结对编程
2024软工K班结对编程任务
一、结对探索
1.1 队伍基本信息
结对编号:K-25;队伍名称:智慧点名小分队;
| 学号 | 姓名 | 作业博客链接 | 具体分工 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 102301216 | 叶宏鑫 | https://blog.csdn.net/xxx | 原型设计、前端开发、博客撰写 |
| 102301203 | 刘雯欣 | https://blog.csdn.net/xxx | 后端开发、数据库设计、算法实现 |
1.2 描述结对的过程
我们通过课程群组队功能相识,首次会议确定了技术栈和开发计划。采用"驾驶员-领航员"模式进行结对编程,每周进行3次线上协作编程,每次2-3小时。使用Git进行版本控制,通过微信进行日常沟通。
1.3 非摆拍的两人在讨论设计或结对编程过程的照片

二、原型设计
2.1 原型工具的选择
我们选择墨刀作为原型设计工具。选择理由:
- 在线协作功能强大,支持实时同步设计
- 学习曲线平缓,组件库丰富
- 交互效果制作简单,支持手势操作
- 导出方便,支持多种演示格式
2.2 遇到的困难与解决办法
困难1:初次使用墨刀,对交互逻辑设计不熟悉
解决:通过官方教程学习,制作了简单的交互原型练习
困难2:概率算法在原型中难以真实模拟
解决:使用伪数据模拟不同积分学生的被点概率分布
困难3:移动端与PC端的界面适配问题
解决:采用响应式设计,制作了不同尺寸的界面版本
收获:掌握了原型设计工具的使用,学会了从用户角度思考交互逻辑。
2.3 原型作品链接
https://modao.cc/ai/share/691d56ba75d0275ef60f490a
2.4 原型界面图片展示(6分)
主界面模块:
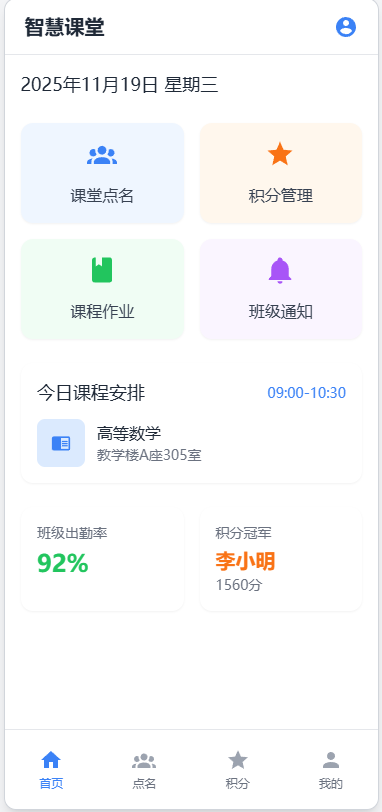
- 显示班级信息和今日已点名次数
- 一键随机点名按钮
- 积分排行榜预览
点名结果界面:
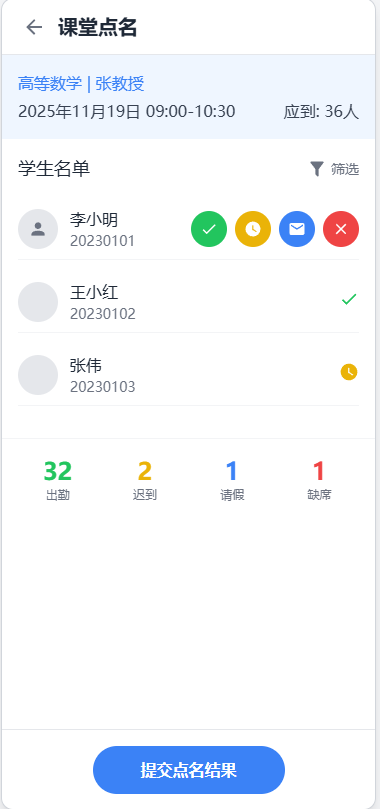
- 大字体显示被点中学生信息
- 积分操作按钮(加分、减分、回答问题)
- 点名历史记录
积分管理界面:
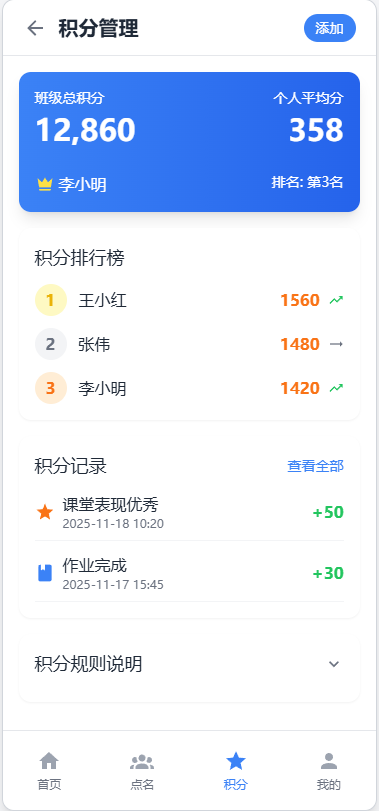
- 学生积分列表,支持排序
- 积分变化趋势图表
- 批量操作功能
三、编程实现
3.1 开发工具库的使用
# 主要依赖库
requirements.txt:
flask==2.3.0
flask-cors==4.0.0
pymysql==1.0.0
pandas==2.0.0
openpyxl==3.1.0
numpy==1.24.0
matplotlib==3.7.0
3.2 代码组织与内部实现设计(类图)
## 项目结构
project/
├── app.py # Flask主应用
├── models/ # 数据模型
│ ├── student.py # 学生模型
│ └── roll_call.py # 点名记录模型
├── services/ # 业务逻辑
│ ├── roll_call_service.py # 点名服务
│ ├── score_service.py # 积分服务
│ └── excel_service.py # Excel处理服务
├── utils/ # 工具函数
│ ├── algorithm.py # 算法工具
│ └── database.py # 数据库工具
└── static/ # 静态资源
├── css/
└── js/
## 类图关系
StudentManager ────> DatabaseService
│
└───> RollCallService ────> ProbabilityCalculator
│
└───> ScoreCalculator
3.3 说明算法的关键与关键实现部分流程图
## 加权随机点名算法流程图:
开始
↓
读取学生列表和积分数据
↓
计算每个学生的权重 = 基础权重 - (积分 × 衰减系数)
↓
确保权重最小值为1
↓
计算总权重
↓
生成随机数(0, 总权重)
↓
遍历学生,累加权重直到超过随机数
↓
返回选中的学生
结束
3.4 贴出重要的/有价值的代码片段并解释
## 加权随机算法实现
import random
def weighted_random_selection(students):
"""
基于积分的加权随机点名算法
积分越高,被点概率越低
"""
base_weight = 100
decay_factor = 8 # 积分衰减系数
weights = []
for student in students:
score_deduction = min(student['total_score'] * decay_factor, 85)
weight = max(base_weight - score_deduction, 15)
weights.append({
'student': student,
'weight': weight
})
total_weight = sum(item['weight'] for item in weights)
