harbor私有仓库
一、harobr介绍
1. Harbor 是什么?
Harbor 是由 VMware 公司开源的企业级容器镜像仓库(Docker Registry)管理工具,专为云原生场景设计,提供镜像存储、权限管理、安全扫描、复制分发等核心功能。它是 CNCF(云原生计算基金会) 毕业项目,已成为 Kubernetes 生态中镜像管理的标准工具。
Harbor 是企业构建容器化基础设施的核心组件,解决了镜像管理中的安全、效率、合规三大痛点。其开箱即用的特性、灵活的扩展能力,以及与 Kubernetes 生态的深度集成,使其成为云原生时代的首选镜像仓库。
2. Harbor 的核心优势
| 优势 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 企业级特性 | 支持 RBAC(基于角色的访问控制)、多租户隔离、审计日志、镜像漏洞扫描、镜像签名(Notary)。 |
| 安全性 | 集成 Clair 漏洞扫描、自动阻止高危镜像、支持 TLS 加密传输和存储。 |
| 高可用性 | 支持分布式部署、镜像跨集群复制、数据库(PostgreSQL)和 Redis 高可用配置。 |
| 扩展性 | 提供 Webhook、REST API、Helm Chart 仓库(OCI 标准),可集成 CI/CD 流水线。 |
| 易用性 | 提供直观的 Web UI,支持 Helm Chart 管理、镜像标签保留策略、垃圾回收(GC)自动化。 |
3. Harbor 的核心作用
-
镜像集中存储
- 统一管理 Docker 镜像、Helm Chart(OCI 格式)、OPA 策略等,避免镜像分散存储。
- 支持多版本镜像保留和快速回滚。
-
镜像安全管控
- 漏洞扫描:自动检测镜像中的 CVE 漏洞,阻断高危镜像运行。
- 内容信任:通过 Notary 服务实现镜像签名和验签,防止篡改。
- 合规审计:记录所有用户操作(如推送、删除镜像),满足 GDPR、等保要求。
-
镜像分发与同步
- 跨集群复制:将镜像自动同步到多个 Harbor 实例或公有云仓库(如 AWS ECR、阿里云 ACR)。
- P2P 预热:结合 Dragonfly 等工具加速大规模镜像分发。
-
资源优化
- 标签保留策略:自动清理过期镜像(如仅保留最近 5 个版本)。
- 垃圾回收:删除无引用的镜像层,释放存储空间。
4. Harbor 与其他工具的对比
| 工具 | Harbor | Docker Registry | JFrog Artifactory |
|---|---|---|---|
| 定位 | 企业级容器镜像仓库 | 基础镜像存储服务 | 通用制品仓库(支持多种格式) |
| 权限管理 | RBAC、多租户 | 无 | RBAC、多租户 |
| 安全扫描 | 集成 Clair | 需第三方插件 | 集成 Xray |
| Helm 支持 | 原生支持 OCI 格式 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 部署复杂度 | 中等 | 简单 | 复杂 |
二、harbor实践
1. 安装docker、docker-compose
省略......
2. 安装harbor
harbor github:https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/releases/tag/v2.8.4
2.1 修改yml配置文件:hostname本机IP/域名,注释https访问,data_volume: ./data数据存放路径,location: ./log/harbor日志存放路径
# 下载docker-harbor
wget https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/releases/download/v2.8.4/harbor-online-installer-v2.8.4.tgz
tar xf harbor-online-installer-v2.8.4.tgz && cd harbor/
# 修改配置文件
cp harbor.yml.tmpl ./harbor.yml
# 修改harbor.yml配置文件
vim harbor.yml
# The IP address or hostname to access admin UI and registry service.
# DO NOT use localhost or 127.0.0.1, because Harbor needs to be accessed by external clients.
# 此处IP/域名,不可以写0.0.0.0
hostname: test.image.com
http:
# port for http, default is 80. If https enabled, this port will redirect to https port
port: 30080
addr: 0.0.0.0
......
......
# https related config
# 该处如无需SSL,则需要注释掉,否则安装error
#https:
# # https port for harbor, default is 443
# port: 443
# # The path of cert and key files for nginx
# certificate: /your/certificate/path
# private_key: /your/private/key/path
......
......
# 配置密码,默认用户:admin,密码:Harbor12345
harbor_admin_password: Harbor12345
......
......
# 定义volume
data_volume: ./data
......
# proxy:
# http_proxy: 192.168.20.213:789
# https_proxy: 192.168.20.213:789
# no_proxy: 127.0.0.1
# components:
# - core
# - jobservice
# - trivy
......
log:
......
rotate_size: 200M
# The directory on your host that store log
location: ./log/harbor
......
# 执行‘install.sh’部署并启动
./install.sh
harbor配置代理后可从Docker Hub官网同步镜像到harbor(按需)
如下是2.8.4修改后配置文件,供参考,修改位置、部署方式同上
点击查看代码
# Configuration file of Harbor
# The IP address or hostname to access admin UI and registry service.
# DO NOT use localhost or 127.0.0.1, because Harbor needs to be accessed by external clients.
hostname: test.temp.com
# http related config
http:
# port for http, default is 80. If https enabled, this port will redirect to https port
port: 80
# https related config
# https:
# # https port for harbor, default is 443
# port: 443
# # The path of cert and key files for nginx
# certificate: /your/certificate/path
# private_key: /your/private/key/path
# # Uncomment following will enable tls communication between all harbor components
# internal_tls:
# # set enabled to true means internal tls is enabled
# enabled: true
# # put your cert and key files on dir
# dir: /etc/harbor/tls/internal
# Uncomment external_url if you want to enable external proxy
# And when it enabled the hostname will no longer used
# external_url: https://reg.mydomain.com:8433
# The initial password of Harbor admin
# It only works in first time to install harbor
# Remember Change the admin password from UI after launching Harbor.
harbor_admin_password: Harbor12345
# Harbor DB configuration
database:
# The password for the root user of Harbor DB. Change this before any production use.
password: root123
# The maximum number of connections in the idle connection pool. If it <=0, no idle connections are retained.
max_idle_conns: 100
# The maximum number of open connections to the database. If it <= 0, then there is no limit on the number of open connections.
