Restlet 学习笔记
摘要:网络上对 restlet 的评判褒贬不一,有的说框架封装的很好,很有弹性,有的说 rest 架构风格本身是一种简单的风格,restlet 过设计以使编程过于复杂,其实我倒不觉得 restlet 有什么复杂,相反很简洁明了,不论他的类结构还是整个体系结构,个人很喜欢,昨天晚上匆匆看看他的文档和实例,很不错!文章例子代码!
正文:
1. Rest简介(摘抄自网络,讲的很到位)
Restlet是一个Java下的轻量级REST框架。通过拥抱REST(REST是一种Web架构风格)它模糊了Web站点和Web服务之间的界限,从而帮助开发人员构建Web应用。每一个主要的REST概念(REST concept)都有一个对应的Java类。你的REST化的Web设计和你的代码之间的映射是非常简单直接的。为什么有必要创建另一种框架?难道Servlet API还不够好用吗?Servlet AIP在1998年发布,从那个时候起它的核心设计一直没有很大的变化。它是Java EE的众多API中最成功的一个,但是它的几个设计缺陷和一些限制损害了它。举个例子,URI模式和它的处理者(handler)之间的映射是受限制的,而且其配置都集中在一个配置文件中。还有,它把socket流的控制直接交给了应用系统开发人员,Servlet容器阻碍了我们充分使用NIO特性对IO操作进行优化。另一个主要问题就是Servlet API鼓励应用开发者在应用或者用户会话级别直接将session状态保存于内存中,尽管这看上去不错,但它造成了Servlet容器扩展性和高可用性的主要问题。为了克服这些问题,就必须实现复杂的负载均衡、session复制、持久化机制。这导致了可扩展性必然成为灾难。
如何看待别的框架中对REST的支持(例如Axis2,或者CXF/XFire)?
这些支持非常有效,但是作用非常有限。我的主要观点是设计这些项目是为了符合WS-*/SOAP Stack,它们与REST世界并不非常契合。在REST世界里,定义了一个全新的范例:面向资源的设计,而非通过远程方法调用这样的范例。例如Axis2仅仅支持GET和POST两种HTTP方法,它需要远程方法的传递需要一个URI参数。这在REST中式不允许的,这种做法也不能被称之为REST化。XFire1.2不支持REST,但是它发布了一个项目用于将POJO映射到REST化的Web服务。这有点类似最近发布的JSR-311,此JSR试图基于一套annotation和助手类标准化这种映射。
REST与HTTP协议
REST软件架构是由Roy Thomas Fielding博士在2000年首次提出的。他为我们描绘了开发基于互联网的网络软件的蓝图。REST软件架构是一个抽象的概念,是一种为了实现这一互联网的超媒体分布式系统的行动指南。利用任何的技术都可以实现这种理念。而实现这一软件架构最著名的就是HTTP协议。通常我们把REST也写作为REST/HTTP,在实际中往往把REST理解为基于HTTP的REST软件架构,或者更进一步把REST和HTTP看作为等同的概念。今天,HTTP是互联网上应用最广泛的计算机协议。HTTP不是一个简单的运载数据的协议,而是一个具有丰富内涵的网络软件的协议。它不仅仅能够对于互联网资源进行唯一定位,而且还能告诉我们对于该资源进行怎样运作。这也是REST软件架构当中最重要的两个理念。而REST软件架构理念是真正理解HTTP协议而形成的。有了REST软件架构理念出现,才使得软件业避免了对HTTP协议的片面理解。只有正确的理论指导,才能避免在软件开发的实际工作过程中少走弯路。
REST与URI(资源定位)
REST软件架构之所以是一个超媒体系统,是因为它可以把网络上所有资源进行唯一的定位,不管你的文件是图片、文件Word还是视频文件,也不管你的文件是txt文件格式、xml文件格式还是其它文本文件格式。它利用支持HTTP的TCP/IP协议来确定互联网上的资源。
REST与CRUD原则
REST软件架构遵循了CRUD原则,该原则告诉我们对于资源(包括网络资源)只需要四种行为:创建(Create)、获取(Read)、更新(Update)和销毁(DELETE)就可以完成对其操作和处理了。其实世界万物都是遵循这一规律:生、变、见、灭。所以计算机世界也不例外。这个原则是源自于我们对于数据库表的数据操作:insert(生)、select(见)、update(变)和delete(灭),所以有时候CRUD也写作为RUDI,其中的I就是insert。这四个操作是一种原子操作,即一种无法再分的操作,通过它们可以构造复杂的操作过程,正如数学上四则运算是数字的最基本的运算一样。
REST与网络服务
尽管在Java语言世界中网络服务目前是以SOAP技术为主,但是REST将是是网络服务的另一选择,并且是真正意义上的网络服务。基于REST思想的网络服务不久的将来也会成为是网络服务的主流技术。REST不仅仅把HTTP作为自己的数据运输协议,而且也作为直接进行数据处理的工具。而当前的网络服务技术都需要使用其它手段来完成数据处理工作,它们完全独立于HTTP协议来进行的,这样增加了大量的复杂软件架构设计工作。REST的思想充分利用了现有的HTTP技术的网络能力。在德国电视台上曾经出现过一个这样的五十万欧元智力题:如何实现网络服务才能充分利用现有的HTTP协议?该问题给出了四个答案:去问微软;WSDL2.0/SOAP1.2;WS-Transfer;根本没有。这个问题告诉我们HTTP并不是一个简单的数据传来传去的协议,而是一个聪明的会表现自己的协议,这也许是REST = Representational State Transfer的真正含义。实际上目前很多大公司已经采用了REST技术作为网络服务,如Google、Amazon等。在Java语言中重要的两个以SOAP技术开始的网络服务框架XFire和Axis也把REST作为自己的另一种选择。它们的新的项目分别是Apache CXF和Axis2。Java语言也制定关于REST网络服务规范:JAX-RS: Java API for RESTful Web Services (JSR 311)。相信还会出现更多与REST相关的激动人心的信息。
