RabbitMQ进阶--分布式事务案例
本节主要讲述一个案例,是使用rabbitmq实现分布式事务,本章从分布式事务以sping的声明式事务,转而到rabbitMQ的分布式事务,一下环境需要的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.amqp</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-rabbit-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-avro</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.17.0</version>
</dependency>
需要的配置文件:
#连接数据库 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/service?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver #rabbitMQ连接 spring.rabbitmq.port=5672 spring.rabbitmq.host=8.137.76.12 spring.rabbitmq.username=admin spring.rabbitmq.password=admin spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host= /
一.spring声明式事务
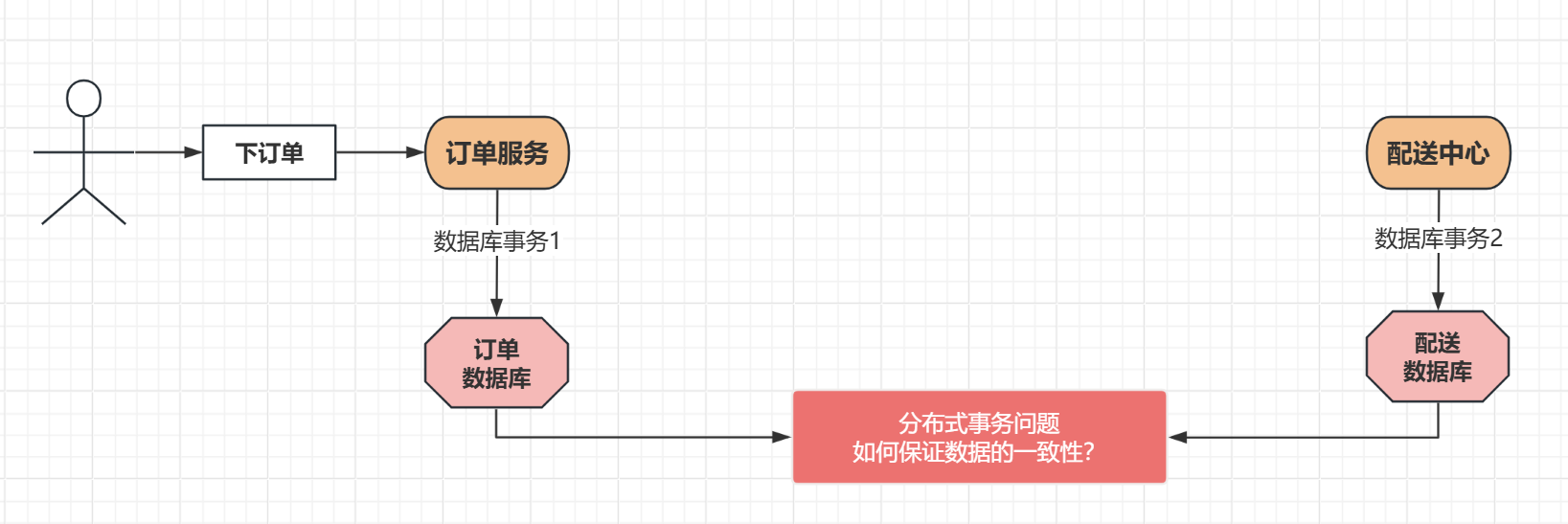
当我们的服务是位于分布式架构的时候,总会有不同的数据库产生不同的事务,各个事务都是跨数据库的,也是跨JVM平台的,在这种情况下需要实现事务就会非常的麻烦,也不是简单是实现就可以做到的,因为这已经是两个或多个独立的事务了,在最开始的架构的时候,我们会用HttqRequest请求来判断另外一个事务是否执行完成,如果事务执行成功,再让自己的事务提交,反之,另外一个事务执行失败,那么自己的事务就回滚。
接下来我们就来看看这种事务的实现:
定义生产者
事务1,业务类:
作用自己先执行一个事务,将信息保存到数据库(本地数据),然后调用HttpRequest请求,查看事务2的执行结果,如果事务2执行失败那么就回滚,否则就提交
import org.cqust.orderservice.dao.OrderDatabaseService; import org.cqust.orderservice.pojo.OrderTable; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.http.client.SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @Service public class OrderService { @Autowired private OrderDatabaseService orderDatabaseService; @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) public void createOrder(OrderTable orderTable) throws Exception{ orderDatabaseService.saveOrder(orderTable); //通过Http请求发送订单信息到运单信息 String s = dispatchHttpApi(orderTable.getOrderId()); if (!s.equals("success")){ throw new Exception("订单创建失败原因是接口调用"); } } private String dispatchHttpApi(String orderId){ SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory factory = new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory(); //连接超时 > 3s factory.setConnectTimeout(3000); //处理超时 > 2s factory.setReadTimeout(2000); RestTemplate template = new RestTemplate(factory); return template.getForObject("http://localhost:9000/dispatcher/order?orderId=" + orderId, String.class); } }
自己存入数据库的dao操作类:
import org.cqust.orderservice.pojo.OrderTable; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import java.util.Date; @Service @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) public class OrderDatabaseService { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //保存订单信息 public void saveOrder (OrderTable orderTable) throws Exception{ //定义sql String sql = "insert into order_table(order_id,user_id,order_content,create_time) value(?,?,?,?)"; int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,orderTable.getOrderId(),orderTable.getUserId(),orderTable.getOrderContent(),new Date(System.currentTimeMillis())); if (count != 1){ throw new Exception("订单创建失败,原因[数据库]"); } //本地保存 saveLocalMessage(orderTable); } }
定制消费者
消费者也是一个独立的事务,当生产者发送来HttpRequest请求之后,开始执行事务,然后返回一个字符串,给另外一个事务进行回滚或提交用:
事务2的控制器:
import org.cqust.dispatcherservice.service.dispatcherService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/dispatcher") public class DispatcherController { @Autowired public dispatcherService ds; //添加订单后添加调度信息 @GetMapping("/order") public String lock(String orderId) throws Exception { ds.dispatcher(orderId); return "success"; } }
事务2的存入数据库操作:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import java.util.Date; import java.util.UUID; @Service @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) public class dispatcherService { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; /** * @Discription 运单的接收 * @param orderId * @throws Exception */ public void dispatcher(String orderId) throws Exception{ //保存定义SQL String sql = "insert into dispatch_table(dispatch_id,order_id,status,user_id,order_content,create_time) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)"; //添加运动记录 int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, UUID.randomUUID().toString(),orderId,0,"1000","一包泡面",new Date(System.currentTimeMillis())); if (count!=1){ throw new Exception("订单创建失败,原因[数据库]"); } } }
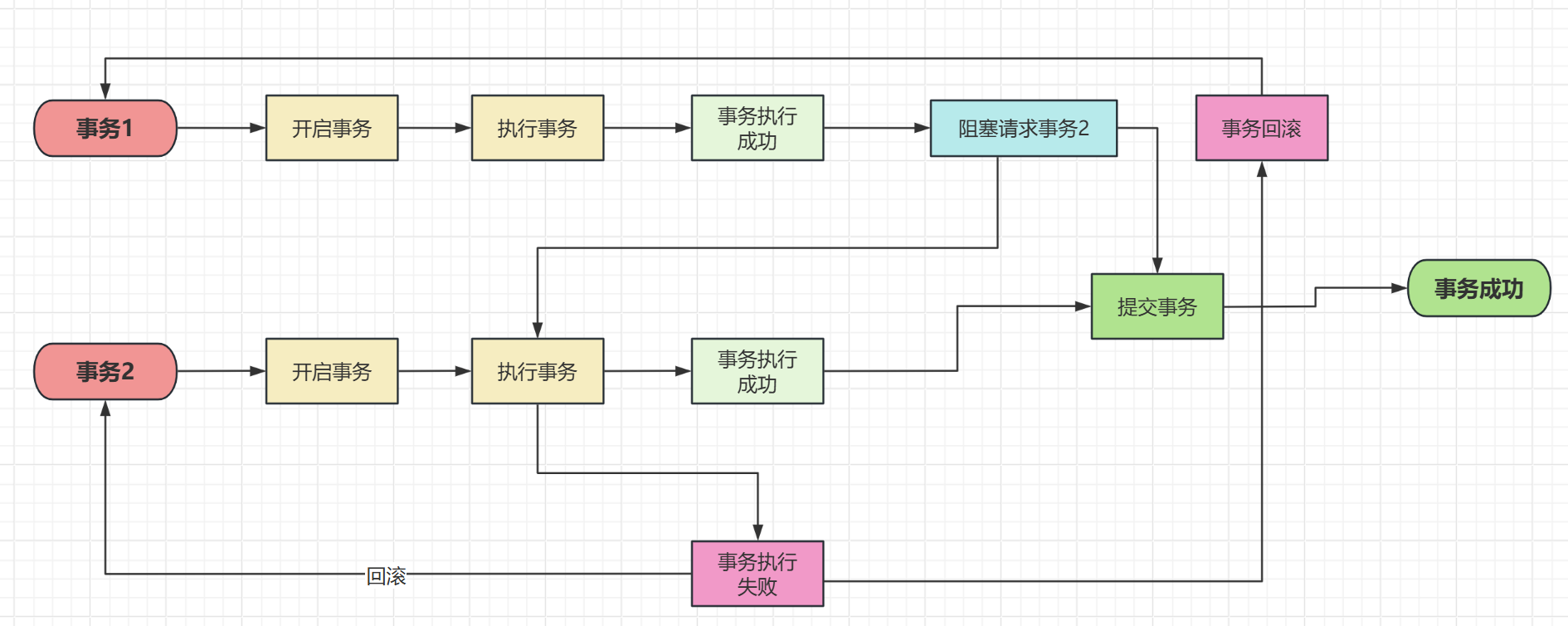
如上当存入数据库之后,就会由控制器返回success到事务1,反之就会抛出一个异常,如果事务1收到success之后就提交事务,反之就回滚事务
接下来我们测试一下,使用生产者中的一个测试方法,因为生产者有调度事务2的Http请求,故而在生产者方测试:
@Autowired private OrderService orderService; @Test void contextLoads() throws Exception { String orderId = "100001"; OrderTable table = new OrderTable(); table.setOrderId(orderId); table.setUserId(1); table.setOrderContent("买了一根烤肠"); orderService.createOrder(table); System.out.println("订单创建成功"); }
