基于小熊派Hi3861鸿蒙开发的IoT物联网学习【二】
HarmonyOS内核开发—信号量开发案例学习记录
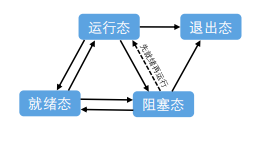
一、LiteOS里面的任务管理介绍:
任务状态通常分为以下四种:
就绪(Ready):该任务在就绪列表中,只等待CPU。
运行(Running):该任务正在执行。
阻塞(Blocked):该任务不在就绪列表中。包含任务被挂起、任务被延时、任务正在等待信号量、读写队列或者等待读写事件等。
退出态(Dead):该任务运行结束,等待系统回收资源。
案例 :cmsis_os2的API任务接口
创建任务:osThreadNew(osThreadFunc_t func,void * argument,const osThreadAttr_t * attr)
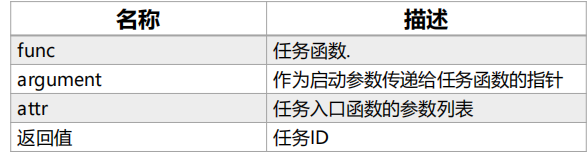
删除某个任务:osThreadTerminate(osThreadId_t thread_id);
任务挂起:osThreadSuspend(osThreadId_t thread_id)
任务恢复:osThreadResume (osThreadId_t thread_id)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "ohos_init.h"
#include "cmsis_os2.h"
osThreadId_t threadHiID;
osThreadId_t threadLoID;
/*****任务一*****/
void threadHi(void)
{
// int sum = 0;
// while (1)
// {
// printf("This is BearPi Harmony Thread1----%d\r\n", sum++);
// usleep(1000000);
// }
printf("enter threadHi\r\n");
osDelay(1); //其作用是让任务阻塞
printf("threadHi delay done\r\n");
osThreadSuspend(threadHiID); //任务挂起
printf("threadHi osThreadResume success\r\n");
osThreadTerminate(threadHiID); //删除某个任务
}
/*****任务二*****/
void threadLo(void)
{
// int sum = 0;
// while (1)
// {
// printf("This is BearPi Harmony Thread2----%d\r\n", sum++);
// usleep(500000);
// }
for (int i = 0;i<10;i++){
printf("enter threadLo\r\n");
}
printf("threadHi osThreadSuspend success\r\n");
osThreadResume(threadHiID); // 任务恢复
osThreadTerminate(threadLoID); //删除某个任务
}
/*****任务创建*****/
static void Thread_example(void)
{
osThreadAttr_t attr;
threadHiID = osThreadNew((osThreadFunc_t)threadHi,NULL,&attr);
if (threadHiID == NULL)
{
printf("Falied to create threadHi!\n");
}
attr.name = "threadLo";
attr.priority = 24 ;
threadLoID =osThreadNew((osThreadFunc_t)threadLo,NULL,&attr);
if (threadLoID== NULL)
{
printf("Falied to create threadLo!\n");
}
}
APP_FEATURE_INIT(Thread_example);
// SYS_RUN(Thread_example);
二、信号量开发案例
基本概念:信号量(Semaphore)是一种实现任务间通信的机制,实现任务之间同步或临界资源的互斥访问。常用于协助一组相
互竞争的任务来访问临界资源。
1、在多任务系统中,各任务之间需要同步或互斥实现临界资源的保护,信号量功能可以为用户提供这方面的支持。
2、通常一个信号量的计数值用于对应有效的资源数,表示剩下的可被占用的互斥资源数。其值的含义分两种情况:
1)0,表示没有积累下来的Post信号量操作,且有可能有在此信号量上阻塞的任务。
2)正值,表示有一个或多个Post信号量操作。
4、以同步为目的的信号量和以互斥为目的的信号量在使用有如下不同:
1)用作互斥时,信号量创建后记数是满的,在需要使用临界资源时,先取信号量,使其变空,这样其他任务需要使用
临界资源时就会因为无法取到信号量而阻塞,从而保证了临界资源的安全。
2)用作同步时,信号量在创建后被置为空,任务1取信号量而阻塞,任务2在某种条件发生后,释放信号量,于是任务
1得以进入READY或RUNNING态,从而达到了两个任务间的同步。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "ohos_init.h"
#include "cmsis_os2.h"
osSemaphoreId_t sem1;
void Thread_Semaphore1(void)
{
osStatus_t status;
while (1)
{
//申请两次sem1信号量,使得Thread_Semaphore2和Thread_Semaphore3能同步执行
status = osSemaphoreRelease(sem1);
if (status!=osOK){
printf("semaphore fail");
}else{
printf("semaphore success");
}
//此处若只申请一次信号量,则Thread_Semaphore2和Thread_Semaphore3会交替运行。
// osSemaphoreRelease(sem1);
// printf("Thread_Semaphore i %d \n",i);
// i=i+1;
// printf("Thread_Semaphore sem1 %d \n",sem1);
// printf("Thread_Semaphore1 Release Semap \n");
osDelay(100);
}
}
void Thread_Semaphore2(void)
{
osStatus_t status;
while (1)
{
//等待sem1信号量
status = osSemaphoreAcquire(sem1, 50U);
if (status!=osOK){
printf("semaphore2 fail");
}else{
printf("semaphore2 success");
}
}
}
void Thread_Semaphore3(void)
{
osStatus_t status;
while (1)
{
//等待sem1信号量
status = osSemaphoreAcquire(sem1, osWaitForever);
if (status!=osOK){
printf("semaphore3 fail");
}else{
printf("semaphore3 success");
}
osDelay(1);
}
}
void Semaphore_example(void)
{
osThreadAttr_t attr;
attr.attr_bits = 0U;
attr.cb_mem = NULL;
attr.cb_size = 0U;
attr.stack_mem = NULL;
attr.stack_size = 1024 * 4;
attr.priority = 24;
attr.name = "Thread_Semaphore1";
if (osThreadNew((osThreadFunc_t)Thread_Semaphore1, NULL, &attr) == NULL)
{
printf("Falied to create Thread_Semaphore1!\n");
}
attr.name = "Thread_Semaphore2";
if (osThreadNew((osThreadFunc_t)Thread_Semaphore2, NULL, &attr) == NULL)
{
printf("Falied to create Thread_Semaphore2!\n");
}
attr.name = "Thread_Semaphore3";
if (osThreadNew((osThreadFunc_t)Thread_Semaphore3, NULL, &attr) == NULL)
{
printf("Falied to create Thread_Semaphore3!\n");
}
sem1 = osSemaphoreNew(4, 0, NULL);
if (sem1 == NULL)
{
printf("Falied to create Semaphore1!\n");
}
}
APP_FEATURE_INIT(Semaphore_example);
BUILD.gn文件:
static_library("semaphore_example") {
sources = [
"Semaphore_example.c"
]
include_dirs = [
"//utils/native/lite/include",
"//kernel/liteos_m/components/cmsis/2.0",
]
}
BUILD.gn
import("//build/lite/config/component/lite_component.gni")
lite_component("app") {
features = [
"A5_kernel_semaphore:semaphore_example"
]
}
代码写完后用hpm dist命令来编译
烧录代码到开发板:
后台log

心有猛虎,细嗅蔷薇



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号