REST与AJAX技术
尽管AJAX技术的出现才不到两年时间,但是AJAX技术遵循了REST的一些重要原则。AJAX技术充分利用了HTTP来获取网络资源并且实现了HTTP没有的对于异步数据进行传输的功能。AJAX技术还使得软件更好地实现分布性功能,在一个企业内只要一个人下载了AJAX引擎,其它企业内部的人员,就可以共享该资源了。AJAX技术遵守REST准则的应用程序中简单和可伸缩的架构,凡是采用AJAX技术的页面简洁而又丰富,一个页面表现了丰富多彩的形态。AJAX技术还使用了一种不同于XML格式的JSON文件格式,这个意义在哪里呢?在REST软件架构下我们不能对于XML文件进行序列化处理,这样程序员必须要使用自己的XML绑定框架。而以序列化的JavaScript对象为基础的JSON已经获得了广泛认可,它被认为能以远比XML更好的方式来序列化和传输简单数据结构,而且它更简洁。这对REST是一个极大贡献和补充。当前的网络应用软件还违背了REST的"无状态服务器"约束。REST服务器只知道自己的状态。REST不关心客户端的状态,客户端的状态自己来管理,这是AJAX技术的应用之地。通过AJAX技术,可以发挥有状态网络客户机的优势。而REST的服务器关心的是从所有网络客户端发送到服务器操作的顺序。这样使得互联网这样一个巨大的网络得到有序的管理。
REST与Rails框架
Ruby on Rails框架(简称Rails或者Rails框架)是一个基于Ruby语言的越来越流行的网络应用软件开发框架。它提供了关于REST最好的支持,也是当今应用REST最成功的一个软件开发框架。Rails框架(从版本1.2.x起)成为了第一个引入REST作为核心思想的主流网络软件开发框架。在Rails框架的充分利用了REST软件架构之后,人们更加坚信REST的重要性和必要性。Rails利用REST软件架构思想对网络服务也提供了一流的支持。从最直观的角度看待REST,它是网络服务最理想的手段,但是Rails框架把REST带到了网络应用软件开发框架。这是一次飞跃,让REST的思想从网络服务的应用提升到了网络应用软件开发。利用REST思想的simply_restful插件已经成为了Rails框架的核心内容。
REST安全性
我们把现有基于SOAP的网络服务和基于REST/HTTP网络服务作个比喻,前者是一种传统的寄信方式,而后者是现代网络的电子邮件方式。要是是寄信和电子邮件都有病毒存在的话,传统的寄信被送到对方就很危险,而电子邮件是开发的,电子邮件供应商比如Google为我们检查了电子邮件是否有病毒。这里并不是说明SOAP网络服务消息包含义病毒,而是说明HTTP是无法处理SOAP信息包究竟好不好,需要额外的软件工具解决这一问题,包括防火墙也用不上和管不了。
REST/HTTP网络服务的信息包可以被防火墙理解和控制。你可以按照操作和链接进行过滤信息包,如你可以规定从外部来的只能读取(GET操作)自己服务器的资源。这样对于系统管理员而言使得软件管理更为简单。REST的安全性还可以利用传输安全协议SSL/TLS、基本和摘要式认证(Basic und Digest Authentication)。除了这些REST自身的安全性功能外,还可以利用像基于信息的Web Services Security(JSR 155)作为REST不错的补充。
2. Restlet 类结构
Uniform 是一个 Abstract 类,定义了和 HTTPMethod 对应的方法如 get,post,delete,put 等等。子类 Restlet 应该是这个框架的核心类了,restlet 有些像 servlet API,可以得到 application和 context 两个对象,其子类分别为链接器,应用,路由器,查找器,组件和过滤器。在看他的表述类结构
3. 脱离 web server 的 restlet
其实说脱离,只是 restlet 自己做了端口监听和 http 协议解析和封装的功能,restlet 设计是以资源设计为中心的,有些像 struts,webwork之 MVC 风格但又不同,他完全符合 rest 体系架构风格,可以很好的和现有的领域模型结合,一个简单的分层结构如图 资源层是对需要显示的领域模型做了显示封装,对表示层提供资源,而对领域层中需要持久化的模型借助 orm 映射器持久化。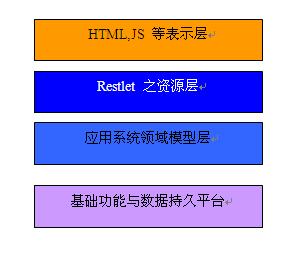 个人觉得 restlet 的应用核心在于服务,像 Axis2和XFire 等都有支持 rest 风格,restlet结合 json 应该是个比较好的实践。
个人觉得 restlet 的应用核心在于服务,像 Axis2和XFire 等都有支持 rest 风格,restlet结合 json 应该是个比较好的实践。
且看下面简单的代码(代码为官方文档里的例子):
对 Resource 封装一下 BaseResource 以方便应用程序使用:
 package org.blogjava.restlet;
package org.blogjava.restlet;2