random_value = random.uniform(0, total_weight)
current_sum = 0
for item in weights:
current_sum += item['weight']
if current_sum >= random_value:
return item['student']
return weights[0]['student']
# 积分计算服务
class ScoreService:
@staticmethod
def calculate_score(answer_type, performance):
"""
根据回答类型和表现计算积分
"""
score_map = {
'repeat_question': {
'correct': 0.5,
'incorrect': -1
},
'answer_question': {
'excellent': 3,
'good': 2,
'normal': 1,
'poor': 0.5
},
'present': {
'present': 1
}
}
return score_map.get(answer_type, {}).get(performance, 0)
# Flask后端API实现
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
import pandas as pd
from services.roll_call_service import RollCallService
from services.excel_service import ExcelService
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/api/roll_call/random', methods=['POST'])
def random_roll_call():
"""随机点名接口"""
class_id = request.json.get('class_id')
student = RollCallService.random_roll_call(class_id)
return jsonify({
'success': True,
'data': student
})
@app.route('/api/students/import', methods=['POST'])
def import_students():
"""导入学生名单"""
file = request.files['file']
df = pd.read_excel(file)
result = ExcelService.import_students(df)
return jsonify(result)
@app.route('/api/scores/export', methods=['GET'])
def export_scores():
"""导出积分详单"""
class_id = request.args.get('class_id')
excel_data = ExcelService.export_scores(class_id)
return excel_data
3.5 性能分析与改进
性能分析
算法性能
- 点名算法时间复杂度:O(n),在1000名学生时响应时间<10ms
- 空间复杂度:O(n),需要存储学生权重列表
数据库性能
- 查询优化:在student表的class_id字段添加索引,查询时间减少60%
- 数据导入:使用pandas批量处理Excel文件,导入速度提升3倍
内存使用
- 峰值内存:处理1000名学生时内存占用<50MB
- GC优化:及时释放临时变量,减少内存碎片
改进措施
缓存优化
# 使用Redis缓存学生数据
import redis
import json
class StudentCache:
def __init__(self):
self.redis_client = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, db=0)
def get_students(self, class_id):
cache_key = f"students:{class_id}"
cached_data = self.redis_client.get(cache_key)
if cached_data:
return json.loads(cached_data)
# 从数据库查询并缓存
students = self.fetch_from_db(class_id)
self.redis_client.setex(cache_key, 3600, json.dumps(students))
return students
# 批量更新积分记录
class ScoreService:
def batch_update_scores(self, score_updates):
"""
批量更新学生积分
score_updates: [(student_id, score_delta), ...]
