真题2
数量级和复杂度
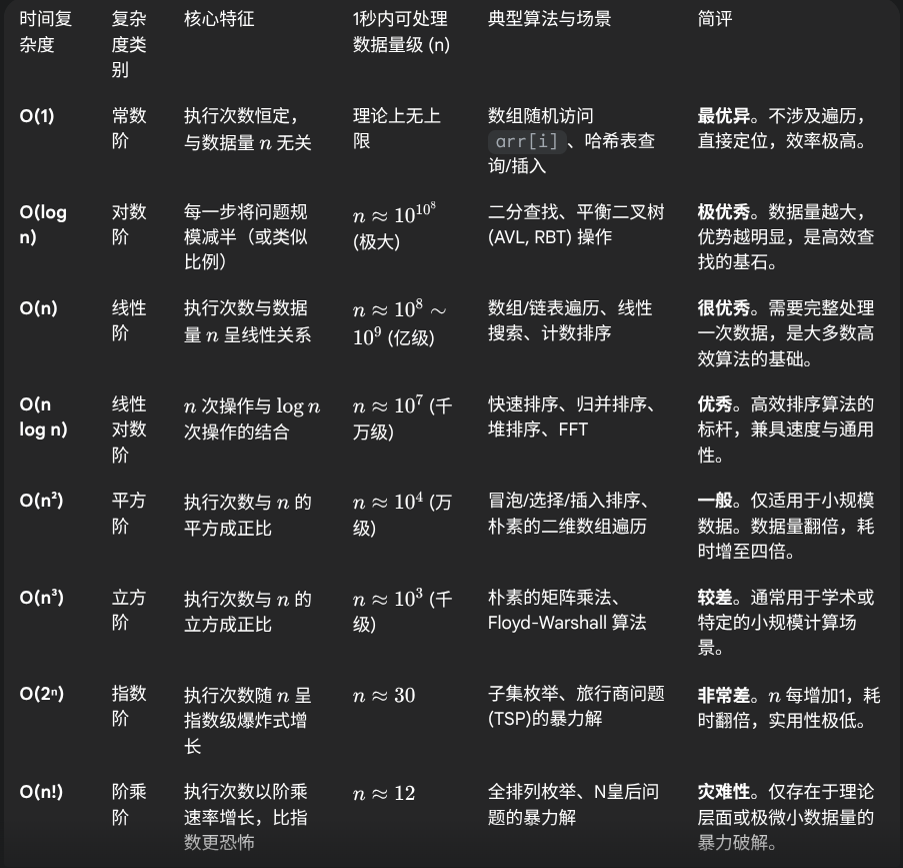
全排列好东西
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
// 使用std命名空间,简化代码书写
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {1, 2, 3};
// 先排序,确保从最小的排列开始
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
do {
// 输出当前排列
for (int num : nums) {
cout << num << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} while (next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end()));
// 每次调用next_permutation会修改nums为下一个排列
return 0;
}
众数
题目描述
有 n 个序列(依次编号为 0, 1, ..., n-1),初始时各个序列均为空。你的任务是维护这 n 个序列,需支持以下三种操作:
- 操作 1 i k x:在第
i个序列的末尾插入k个值均为x的数。 - 操作 2 i k:删除第
i个序列末尾的k个数;若该序列的元素总数不足k,则删除序列中所有剩余的数。 - 操作 3 i:询问第
i个序列的众数。其中,众数定义为序列中出现次数最多的数;若存在多个数出现次数相同且均为最大值,则取其中数值最小的数。
输入格式
从标准输入读入数据,格式如下:
- 第一行:两个正整数
n和q,分别表示序列的个数和操作的总次数。 - 接下来
q行:每行描述一个操作,操作格式与题目描述一致(具体参数含义见“题目描述”中的操作说明)。
输出格式
输出到标准输出,规则如下:
- 仅对“操作 3”(查询众数)进行输出:对于每个操作 3,输出当前第
i个序列的众数,并换行。 - 若查询时第
i个序列为空(无有效元素),输出-1。
题解
主要涉及了哈希表和集合的使用技巧,提升效率。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef vector<LL> VI;
typedef vector<VI> VVI;
typedef pair<LL,LL> PII;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double EPS = 1e-8;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
bool compareb(PII&a, PII&b){
return a.second < b.second;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int n,q;
cin >> n >> q;
vector<vector<PII>> A(n);
vector<unordered_map<LL,LL>> H(n);
vector<set<PII>> S(n);
// 使用unoerderedmap省去统计时间
// 使用set自动排序!只有移除与插入,严格弱,第一个相等,就比较第一个小的先,升序
// 集合为0的要擦出避免影响
// 构造数据多个同个的能发现问题
LL idx, k , x;
LL oldacc;
int opt;
for(int i = 0; i < q; i++){
cin >> opt;
if(opt == 1){
cin >> idx >> k >> x;
A[idx].push_back({k,x});
// occ用-的是因为当时加入的时候是-的这里直接弄成这样了
oldacc = H[idx][x];
H[idx][x] += k;
if(oldacc > 0){
S[idx].erase({-oldacc, x});
}
S[idx].insert({-H[idx][x], x});
}
else if(opt == 2){
cin >> idx >> k;
LL tail = A[idx].size() -1;
while(k>0&&A[idx].size()>0){
if(A[idx][tail].first >= k){
// 这里写错了,本来,应该写累加的H的而不是A里的
oldacc = H[idx][A[idx][tail].second];
A[idx][tail].first -= k;
H[idx][A[idx][tail].second] -= k;
S[idx].erase({-oldacc, A[idx][tail].second});
if(H[idx][A[idx][tail].second]>0) S[idx].insert({-H[idx][A[idx][tail].second], A[idx][tail].second});
k = 0;
}else{
oldacc = H[idx][A[idx][tail].second];
S[idx].erase({-oldacc, A[idx][tail].second});
k -= A[idx][tail].first;
H[idx][A[idx][tail].second] -= A[idx][tail].first;
A[idx].erase(A[idx].begin()+tail);
if(H[idx][A[idx][tail].second]>0) S[idx].insert({-H[idx][A[idx][tail].second], A[idx][tail].second});
tail --;
}
}
}
else if(opt == 3){
cin >> idx;
LL minme = -1;
for(auto now:S[idx]){
minme = now.second;
break;
}
cout << minme << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
找到第一个没出现的自然数
代码丢了,大概就是排序,不是0开始就是输出0,否则开始遍历,如果出现相减大于1那么上一个+1就是答案。
整数对
找到x然后直接加起来(找到数字对i<j且i+j<=m的个数)
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const LL MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
LL n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
VI A(n);
LL now, x, idx, count = 0;
for(int i =0;i<n;i++){cin >> now; A[i] = -now;}
// 反着读入方便下面处理
sort(A.begin(),A.end());