3
 import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map;4

5
 import org.restlet.Context;
import org.restlet.Context; 6
 import org.restlet.data.Request;
import org.restlet.data.Request; 7
 import org.restlet.data.Response;
import org.restlet.data.Response; 8
 import org.restlet.resource.Resource;
import org.restlet.resource.Resource; 9
 import org.restlet.Application;
import org.restlet.Application;10

11

 /** *//**
/** *//** 12
 * Base resource class that supports common behaviours or attributes shared by
* Base resource class that supports common behaviours or attributes shared by 13
 * all resources.
* all resources. 14
 *
* 15
 */
*/ 16

 public abstract class BaseResource extends Resource
public abstract class BaseResource extends Resource  {
{17

18

 public BaseResource(Context context, Request request, Response response)
public BaseResource(Context context, Request request, Response response)  {
{ 19
 super(context, request, response);
super(context, request, response); 20
 }
}21

22

 /** *//**
/** *//** 23
 * Returns the map of items managed by this application.
* Returns the map of items managed by this application. 24
 *
* 25
 * @return the map of items managed by this application.
* @return the map of items managed by this application. 26
 */
*/ 27

 protected Map<String, Item> getItems()
protected Map<String, Item> getItems()  {
{ 28
 return ((FirstResourceApplication) getContext().getAttributes().get(
return ((FirstResourceApplication) getContext().getAttributes().get( 29
 Application.KEY)).getItems();
Application.KEY)).getItems(); 30
 }
} 31
 }
}32

33

实现 Application 类,定义路由(URI ->Resource 的映射)
 package org.blogjava.restlet;
package org.blogjava.restlet;2

3
 import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map; 4
 import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;5

