回滚莫队小记
前言
回滚莫队这个名字我几百年前就听过了,一直以为很高大上,但是今天学习后才发现非常的简单~就写篇博客吧
介绍
回滚莫队是什么?有什么用处?
首先考虑这样一个问题:求区间内相同颜色的距离最大值。莫队可以写吧,但好像有点问题,删除元素时不好维护哇 qwq,若是最大值,就得知道次大值,然后次次大值,次次次大值……
于是回滚莫队诞生啦!
名字里有个“回滚”,它到底回滚在哪里呢?
我知道你很急,但是别急,类似普通莫队,先将询问排序,以左端点所在的块的位置为第一关键字,再以右端点为第二关键字排序。
接下来就是一个个处理每一个块里的询问了(这里处理的是左端点在这个块内的询问),按照排序的顺序来处理。我们会发现右端点是递增的,而左端点是在这个块内左右横跳。下面给个图:
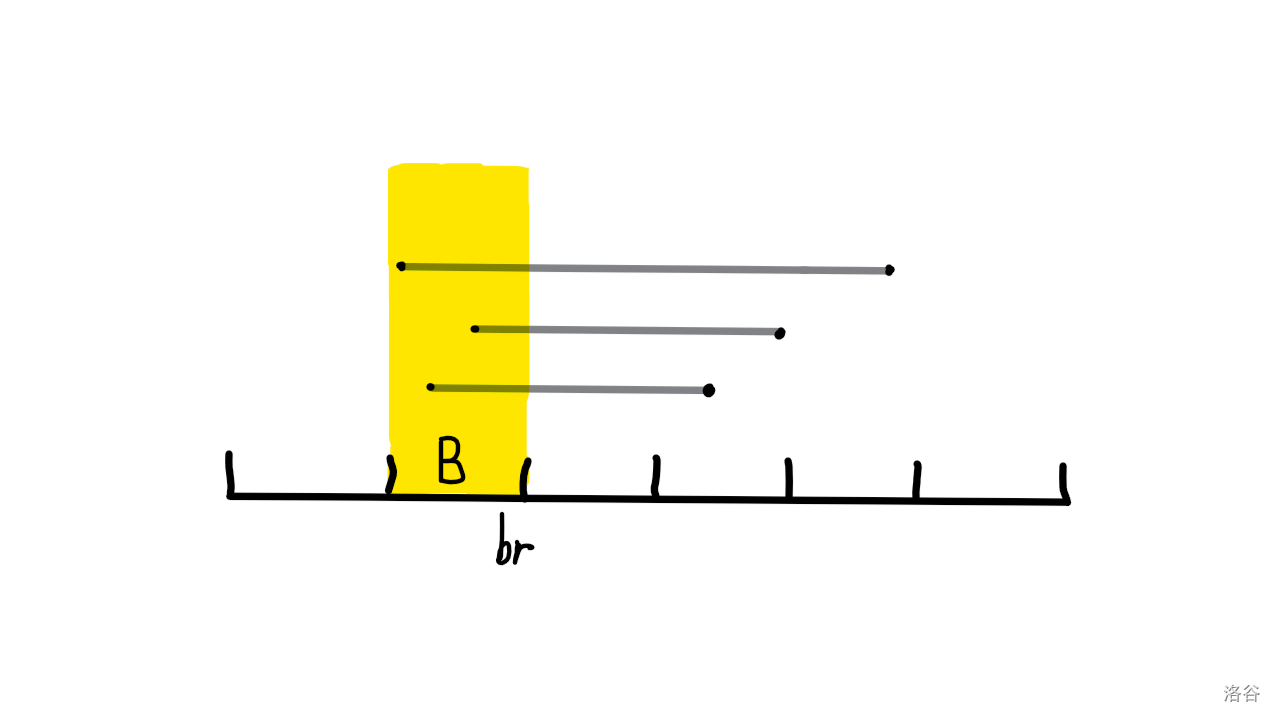
如上图所示,序列已分为若干个块。设当前要处理的块为 \(B\)(黄色区域),然后有若干个询问(灰色线条),设 \(B\) 的右端点为 \(br\),当前询问 \([ql,qr]\)。
那么我们初始化 \(l=br+1,r=br\),接下来 \(r\) 调整至 \(qr\),记录答案,再将 \(l\) 拓展至 \(ql\),答案找出。然后将 \(l\) 退回至 \(br+1\),答案回到记录的那个版本,清空原本 \(l\) 至 \(br\) 的贡献,等待下一次询问,这就是回滚莫队的“回滚”过程了。
可见,回滚莫队的主要思想就是不删除,只加入,避免看普通莫队存在的问题了。
下面给几道例题:
歴史の研究
模版题,只需维护每个数的出现次数。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define mk make_pair
#define ll long long
#define space putchar(' ')
#define enter putchar('\n')
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int x = 0, f = 1;
char c = getchar();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') f = c == '-' ? -1 : f, c = getchar();
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = (x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48), c = getchar();
return x*f;
}
inline void write(int x) {
if (x < 0) x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9) write(x/10);
putchar('0'+x%10);
}
const int N = 1e5+5;
int n, m, b, bn, tot, a[N], a_[N], _[N], be[N], cnt[N];
struct que {
int l, r, id;
bool operator < (const que &x) const { return (be[l]^be[x.l]) ? be[l] < be[x.l] : r < x.r; }
} q[N];
int calc(int l, int r) {
int ans = 0, cnt[N] = {0};
for (int i = l; i <= r; ++i) ++cnt[a[i]];
for (int i = l; i <= r; ++i) ans = max(ans, cnt[a[i]]*a_[a[i]]);
return ans;
}
signed main() {
n = read(), m = read(), b = sqrt(n), bn = n/b+(n%b != 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = a_[i] = read(), be[i] = (i-1)/b+1;
sort(a_+1, a_+n+1);
tot = unique(a_+1, a_+n+1)-a_-1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = lower_bound(a_+1, a_+tot+1, a[i])-a_;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) q[i].l = read(), q[i].r = read(), q[i].id = i;
sort(q+1, q+m+1);
for (int i = 1, j = 1; j <= bn; ++j) {
int br = min(j*b, n), l = br+1, r = br, ans = 0;
for (; be[q[i].l] == j; ++i) {
if (be[q[i].l] == be[q[i].r]) { _[q[i].id] = calc(q[i].l, q[i].r); continue; }
while (r < q[i].r) {
++r;
++cnt[a[r]];
ans = max(ans, cnt[a[r]]*a_[a[r]]);
}
int tmp = ans;