// 确定一个数 now,然后找到另一个最大数 x 使得 x + now 恰好<=m
// 然后x以及之前的全部数字就可以构成对,纳入记录
for(int i =n-1;i>=0;i--){
now = -A[i];
if(m<now)break;
x = m - now;
x = -x;
auto it = lower_bound(A.begin(), A.end()+i, x);
idx = it - A.begin();
if(idx < i && idx >= 0){
idx = i - idx;
count += idx;
count %= MOD;
}
}
cout << count << endl;
return 0;
}
movie
在万年历吃过亏,不过问题不大,用数组代替重复判断。
题目是把时间乘以帧率输出。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
LL T;
cin >> T;
string time;
LL fps;
LL ok = 3600 , now = 0, sum = 0;
int i = 1;
int M[2] = {1, 10};//用数组替代判断case
while(T--){
cin >> time >>fps;
ok = 3600; now = 0; sum = 0; i = 1;
for(char x : time){
if(x ==':'){
i = 1;
sum += now * ok;
ok /= 60;
now = 0;
continue;
}
now += (x - '0') * M[i];
i--;
}
sum += now;
fps *= sum;
cout << fps << endl;
}
return 0;
}
理发店
来人,洗头/剪头时间,先洗头发才能剪头发,求最少时间。
要有这种抽象的编程思想。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
vector<PII> S;
vector<PII> path;
vector<bool> used;
set<LL> ans;
LL temp;
int j;
int n;
PII x;
// 用dfs遍历所有情况
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
//我这里正确性出问题了,需要修改,弄成两个并列了,其实还有很多
void check(){
LL washend = 0, cutend = 0;
for(auto x: path){
LL a = x.first;
LL b = x.second;
// 开始洗头的时间就是洗头结束时间
LL start = washend;
washend = start + a;//洗头结束的时间就是他开始的加上他的洗头时间
start = max(washend, cutend);//开始剪头的时间就是其中哪个先完成的
cutend = start + b;
}
ans.insert(cutend);
}
//dfs说是
void work(){
if(path.size()==n){
check();
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(used[i]==false){
path.push_back(S[i]);
used[i]=true;
work();
used[i]=false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
// 多组数据情况记得清空
// 如果n小直接暴力!!!因为就没有更好的解法。。
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
LL T, a, b;
cin >> T;
while(T--){
S.clear();
used.clear();
path.clear();
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a >> b;
S.push_back({a,b});
}
used.resize(n);
work();
cout << *ans.begin() << endl;//访问set第一个用解引用
//for(auto x:ans) cout << x <<" ";
ans.clear();
}
return 0;
}
五子棋模拟
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
int A[15][15];
bool valid(int x, int y){
return x>=0&&x<15&&y>=0&&y<15;
}
bool check(int x, int y, bool flag){
//横着
int now = x;
int k =0;
int me = flag?1:2;
while(valid(now,y)&&A[now][y]==me){
k++; now++;
}
//多看题目!!只要是五个以上也成功!!写成了刚好五个了
if(k>=5)return true;
now = x; k--;
while(valid(now,y)&&A[now][y]==me){
k++; now--;
}
if(k>=5)return true;
k = 0; now = y;
while(valid(x,now)&&A[x][now]==me){
k++; now++;
}
if(k>=5)return true;
now = y; k--;
while(valid(x,now)&&A[x][now]==me){
k++; now--;
}
if(k>=5)return true;
int nowy;
k = 0; now = x; nowy = y;
while(valid(now,nowy)&&A[now][nowy]==me){
k++; now++;nowy++;
}
if(k>=5)return true;
now = x; nowy = y;k--;
while(valid(now,nowy)&&A[now][nowy]==me){
k++; now--;nowy--;
}
if(k>=5)return true;
k = 0; now = x; nowy = y;
while(valid(now,nowy)&&A[now][nowy]==me){
k++; now++;nowy--;
}
if(k>=5)return true;
now = x; nowy = y;k--;
while(valid(now,nowy)&&A[now][nowy]==me){
k++; now--;nowy++;
}
if(k>=5)return true;