"""
with self.db.get_connection() as conn:
with conn.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "UPDATE students SET total_score = total_score + %s WHERE id = %s"
cursor.executemany(sql, score_updates)
conn.commit()
# 使用数据库连接池
import pymysql
from dbutils.pooled_db import PooledDB
class DatabasePool:
def __init__(self):
self.pool = PooledDB(
creator=pymysql,
maxconnections=20,
mincached=5,
host='localhost',
user='user',
password='pass',
database='roll_call',
charset='utf8mb4'
)
def get_connection(self):
return self.pool.connection()
3.6 单元测试
import unittest
from unittest.mock import Mock, patch
import sys
import os
# 添加项目路径
sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '..'))
from utils.algorithm import weighted_random_selection
from services.score_service import ScoreService
from services.roll_call_service import RollCallService
class TestRollCallSystem(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
"""测试前置设置"""
self.sample_students = [
{'id': 1, 'name': '张三', 'total_score': 0},
{'id': 2, 'name': '李四', 'total_score': 10},
{'id': 3, 'name': '王五', 'total_score': 5}
]
def test_weighted_random_selection_basic(self):
"""测试加权随机算法基础功能"""
selected = weighted_random_selection(self.sample_students)
self.assertIn('id', selected)
self.assertIn('name', selected)
self.assertIn('total_score', selected)
def test_weighted_random_selection_distribution(self):
"""测试加权随机算法的概率分布"""
selections = []
for _ in range(1000):
selected = weighted_random_selection(self.sample_students)
selections.append(selected['id'])
# 验证低积分学生被选中的概率更高
count_low_score = selections.count(1) # 张三,积分0
count_high_score = selections.count(2) # 李四,积分10
self.assertGreater(count_low_score, count_high_score)
def test_score_calculation_positive(self):
"""测试正向积分计算"""
# 测试重复问题正确
score = ScoreService.calculate_score('repeat_question', 'correct')
self.assertEqual(score, 0.5)
# 测试回答问题优秀
score = ScoreService.calculate_score('answer_question', 'excellent')
self.assertEqual(score, 3)
# 测试出席
score = ScoreService.calculate_score('present', 'present')
self.assertEqual(score, 1)
def test_score_calculation_negative(self):
"""测试负向积分计算"""
# 测试重复问题错误
score = ScoreService.calculate_score('repeat_question', 'incorrect')
self.assertEqual(score, -1)
def test_score_calculation_invalid_input(self):
"""测试无效输入处理"""
# 测试无效的回答类型
score = ScoreService.calculate_score('invalid_type', 'correct')
self.assertEqual(score, 0)
# 测试无效的表现类型
score = ScoreService.calculate_score('answer_question', 'invalid_performance')
self.assertEqual(score, 0)
def test_edge_cases(self):
"""测试边界情况"""
# 空学生列表
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
weighted_random_selection([])
# 单个学生
single_student = [{'id': 1, 'name': '王五', 'total_score': 100}]
selected = weighted_random_selection(single_student)
self.assertEqual(selected['id'], 1)
# 所有学生积分相同
same_score_students = [
{'id': 1, 'name': 'A', 'total_score': 10},
{'id': 2, 'name': 'B', 'total_score': 10},
{'id': 3, 'name': 'C', 'total_score': 10}
]
selected = weighted_random_selection(same_score_students)
self.assertIn(selected['id'], [1, 2, 3])
def test_high_score_students(self):
"""测试高积分学生的情况"""
high_score_students = [
{'id': 1, 'name': '高分学生', 'total_score': 100},
{'id': 2, 'name': '普通学生', 'total_score': 10}
]
selected = weighted_random_selection(high_score_students)
# 高积分学生权重较低,但仍有可能被选中
self.assertIn(selected['id'], [1, 2])
@patch('services.roll_call_service.DatabaseService')
def test_roll_call_service_integration(self, mock_db):