6
 import org.restlet.Application;
import org.restlet.Application; 7
 import org.restlet.Context;
import org.restlet.Context; 8
 import org.restlet.Restlet;
import org.restlet.Restlet; 9
 import org.restlet.Router;
import org.restlet.Router;10

11

 public class FirstResourceApplication extends Application
public class FirstResourceApplication extends Application  {
{12

13

 /** *//** The list of items is persisted in memory. */
/** *//** The list of items is persisted in memory. */ 14
 private final Map<String, Item> items;
private final Map<String, Item> items;15

16

 public FirstResourceApplication(Context parentContext)
public FirstResourceApplication(Context parentContext)  {
{ 17
 super(parentContext);
super(parentContext); 18
 // We make sure that this attribute will support concurrent access.
// We make sure that this attribute will support concurrent access. 19
 items = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Item>();
items = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Item>(); 20
 }
}21

22

 /** *//**
/** *//** 23
 * Creates a root Restlet that will receive all incoming calls.
* Creates a root Restlet that will receive all incoming calls. 24
 */
*/ 25
 @Override
@Override 26

 public synchronized Restlet createRoot()
public synchronized Restlet createRoot()  {
{ 27
 // Create a router Restlet that defines routes.
// Create a router Restlet that defines routes. 28
 Router router = new Router(getContext());
Router router = new Router(getContext());29

30
 // Defines a route for the resource "list of items"
// Defines a route for the resource "list of items" 31
 router.attach("/items", ItemsResource.class);
router.attach("/items", ItemsResource.class); 32
 // Defines a route for the resource "item"
// Defines a route for the resource "item" 33
 router.attach("/items/{itemName}", ItemResource.class);
router.attach("/items/{itemName}", ItemResource.class);34

35
 return router;
return router; 36
 }
}37

38

 /** *//**
/** *//** 39
 * Returns the list of registered items.
* Returns the list of registered items. 40
 *
* 41
 * @return the list of registered items.
* @return the list of registered items. 42
 */
*/ 43

 public Map<String, Item> getItems()
public Map<String, Item> getItems()  {
{ 44
 return items;
return items; 45
 }
} 46
 }
} 47

资源类实现:

 public class ItemResource extends BaseResource
public class ItemResource extends BaseResource  {
{2

3

 /** *//** The underlying Item object. */
/** *//** The underlying Item object. */ 4
 Item item;
Item item;5

6

 /** *//** The sequence of characters that identifies the resource. */
/** *//** The sequence of characters that identifies the resource. */ 7
 String itemName;
String itemName;8

9

 public ItemResource(Context context, Request request, Response response)
public ItemResource(Context context, Request request, Response response)  {
{ 10
 super(context, request, response);
super(context, request, response);11

12
 // Get the "itemName" attribute value taken from the URI template
// Get the "itemName" attribute value taken from the URI template 13
 // /items/{itemName}.
// /items/{itemName}. 14
 this.itemName = (String) getRequest().getAttributes().get("itemName");
this.itemName = (String) getRequest().getAttributes().get("itemName");15

16
 // Get the item directly from the "persistence layer".
// Get the item directly from the "persistence layer". 17
 this.item = getItems().get(itemName);
this.item = getItems().get(itemName);18

19

 if (this.item != null)
if (this.item != null)  {
{ 20
 // Define the supported variant.
// Define the supported variant. 21
 getVariants().add(new Variant(MediaType.TEXT_XML));
getVariants().add(new Variant(MediaType.TEXT_XML)); 22
 }
} 23
 }
}24

25

 /** *//**
/** *//** 26
 * This resource supports DELETE requests.
* This resource supports DELETE requests. 27
 */
*/ 28
 @Override
@Override 29

 public boolean allowDelete()
public boolean allowDelete()  {
{ 30
 return true;
return true; 31
 }
}32

33

 /** *//**
/** *//** 34
 * This resource supports PUT requests.
* This resource supports PUT requests. 35
 */
*/ 36
 @Override
@Override 37

 public boolean allowPut()
public boolean allowPut()  {
{ 38
 return true;
return true; 39
 }
}40

41

 /** *//**
/** *//** 42
 * Handle DELETE requests.
* Handle DELETE requests. 43
 */
*/ 44
 @Override
@Override 45

 public void delete()
public void delete()  {
{ 46

 if (item != null)
if (item != null)  {
{ 47
 // Remove the item from the list.
// Remove the item from the list. 48
 getItems().remove(item.getName());
getItems().remove(item.getName()); 49
 }
}50