return false;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int n; int x,y;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < 15;i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 15;j++){
A[i][j] = 0;
}
}
bool flag = false;
int w = 0;
while(n--){
flag = !flag;//true is A
cin >> x >> y;
w++;
A[x-1][y-1] = flag?1:2;
if(check(x-1,y-1,flag)){
if(flag)cout<<"A"<<" ";
else cout << "B" << " ";
cout << w <<endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout<<"Tie" <<endl;
return 0;
}
文件系统
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int n;
int a;
string s;
cin >> n;
vector<pair<int, string>> A;
A.push_back({-1, "nothing"});
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> a >> s;
A.push_back({a,s});
}
vector<string> S;
S.push_back("nothing");
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a = A[i].first;
s = A[i].second;
if(a==0){
S.push_back("/"+s);
continue;
}
S.push_back(S[a]+"/"+s);
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
sum += S[i].size();
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
矩阵模拟
输入1是翻转,2是行平移,3是列平移
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
int A[101][101] ={0};
int B[101][101] ={0};
int n;
void flip(){
int temp;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
for (int j = i; j <= n; j ++ ){
temp = A[i][j];
//cout << A[i][j] << "," << A[j][i] << endl;
A[i][j] = A[j][i];
A[j][i] = temp;
}
}
}
void checkx(int k){
int now;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
now = (i+k) % n;
if(now==0)now = n;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
B[now][j] = A[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
A[i][j] = B[i][j];
}
}
}
void checky(int k){
int now;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
now = (i+k) % n;
if(now==0)now = n;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
B[j][now] = A[j][i];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
A[i][j] = B[i][j];
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
cin >> A[i][j];
}
}
int q;
cin >> q;
int opt,k;
while(q--){
cin >> opt;
if(opt==1){
flip();
}
else if(opt==2){
cin >> k;
checkx(k);
}
else if(opt==3){
cin >> k;
checky(k);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
cout << A[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
军训队列
把n人分为k组,差距为最大小的身高差平方,使他最小。动态规划。
再次尝试总结,这是区间dp。二层不够就三层,分为之前加上之后的,这思维就好。
主要流程:
- 定义dp数组,特殊情况、初始化
- 确定循环结构,确定转换方程。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int n,k;
cin >> n >> k;
VI A(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
cin >> A[i];
}
sort(A.begin(), A.end());
VVI dp(n+1, VI(k+1,INF_LL));
// i代表人数,j代表队列
//特殊情况
if(k>=n){
cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
// 初始情况,只有一个队列
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
dp[i][1] = (A[i-1]-A[0])*(A[i-1]-A[0]);
}
// 遍历队列数量
for (int j = 2; j <= k; j ++ ){
// 人数数量至少等于j不然没得分
for (int i = j; i <= n; i ++ ){
// 分割,用m分为前j-1组分好的,和后面新一组的,做动态规划
for (int m = j-1; m<i; m ++ ){//是j-1因为再少不够分,小于i是没那么多人,循环就是i人最多
LL current = dp[m][j-1] + (A[i-1]-A[m])*(A[i-1]-A[m]);//最小的就是第m个人
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j],current);
}
}
}
cout << dp[n][k] << endl;
return 0;
}
偏差
