java-直接选择排序
直接选择排序是一种简单的排序方法,它每次从当前待排序的区间中选择出最小的元素,把该元素与该区间的第一个元素交换。
第一次从a[0]~a[n-1]中选取最小值,与a0]交换,第二次从a[1]~a[n-1]中选取最小值,与a[1]交换,....,第i次从a[i-1]~a[n-1]中选取最小值,与a[i-1]交换,.....,第n-1次从a[n-2]~a[n-1]中选取最小值,与a[n-2]交换,总共通过n-1次,得到一个按排序码从小到大排列的有序序列。
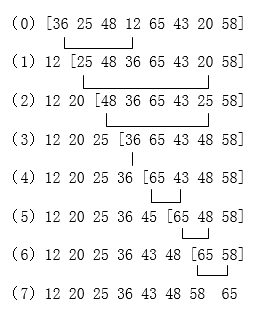
例如:假定n = 8,数组a中8个元素的排序码为:
(36,25,48,12,65,43,20,58)
如图给出了进行每次选择并交换后各排序码位置的变动情况,中括号中为待排序区间,中括号前面为已经排好的元素。
直接选择排序的算法用java描述为:
1 public static void selectionSort(int[] a,int n) { 2 if(n>a.length) { 3 System.out.println("超出数组长度"); 4 System.exit(1); 5 } 6 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { //i表示次数,共进行n-1次选择和交换 7 int minIndex = i-1; //用minIndex表示最小元素的下标 8 for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {//找到当前排序区间中最小元素的下标 9 if(a[minIndex]>a[j]) {//如果后面的元素小于当前最小元素,则用minIndex记录下后面最小元素的下标 10 minIndex = j; 11 } 12 } 13 if(minIndex != i) {//如果minIndex==i,说明minIndex就是当前排序区间首位元素的下标,因此不用交换 14 int temp = a[i]; 15 a[i] = a[minIndex]; 16 a[minIndex] = temp; 17 } 18 } 19 }
完整代码并测试:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class SelectionSort { 4 public static void selectionSort(int[] a,int n) { 5 if(n>a.length) { 6 System.out.println("超出数组长度"); 7 System.exit(1); 8 } 9 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { //i表示次数,共进行n-1次选择和交换 10 int minIndex = i-1; //用minIndex表示最小元素的下标 11 for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {//找到当前排序区间中最小元素的下标 12 if(a[minIndex]>a[j]) {//如果后面的元素小于当前最小元素,则用minIndex记录下后面最小元素的下标 13 minIndex = j; 14 } 15 } 16 if(minIndex != i-1) {//如果minIndex==i-1,说明minIndex就是当前排序区间首位元素的下标,因此不用交换 17 int temp = a[i-1]; 18 a[i-1] = a[minIndex]; 19 a[minIndex] = temp; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 24 public static void main(String[] args) { 25 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 26 System.out.println("请输入元素的个数"); 27 int n = input.nextInt(); 28 int[] a = new int[n]; 29 System.out.println("请依次输入元素"); 30 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { 31 a[i] = input.nextInt(); 32 } 33 System.out.println("请输入待排元素的个数"); 34 int m = input.nextInt(); 35 selectionSort(a,m); 36 System.out.println("排序之后"); 37 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { 38 System.out.print(a[i]+" "); 39 } 40 } 41 }
请输入元素的个数
8
请依次输入元素
36 25 48 12 65 43 20 58
请输入待排元素的个数
8
排序之后
12 20 25 36 43 48 58 65
效率:
在直接选择排序中,共需要进行n-1次选择和交换,每次选择需要比较n-i 次(1<=i<=n-1),每次交换最多需要3次移动,因此,总的比较次数:C=(n*n - n)/2,
总的移动次数(最大值): 3(n-1).由此可知,直接选择排序的时间复杂度为 O(n^2)。由于在直接选择排序中存在着前后元素之间的互换,因而可能会改变相同元素的前后位置,如4,3,4,2 第一次4和2交换,第一个4跑到了第3个4之后,所以此方法是不稳定的。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号