# Note: the default number of connections is 1024 for postgres of harbor.
max_open_conns: 900
# The maximum amount of time a connection may be reused. Expired connections may be closed lazily before reuse. If it <= 0, connections are not closed due to a connection's age.
# The value is a duration string. A duration string is a possibly signed sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as "300ms", "-1.5h" or "2h45m". Valid time units are "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s", "m", "h".
conn_max_lifetime: 5m
# The maximum amount of time a connection may be idle. Expired connections may be closed lazily before reuse. If it <= 0, connections are not closed due to a connection's idle time.
# The value is a duration string. A duration string is a possibly signed sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as "300ms", "-1.5h" or "2h45m". Valid time units are "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s", "m", "h".
conn_max_idle_time: 0
# The default data volume
data_volume: ./data
# Harbor Storage settings by default is using /data dir on local filesystem
# Uncomment storage_service setting If you want to using external storage
# storage_service:
# # ca_bundle is the path to the custom root ca certificate, which will be injected into the truststore
# # of registry's containers. This is usually needed when the user hosts a internal storage with self signed certificate.
# ca_bundle:
# # storage backend, default is filesystem, options include filesystem, azure, gcs, s3, swift and oss
# # for more info about this configuration please refer https://docs.docker.com/registry/configuration/
# filesystem:
# maxthreads: 100
# # set disable to true when you want to disable registry redirect
# redirect:
# disable: false
# Trivy configuration
#
# Trivy DB contains vulnerability information from NVD, Red Hat, and many other upstream vulnerability databases.
# It is downloaded by Trivy from the GitHub release page https://github.com/aquasecurity/trivy-db/releases and cached
# in the local file system. In addition, the database contains the update timestamp so Trivy can detect whether it
# should download a newer version from the Internet or use the cached one. Currently, the database is updated every
# 12 hours and published as a new release to GitHub.
trivy:
# ignoreUnfixed The flag to display only fixed vulnerabilities
ignore_unfixed: false
# skipUpdate The flag to enable or disable Trivy DB downloads from GitHub
#
# You might want to enable this flag in test or CI/CD environments to avoid GitHub rate limiting issues.
# If the flag is enabled you have to download the `trivy-offline.tar.gz` archive manually, extract `trivy.db` and
# `metadata.json` files and mount them in the `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db` path.
skip_update: false
#
# The offline_scan option prevents Trivy from sending API requests to identify dependencies.
# Scanning JAR files and pom.xml may require Internet access for better detection, but this option tries to avoid it.
# For example, the offline mode will not try to resolve transitive dependencies in pom.xml when the dependency doesn't
# exist in the local repositories. It means a number of detected vulnerabilities might be fewer in offline mode.
# It would work if all the dependencies are in local.
# This option doesn't affect DB download. You need to specify "skip-update" as well as "offline-scan" in an air-gapped environment.
offline_scan: false
#
# Comma-separated list of what security issues to detect. Possible values are `vuln`, `config` and `secret`. Defaults to `vuln`.
security_check: vuln
#
# insecure The flag to skip verifying registry certificate
insecure: false
# github_token The GitHub access token to download Trivy DB
#
# Anonymous downloads from GitHub are subject to the limit of 60 requests per hour. Normally such rate limit is enough
# for production operations. If, for any reason, it's not enough, you could increase the rate limit to 5000
# requests per hour by specifying the GitHub access token. For more details on GitHub rate limiting please consult
# https://developer.github.com/v3/#rate-limiting
#
# You can create a GitHub token by following the instructions in
# https://help.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/creating-a-personal-access-token-for-the-command-line
#
# github_token: xxx
jobservice:
# Maximum number of job workers in job service
max_job_workers: 10
# The jobLogger sweeper duration (ignored if `jobLogger` is `stdout`)
logger_sweeper_duration: 1 #days
notification:
# Maximum retry count for webhook job
webhook_job_max_retry: 3
# HTTP client timeout for webhook job
webhook_job_http_client_timeout: 3 #seconds
# Log configurations
log:
# options are debug, info, warning, error, fatal
level: info
# configs for logs in local storage
local:
# Log files are rotated log_rotate_count times before being removed. If count is 0, old versions are removed rather than rotated.
rotate_count: 50
# Log files are rotated only if they grow bigger than log_rotate_size bytes. If size is followed by k, the size is assumed to be in kilobytes.
# If the M is used, the size is in megabytes, and if G is used, the size is in gigabytes. So size 100, size 100k, size 100M and size 100G
# are all valid.
rotate_size: 200M
# The directory on your host that store log
location: ./log/harbor
# Uncomment following lines to enable external syslog endpoint.
# external_endpoint:
# # protocol used to transmit log to external endpoint, options is tcp or udp
# protocol: tcp
# # The host of external endpoint
# host: localhost
# # Port of external endpoint
# port: 5140
#This attribute is for migrator to detect the version of the .cfg file, DO NOT MODIFY!