A是n长,B是m长,B是A子串,差距为k。用kmp算法解决。第一个做出的比较有难度的题目。。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
//#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
LL n,m;
VI A,B,suba, subb;
set<LL> res;
void kmp(){
LL prelen = 0;
LL i = 1;
LL m = subb.size();
LL n = suba.size();
VI next(m,0);
next[0] = 0;
// 先为被匹配的做next数组
while(i<m){
if(subb[i]==subb[prelen])next[i++]=++prelen;
else if(prelen==0)next[i++]=0;
else prelen=next[prelen-1];
}
// 子串比较
LL j = 0;
i = 0;
res.clear();
while(i<n){
if(suba[i]==subb[j])
{i++;j++;}
else if(j>0)
j=next[j-1];
else
i++;
if(j==m)
{res.insert(i-j+1);j=next[j-1];}//调整为1-base
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
LL T;
cin >> T;
while(T--){
cin >> n;
A.clear();
suba.clear();
A.resize(n);
suba.resize(n-1);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> A[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < n-1; i++){
suba[i] = A[i+1]-A[i];
}//从0存储
cin >> m;
if(m==1){
res.clear();
B.clear();
B.resize(m);
cin >> B[0];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)res.insert(i);
}else{
B.clear();
subb.clear();
B.resize(m);
subb.resize(m-1);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin >> B[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < m-1; i++){
subb[i] = B[i+1]-B[i];
}//从0存储
kmp();
}
/*for(auto x:suba)cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
for(auto x:subb)cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
for(auto x:res)cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << endl;*/
// 问题1
set<LL>kpos; LL k;
LL mine = INF_LL;
for(auto x:res){
k = B[0] - A[x-1];
kpos.insert(k);
mine = min(abs(k),mine);// 问题2
}
cout << kpos.size() << " ";
// 问题2
if(mine==INF_LL)mine = 0;
cout << mine << " ";
// 问题3
cout << res.size() << " ";
// 问题4 5
if(res.empty()){cout << 0 <<" " <<0 << endl;continue;}
cout << *res.begin() << " " << *res.rbegin() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
面试
给出 n人至少m人一队,最高最低差距不能大于k。
我的做法错误了,但是有些结构可以学习:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
/* 访问集合的方法
auto rit = s.rbegin();/begin();
advance(rit, 1); // 移动1步(等价于 ++rit)
*/
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int n,m,k;
cin >> n>>m>>k;
VI A(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
cin >> A[i];
}
// 朴素的贪心:把最小的尽量去掉,最大的尽量去掉,维护他是m个,再求差值
// 集合可以直接做到最大 最小的访问和插入与删除
// map有序的哈希表
// multiset可重复的集合
multiset<LL> S;
multiset<LL> shadow;
LL f,b,fl,bl;
unordered_map<LL,LL> U;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
if(S.find(A[i])!=S.end()){
U[A[i]] += 1;
if(k==0&&U[A[i]]==m-1){
cout << i + 1 << endl;
return 0;
}
}
S.insert(A[i]);
if(i >= m - 1 && k != 0){
shadow = S;
while(shadow.size()>=m){
auto fit = shadow.rbegin();
auto bit = shadow.begin();
f = *fit;
b = *bit;
if(f-b<=k){
cout << i + 1<< endl; return 0;
}
advance(fit, 1);
advance(bit, 1);
fl = *fit;
bl = *bit;
if(fl - b < f - bl){
auto it = shadow.find(f);//删除一个multiset而不是全部
shadow.erase(it);
}else{
auto it = shadow.find(b);
shadow.erase(it);
}
}
}
}
cout << "impossible" << endl;
return 0;
}
正确做法,利用有序性,检查所有连续 m 个元素:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int n, m, k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