当然两个数据库表需要连接上,表结构可以复制:
#消费者的数据表 CREATE TABLE `dispatch_table` ( `dispatch_id` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL, `order_id` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL, `status` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `user_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `order_content` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL, `create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; #生产者的数据表 CREATE TABLE `order_table` ( `order_id` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL, `user_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `order_content` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL, `create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
上面构造的是一个正常的事务,故而两个表肯定是都会新增一条数据的,接下来运行:
模拟分布式事务失败
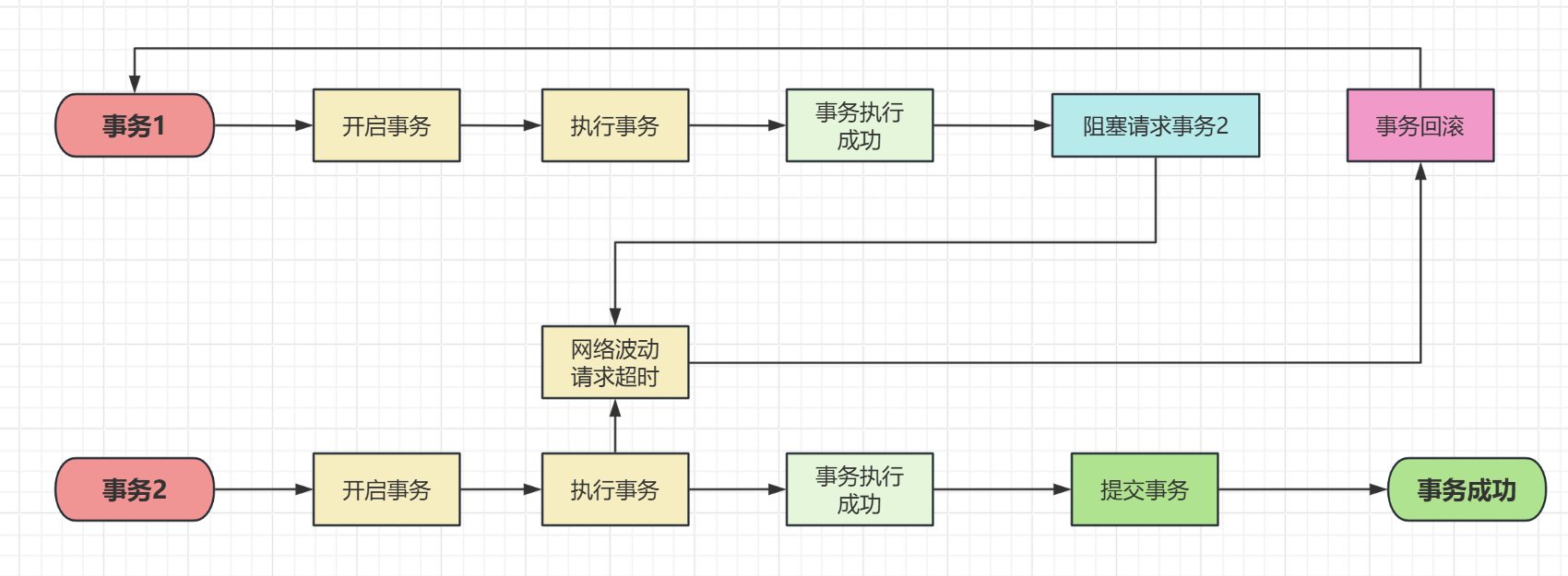
像上面这种以阻塞请求的方式实现两个事务的同时从而保证数据一致性有一个很大的问题,那就是网络波动,如果事务2的网络一直波动,那么有很大的问题,事务1是阻塞等待,如果事务2一直返回,那么事务1就会一直阻塞,这对于高并发的场景是致命的,但是如果设置事务1进行一个超时就不再等待,让事务回滚,可以解决事务1所在的服务不会重复等待,但是又有一个新的问题,那就是因为网络波动后事务1因为事务2超时了,所以进行了回滚;而如果事务2只是因为网络波动的原因而执行成功了,那么就会发生事务的不一致性。
接下来我们模拟一下上面这种情况,很简单,只需要修改生产者请求的读取时间:
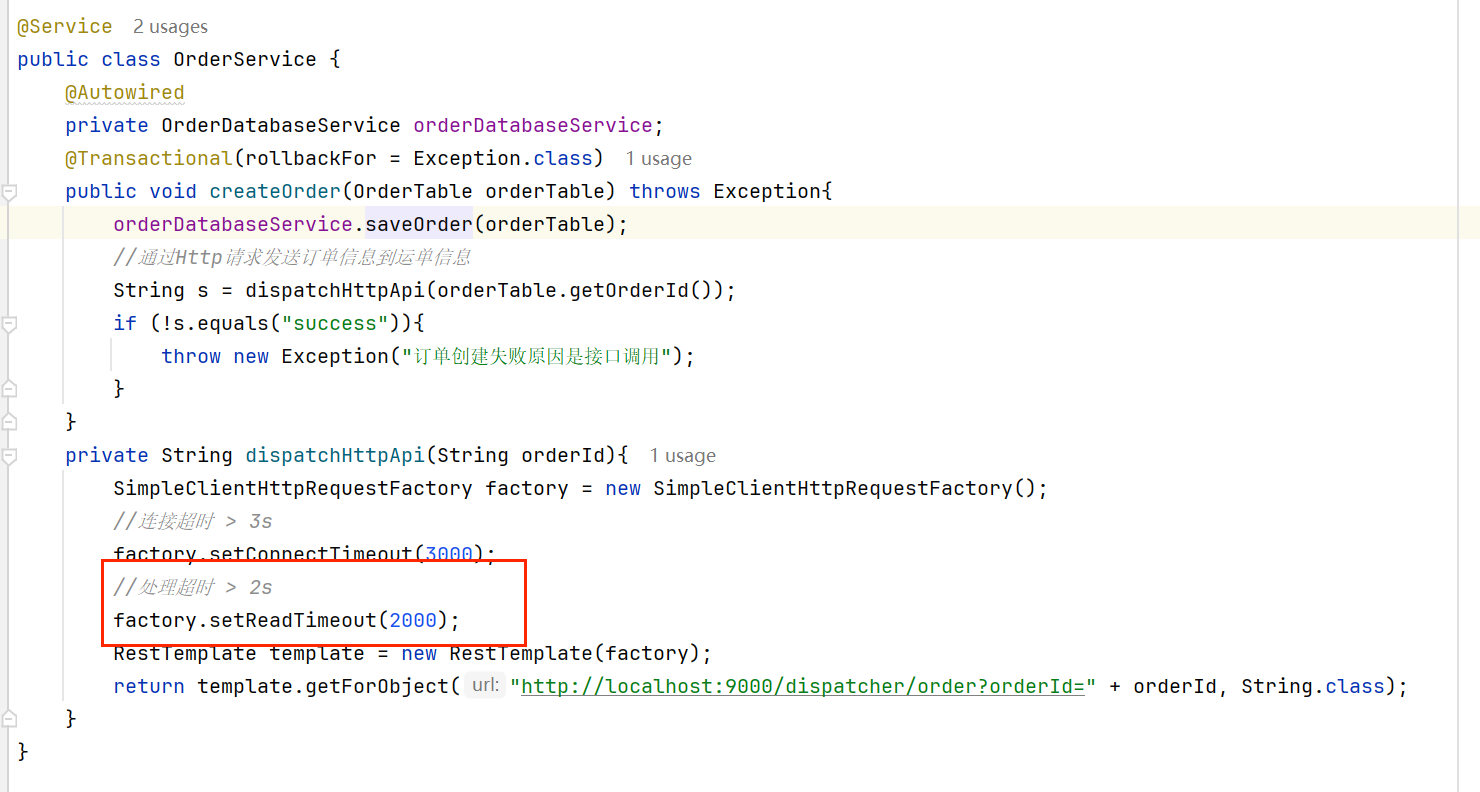
设置一次请求处理时间为2s,超时则抛出异常请求超时(或者说读已超时)
修改消费者的处理时间:
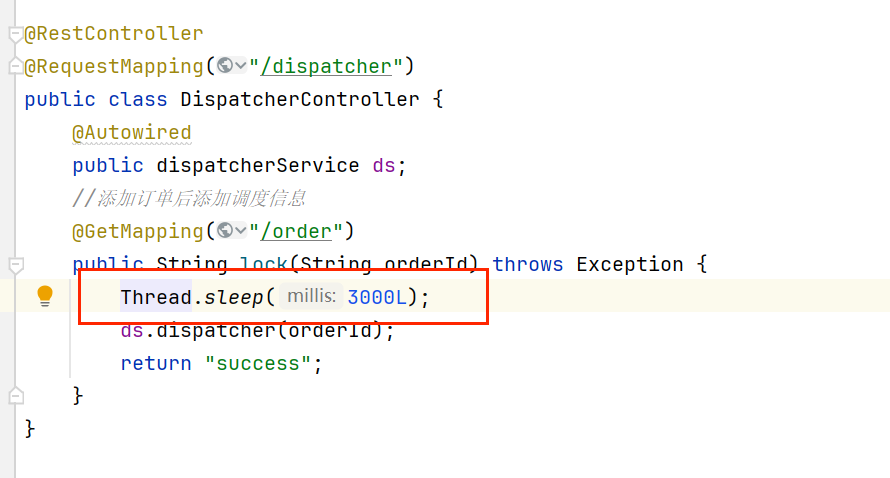
让消费者存数据库先线程休眠3s,那么生产的Http请求肯定会超时,那么事务1就会回滚,而事务2休眠3s之后就会存入数据库,那么就会发生生产者回滚了,而消费者没回滚而存入数据库的情况:
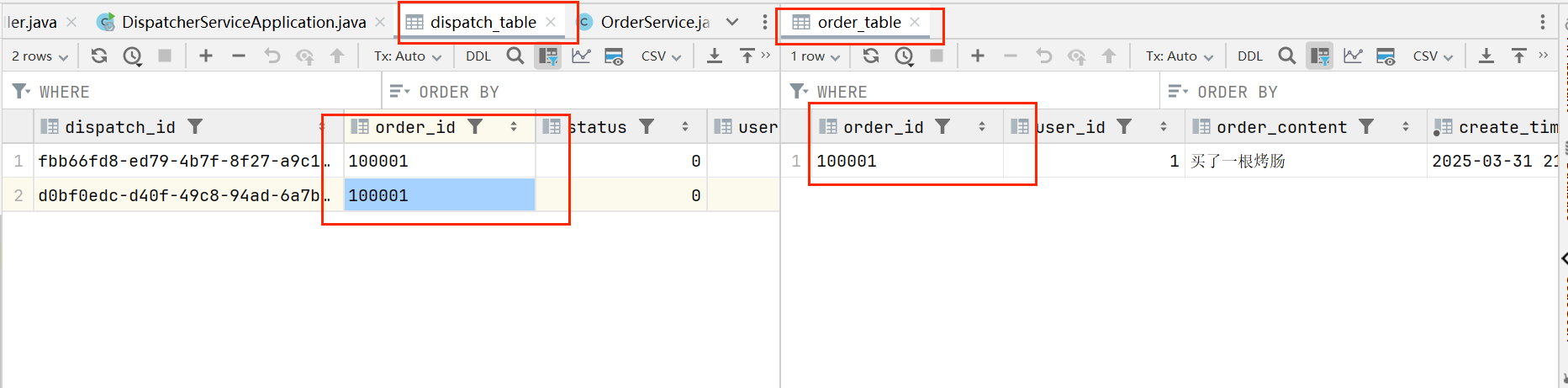
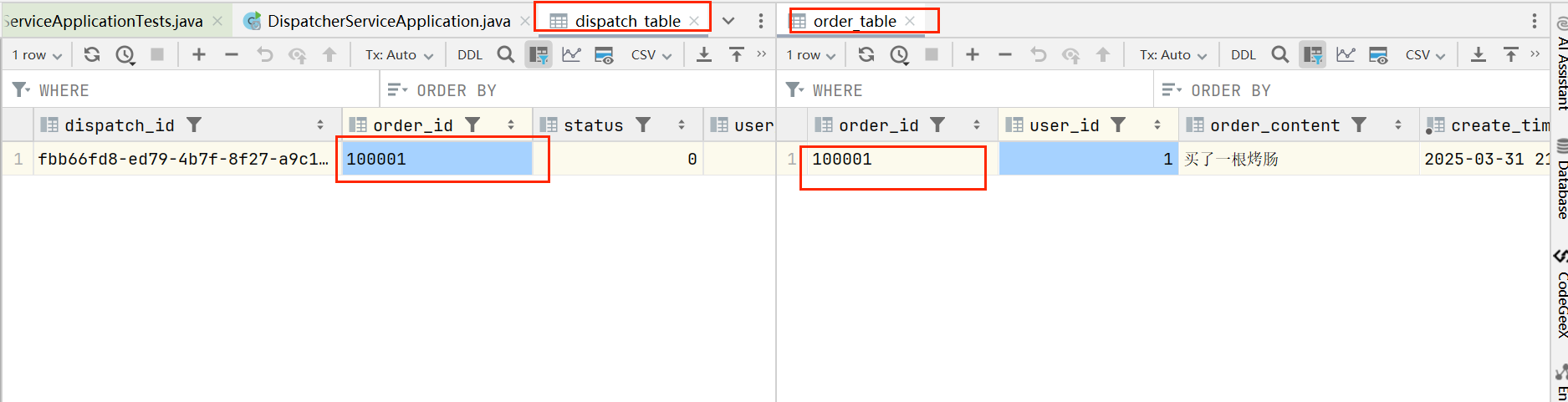
如上,我们会发现消费者的数据库表果然比生产者的数据多一条,那么这就是由网络波动使得两个分布式事务最终数据不一致性的案例,解决的方式有很多,没有最好只有更适合自己的业务场景的解决方式。
这里我们使用的是RabitMQ的消息中间件
二.RabbitMQ可靠生产和可靠消费
使用RabbitMQ的解决方式:解耦
spring的声明式事务会有一个很大的特点就是两个事务的耦合性太高了,一个事务需要阻塞监听另一个服务的事务,这使得两个服务具有很大的耦合性,可以这么说事务1的成功与否需要事务2来确定,引入RabbitMQ后我们就可以解耦、削峰
使用这种方式实现数据一致性,不再需要两个事务进行通信,而是生产者执行成功之后将消费者也需要执行交给RabbitMQ,生产者只管将需要消费者执行入库的信息交给RabbitMQ,然后消费者一直监听RabbitMQ,当有消息之后,就进行执行,这样两个事务就实现了解耦,生产者只管执行自己的事务,然后投递信息,消费者只管监听消息,然后执行事务,当然,会存在速度不匹配的问题,就会发生数据在某个时刻数据会不一致,但是可以保证数据的最终一致性。
重构上面的spring声明式事务的代码
生产者
生产者的业务类:需要完成存储数据,然后投递相关订单信息到RabbitMQ中就完成了,不需要处理另外一个服务回馈,现在我们需要保证的是消息能正常投递到RabbitMQ:
正常投递信息业务类:
import org.cqust.orderservice.dao.OrderDatabaseService; import org.cqust.orderservice.mq.OrderMQService; import org.cqust.orderservice.pojo.OrderTable; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class MQOrderService { @Autowired private OrderDatabaseService orderDatabaseService; @Autowired private OrderMQService orderService; //创建订单 public void createOrder(OrderTable orderTable) throws Exception{ // 1.订单信息:插入到订单系统,订单数据事务 orderDatabaseService.saveOrder(orderTable); //通过rabbitMQ发送订单信息到运单系统,投递消息 orderService.sendMessage(orderTable); } }
第一个方法是存入数据库表:
import org.cqust.orderservice.pojo.OrderTable; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import java.util.Date; @Service @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) public class OrderDatabaseService { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //保存订单信息 public void saveOrder (OrderTable orderTable) throws Exception{ //定义sql String sql = "insert into order_table(order_id,user_id,order_content,create_time) value(?,?,?,?)"; int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,orderTable.getOrderId(),orderTable.getUserId(),orderTable.getOrderContent(),new Date(System.currentTimeMillis())); if (count != 1){ throw new Exception("订单创建失败,原因[数据库]"); } //本地保存 saveLocalMessage(orderTable); } }
第二个方法就是需要发送消息到RabbitMQ:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct; import org.cqust.orderservice.pojo.OrderTable; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class OrderMQService { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void sendMessage(OrderTable orderTable) throws JsonProcessingException { //转换为json ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); String order = mapper.writeValueAsString(orderTable); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("order_fanout_exchange","",order,new CorrelationData(orderTable.getOrderId())); } }
发送订单信息给交换机,当然,这里的订单信息需要可以序列化的类,并且转换为JSON对象投递到交换机
消费者
消费者则需要监听RabbitMQ的消息队列,然后有消息之后将JSON对象反序列化后转换为对象,然后存储到数据库,实现数据的最终一致性
