实验5
task1.1
编程代码
#include <stdio.h> #define N 4 int main() { int x[N] = {1, 9, 8, 4}; int i; int *p; // 方式1:通过数组名和下标遍历输出数组元素 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) printf("%d", x[i]); printf("\n"); // 方式2:通过指针变量遍历输出数组元素 (写法1) for (p = x; p < x + N; ++p) printf("%d", *p); printf("\n"); // 方式2:通过指针变量遍历输出数组元素(写法2) p = x; for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) printf("%d", *(p + i)); printf("\n"); // 方式2:通过指针变量遍历输出数组元素(写法3) p = x; for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) printf("%d", p[i]); printf("\n"); return 0; }
运行截图

1.2
编程代码
#include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> int main() { int x[2][4] = {{1, 9, 8, 4}, {2, 0, 4, 9}}; int i, j; int *p; // 指针变量,存放int类型数据的地址 int(*q)[4]; // 指针变量,指向包含4个int型元素的一维数组 // 使用数组名、下标访问二维数组元素 for (i = 0; i < 2; ++i) { for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j) printf("%d", x[i][j]); printf("\n"); } //使用指针变量p间接访问二维数组元素 for (p = &x[0][0], i = 0; p < &x[0][0] + 8; ++p, ++i) { printf("%d", *p); if ((i + 1) % 4 == 0) printf("\n"); } // 使用指针变量q间接访问二维数组元素 for (q = x; q < x + 2; ++q) { for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j) printf("%d", *(*q + j)); printf("\n"); }system("pause"); return 0; }
运行截图
task2.1
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define N 80 int main() { char s1[] = "Learning makes me happy"; char s2[] = "Learning makes me sleepy"; char tmp[N]; printf("sizeof(s1) vs. strlen(s1): \n"); printf("sizeof(s1) = %d\n", sizeof(s1)); printf("strlen(s1) = %d\n", strlen(s1)); printf("\nbefore swap: \n"); printf("s1: %s\n", s1); printf("s2: %s\n", s2); printf("\nswapping...\n"); strcpy(tmp, s1); strcpy(s1, s2); strcpy(s2, tmp); printf("\nafter swap: \n"); printf("s1: %s\n", s1); printf("s2: %s\n", s2); system("pause"); return 0; }
运行截图
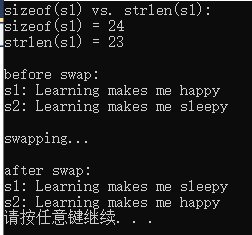
2 计算的是s1算上终止符号所有字符的个数 统计的是s1不算终止符的个数
不能
更换
2.2
编程代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define N 80 int main() { char *s1 = "Learning makes me happy"; char *s2 = "Learning makes me sleepy"; char *tmp; printf("sizeof(s1) vs. strlen(s1): \n"); printf("sizeof(s1) = %d\n", sizeof(s1)); printf("strlen(s1) = %d\n", strlen(s1)); printf("\nbefore swap: \n"); printf("s1: %s\n", s1); printf("s2: %s\n", s2); printf("\nswapping...\n"); tmp = s1; s1 = s2; s2 = tmp; printf("\nafter swap: \n"); printf("s1: %s\n", s1); printf("s2: %s\n", s2); system("pause"); return 0; }
运行截图
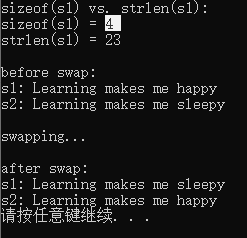
一串字符 s1中单词的个数 s1中不算终止符号所有字符的个数
可以
交换的是s1 和s2 的地址
交换了
task3
编程代码
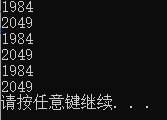
#include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> void str_cpy(char *target, const char *source); void str_cat(char *str1, char *str2); int main() { char s1[80], s2[20] = "1984"; str_cpy(s1, s2); puts(s1); str_cat(s1, " Animal Farm"); puts(s1); system("pause"); return 0; } void str_cpy(char *target, const char *source) { while (*target++ = *source++) ; } void str_cat(char *str1, char *str2) { while (*str1) str1++; while (*str1++ = *str2++) ;}
运行截图