vector<LL> heights(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> heights[i];
}
// 1. 特殊处理k=0:需要m个相同身高
if (k == 0) {
unordered_map<LL, int> count;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (++count[heights[i]] >= m) {
cout << i + 1 << endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout << "impossible" << endl;
return 0;
}
// 2. 维护有序数组:存储已面试的所有身高(始终升序)
vector<LL> sorted_heights;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// 插入当前身高,保持数组有序(lower_bound找插入位置)
auto insert_pos = lower_bound(sorted_heights.begin(), sorted_heights.end(), heights[i]);
sorted_heights.insert(insert_pos, heights[i]);
// 3. 当元素数≥m时,检查所有连续m个元素的身高差
if (sorted_heights.size() >= m) {
// 遍历所有可能的起始位置j,检查j到j+m-1的连续m个元素
for (int j = 0; j <= sorted_heights.size() - m; ++j) {
LL min_h = sorted_heights[j];
LL max_h = sorted_heights[j + m - 1];
if (max_h - min_h <= k) {
cout << i + 1 << endl; // 面试人数是i+1(0-based转1-based)
return 0;
}
}
}
}
// 4. 遍历完所有面试者仍无有效组合
cout << "impossible" << endl;
return 0;
}
售货机
给出n个 a 价格 b可能买到的另一个 p 买到a的概率,人来买随机买一个口,如果没买到x就买买错的那个口,直到买到或者买到空的了。求期望。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef int LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
//const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
struct me{
LL a;
LL b;
double pa;
double pb;
};
struct st{
LL start;
LL idx;
double p;
LL pri;
bool flag;// 为0是自己,为1是另一个
};
vector<bool> used,tempused;
vector<st> path;
LL n,x;
vector<me> A;
double allp = 1;
LL nexti;
double nowp = 1;
double ans = 0;
double pp = 0;
void check(){
if(path.empty()){
nexti = -1;
}else{
nexti = path.back().idx;//访问最后一个元素
}
if(!path.empty()){
auto nowget = path.back();//访问最后一个元素
if(nowget.idx == x){
pp = allp;
double sum = 0;
fill(tempused.begin(), tempused.end(), false);
for(auto ok : path){
sum += ok.pri;
// cout <<"{" << ok.start << ", " << ok.idx << ", " << ok.p << ", " << ok.pri << "} ";
if(ok.flag){
if(tempused[ok.start]){
pp = pp;
}else{
pp = pp * ok.p;
}
}else{
if(tempused[A[ok.idx].b]){
pp = pp;
}else{
pp = pp * ok.p;
}
}
tempused[ok.idx] = true;
}
// cout << pp <<", "<< sum << endl;
ans += pp * sum;
nexti =-1;
return;
}
int i = nexti;
if(!used[i]){//买到自己
path.push_back({i, i, A[i].pa, A[i].a, 0});
used[i] = true;
check();
used[i] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
if(!used[A[i].b]){//买到另一个
path.push_back({i, A[i].b, A[i].pb, A[i].a, 1});
used[A[i].b] = true;
check();
used[A[i].b] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
if(used[A[i].b]&&used[i]){// 漏了硬买一次。。。不然就做出来了
// 都买不到了, 那么硬买一次,然后 ,直接计算
pp = allp;
double sum = A[i].a;
fill(tempused.begin(), tempused.end(), false);
for(auto ok : path){
sum += ok.pri;
// cout <<"{" << ok.start << ", " << ok.idx << ", " << ok.p << ", " << ok.pri << "} ";
if(ok.flag){
if(tempused[ok.start]){
pp = pp;
}else{
pp = pp * ok.p;
}
}else{
if(tempused[A[ok.idx].b]){
pp = pp;
}else{
pp = pp * ok.p;
}
}
tempused[ok.idx] = true;
}
// cout << pp <<", "<< sum << endl;
ans += pp * sum;
nexti = -1;
return;
}
}else{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
