在计算机科学中,堆(Heap)是一种基于树(Tree)的特殊的数据结构。堆需要满足堆特性(Heap Property):如果节点 A 是节点 B 的父节点,则节点 A 中的键值与节点 B 中的键值的比较顺序关系将适用于堆中的所有节点。也就是可以总结为两种情况。
- 父节点的键值大于等于子节点的键值 A(Parent(i)) ≥ A[i] ,则根节点的键值为堆中的最大值。这种类型的堆叫做最大堆(Max Heap)。
- 父节点的键值小于等于子节点的键值 A(Parent(i)) ≤ A[i],则根节点的键值为堆中的最小值。这种类型的堆叫做最小堆(Min Heap)。
由于堆中的最大值或最小值总是被存储在根节点(Root Node)中,所以名字称为堆。堆不是一种排序的数据结构,可认为是部分排序的结构。从堆的图形结构来看,在相同层级中的节点间没有任何特定的关系,即使是兄弟节点。
堆经常被应用于优先队列(Priority Queue),当你需要找到队列中最高优先级或者最低优先级的元素时,使用堆结构可以帮助你快速的定位元素。
堆实现与基本操作
常见的堆实现为二叉堆(Binary Heap),其实际上是一颗二叉树(Binary Tree),并且是一颗完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree)。如下图中展示了一个完全二叉的最大堆。
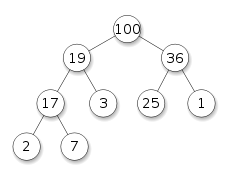
当堆被实现为完全二叉树时,其高度为最小高度。如果堆中有 n 个节点,则最小高度为 Θ(lg n)。
实现堆结构时通常使用数组结构(Array),并且元素间不需要指针引用。使用完全二叉树或者满二叉树实现堆时可以保持最优的空间效率。通常第一个元素或最后一个元素将保存根节点,根节点后紧跟着其两个子节点,两个子节点后将紧跟着 4 个这两个子节点的子节点,以此类推。因此,在一个以 0 为起点的数组中,位置 i 处的节点的子节点的位置将位于 2i+1 和 2i+2 处。平衡一个堆的操作将使用元素互换的方式,所以对堆进行排序无需使用额外的空间,堆排序(heapsort)即是用了这种就地排序(In-Place)的方式。
堆排序
堆排序(Heap Sort)是指利用堆这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法。二叉堆数据结构是一种数组对象,它可以被视为一棵完全二叉树。树中每个节点与数组中存放该节点值的那个元素对应。在堆排序算法中,我们使用最大堆。
堆节点的访问
通常堆是通过一维数组来实现的。在数组起始为 0 的情形中,如果 i 为当前节点的索引,则有
- 父节点在位置 floor((i-1)/2);
- 左子节点在位置 (2*i+1);
- 右子节点在位置 (2*i+2);
堆的操作
在堆的数据结构中,堆中的最大值总是位于根节点。堆中定义以下几种操作:
- 最大堆调整(Max-Heapify):将堆的末端子节点作调整,使得子节点永远小于父节点,保持最大堆性质的关键。运行时间为 O(lg n)。
- 创建最大堆(Build-Max-Heap):在无序的输入数组基础上构造出最大堆。运行时间为 O(n)。
- 堆排序(HeapSort):对一个数组进行原地排序,卸载位在第一个数据的根节点,并做最大堆调整的递归运算。运行时间为 O(n*lg n)。
- 抽取最大值(Extract-Max):相当于执行一次最大堆调整,最大值在根处。运行时间为 O(lg n)。

算法复杂度
- 最差时间复杂度 O(n*logn)
- 平均时间复杂度 Θ(n*logn)
- 最优时间复杂度 O(n*logn)
- 最差空间复杂度 O(n),辅助空间 O(1)
示例代码
1 class Program
2 {
3 static void Main(string[] args)
4 {
5 int[] unsorted = { 4, 9, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7, 1, 8 };
6
7 HeapSortByMaxHeap(unsorted);
8
9 foreach (var key in unsorted)
10 {
11 Console.Write("{0} ", key);
12 }
13
14 Console.Read();
15 }
16
17 static void HeapSortByMaxHeap(int[] unsorted)
18 {
19 // build the heap in array so that largest value is at the root
20 BuildMaxHeap(unsorted);
21
22 // swap root node and the last heap node
23 for (int i = unsorted.Length - 1; i >= 1; i--)
24 {
25 // array[0] is the root and largest value.