task4
编程代码
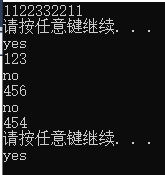
#include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define N 80 int func(char *); int main() { char str[80]; while (gets(str) != NULL) { if (func(str)) printf("yes\n"); else printf("no\n"); } return 0; } int func(char *str) { char *begin, *end; begin = end = str; while (*end) end++; end--; while (begin < end) { if (*begin != *end) return 0; else { begin++; end--; } }system("pause"); return 1; }
运行截图
task5
编程代码
#include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define N 80 void func(char *); int main() { char s[N]; while (scanf("%s", s) != EOF) { func(s); puts(s); } system("pause"); return 0; } void func(char *str) { int i; char *p1, *p2, *p; p1 = str; while (*p1 == '*') p1++; p2 = str; while (*p2) p2++; p2--; while (*p2 == '*') p2--; p = str; i = 0; while (p < p1) { str[i] = *p; p++; i++; } while (p <= p2) { if (*p != '*') { str[i] = *p; i++; } p++; } while (*p != '\0') { str[i] = *p; p++; i++; } str[i] = '\0'; }
运行截图
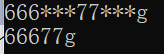
task6.1
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> void sort(char *name[], int n); int main() { char *course[4] = {"C Program", "C++ Object Oriented Program", "Operating System", "Data Structure and Algorithms"}; int i; sort(course, 4); for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) printf("%s\n", course[i]); return 0; } void sort(char *name[], int n) { int i, j; char *tmp; for (i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) for (j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; ++j) if (strcmp(name[j], name[j + 1]) > 0) { tmp = name[j]; name[j] = name[j + 1]; name[j + 1] = tmp; } }

task6.2
编程代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include<stdlib.h> void sort(char *name[], int n); int main() { char *course[4] = {"C Program", "C++ Object Oriented Program", "Operating System", "Data Structure and Algorithms"}; int i; sort(course, 4); for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) printf("%s\n", course[i]); system("pause"); return 0; } void sort(char *name[], int n) { int i, j, k; char *tmp; for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { k = i; for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) if (strcmp(name[j], name[k]) < 0) k = j; if (k != i) { tmp = name[i]; name[i] = name[k]; name[k] = tmp; } } }
运行截图

储存位置发生了变化
task7
编程代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define N 5 int check_id(char *str); int main() { char *pid[N] = {"31010120000721656X", "330106199609203301", "53010220051126571", "510104199211197977", "53010220051126133Y"}; int i; for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) if (check_id(pid[i])) printf("%s\tTrue\n", pid[i]); else printf("%s\tFalse\n", pid[i]); system("pause"); return 0; } int check_id(char *str) { char *p=str; while((*p >= '0' && *p <= '9')||*p=='X') p++; if(*p == '\0' && strlen(str) == 18) return 1; else return 0; }
运行截图
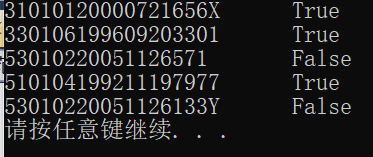
task8
编程代码
#include <stdio.h> #define N 80 #include<stdlib.h> void encoder(char *s); void decoder(char *s); int main() { char words[N]; printf("输入英文文本: "); gets(words); printf("编码后的英文文本: "); encoder(words); printf("%s\n", words); printf("对编码后的英文文本解码: "); decoder(words); printf("%s\n", words); system("pause"); return 0; } void encoder(char *s) {int i; for(i=0;*(s+i)!=0;i++) {if((*(s+i)>=65&&*(s+i)<90)||(*(s+i)>=97&&*(s+i)<122)) {*(s+i)+=1;continue;} if(*(s+i)==90) {*(s+i)=65;continue;} if(*(s+i)==122) {*(s+i)=97;continue;} } } void decoder(char *s) {int i; for(i=0;*(s+i)!=0;i++) {if(*(s+i)>65&&*(s+i)<=90) {*(s+i)-=1;continue;} if(*(s+i)>97&&*(s+i)<=122) {*(s+i)-=1;continue;} if(*(s+i)==65) {*(s+i)=90;continue;} if(*(s+i)==97) {*(s+i)=122;continue;} } }
运行截图



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号