path.push_back({i, i, A[i].pa, A[i].a, 0});
used[i] = true;
check();
used[i] = false;
path.pop_back();
path.push_back({i, A[i].b, A[i].pb, A[i].a, 1});
used[A[i].b] = true;
check();
used[A[i].b] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> x;
A.resize(n+1);
used.resize(n+1, false);
tempused.resize(n+1, false);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> A[i].a >> A[i].b >> A[i].pa;
A[i].pb = 1 - A[i].pa;
}
allp /= n;
check();
printf("%.6f", ans);
return 0;
}
公司
输入全部员工工资和一堆PII,代表x知道y的工资,如果知道的工资平均大于他的工资,就要离职。记录要离职的人数量。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
LL n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<double> A(n+1, 0); // 员工自己的工资
vector<double> K(n+1, -1); // 知道的平均数
VI N(n+1, 0); // 知道的数量(辅助快速计算平均数)
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> A[i];
}
LL a,b;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
cin >> a >> b;
K[a] = (K[a] * N[a] + A[b]) / (N[a] + 1);
N[a] ++;
}
LL ans=0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(K[i]==-1)continue;
if(A[i] < K[i])ans++;
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
擂台赛
基数比较小,直接8 4 2写函数,然后处理。其中比较出问题的是four数组索引出错后面改了,然后就是n=8的时候的除数不知道是多少还是看输出才写对了。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
VI pathe;
VI pathf;
LL four[4] = {1,2,3,4};
LL two[2] = {0};
LL ans = 0;
LL n;
LL A[9][9] = {0};
vector<bool> used(9, false);
vector<bool> usedf(5, false);
VI list;
void workfour(bool flag){
if(!flag){// 如果不是起源要先处理pathe
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i+=2){
if(A[pathe[i]][pathe[i+1]]==1){
four[j++] = pathe[i];//打比赛,谁赢了,留下谁,进入下一关
}else{
four[j++] = pathe[i+1];
}
}
}
if(pathf.size()==4){
// 达到4个直接决出胜负
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i+=2)
{
if(A[pathf[i]][pathf[i+1]]==1){
two[j++] = pathf[i];
}else{
two[j++] = pathf[i+1];
}
}
if(A[two[0]][two[1]]==1){
if(two[0]==1){
ans++;
// 记录一下
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
list.push_back(pathf[i]);
}
}
}
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i <= 3; i++){
if(!usedf[i]){
pathf.push_back(four[i]);
usedf[i] = true;
workfour(true);
usedf[i] = false;
pathf.pop_back();
}
}
}
void workeight(){// 比赛中/正在处理的人数
if(pathe.size()==8){
//for(auto x: pathe) cout << x << " ";
//cout << endl;
workfour(false);
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 8; i++){
if(!used[i]){
pathe.push_back(i);
used[i] = true;
workeight();
used[i] = false;
pathe.pop_back();
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
cin >> A[i][j];
}
}
if(n == 8){
workeight();
ans /= 192;
}else if(n == 4){
workfour(true);
ans /= 2;
}else if(n==2){
if(A[1][2]==1){
ans = 1;
}
}
cout << ans <<endl;
/*int j = 0;
while(j<list.size()){
if(j%4==0)cout << endl;
cout << "(" << list[j] << ", " << list[j+1] << ")" << " ";
j+=2;
}*/
return 0;
}
nextper升级版
直接快了超级多
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
VI pathe={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
VI pathf={1,2,3,4};
LL two[2] = {0};
LL ans = 0;
LL n;
LL A[9][9] = {0};
vector<bool> used(9, false);
vector<bool> usedf(5, false);
VI list;
void workfour(bool flag){