51
 // Tells the client that the request has been successfully fulfilled.
// Tells the client that the request has been successfully fulfilled. 52
 getResponse().setStatus(Status.SUCCESS_NO_CONTENT);
getResponse().setStatus(Status.SUCCESS_NO_CONTENT); 53
 }
}54

55
 @Override
@Override 56

 public Representation getRepresentation(Variant variant)
public Representation getRepresentation(Variant variant)  {
{57

58

 if (MediaType.TEXT_XML.equals(variant.getMediaType()))
if (MediaType.TEXT_XML.equals(variant.getMediaType()))  {
{ 59
 // Generate the XML representation of this resource.
// Generate the XML representation of this resource. 60

 try
try  {
{ 61
 // Generate a DOM document representing the item.
// Generate a DOM document representing the item. 62
 DomRepresentation representation = new DomRepresentation(
DomRepresentation representation = new DomRepresentation( 63
 MediaType.TEXT_XML);
MediaType.TEXT_XML); 64
 Document d = representation.getDocument();
Document d = representation.getDocument();65

66
 Element eltItem = d.createElement("item");
Element eltItem = d.createElement("item"); 67
 d.appendChild(eltItem);
d.appendChild(eltItem); 68
 Element eltName = d.createElement("name");
Element eltName = d.createElement("name"); 69
 eltName.appendChild(d.createTextNode(item.getName()));
eltName.appendChild(d.createTextNode(item.getName())); 70
 eltItem.appendChild(eltName);
eltItem.appendChild(eltName);71

72
 Element eltDescription = d.createElement("description");
Element eltDescription = d.createElement("description"); 73
 eltDescription.appendChild(d.createTextNode(item
eltDescription.appendChild(d.createTextNode(item 74
 .getDescription()));
.getDescription())); 75
 eltItem.appendChild(eltDescription);
eltItem.appendChild(eltDescription);76

77
 d.normalizeDocument();
d.normalizeDocument();78

79
 // Returns the XML representation of this document.
// Returns the XML representation of this document. 80
 return representation;
return representation; 81

 } catch (IOException e)
} catch (IOException e)  {
{ 82
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace(); 83
 }
} 84
 }
}85

86
 return null;
return null; 87
 }
}88

89

 /** *//**
/** *//** 90
 * Handle PUT requests.
* Handle PUT requests. 91
 */
*/ 92
 @Override
@Override 93

 public void put(Representation entity)
public void put(Representation entity)  {
{ 94
 // Tells if the item is to be created of not.
// Tells if the item is to be created of not. 95
 boolean creation = (item == null);
boolean creation = (item == null);96

97
 // The PUT request updates or creates the resource.
// The PUT request updates or creates the resource. 98

 if (item == null)
if (item == null)  {
{ 99
 item = new Item(itemName);
item = new Item(itemName); 100
 }
}101

102
 // Update the description.
// Update the description. 103
 Form form = new Form(entity);
Form form = new Form(entity); 104
 item.setDescription(form.getFirstValue("description"));
item.setDescription(form.getFirstValue("description"));105

106
 // Update the item in the list.
// Update the item in the list. 107
 getItems().put(item.getName(), item);
getItems().put(item.getName(), item);108

109

 if (creation)
if (creation)  {
{ 110
 getResponse().setStatus(Status.SUCCESS_CREATED);
getResponse().setStatus(Status.SUCCESS_CREATED); 111

 } else
} else  {
{ 112
 getResponse().setStatus(Status.SUCCESS_OK);
getResponse().setStatus(Status.SUCCESS_OK); 113
 }
} 114
 }
}115

116
 }
} 117

118

客户端和服务器类,服务器类代替 web server 做监听和 Http 协议处理。
 package org.blogjava.restlet;
package org.blogjava.restlet;2

3
 import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.IOException;4

5
 import org.restlet.Client;
import org.restlet.Client; 6
 import org.restlet.data.Form;
import org.restlet.data.Form; 7
 import org.restlet.data.Protocol;
import org.restlet.data.Protocol; 8
 import org.restlet.data.Reference;
import org.restlet.data.Reference; 9
 import org.restlet.data.Response;
import org.restlet.data.Response; 10
 import org.restlet.resource.Representation;
import org.restlet.resource.Representation;11

