什么?有个 SQL 执行了 8 秒!
哪里出了问题?臣妾不知道啊,得找 DBA 啊。
DBA 人呢?离职了!!擦!!!
程序员在无处寻求帮助时,就得想办法自救,努力让自己变成 "伪 DBA"。
索引
- 找出哪些表的 Index 需要改进
- 在指定数据库中查找哪些表的 Index 需要改进
- 根据缓存的查询计划判断 SP 是否需要优化
- 发现那些 Index 的写远多于读的表
- 查看 Index 的 Statistics 最后更新时间
- 查看哪些 Index 被修改的最频繁
- 查看 Index 碎片化指数
- 哪个 Index 上的读操作最活跃
- 哪个 Index 上的写操作最活跃
- 查看 Index 所使用的 Buffer 数量
- 按照 IO Latch 等待请求对索引进行排行
找出哪些表的 Index 需要改进
SELECT CONVERT(DECIMAL(18, 2), user_seeks * avg_total_user_cost * (avg_user_impact * 0.01)) AS [index_advantage]
,migs.last_user_seek
,mid.[statement] AS [Database.Schema.Table]
,mid.equality_columns
,mid.inequality_columns
,mid.included_columns
,migs.unique_compiles
,migs.user_seeks
,migs.avg_total_user_cost
,migs.avg_user_impact
FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats AS migs WITH (NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups AS mig WITH (NOLOCK) ON migs.group_handle = mig.index_group_handle
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_details AS mid WITH (NOLOCK) ON mig.index_handle = mid.index_handle
ORDER BY index_advantage DESC
OPTION (RECOMPILE);
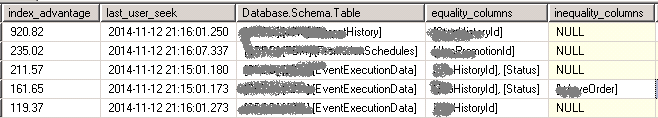
这里查询出的数据,只是说明数据寻址时间有点儿长,不一定就是缺少索引所引起的。
在指定数据库中查找哪些表的 Index 需要改进
SELECT DISTINCT CONVERT(DECIMAL(18, 2), user_seeks * avg_total_user_cost * (avg_user_impact * 0.01)) AS [index_advantage]
,migs.last_user_seek
,mid.[statement] AS [Database.Schema.Table]
,mid.equality_columns
,mid.inequality_columns
,mid.included_columns
,migs.unique_compiles
,migs.user_seeks
,migs.avg_total_user_cost
,migs.avg_user_impact
,OBJECT_NAME(mid.[object_id]) AS [Table Name]
,p.rows AS [Table Rows]
FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats AS migs WITH (NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups AS mig WITH (NOLOCK) ON migs.group_handle = mig.index_group_handle
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_details AS mid WITH (NOLOCK) ON mig.index_handle = mid.index_handle
INNER JOIN sys.partitions AS p WITH (NOLOCK) ON p.[object_id] = mid.[object_id]
WHERE mid.database_id = DB_ID()
ORDER BY index_advantage DESC
OPTION (RECOMPILE);

根据缓存的查询计划判断 SP 是否需要优化
SELECT TOP (25) OBJECT_NAME(objectid) AS [ObjectName]
,query_plan
,cp.objtype
,cp.usecounts
FROM sys.dm_exec_cached_plans AS cp WITH (NOLOCK)
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_query_plan(cp.plan_handle) AS qp
WHERE CAST(query_plan AS NVARCHAR(MAX)) LIKE N'%MissingIndex%'
AND dbid = DB_ID()
ORDER BY cp.usecounts DESC
OPTION (RECOMPILE);
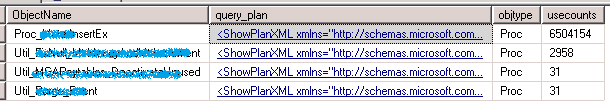
发现那些 Index 的写远多于读的表
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(s.[object_id]) AS [Table Name]
,i.[name] AS [Index Name]
,i.index_id
,i.is_disabled
,i.is_hypothetical
,i.has_filter
,i.fill_factor
,user_updates AS [Total Writes]
,user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups AS [Total Reads]
,user_updates - (user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups) AS [Difference]
FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats AS s WITH (NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK) ON s.[object_id] = i.[object_id]
AND i.index_id = s.index_id
WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(s.[object_id], 'IsUserTable') = 1
AND s.database_id = DB_ID()
AND user_updates > (user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups)
AND i.index_id > 1
ORDER BY [Difference] DESC
,[Total Writes] DESC
,[Total Reads] ASC
OPTION (RECOMPILE);
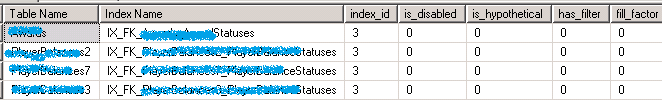
由于对索引的写操作远多于读操作,看起来 Index 的帮助不大,但需要根据业务需求来判断是否能够 Drop 掉该索引。
查看 Index 的 Statistics 最后更新时间
SELECT SCHEMA_NAME(o.[schema_id]) + N'.' + o.[name] AS [Object Name]
,o.type_desc AS [Object Type]
,i.[name] AS [Index Name]
,STATS_DATE(i.[object_id], i.index_id) AS [Statistics Date]
,s.auto_created
,s.no_recompute
,s.user_created
,st.row_count
,st.used_page_count
FROM sys.objects AS o WITH (NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK) ON o.[object_id] = i.[object_id]
INNER JOIN sys.stats AS s WITH (NOLOCK) ON i.[object_id] = s.[object_id]
AND i.index_id = s.stats_id
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_partition_stats AS st WITH (NOLOCK) ON o.[object_id] = st.[object_id]
AND i.[index_id] = st.[index_id]
WHERE o.[type] IN (
'U'
,'V'
)
AND st.row_count > 0
ORDER BY STATS_DATE(i.[object_id], i.index_id) DESC
OPTION (RECOMPILE);
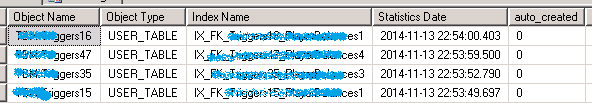
参考资料:
- Statistics
- UPDATE STATISTICS (Transact-SQL)
- sp_updatestats (Transact-SQL)
- Rebuilding Indexes vs. Updating Statistics
- Does a re-index update statistics?