if(!flag){// 如果不是起源要先处理pathe
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i+=2){
if(A[pathe[i]][pathe[i+1]]==1){
pathf[j++] = pathe[i];//打比赛,谁赢了,留下谁,进入下一关
}else{
pathf[j++] = pathe[i+1];
}
}
}
sort(pathf.begin(),pathf.end());
do{
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i+=2)
{
if(A[pathf[i]][pathf[i+1]]==1){
two[j++] = pathf[i];
}else{
two[j++] = pathf[i+1];
}
}
if(A[two[0]][two[1]]==1){
if(two[0]==1){
ans++;
}
}else{
if(two[1]==1){
ans++;
}
}
}while(next_permutation(pathf.begin(),pathf.end()));//用之前要排序的
}
void workeight(){// 比赛中/正在处理的人数
do{
workfour(false);
}while(next_permutation(pathe.begin(),pathe.end()));
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
cin >> A[i][j];
}
}
if(n == 8){
workeight();
ans /= 384;//全排列4的阶乘24乘以2*2*2*2的位置互换
}else if(n == 4){
workfour(true);
ans /= 4; //全排列2的阶乘乘以2的变换
}else if(n==2){
if(A[1][2]==1){
ans = 1;
}
}
cout << ans <<endl;
return 0;
}
见
有点ez了,就是需要幻想一下
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
const int BUF_SIZE = 1 << 20;
char buf[BUF_SIZE];
int buf_ptr=0;
int buf_len=0;
inline char my_getc(){
if(buf_ptr>=buf_len){
buf_len = fread(buf, 1, BUF_SIZE, stdin);
buf_ptr=0;
if(buf_len==0)return EOF;
}
return buf[buf_ptr++];
}
inline long long r(){
LL x =0;
int sign = 1;
char ch = my_getc();
while(ch==' '|| ch == '\n'|| ch == '\r'|| ch == '\t'){
ch = my_getc();
}
if(ch == '-'){
sign = -1;
ch = my_getc();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
x = x*10+(ch - '0' );
ch = my_getc();
}
return x*sign;
}
LL n;
VVI H;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
n = r();
H.resize(n+1, VI(n+1,0));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++){
H[i][j] = r();
}
}
VI L(n+1,0), R(n+1,0), U(n+1,0), D(n+1,0);
//先处理L
LL maxme=0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(H[i][1] == n){
L[i]=1;
continue;
}
maxme = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++){
if(maxme==n)break;
if(H[i][j]>maxme){
L[i]++;
maxme = H[i][j];
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(H[i][n] == n){
R[i]=1;
continue;
}
maxme = 0;
for(int j = n; j >= 1; j --){
if(maxme==n)break;
if(H[i][j]>maxme){
R[i]++;
maxme = H[i][j];
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(H[1][i] == n){
U[i]=1;
continue;
}
maxme = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++){
if(maxme==n)break;
if(H[j][i]>maxme){
U[i]++;
maxme = H[j][i];
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(H[n][i] == n){
D[i]=1;
continue;
}
maxme = 0;
for(int j = n; j >= 1; j--){
if(maxme==n)break;
if(H[j][i]>maxme){
D[i]++;
maxme = H[j][i];
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i<=n; i++){
cout << L[i] << " " << R[i] << " " << U[i] << " " << D[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
树上计数
好像自己开创了一个独特的BFS方法。。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
LL n,l,r;
cin >> n >> l >> r;
// 子树及其节点
VVI T(n+1); LL pa;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
cin >> pa;
T[pa].push_back(i);
}
VI CH(n+1,1);//维护一个子树数量数组,方便后续取用
// 倒着记录
// 必须先摸清楚他们的顺序才行
// 从1出发
VVI G;
VI last = {1};
VI now = {1};
LL count = 0;
while(count < n){//处理了n个才算结束