12

 public class FirstResourceClientMain
public class FirstResourceClientMain  {
{13

14

 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException  {
{ 15
 // Define our Restlet HTTP client.
// Define our Restlet HTTP client. 16
 Client client = new Client(Protocol.HTTP);
Client client = new Client(Protocol.HTTP);17

18
 // The URI of the resource "list of items".
// The URI of the resource "list of items". 19
 Reference itemsUri = new Reference(
Reference itemsUri = new Reference( 20
 "http://localhost:8182/firstResource/items");
"http://localhost:8182/firstResource/items");21

22
 // Create a new item
// Create a new item 23
 Item item = new Item("item1", "this is an item.");
Item item = new Item("item1", "this is an item."); 24
 Reference itemUri = createItem(item, client, itemsUri);
Reference itemUri = createItem(item, client, itemsUri); 25

 if (itemUri != null)
if (itemUri != null)  {
{ 26
 // Prints the representation of the newly created resource.
// Prints the representation of the newly created resource. 27
 get(client, itemUri);
get(client, itemUri); 28
 }
}29

30
 // Prints the list of registered items.
// Prints the list of registered items. 31
 get(client, itemsUri);
get(client, itemsUri);32

33
 // Update the item
// Update the item 34
 item.setDescription("This is an other description");
item.setDescription("This is an other description"); 35
 updateItem(item, client, itemUri);
updateItem(item, client, itemUri);36

37
 // Prints the list of registered items.
// Prints the list of registered items. 38
 get(client, itemsUri);
get(client, itemsUri);39

40
 // delete the item
// delete the item 41
 deleteItem(client, itemUri);
deleteItem(client, itemUri);42

43
 // Print the list of registered items.
// Print the list of registered items. 44
 get(client, itemsUri);
get(client, itemsUri); 45
 }
}46

47

 /** *//**
/** *//** 48
 * Try to create a new item.
* Try to create a new item. 49
 *
* 50
 * @param item
* @param item 51
 * the new item.
* the new item. 52
 * @param client
* @param client 53
 * the Restlet HTTP client.
* the Restlet HTTP client. 54
 * @param itemsUri
* @param itemsUri 55
 * where to POST the data.
* where to POST the data. 56
 * @return the Reference of the new resource if the creation succeeds, null
* @return the Reference of the new resource if the creation succeeds, null 57
 * otherwise.
* otherwise. 58
 */
*/ 59
 public static Reference createItem(Item item, Client client,
public static Reference createItem(Item item, Client client, 60

 Reference itemsUri)
Reference itemsUri)  {
{ 61
 // Gathering informations into a Web form.
// Gathering informations into a Web form. 62
 Form form = new Form();
Form form = new Form(); 63
 form.add("name", item.getName());
form.add("name", item.getName()); 64
 form.add("description", item.getDescription());
form.add("description", item.getDescription()); 65
 Representation rep = form.getWebRepresentation();
Representation rep = form.getWebRepresentation();66

67
 // Launch the request
// Launch the request 68
 Response response = client.post(itemsUri, rep);
Response response = client.post(itemsUri, rep); 69

 if (response.getStatus().isSuccess())
if (response.getStatus().isSuccess())  {
{ 70

 if (response.isEntityAvailable())
if (response.isEntityAvailable())  {
{ 71

 try
try  {
{ 72
 // Always consume the response's entity, if available.
// Always consume the response's entity, if available. 73
 response.getEntity().write(System.out);
response.getEntity().write(System.out); 74

 } catch (IOException e)
} catch (IOException e)  {
{ 75
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace(); 76
 }
} 77
 }
}78

79
 return response.getEntity().getIdentifier();
return response.getEntity().getIdentifier(); 80
 }
}81