while (l > q[i].l) {
--l;
++cnt[a[l]];
ans = max(ans, cnt[a[l]]*a_[a[l]]);
}
_[q[i].id] = ans, ans = tmp;
while (l <= br) {
--cnt[a[l]];
++l;
}
}
while (r > br) --cnt[a[r]], --r;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) write(_[i]), enter;
return 0;
}
P5906 【模板】回滚莫队&不删除莫队
这个题是介绍中给的一个例子,维护最后一次出现的位置和第一次出现的位置即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define mk make_pair
#define ll long long
#define space putchar(' ')
#define enter putchar('\n')
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int x = 0, f = 1;
char c = getchar();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') f = c == '-' ? -1 : f, c = getchar();
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = (x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48), c = getchar();
return x*f;
}
inline void write(int x) {
if (x < 0) x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9) write(x/10);
putchar('0'+x%10);
}
const int N = 2e5+5;
int n, m, b, bn, tot, a[N], a_[N], _[N], be[N], st[N], ed[N];
struct que {
int l, r, id;
bool operator < (const que &x) const { return (be[l]^be[x.l]) ? be[l] < be[x.l] : r < x.r; }
} q[N];
int calc(int l, int r) {
int ans = 0, lst[N];
for (int i = l; i <= r; ++i) lst[a[i]] = 0;
for (int i = l; i <= r; ++i) lst[a[i]] ? ans = max(ans, i-lst[a[i]]) : lst[a[i]] = i;
return ans;
}
int main() {
n = read(), b = sqrt(n), bn = n/b+(n%b != 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = a_[i] = read(), be[i] = (i-1)/b+1;
sort(a_+1, a_+n+1);
tot = unique(a_+1, a_+n+1)-a_-1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = lower_bound(a_+1, a_+tot+1, a[i])-a_;
m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) q[i].l = read(), q[i].r = read(), q[i].id = i;
sort(q+1, q+m+1);
for (int i = 1, j = 1; j <= bn; ++j) {
int br = min(j*b, n), l = br+1, r = br, ans = 0;
vector <int> cl;
for (; be[q[i].l] == j; ++i) {
if (be[q[i].l] == be[q[i].r]) { _[q[i].id] = calc(q[i].l, q[i].r); continue; }
while (r < q[i].r) {
++r;
ed[a[r]] = r;
if (!st[a[r]]) st[a[r]] = r, cl.pb(a[r]);
ans = max(ans, r-st[a[r]]);
}
int tmp = ans;
while (l > q[i].l) {
--l;
if (ed[a[l]]) ans = max(ans, ed[a[l]]-l);
else ed[a[l]] = l;
}
_[q[i].id] = ans, ans = tmp;
while (l <= br) {
if (ed[a[l]] == l) ed[a[l]] = 0;
++l;
}
}
for (int x:cl) st[x] = ed[x] = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) write(_[i]), enter;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号