_version: 2.8.0
# Uncomment external_database if using external database.
# external_database:
# harbor:
# host: harbor_db_host
# port: harbor_db_port
# db_name: harbor_db_name
# username: harbor_db_username
# password: harbor_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# max_idle_conns: 2
# max_open_conns: 0
# notary_signer:
# host: notary_signer_db_host
# port: notary_signer_db_port
# db_name: notary_signer_db_name
# username: notary_signer_db_username
# password: notary_signer_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# notary_server:
# host: notary_server_db_host
# port: notary_server_db_port
# db_name: notary_server_db_name
# username: notary_server_db_username
# password: notary_server_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# Uncomment redis if need to customize redis db
# redis:
# # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeable
# # registry_db_index: 1
# # jobservice_db_index: 2
# # trivy_db_index: 5
# # it's optional, the db for harbor business misc, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it.
# # harbor_db_index: 6
# # it's optional, the db for harbor cache layer, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it.
# # cache_layer_db_index: 7
# Uncomment external_redis if using external Redis server
# external_redis:
# # support redis, redis+sentinel
# # host for redis: <host_redis>:<port_redis>
# # host for redis+sentinel:
# # <host_sentinel1>:<port_sentinel1>,<host_sentinel2>:<port_sentinel2>,<host_sentinel3>:<port_sentinel3>
# host: redis:6379
# password:
# # Redis AUTH command was extended in Redis 6, it is possible to use it in the two-arguments AUTH <username> <password> form.
# # username:
# # sentinel_master_set must be set to support redis+sentinel
# #sentinel_master_set:
# # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeable
# registry_db_index: 1
# jobservice_db_index: 2
# trivy_db_index: 5
# idle_timeout_seconds: 30
# # it's optional, the db for harbor business misc, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it.
# # harbor_db_index: 6
# # it's optional, the db for harbor cache layer, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it.
# # cache_layer_db_index: 7
# Uncomment uaa for trusting the certificate of uaa instance that is hosted via self-signed cert.
# uaa:
# ca_file: /path/to/ca
# Global proxy
# Config http proxy for components, e.g. http://my.proxy.com:3128
# Components doesn't need to connect to each others via http proxy.
# Remove component from `components` array if want disable proxy
# for it. If you want use proxy for replication, MUST enable proxy
# for core and jobservice, and set `http_proxy` and `https_proxy`.
# Add domain to the `no_proxy` field, when you want disable proxy
# for some special registry.
proxy:
http_proxy:
https_proxy:
no_proxy:
components:
- core
- jobservice
- trivy