26 // the swap moves it in front of the sorted elements
27 int max = unsorted[0];
28 unsorted[0] = unsorted[i];
29 unsorted[i] = max; // now, the largest one is at the end
30
31 // the swap ruined the heap property, so restore it
32 // the heap size is reduced by one
33 MaxHeapify(unsorted, 0, i - 1);
34 }
35 }
36
37 static void BuildMaxHeap(int[] unsorted)
38 {
39 // put elements of array in heap order, in-place
40 // start is assigned the index in array of the last parent node
41 // the last element in 0-based array is at index count-1;
42 // find the parent of that element
43 for (int i = (unsorted.Length / 2) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
44 {
45 // move a node down in the tree, as long as needed
46 // shift down the node at index start to the proper place
47 // such that all nodes below the start index are in heap order
48 MaxHeapify(unsorted, i, unsorted.Length - 1);
49 }
50 // after shifting down the root all nodes/elements are in heap order
51 }
52
53 static void MaxHeapify(int[] unsorted, int root, int bottom)
54 {
55 int rootValue = unsorted[root];
56 int left = root * 2 + 1; // start from left child
57
58 // while the root has at least one child
59 while (left <= bottom)
60 {
61 // has more children
62 if (left < bottom)
63 {
64 // if there is a right child and that child is greater
65 if (unsorted[left] < unsorted[left + 1])
66 {
67 left = left + 1;
68 }
69 }
70
71 // compare root and the older children
72 if (rootValue < unsorted[left])
73 {
74 // swap
75 unsorted[root] = unsorted[left];
76 root = left;
77
78 // repeat to continue sifting down the child now
79 left = root * 2 + 1; // continue from left child
80 }
81 else
82 {
83 left = bottom + 1;
84 }
85 }
86
87 unsorted[root] = rootValue;
88 }
89
90 static void HeapSortByMinHeap(int[] unsorted)
91 {
92 BuildMinHeap(unsorted);
93
94 for (int i = unsorted.Length - 1; i >= 1; i--)
95 {
96 int min = unsorted[0];
97 unsorted[0] = unsorted[i];
98 unsorted[i] = min;
99
100 MinHeapify(unsorted, 0, i - 1);
101 }
102
103 // reverse
104 for (int i = 0; i < (unsorted.Length / 2); i++)
105 {
106 int t = unsorted[i];
107 unsorted[i] = unsorted[unsorted.Length - 1 - i];
108 unsorted[unsorted.Length - 1 - i] = t;
109 }
110 }
111
112 static void BuildMinHeap(int[] unsorted)
113 {
114 for (int i = (unsorted.Length / 2) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
115 {
116 MinHeapify(unsorted, i, unsorted.Length - 1);
117 }
118 }
119
120 static void MinHeapify(int[] unsorted, int root, int bottom)
121 {
122 int rootValue = unsorted[root];
123 int left = root * 2 + 1; // start from left child
124
125 // while the root has at least one child
126 while (left <= bottom)
127 {
128 // has more children
129 if (left < bottom)
130 {
131 // if there is a right child and that child is smaller
132 if (unsorted[left] > unsorted[left + 1])
133 {
134 left = left + 1;
135 }
136 }
137
138 // compare root and the older children
139 if (rootValue > unsorted[left])
140 {
141 // swap
142 unsorted[root] = unsorted[left];
143 root = left;
144
145 // repeat to continue sifting down the child now
146 left = root * 2 + 1; // continue from left child
147 }
148 else
149 {
150 left = bottom + 1;
151 }
152 }
153
154 unsorted[root] = rootValue;
155 }
156 }







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号