 nextIndex++; // 增加数组修改次数 expectedModCount++; } public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); // 遍历剩余链表 while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) { // 执行 action 逻辑 action.accept(next.item); // lastReturned 指向 next lastReturned = next; // next 指向下一个节点 next = next.next; // nextIndex 加一。 nextIndex++; } // 校验是否数组发生了变化 checkForComodification(); } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号