# metric:
# enabled: false
# port: 9090
# path: /metrics
# Trace related config
# only can enable one trace provider(jaeger or otel) at the same time,
# and when using jaeger as provider, can only enable it with agent mode or collector mode.
# if using jaeger collector mode, uncomment endpoint and uncomment username, password if needed
# if using jaeger agetn mode uncomment agent_host and agent_port
# trace:
# enabled: true
# # set sample_rate to 1 if you wanna sampling 100% of trace data; set 0.5 if you wanna sampling 50% of trace data, and so forth
# sample_rate: 1
# # # namespace used to differenciate different harbor services
# # namespace:
# # # attributes is a key value dict contains user defined attributes used to initialize trace provider
# # attributes:
# # application: harbor
# # # jaeger should be 1.26 or newer.
# # jaeger:
# # endpoint: http://hostname:14268/api/traces
# # username:
# # password:
# # agent_host: hostname
# # # export trace data by jaeger.thrift in compact mode
# # agent_port: 6831
# # otel:
# # endpoint: hostname:4318
# # url_path: /v1/traces
# # compression: false
# # insecure: true
# # # timeout is in seconds
# # timeout: 10
# Enable purge _upload directories
upload_purging:
enabled: true
# remove files in _upload directories which exist for a period of time, default is one week.
age: 168h
# the interval of the purge operations
interval: 24h
dryrun: false
# Cache layer configurations
# If this feature enabled, harbor will cache the resource
# `project/project_metadata/repository/artifact/manifest` in the redis
# which can especially help to improve the performance of high concurrent
# manifest pulling.
# NOTICE
# If you are deploying Harbor in HA mode, make sure that all the harbor
# instances have the same behaviour, all with caching enabled or disabled,
# otherwise it can lead to potential data inconsistency.
cache:
# not enabled by default
enabled: false
# keep cache for one day by default
expire_hours: 24
2.2 私有仓库为HTTP协议,需daemon.json解析仓库位置
客户端配置
tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-"EOF"
{
"data-root": "/data1/docker/",
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts":{
"max-size": "50m",
"max-file": "1"
},
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
"live-restore": true,
"insecure-registries": [
"192.168.2.12:30080",
"test.image.com:30080"],
}
EOF
# 重载配置文件,重启docker
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker
2.3 docker-compose常用命令
# 在docker-compose.yml文件目录下执行
docker-compose down
docker-compose up -d
2.4 打包自定义镜像、上传至私有仓库
# 语法格式 docker tag srcname:tag des/lib/name:tag(docker tag 原名称:标签 仓库IP/库/名字:标签)
# 登录hrabor:docker login xx.xx.xx.xx;示例:docker login 192.168.2.12:30080 -uadmin -p12345
# 示例
docker tag myweb:v0.1.24 192.168.2.12:30080/xr/myweb:v0.1.24
docker push 192.168.2.12:30080/myweb:v0.1.24
# 域名
docker tag myweb:v0.1.24 test.image.com:30080/xr/myweb:v0.1.24
docker push test.image.com:30080/myweb:v0.1.24
客户端上传镜像配置第三步,第五步私有库上传、下载
私有仓库镜像命名规则
[仓库IP/域名]/库/名字:标签 --语法格式 docker tag srcname:tag des/lib/name:tag(docker tag 原名称:标签 仓库IP/库/名字:标签)
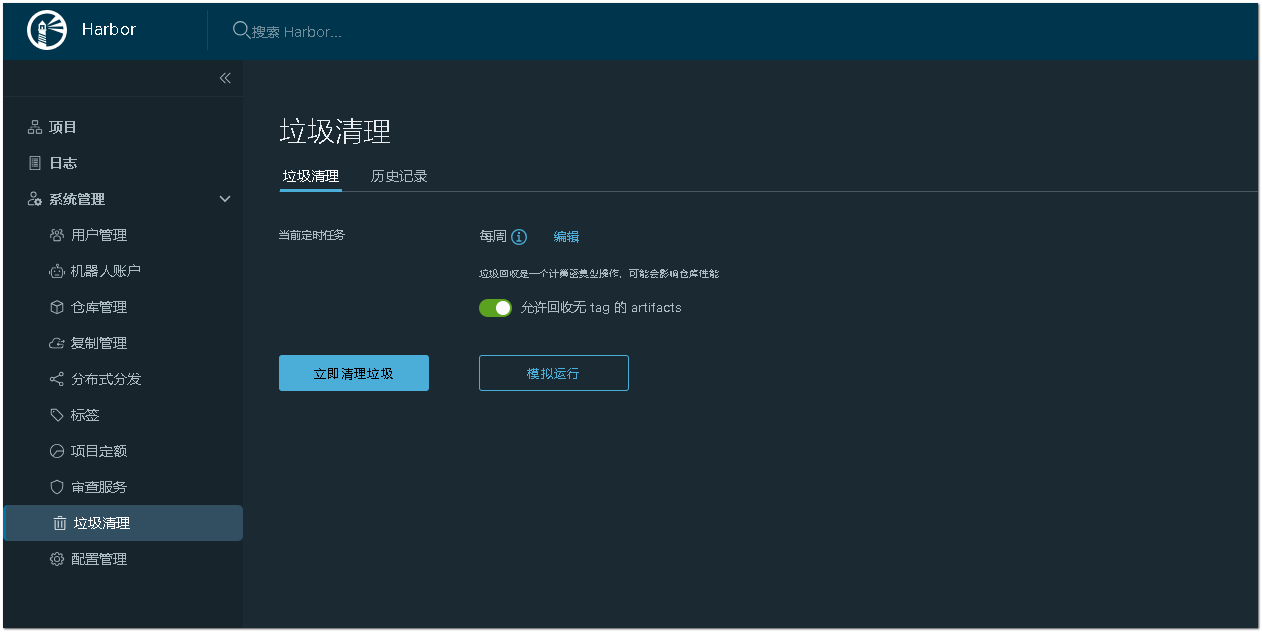
3. harbor定期清理镜像
4. 机器人账户与jenkins调用
配置机器人账户供Jenkins发布时上传镜到仓库,机器人可单独配置权限
机器人账户不能应用于Jenkins,有变量问题#待补充#
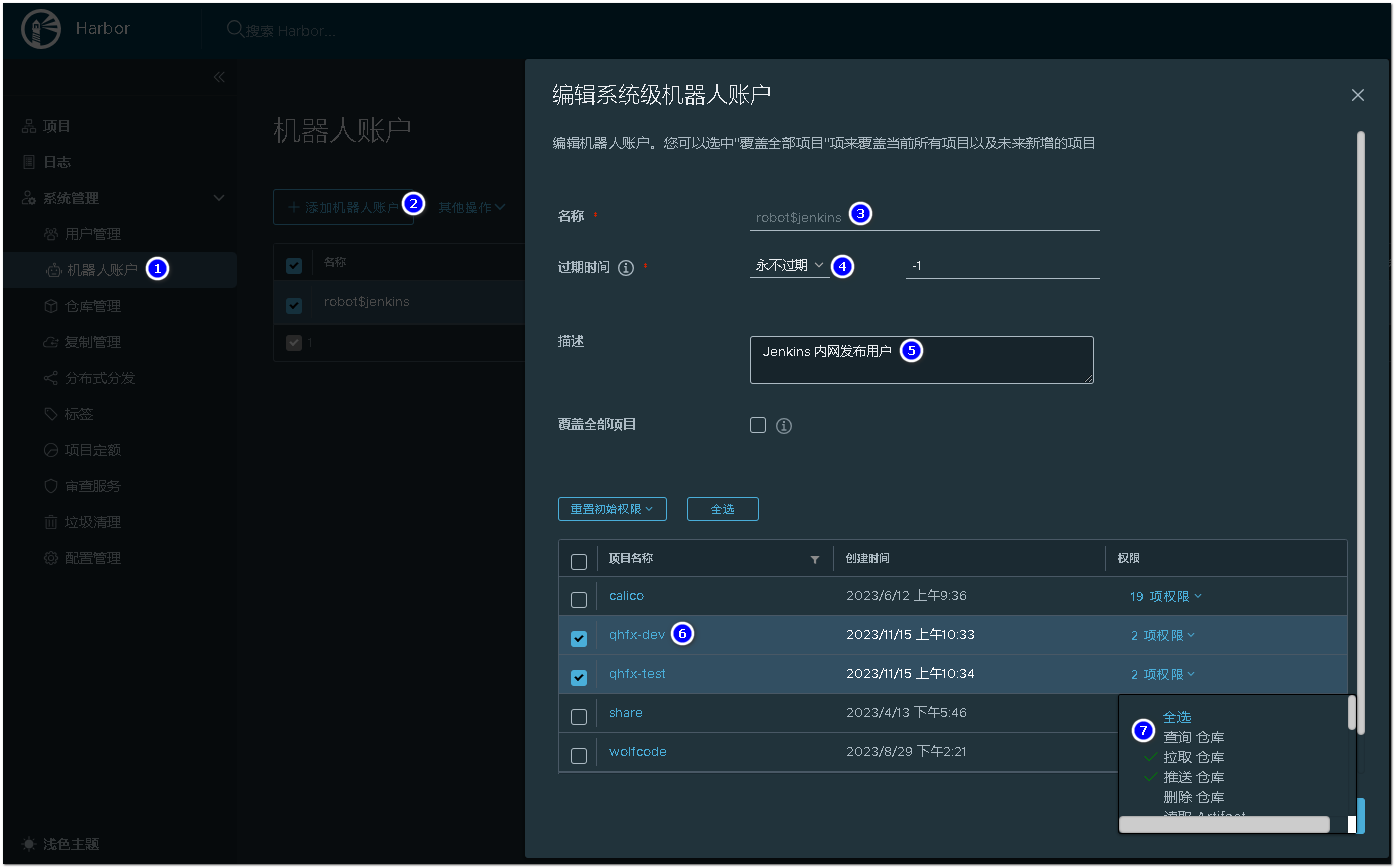
harbor机器人用户名都会包含$,登录是将$进行转义
echo "${password}" |docker login -u 'robot\$jenkins' --password-stdin ${harbor_url}