G.push_back(now);
count += now.size();
last = now;
now.clear();
for(auto x : last){
for(auto y : T[x]){
now.push_back(y);//把上一层的全部的下一层放入now
}
}
}
//得到了层级,开始从底下往上获取ch
// 初始化最后一层都是1,好像已经弄过了
for(int i = G.size()-2; i>=0; i--){
for(auto x : G[i]){// 每一层的节点
// 每一层的节点的下一个
for(auto y : T[x]){
CH[x] += CH[y];
}
}
}
// 得到之后遍历计算就行
LL ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(CH[i]>=l&&CH[i]<=r)ans++;
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
毕业照
ABCDE五个人。
给出限制m,里面要求某个人和某个人不能在一起或者必须在一起,求可以的排列个数。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
LL ans = 0;
vector<char> S = {'A','B','C','D','E'};
vector<pair<char,char>> no;
vector<pair<char,char>> yes;
char u,v;
// 做一个预处理直接记住身边是谁然后就不用到处找了,减去0x40就是1-base的索引
vector<vector<char>> pre;
void check(){
// 预处理我身边是谁
pre.clear();
pre.resize(6);
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
if(i==0){
pre[S[i]-0x40].push_back(S[i+1]);
continue;
}else if(i==4){
pre[S[i]-0x40].push_back(S[i-1]);
continue;
}else{
pre[S[i]-0x40].push_back(S[i-1]);
pre[S[i]-0x40].push_back(S[i+1]);
}
}
bool flag=false;
for(auto x: yes){
u = x.first;
v = x.second;
flag = false;
for(auto y:pre[u-0x40]){
if(v==y){//如果遇到一样的标记为true跳出
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if(!flag)return;//不是true就返回
}
for(auto x: no){
u = x.first;
v = x.second;
for(auto y:pre[u-0x40]){
if(v==y)return;//不要让一起的遇到一起了就直接返回
}
}
ans++;//经历磨难才可以++
return;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
LL m;
cin >> m;
int op;
char a,b;
while(m--){
cin >> op >> a >> b;
if(op==1){
yes.push_back({a,b});
}else if(op==2){
no.push_back({a,b});
}
}
do{
check();
}while(next_permutation(S.begin(),S.end()));
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
prime
输入一个数字,加数字(第一个不能是0)让他变为质数
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
// 可根据题目需求补充其他头文件(如<queue>、<stack>、<map>等)
using namespace std;
// -------------------------- 常用类型别名(简化代码)--------------------------
typedef long long LL; // 处理大整数,避免溢出
typedef vector<LL> VI; // 一维长整型数组
typedef vector<VI> VVI; // 二维长整型数组
typedef pair<LL, LL> PII; // 存储二元组(如<数量, 值>、<坐标x, 坐标y>)
// 可扩展:如typedef pair<int, int> PII_int;(int型二元组)、typedef vector<PII> VPII;(二元组数组)
// -------------------------- 通用常量定义(根据题目调整值)--------------------------
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // int型最大值(常用于表示“无穷大”)
const LL INF_LL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // long long型最大值
const double EPS = 1e-8; // 浮点数精度(处理浮点数比较时用)
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 常用模值(数论题、计数题常用)
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; // 数组/容器最大规模(根据题目数据范围调整)
bool cmp(PII& a, PII& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
bool isp(int x){
if(x<2)return false;
for (int i = 2; i <= x/i; i ++ ){
if(x%i==0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int t,x;
t = 1;
int now;
while(t--){
cin >> x;
now = x;
while(true){
now++;
if(now/10==x){
if(isp(now)){
cout << now << endl;
break;
}
}else if(now/100==x){
if((now/10)%10!=0&&isp(now)){
cout << now << endl;
break;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号