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import jakarta.servlet.annotation.HandlesTypes; import org.cqust.dispatcherservice.pojo.OrderTable; import org.cqust.dispatcherservice.service.dispatcherService; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Correlation; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData; import org.springframework.amqp.support.AmqpHeaders; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Header; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class OrderMqConsumer { @Autowired private dispatcherService ds; private int count = 1; //@RabbitListener(queues = {"order.queue"}) public void messageConsumer(String orderMsg, Channel channel, CorrelationData correlationData, @Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long tag) throws Exception{ //将json对象转换为 orderTable对象 ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); OrderTable table = mapper.readValue(orderMsg, OrderTable.class); //模拟消费者发生错误 //获取消息队列的消息 System.out.println("收到的MQ消息是:"+table+",count="+count++); ds.dispatcher(table.getOrderId()); } }
如上的配置,生产者和消费者的关系,正常可以完成消息的投递和消费:
启动生产者:
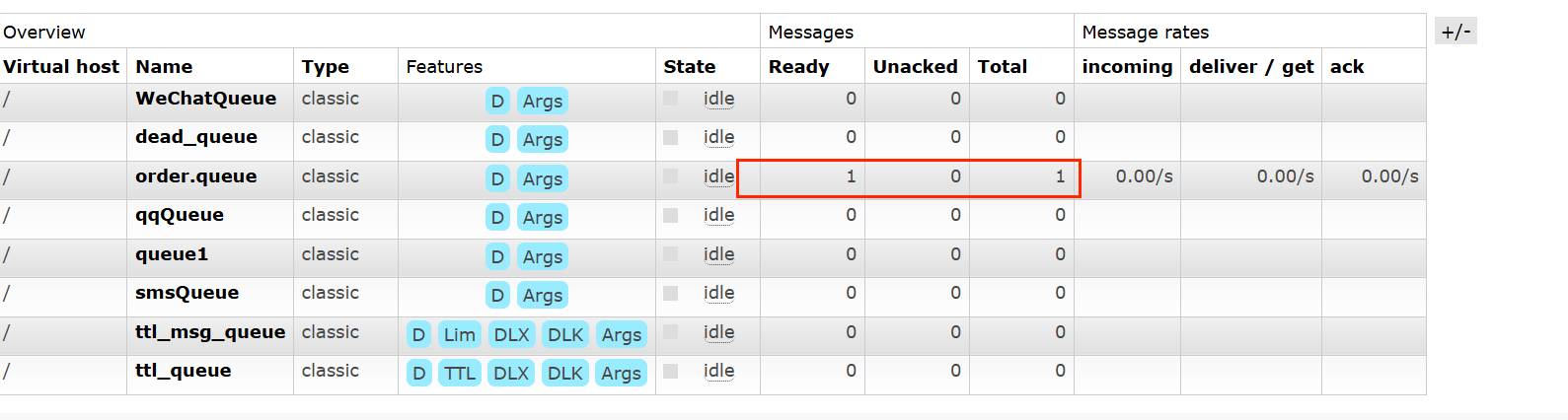
生产者数据库表:
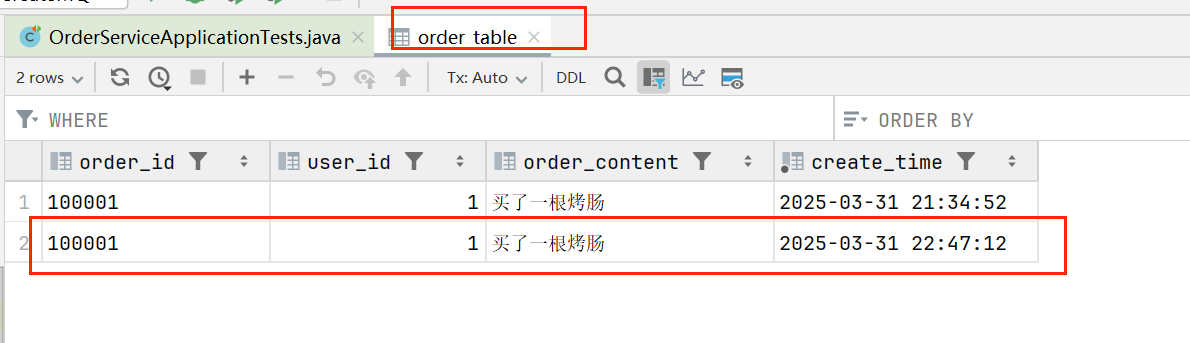
启动消费者进行消费消息:
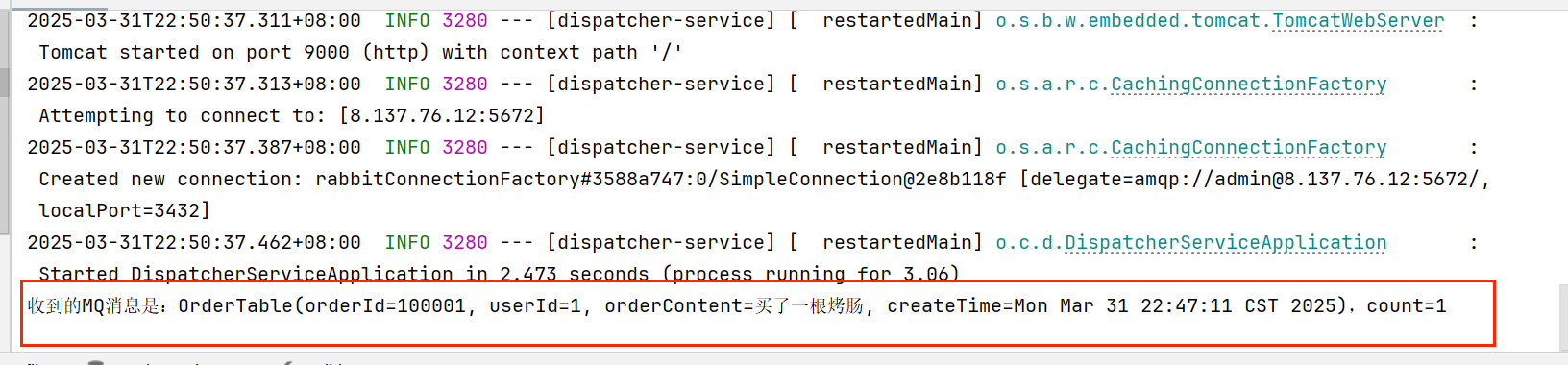
消费者数据库:
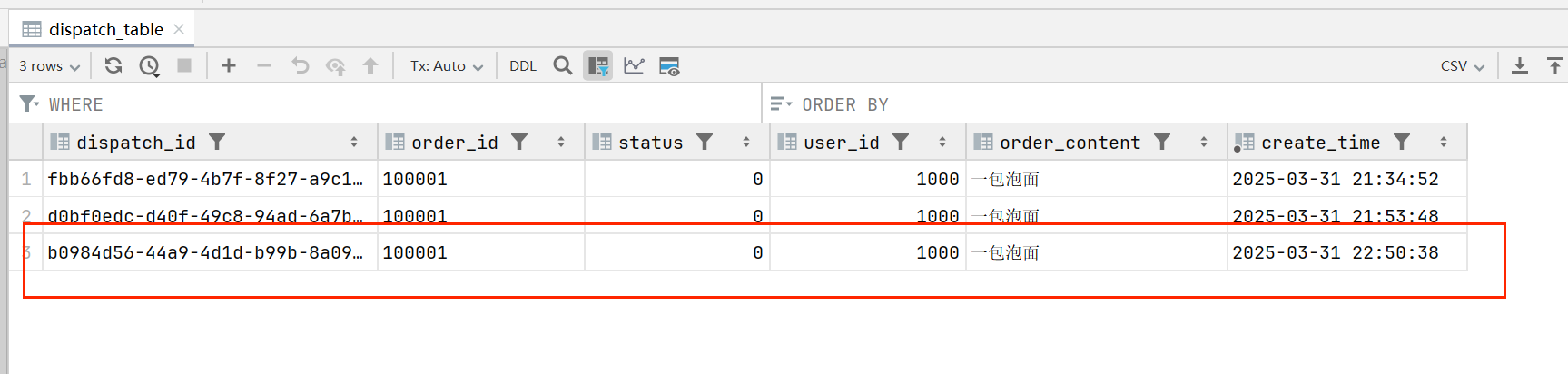
如上,正常的生产消费是没有问题的,但是这些我们就需要解决一下生产者和消费者的可靠性的
上面的是简单的消息的简单投递和消费,但是RabbitMQ并没有进行反馈,可以说在这两个服务之中,我们根本不知道到底生产者有没有将消息可靠的投递到RabbitMQ,同时也不知道消费者有没有可靠的将消费信息进行消费
生产者的可靠生产
可靠生产需要将RabbitMQ的配置为手动应答,也就是每一次发送消息到RabbitMQ之后,都会有一个返回值到到springBoot,可以根据手动应答的结果判断是否正常的投递到RabbitMQ中,
改造投递消息的业务类:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct; import org.cqust.orderservice.pojo.OrderTable; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class OrderMQService { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //在构造函数调用之后的一个回调方法,构造函数之后执行,init函数之前执行 @PostConstruct //在bean初始化之后就完成了它的任务即设置confirm方法 public void regCallback(){ //设置confirm,标志每次投递到rabbitMQ时,都会触发 ConfirmCallback 的 confirm 方法,而不是regCallback方法 rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback() { @Override public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String s) { System.out.println("s:"+s); //如果ack为true表示消息已经收到 if (!ack){ //这里可能需要进行其它方式存储,MQ应答失败 System.out.println("MQ应答失败,orderId是:"+correlationData.getId()); return; } try { String sql = "update order_temp set user_id = 10 where order_id=?"; int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,correlationData.getId()); if (count == 1){ System.out.println("本地消息修改成功,消息成功投递到队列"); } }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("本地消息修改失败,出现异常:"+e.getMessage()); } } }); } public void sendMessage(OrderTable orderTable) throws JsonProcessingException { //转换为json ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); String order = mapper.writeValueAsString(orderTable); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("order_fanout_exchange","",order,new CorrelationData(orderTable.getOrderId())); } }
第一个方法的作用:
当Spring容器初始化 OrderMQService Bean时:
- Spring会先完成依赖注入(
rabbitTemplate和jdbcTemplate)。 - 然后调用
regCallback()方法,设置rabbitTemplate的ConfirmCallback。
第二个方法:
发送订单信息给交换机,当然,这里的订单信息需要可以序列化的类,并且转换为JSON对象投递到交换机
这里还需要创建一个数据库到本地,用于备份那些没有正常投递的信息,然后等待机会定时发送到RabbitMQ,如果RabbitMQ应答为ture就修改已经投递信息的状态,反之则存入备份数据库。
修改RabbitMQ为手动应答:每条消息都有一个唯一的标识(如 CorrelationData),生产者可以通过这个标识与Broker的确认信息进行关联。
#配置rabbitmq的确认机制
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirm-type=correlated
如上配置之后生产者就可以进行可靠消费,根据RabbitMQ的回值确定是否投递信息成功,不成功则存储到冗余数据库,等待一定时延后发送。
运行结果:
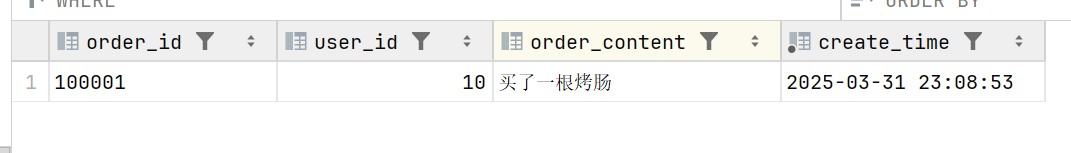
投递成功修改为userid = 10,当需要重发时,会检查userid 不等于10的进行重发
如上使用本地存储的方式解决生产者可靠生产的问题
消费者的可靠消费
可靠消费的前提是需要生产者的可靠生产,当消息被正常的投递到RabbitMQ,消费者才能正常的去消费消息。
消费者的重试机制
当消费者的处理逻辑发生错误时,SpringBoot会一直尝试重试,只要是逻辑错误,那么重试就会一直错,一直错一直重试,就会挤爆RabbitMQ的空间,为了,避免这种情况,我们需要配置重试机制,重试机制必须存在,因为网络可能会不稳定,没有重试机制会导致单次消费有可能失败,故而需要重试,如果是代码逻辑错误,需要人为的修改代码,而不是让重试机制挤爆RabbitMQ的队列空间:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import jakarta.servlet.annotation.HandlesTypes; import org.cqust.dispatcherservice.pojo.OrderTable; import org.cqust.dispatcherservice.service.dispatcherService; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Correlation; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData; import org.springframework.amqp.support.AmqpHeaders; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Header; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class OrderMqConsumer { @Autowired private dispatcherService ds; private int count = 1; @RabbitListener(queues = {"order.queue"}) public void messageConsumer(String orderMsg, Channel channel, CorrelationData correlationData, @Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long tag) throws Exception{ //将json对象转换为 orderTable对象 ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); OrderTable table = mapper.readValue(orderMsg, OrderTable.class); //模拟消费者发生错误 System.out.println(1/0); //获取消息队列的消息 System.out.println("收到的MQ消息是:"+table+",count="+count++); ds.dispatcher(table.getOrderId()); } }