参考:https://v3-1.docs.kubesphere.io/zh/docs/devops-user-guide/how-to-integrate/harbor/
// git凭证ID
def git_auth = "xxxx-37a7-4199-9c85-xxxxx"
// git URL
def git_url = "http://192.168.0.50/xx-xx/xr-platform.git"
// images tag
def images_tag = "latest"
// harbor_url
def harbor_url = "192.168.0.50"
// harbor_project
def harbor_project = "meta-xr"
// harbor 凭证
def harbor_auth = "xxxx-2347-4eee-b58f-xxxxx"
// mail 凭证id
def mail_auth = "xxxx-d8fe-4450-ac4b-xxxxx"
// mail 接收用户
def mail_to_user = "xxx@xx.com.cn,xxx@xx.com.cn"
node {
stage('docker build image') {
stage("push harbor") {
// 镜像名称
def images_name_latest="nginx"
def images_name="nginx:v2"
sh """
docker pull nginx:latest
"""
// 镜像打标签
sh """docker tag ${images_name_latest} ${harbor_url}/nginx/${images_name}"""
// 镜像推送至harbor
withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: "${harbor_auth}", passwordVariable: 'password', usernameVariable: 'username')]) {
// 登录harbor
sh """
echo "${password}" |docker login -u 'robot\$jenkins' --password-stdin ${harbor_url}
# 上传镜像
docker push "${harbor_url}/${images_name_latest}/${images_name}"
# 清理未使用的镜像
# docker image prune -a -f
"""
echo "上传镜像成功"
}
}
}
stage('email'){
echo "测试发送邮件"
// 设置生成模板文件
configFileProvider([configFile(fileId: "${mail_auth}",
targetLocation: 'email.html',
variable: 'Always')]) {
// 读取模板 变量名是邮件模板名
template = readFile encoding: 'UTF-8', file: "${Always}"
// 发送邮件
emailext(subject: 'Jenkins构建通知',
attachLog: true,
recipientProviders: [requestor()],
to: "${mail_to_user}",
body: """${template}""")
}
}
}
5. 离线安装Harbor 2.8.4
5.1 将tar包放在指定目录下,解压后进入harbor目录,执行images-load.sh脚本上载镜像
[root@jenkins-1 harbor]# tar xf harbor.tar && cd harbor
[root@jenkins-1 harbor]# ls
common docker-compose.yml harbor-online-installer-v2.8.4.tgz harbor.yml.tmpl images-tar LICENSE
common.sh harbor harbor.yml images-load.sh install.sh prepare
[root@jenkins-1 harbor]# sh images-load.sh
# 启动harbor
docker-compose up -d
# 访问harbor,默认URL IP:60080,例:http://192.168.0.3:60080
user:admin
pass:Harbor12345
6. harbor部署https访问
基于参考得出结论
先生成自签证书,然后将证书绝对路径配置yaml文件中,执行
./prepare,然后docker-compose up -d,此时通过浏览器即可使用https访问harbor了。未实际部署,有待验证。
[root@harbor harbor]# pwd
/data1/test
[root@harbor test]# tar xf harbor-online-installer-v2.8.4.tgz
[root@harbor test]# ls
harbor harbor-online-installer-v2.8.4.tgz
[root@harbor test]# cd harbor/
[root@harbor harbor]# ls
common.sh harbor.yml.tmpl install.sh LICENSE prepare
[root@harbor harbor]# cp harbor.yml.tmpl ./harbor.yml
[root@harbor harbor]# cat harbor.yml |more
# Configuration file of Harbor
# The IP address or hostname to access admin UI and registry service.
# DO NOT use localhost or 127.0.0.1, because Harbor needs to be accessed by external clients.
hostname: reg.mydomain.com
# http related config
http:
# port for http, default is 80. If https enabled, this port will redirect to https port
port: 80
# https related config
https:
# https port for harbor, default is 443
port: 443
# The path of cert and key files for nginx
##########################意思证书在哪就写哪##########################
certificate: /your/certificate/path
private_key: /your/private/key/path
......
