【题解】简单题 By 5ab as a juruo
题目
题目来源:CCF CQOI2006;
评测地址:Luogu#5057。
题目描述
有一个 \(n\) 个元素的数组,每个元素初始均为 \(0\)。
有 \(m\) 条指令,要么让其中一段连续序列数字反转——\(0\) 变 \(1\),\(1\) 变 \(0\)(操作 1),要么询问某个元素的值(操作 2)。
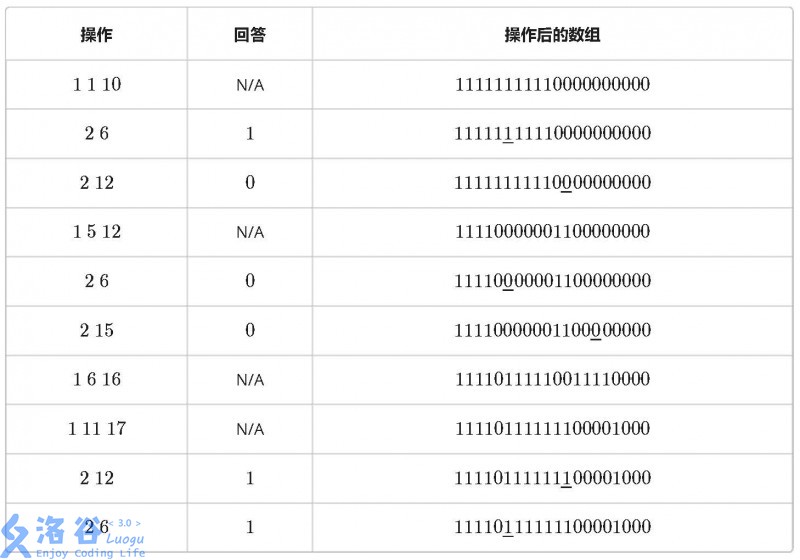
例如当 n = 20 时,10 条指令如下:
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 \(n\)、\(m\),表示数组的长度和指令的条数;
以下 \(m\) 行,每行的第一个数 \(t\) 表示操作的种类:
- 若 \(t=1\),则接下来有两个数 \(L\)、\(R\),表示区间 \([L, R]\) 的每个数均反转;
- 若 \(t=2\),则接下来只有一个数 \(i\),表示询问的下标。
输出格式
每个操作 2 输出一行(非 \(0\) 即 \(1\)),表示每次操作 2 的回答。
数据规模及约定
评测时间限制 \(1000\ \textrm{ms}\),空间限制 \(512\ \textrm{MiB}\)。
- 对于 \(50\%\) 的数据,\(1\le n\le 10^3\),\(1\le m\le 10^4\);
- 对于 \(100\%\) 的数据,\(1\le n\le 10^5\),\(1\le m\le 5\times 10^5\)。
保证 \(1\le L\le R\le n\)。
分析
题意很清楚。将一个 \(0/1\) 数列区间求反,单点查询,是一道不折不扣的数据结构题。
看到区间修改,首先想到的就是线段树。但是 \(m\le 5\times 10^5\),线段树常数又大,很容易超时。所以,我们考虑树状数组。
注意到区间求反就是区间异或运算,所以可以用树状数组维护。再用区间查询差分来单点查询。实际测试 在不吸氧的情况下跑到将近 \(100\) ms。
Code
注意区分树状数组的单点/区间和实际操作的单点/区间,因为树状数组存储的实际上是差分操作后的原数列。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
const int max_n = 100000;
bool tr[max_n+1] = {};
int n;
inline int lowbit(int x) { return x & -x; }
inline int read() // 10^6 的输入,加上快读比较保险
{
int ch = getchar(), t = 1, n = 0;
while (isspace(ch)) { ch = getchar(); }
if (ch == '-') { t = -1, ch = getchar(); }
while (isdigit(ch)) { n = n * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); }
return n * t;
}
void add(int p) // 树状数组单点修改
{
while (p <= n)
{
tr[p] ^= true;
p += lowbit(p);
}
}
bool get(int p) // 树状数组的区间查询
{
bool res = false;
while (p > 0)
{
res ^= tr[p];
p -= lowbit(p);
}
return res;
}
void modify(int l, int r) // 原数组的区间修改 <- 差分数组的单点修改
{
add(l);
if (r != n)
add(r+1);
}
int main()
{
int m, opt, ta, tb;
n = read(), m = read(); // 输入
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
opt = read(); // 编号
if (opt == 1) // 修改操作
{
ta = read(), tb = read();
modify(ta, tb);
}
else // 查询操作
{
ta = read();
printf("%d\n", get(ta)); // 原数组的单点查询 <- 差分数组的前缀和(误,应该是 xor)
}
}
return 0;
}
后记
这道题比较卡常,如果线段树常数比较大的话可能就过不了。
做数据结构题时,最好用最适合的数据结构,而非功能最强大的。否则用暴力不香吗
本文来自博客园,作者 5ab,转载请注明链接哦 qwq
博客迁移啦,来看看新博客吧 -> https://5ab-juruo.oier.space/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号