例如上面的代码,我们会发现System.out.println(1/0);是代码层面的错误,但是SPringleBoot不知道,他会一直重试连接,然后一直失败导致线程阻塞,正常的情况应该是保证重试的是连接问题,又要保证代码逻辑错误不会让RabbitMQ和springBoot一直重试,故而配置application.properties文件:
#是否开启失败重连 spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry.enabled=true #重连次数 spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry.max-attempts=10 #每次重连间隔 spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry.initial-interval=2000ms
配置允许重试,并且最大重连次数为1次,重连间隔为2s
死信队列
使用手动应答模式主要是解决,springBoot需要手动的向RabbitMQ应答,说明消费者已经成功的将消息进行消费
#手动确认ack,需要代码层面的控制
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.acknowledge-mode=manual
如果没有被手动确认的消息,则使用try -- catch来进行捕获,然后将其转发到死信队列,避免一直重复的尝试,导致线程阻塞
使用config配置类绑定死信队列:
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding; import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder; import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.util.HashMap; @Configuration public class RabbitMQConfiguration { @Bean public FanoutExchange deadExchange(){ return new FanoutExchange("dead_order_fanout_exchange",true,false); } @Bean public Queue deadOrderQueue(){ return new Queue("dead_queue",true); } @Bean public Binding bindingDead(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(deadOrderQueue()).to(deadExchange()); } @Bean public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){ return new FanoutExchange("order_fanout_exchange",true,false); } @Bean public Queue orderQueue(){ HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("x-dead-letter-exchange","dead_order_fanout_exchange"); return new Queue("order_queue",true,false,false,map); } @Bean public Binding bindingQueue(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(orderQueue()).to(fanoutExchange()); } }
重构消费者代码块:
@Service public class OrderMqConsumer { @Autowired private dispatcherService ds; private int count = 1; @RabbitListener(queues = {"order_queue"}) public void messageConsumer(String orderMsg, Channel channel, CorrelationData correlationData, @Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long tag) throws Exception{ try { //将json对象转换为 orderTable对象 ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); OrderTable table = mapper.readValue(orderMsg, OrderTable.class); //获取消息队列的消息 System.out.println("收到的MQ消息是:"+table+",count="+count++); //模拟消费者发生错误 System.out.println(1/0); ds.dispatcher(table.getOrderId()); //手动确认已经消费消息,false:只确定为tag的消息;true:确定所有小于tag数字的消息 channel.basicAck(tag,false); }catch (Exception e){ //出现异常,需要根据实际情况去转发 // 参数1:消息的tag ,参数2:是否多条处理,参数3:是否重复,不重发就会丢弃,如果有消息队列就会转换到消息队列中 channel.basicNack(tag,false,false); } } }
这里主要测试发生错误的时候,会被try--catch捕获,然后不重发当前信息,而是转发到死信队列中
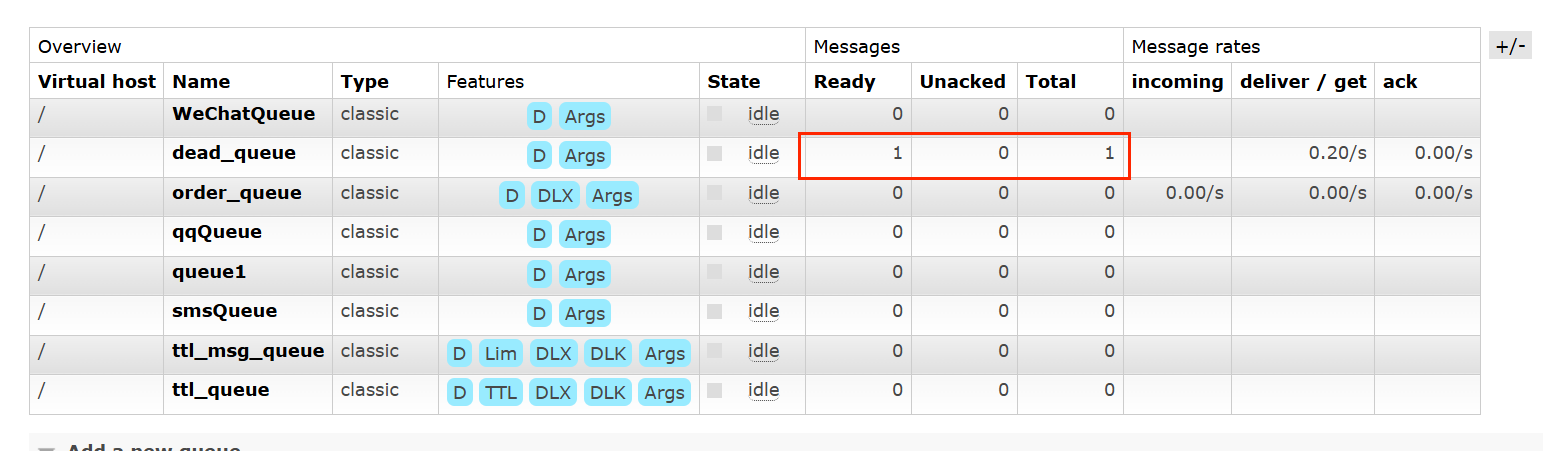
同时我们还可以监测死信队列,再次处理这个消息,当然,如果在死信队列消息还是被try -- catch捕获到了,那么说明需要人工来干预了
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import org.cqust.dispatcherservice.pojo.OrderTable; import org.cqust.dispatcherservice.service.dispatcherService; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData; import org.springframework.amqp.support.AmqpHeaders; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Header; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class deadMQConsumer { @Autowired private dispatcherService ds; private int count = 1; @RabbitListener(queues = {"dead_queue"}) public void messageConsumer(String orderMsg, Channel channel, CorrelationData correlationData, @Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long tag) throws Exception{ try { //将json对象转换为 orderTable对象 ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); OrderTable table = mapper.readValue(orderMsg, OrderTable.class); //获取消息队列的消息 System.out.println("收到的MQ消息是:"+table+",count="+count++); ds.dispatcher(table.getOrderId()); //手动确认已经消费消息,false:只确定为tag的消息;true:确定所有小于tag数字的消息 channel.basicAck(tag,false); }catch (Exception e){ //在死信队列依旧发生错误,说明需要额外的处理了 System.out.println("比如持久化到DB"); System.out.println("手动解决"); } } }
结果:
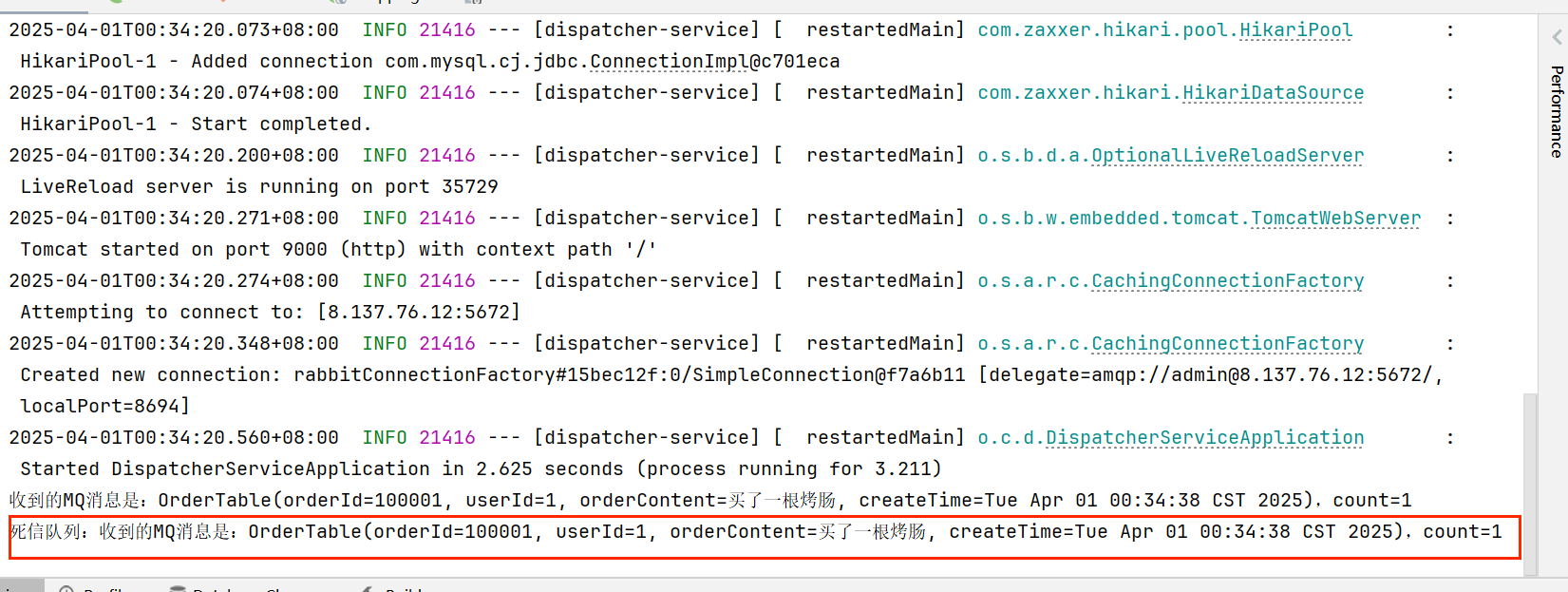
总结:
使用手动确认和手动应答是解决RabbitMQ的可靠生产和可靠消费的有效方式,基于可靠消费和可靠生产,就可以实现数据的最终一致性
还是那句话,实现两个独立服务最终一致性的方式有很多,关键在于你的业务场景。
-----END-----


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号