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/birkhoffxia/articles/17547907.htmlhttps://schnappi618.github.io/2020/04/20/harbor/harbor%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AEhttps/
官网:https://goharbor.io/docs/1.10/install-config/configure-https/
7. harbor同步公共镜像
harbor.yml文件加代理,而后全新安装/升级安装。
proxy:
http_proxy: 10.0.0.213:7890
https_proxy: 10.0.0.213:7890
no_proxy: 127.0.0.1
components:
- core
- jobservice
- trivy
sh install.sh
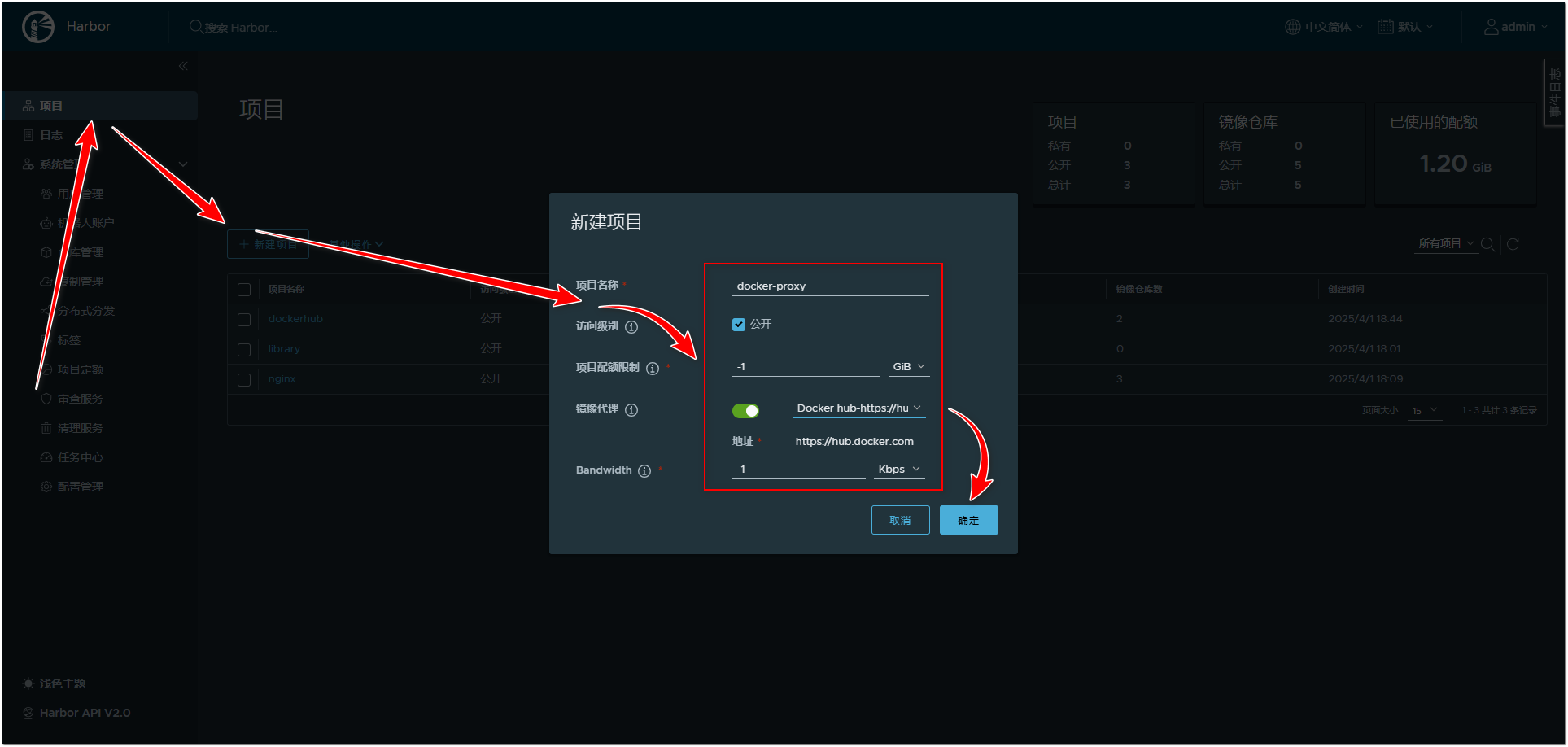
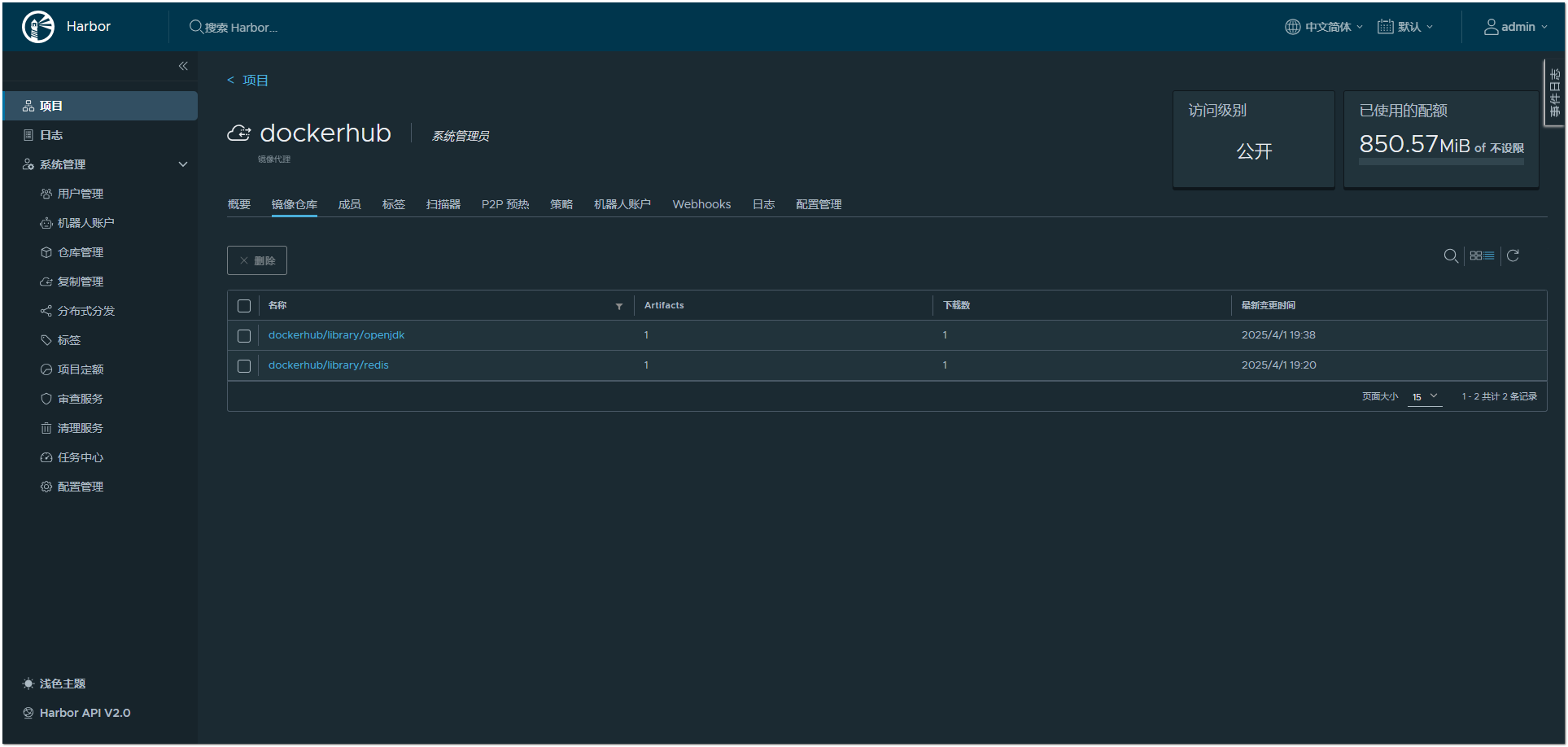
官方镜像缓存后默认会被加上library,实际内网使用可以去掉library
# 默认拉取命令
docker pull 192.168.2.12:30080/docker-proxy/library/openjdk:latest
# 实际可以写成
[root@test harbor]# docker pull 192.168.2.12:30080/docker-proxy/openjdk
Using default tag: latest
latest: Pulling from dockerhub/openjdk
197c1adcd755: Pull complete
57b698b7af4b: Pull complete
95a27dbe0150: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:9b448de897d211c9e0ec635a485650aed6e28d4eca1efbc34940560a480b3f1f
Status: Downloaded newer image for 192.168.2.12:30080/docker-proxy/openjdk:latest
192.168.2.12:30080/dockerhub/openjdk:latest
同步hub镜像库(大佬膜拜)
参考:https://blog.k8s.li/sync-dockerhub-library-images.html
https://blog.k8s.li/sync-dockerhub-library-images.html#%E6%81%B0%E7%83%82%E9%92%B1%EF%BC%9F
7.1 harbor缓存镜像无法自动打tags
升级上来的没有tags,githubissues2.5.3就有这个问题,我是从2.5.6-->2.10.0-->2.12.2,tags始终不识别,起初都不管用,过了一天,分发的那台(v2.12.2-73072d0d)自己正常了;