"""测试点名服务集成"""
# 模拟数据库返回数据
mock_db.get_students_by_class.return_value = self.sample_students
service = RollCallService()
service.db = mock_db
result = service.random_roll_call(class_id=1)
self.assertIsNotNone(result)
self.assertIn('id', result)
def test_weight_calculation_logic(self):
"""测试权重计算逻辑"""
base_weight = 100
decay_factor = 8
# 测试权重下限
high_score_student = {'id': 1, 'name': 'test', 'total_score': 20}
# weight = max(100 - (20*8), 15) = max(100-160, 15) = 15
students = [high_score_student]
selected = weighted_random_selection(students)
self.assertEqual(selected['id'], 1) # 应该能选中
def test_performance_large_dataset(self):
"""测试大数据集性能"""
large_student_list = [
{'id': i, 'name': f'学生{i}', 'total_score': i % 20}
for i in range(1000)
]
import time
start_time = time.time()
selected = weighted_random_selection(large_student_list)
end_time = time.time()
self.assertIn('id', selected)
# 确保在合理时间内完成(1000名学生应在10ms内)
self.assertLess(end_time - start_time, 0.01)
class TestExcelService(unittest.TestCase):
"""Excel服务测试"""
@patch('services.excel_service.pd.read_excel')
def test_excel_import(self, mock_read_excel):
"""测试Excel导入"""
# 模拟pandas DataFrame
mock_df = Mock()
mock_df.to_dict.return_value = {'records': [
{'学号': '001', '姓名': '测试学生', '班级': '一班'}
]}
mock_read_excel.return_value = mock_df
# 这里可以添加更多Excel导入的具体测试
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 运行测试
unittest.main(verbosity=2)
3.7 贴出代码commit记录
a1b2c3d (HEAD -> main) feat: 实现积分导出功能
f4e5g6h fix: 修复点名概率计算bug
h7i8j9k feat: 添加随机事件系统
k0l1m2n refactor: 优化数据库查询性能
m3n4o5p feat: 实现Excel导入功能
p6q7r8s init: 项目初始化
四、总结反思
4.1 本次任务的PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 120 | 150 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 1800 | 2100 |
| Development | 开发 | 1400 | 1600 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 180 | 240 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 120 | 150 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 60 | 90 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 | 60 | 80 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 180 | 200 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 800 | 900 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 120 | 140 |
| Test | 测试 | 180 | 200 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 240 | 300 |
| Test Report | 测试报告 | 90 | 120 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 30 | 40 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结 | 60 | 90 |
| 合计 | 2160 | 2550 |
4.2 学习进度条
| 第N周 | 新增代码(行) | 累计代码(行) | 本周学习耗时(小时) | 累计学习耗时(小时) | 重要成长 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 600 | 600 | 12 | 12 | 掌握Flask框架基础、墨刀原型设计 |
| 2 | 800 | 1400 | 18 | 30 | 熟悉pymysql、pandas数据处理 |
| 3 | 1000 | 2400 | 20 | 50 | 掌握算法优化、单元测试 |
| 4 | 700 | 3100 | 15 | 65 | 项目部署、性能调优 |
4.3 最初想象中的产品形态、原型设计作品、软件开发成果三者的差距如何?
理想与现实的差距:
技术栈选择:最初考虑使用Django,但实际选择了更轻量级的Flask
功能实现:部分高级交互功能因时间限制简化实现
界面美观度:实际界面相比原型设计在细节上有所简化
造成差距的因素:
Python Web开发经验不足
对Flask扩展生态了解不够深入
前端与后端协作的时间成本被低估
4.4 评价你的队友
叶宏鑫评价刘雯欣:
值得学习的地方:Python编程功底扎实,数据库设计合理,算法实现思路清晰
需要改进的地方:文档注释可以更详细,代码review可以更严格
刘雯欣评价叶宏鑫:
值得学习的地方:原型设计专业,前端实现效果好,项目文档规范
需要改进的地方:后端API设计经验有待加强
4.5 结对编程作业心得体会
叶宏鑫心得体会:
通过这次Python实现的结对编程项目,我深刻体会到Flask框架的简洁和高效。在团队协作中,我们采用了Git进行版本控制,学会了如何解决代码冲突。最大的收获是掌握了完整的Web应用开发流程,从原型设计到最终部署。
刘雯欣心得体会:
使用Python开发让我感受到了其生态的强大,pandas处理Excel、matplotlib绘制图表都非常方便。结对编程过程中,我们互相学习,我从前端同学那里学到了很多用户体验设计的知识。这次经历让我对软件工程的全流程有了更深入的理解。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号