82
 return null;
return null; 83
 }
}84

85

 /** *//**
/** *//** 86
 * Prints the resource's representation.
* Prints the resource's representation. 87
 *
* 88
 * @param client
* @param client 89
 * client Restlet.
* client Restlet. 90
 * @param reference
* @param reference 91
 * the resource's URI
* the resource's URI 92
 * @throws IOException
* @throws IOException 93
 */
*/ 94
 public static void get(Client client, Reference reference)
public static void get(Client client, Reference reference) 95

 throws IOException
throws IOException  {
{ 96
 Response response = client.get(reference);
Response response = client.get(reference); 97

 if (response.getStatus().isSuccess())
if (response.getStatus().isSuccess())  {
{ 98

 if (response.isEntityAvailable())
if (response.isEntityAvailable())  {
{ 99
 response.getEntity().write(System.out);
response.getEntity().write(System.out); 100
 }
} 101
 }
} 102
 }
}103

104

 /** *//**
/** *//** 105
 * Try to update an item.
* Try to update an item. 106
 *
* 107
 * @param item
* @param item 108
 * the item.
* the item. 109
 * @param client
* @param client 110
 * the Restlet HTTP client.
* the Restlet HTTP client. 111
 * @param itemUri
* @param itemUri 112
 * the resource's URI.
* the resource's URI. 113
 */
*/ 114

 public static boolean updateItem(Item item, Client client, Reference itemUri)
public static boolean updateItem(Item item, Client client, Reference itemUri)  {
{ 115
 // Gathering informations into a Web form.
// Gathering informations into a Web form. 116
 Form form = new Form();
Form form = new Form(); 117
 form.add("name", item.getName());
form.add("name", item.getName()); 118
 form.add("description", item.getDescription());
form.add("description", item.getDescription()); 119
 Representation rep = form.getWebRepresentation();
Representation rep = form.getWebRepresentation();120

121
 // Launch the request
// Launch the request 122
 Response response = client.put(itemUri, rep);
Response response = client.put(itemUri, rep); 123

 if (response.isEntityAvailable())
if (response.isEntityAvailable())  {
{ 124

 try
try  {
{ 125
 // Always consume the response's entity, if available.
// Always consume the response's entity, if available. 126
 response.getEntity().write(System.out);
response.getEntity().write(System.out); 127

 } catch (IOException e)
} catch (IOException e)  {
{ 128
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace(); 129
 }
} 130
 }
} 131
 return response.getStatus().isSuccess();
return response.getStatus().isSuccess(); 132
 }
}133

134

 /** *//**
/** *//** 135
 * Try to delete an item.
* Try to delete an item. 136
 *
* 137
 * @param client
* @param client 138
 * the Restlet HTTP client.
* the Restlet HTTP client. 139
 * @param itemUri
* @param itemUri 140
 * the resource's URI.
* the resource's URI. 141
 */
*/ 142

 public static boolean deleteItem(Client client, Reference itemUri)
public static boolean deleteItem(Client client, Reference itemUri)  {
{ 143
 // Launch the request
// Launch the request 144
 Response response = client.delete(itemUri);
Response response = client.delete(itemUri); 145

 if (response.isEntityAvailable())
if (response.isEntityAvailable())  {
{ 146

 try
try  {
{ 147
 // Always consume the response's entity, if available.
// Always consume the response's entity, if available. 148
 response.getEntity().write(System.out);
response.getEntity().write(System.out); 149

 } catch (IOException e)
} catch (IOException e)  {
{ 150
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace(); 151
 }
} 152
 }
}153

154
 return response.getStatus().isSuccess();
return response.getStatus().isSuccess(); 155
 }
}156

157
 }
} 158
 package org.blogjava.restlet;
package org.blogjava.restlet; 159
 import org.restlet.Component;
import org.restlet.Component; 160
 import org.restlet.data.Protocol;
import org.restlet.data.Protocol;161

162

 public class FirstResourceServerMain
public class FirstResourceServerMain  {
{163

164

 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception  {
{ 165
 // Create a new Component.
// Create a new Component. 166
 Component component = new Component();
Component component = new Component();167

168
 // Add a new HTTP server listening on port 8182.
// Add a new HTTP server listening on port 8182. 169
 component.getServers().add(Protocol.HTTP, 8182);
component.getServers().add(Protocol.HTTP, 8182);170

171
 // Attach the sample application.
// Attach the sample application. 172
 component.getDefaultHost().attach("/firstResource",
component.getDefaultHost().attach("/firstResource", 173
 new FirstResourceApplication(component.getContext()));
new FirstResourceApplication(component.getContext()));174

175
 // Start the component.
// Start the component. 176
 component.start();
component.start(); 177
 }
}178