现象描述: 升级从2.5.6-->2.10.0-->2.12.2,缓存镜像,发现不能自动打tag,多次尝试均未成功,可能是受其它仓库影响,于最新建了一台机器直接安装2.12.2,缓存镜像发现问题相同(此时仓库中只有MySQL镜像,没有其它的仓库及镜像),于是将仓库备份后,在另一台机子上启动,调试pgsql,删除关联数据条目,删除harbor本地缓存,重启harbor,再次拉取镜像,tags依旧为空,库不干净了?清空库,清空本地缓存,重启,拉取镜像,tags为空;
重建harbor 2.12.2做镜像分发,当日不管用,不折腾了,第二天下午一点tags居然正常了(时段内没操作过),期间新建了一台试了2.12.0版本,也是当时无tags,过了没一会也正常了,分发和新建tags需要数据整合时长,升级上来的版本中tags依旧是不显示,github早有人反馈tags事件,说是docker问题,尝试了四种方式:升级、镜像分发、清空库 本地缓存、新建,不稳定,有机会待补充
升级版本 v2.12.2-73072d0d
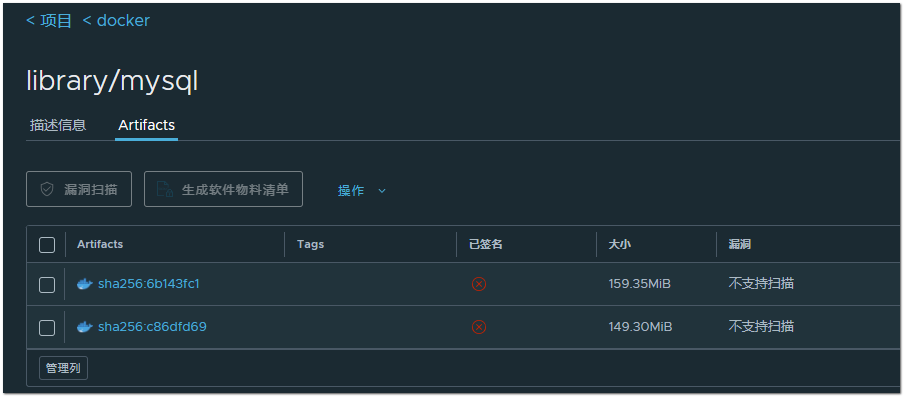
分发版本 v2.12.2-73072d0d
此时库、镜像数与升级版本一致
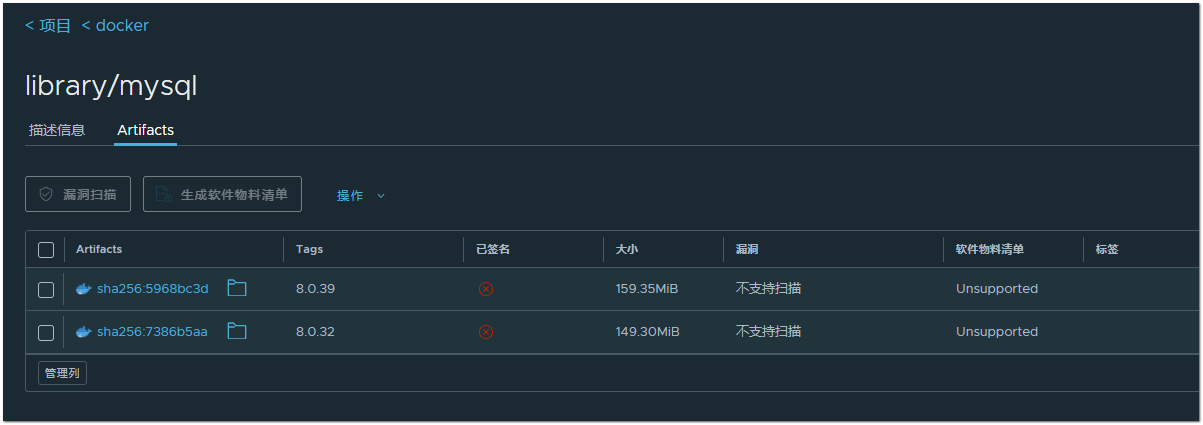
搭建版本 v2.12.0-9da38ae0
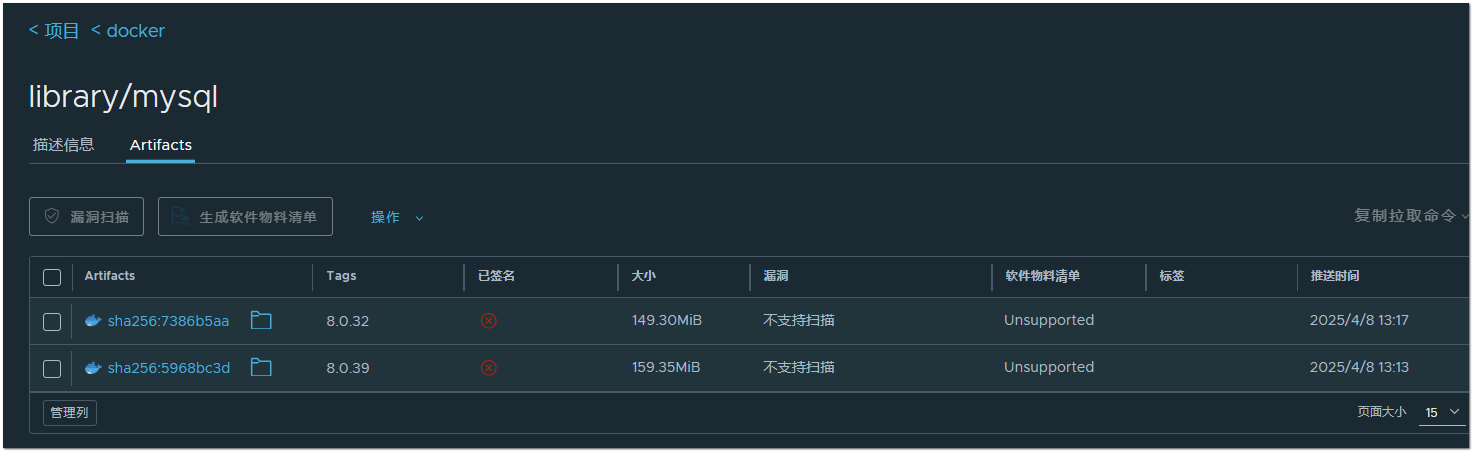
参考:https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/issues/17798
https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/issues/15591#issuecomment-927742241
8. harbor内网、公网同时使用
# 公网域名/ip,不可写成 0.0.0.0,,镜像上传后名称会是该IP/域名
hostname: your.harbor.domain
http:
# port for http, default is 80. If https enabled, this port will redirect to https port
port: 30081
# 绑定IP
addr: 0.0.0.0
## https related config
#https:
# # https port for harbor, default is 443
# port: 443
# # The path of cert and key files for nginx
# certificate: /your/certificate/path
# private_key: /your/private/key/path
# ...
镜像上传harbor后,harbor显示的镜像名是your.harbor.domain/node/node:14.14.0,不显示内网镜像名192.168.0.100/node/node:14.14.0,但使用内网harbor地址也是可以拉取的。
公网:your.harbor.domain/node/node:14.14.0
内网:192.168.0.100/node/node:14.14.0
9. 升级与回滚
写在前面:
计划升级2.5.6-->2.12.2,测试升级2.5.6-->2.12.2,平台登录后,原数据、配置不显示,回滚后配置正常,2.8.0-->2.12.2不显示旧数据,2.10.0-->2.12.2显示旧数据,最终2.5.6-->2.10.0-->2.12.2,跨多个版本一定要多测试一定要多测试
测试了中间多个版本升级、回滚,数据路径引用、版本、配置文件,各种乱七八糟的问题
[root@test harbor]# mv harbor{,-bak}
[root@test harbor]# ls
harbor-bak harbor-online-installer-v2.10.0.tgz
[root@test harbor]# tar xf harbor-online-installer-v2.10.0.tgz
[root@test harbor]# ls
harbor harbor-bak harbor-online-installer-v2.10.0.tgz
# 拷贝数据目录、harbor.yml文件到新版本目录下,我是将他们放在一起的
[root@test harbor]# cp -r harbor-bak/{data,harbor.yml} harbor
[root@test harbor]# cd harbor
[root@test harbor]# ls
common.sh data harbor.yml harbor.yml.tmpl install.sh LICENSE prepare
# 数据目录与旧版本数据目录保持一致,我放在同级了
[root@test harbor]# cat harbor.yml.tmpl |grep ^data_volume
data_volume: ./data
# v2.12.0 版本与升级版本一致
[root@test harbor]# docker run -it --rm -v /:/hostfs goharbor/prepare:v2.12.2 migrate -i /data1/harbor/test/harbor/harbor.yml
migrating to version 2.11.0
migrating to version 2.12.0
Written new values to /data1/harbor/test/harbor/harbor.yml
####################################################################################3
# 失败了,5.6.0-->2.12.2,跨版本过多,可以登录,旧数据不显示,最终2.5.6-->2.10.0-->2.12.2
[root@test harbor]# docker run -it --rm -v /:/hostfs goharbor/prepare:v2.12.0 migrate -i /data1/harbor/test/harbor/harbor.yml
migrating to version 2.6.0
migrating to version 2.7.0
migrating to version 2.8.0
migrating to version 2.9.0
migrating to version 2.10.0
migrating to version 2.11.0
migrating to version 2.12.0
Written new values to /data1/harbor/test/harbor/harbor.yml
我希望、我希望你没有活在别人希望的希望里。
本文来自博客园,作者:-2287-,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/2287keybord/p/18806561



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号