179
 }
} 180

181

4.和现有 servlet 容器结合的例子
配置 web.xml
 <context-param>
<context-param> 2
 <param-name>org.restlet.application</param-name>
<param-name>org.restlet.application</param-name> 3
 <param-value>
<param-value> 4
 org.blogjava.helloworld.FirstStepsApplication
org.blogjava.helloworld.FirstStepsApplication 5
 </param-value>
</param-value> 6
 </context-param>
</context-param> 7
 <!-- Restlet adapter -->
<!-- Restlet adapter --> 8
 <servlet>
<servlet> 9
 <servlet-name>RestletServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-name>RestletServlet</servlet-name> 10
 <servlet-class>
<servlet-class> 11
 com.noelios.restlet.ext.servlet.ServerServlet
com.noelios.restlet.ext.servlet.ServerServlet 12
 </servlet-class>
</servlet-class> 13
 </servlet>
</servlet> 14
 <!-- Catch all requests -->
<!-- Catch all requests --> 15
 <servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping> 16
 <servlet-name>RestletServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-name>RestletServlet</servlet-name> 17
 <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> 18
 </servlet-mapping>
</servlet-mapping>19

20

实现 Application 和 Resource 资源类

2

 public class FirstStepsApplication extends Application
public class FirstStepsApplication extends Application  {
{3

4

 public FirstStepsApplication(Context parentContext)
public FirstStepsApplication(Context parentContext)  {
{ 5
 super(parentContext);
super(parentContext); 6
 }
}7

8

 /** *//**
/** *//** 9
 * Creates a root Restlet that will receive all incoming calls.
* Creates a root Restlet that will receive all incoming calls. 10
 */
*/ 11
 @Override
@Override 12

 public synchronized Restlet createRoot()
public synchronized Restlet createRoot()  {
{ 13
 // Create a router Restlet that routes each call to a
// Create a router Restlet that routes each call to a 14
 // new instance of HelloWorldResource.
// new instance of HelloWorldResource. 15
 Router router = new Router(getContext());
Router router = new Router(getContext());16

17
 // Defines only one route
// Defines only one route 18
 router.attachDefault(HelloWorldResource.class);
router.attachDefault(HelloWorldResource.class);19

20
 return router;
return router; 21
 }
} 22
 }
} 23

24

25
 package org.blogjava.helloworld;
package org.blogjava.helloworld;26

27
 import org.restlet.Context;
import org.restlet.Context; 28
 import org.restlet.data.MediaType;
import org.restlet.data.MediaType; 29
 import org.restlet.data.Request;
import org.restlet.data.Request; 30
 import org.restlet.data.Response;
import org.restlet.data.Response; 31
 import org.restlet.resource.Representation;
import org.restlet.resource.Representation; 32
 import org.restlet.resource.Resource;
import org.restlet.resource.Resource; 33
 import org.restlet.resource.StringRepresentation;
import org.restlet.resource.StringRepresentation; 34
 import org.restlet.resource.Variant;
import org.restlet.resource.Variant;35

36

 /** *//**
/** *//** 37
 * Resource which has only one representation.
* Resource which has only one representation. 38
 *
* 39
 */
*/ 40

 public class HelloWorldResource extends Resource
public class HelloWorldResource extends Resource  {
{41

42
 public HelloWorldResource(Context context, Request request,
public HelloWorldResource(Context context, Request request, 43

 Response response)
Response response)  {
{ 44
 super(context, request, response);
super(context, request, response);45

46
 // This representation has only one type of representation.
// This representation has only one type of representation. 47
 getVariants().add(new Variant(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN));
getVariants().add(new Variant(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)); 48
 }
}49

50

 /** *//**
/** *//** 51
 * Returns a full representation for a given variant.
* Returns a full representation for a given variant. 52
 */
*/ 53
 @Override
@Override 54

 public Representation getRepresentation(Variant variant)
public Representation getRepresentation(Variant variant)  {
{ 55
 Representation representation = new StringRepresentation(
Representation representation = new StringRepresentation( 56
 "hello, world,just a simple example!", MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN);
"hello, world,just a simple example!", MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN); 57
 return representation;
return representation; 58
 }
} 59
 }
}60

61

作者:KeerDi —— 北方的后生
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/keerdi/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号