- SQL Server Index and Statistics Maintenance
查看哪些 Index 被修改的最频繁
SQL Server 2008 R2
SELECT TableName = OBJECT_NAME(s.[object_id])
,SchemaName = SCHEMA_NAME(o.[schema_id])
,IndexName = i.[name]
,user_updates
,i.is_primary_key
FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats s
JOIN sys.objects O ON s.[object_id] = O.[object_id]
JOIN sys.indexes i ON s.[object_id] = i.[object_id]
AND s.index_id = i.index_id
WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(s.[object_id], 'IsMsShipped') = 0
AND user_seeks = 0
AND user_scans = 0
AND user_lookups = 0
AND i.NAME IS NOT NULL -- Ignore HEAP indexes.
ORDER BY user_updates DESC
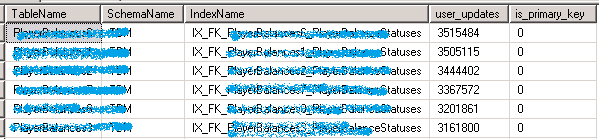
The user_updates counter indicates the level of maintenance on the index caused by insert, update, or delete operations on the underlying table or view.
SQL Server 2012
SELECT o.[name] AS [Object Name]
,o.[object_id]
,o.type_desc
,s.[name] AS [Statistics Name]
,s.stats_id
,s.no_recompute
,s.auto_created
,sp.modification_counter
,sp.rows
,sp.rows_sampled
,sp.last_updated
FROM sys.objects AS o WITH (NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN sys.stats AS s WITH (NOLOCK) ON s.object_id = o.object_id
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_db_stats_properties(s.object_id, s.stats_id) AS sp
WHERE o.type_desc NOT IN (
N'SYSTEM_TABLE'
,N'INTERNAL_TABLE'
)
AND sp.modification_counter > 0
ORDER BY sp.modification_counter DESC
,o.[name]
OPTION (RECOMPILE);
查看 Index 碎片化指数
SELECT DB_NAME(ps.database_id) AS [Database Name]
,OBJECT_NAME(ps.[object_id]) AS [Object Name]
,i.[name] AS [Index Name]
,ps.index_id
,ps.index_type_desc
,ps.avg_fragmentation_in_percent
,ps.fragment_count
,ps.page_count
,i.fill_factor
,i.has_filter
,i.filter_definition
FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats(DB_ID(), NULL, NULL, NULL, N'LIMITED') AS ps
INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK) ON ps.[object_id] = i.[object_id]
AND ps.index_id = i.index_id
WHERE ps.database_id = DB_ID()
AND ps.page_count > 2500
ORDER BY ps.avg_fragmentation_in_percent DESC
OPTION (RECOMPILE);
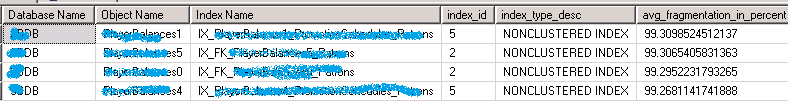
参考资料:
- Stop Worrying About SQL Server Fragmentation
- Importance of index maintenance
- Reorganize and Rebuild Indexes
- Fragmentation and Index Maintenance Tips
- Index Fragmentation–"If it isn’t broken, don’t fix it"
哪个 Index 上的读操作最活跃
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(s.[object_id]) AS [ObjectName]
,i.[name] AS [IndexName]
,i.index_id
,user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups AS [Reads]
,s.user_updates AS [Writes]
,i.type_desc AS [IndexType]
,i.fill_factor AS [FillFactor]
,i.has_filter
,i.filter_definition
,s.last_user_scan
,s.last_user_lookup
,s.last_user_seek
FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats AS s WITH (NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK) ON s.[object_id] = i.[object_id]
WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(s.[object_id], 'IsUserTable') = 1
AND i.index_id = s.index_id
AND s.database_id = DB_ID()
ORDER BY user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups DESC
OPTION (RECOMPILE);

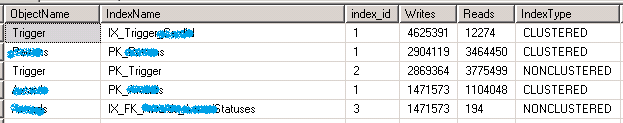
哪个 Index 上的写操作最活跃
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(s.[object_id]) AS [ObjectName]
,i.[name] AS [IndexName]
,i.index_id
,s.user_updates AS [Writes]
,user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups AS [Reads]
,i.type_desc AS [IndexType]
,i.fill_factor AS [FillFactor]
,i.has_filter
,i.filter_definition
,s.last_system_update
,s.last_user_update
FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats AS s WITH (NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK) ON s.[object_id] = i.[object_id]
WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(s.[object_id], 'IsUserTable') = 1
AND i.index_id = s.index_id
AND s.database_id = DB_ID()
ORDER BY s.user_updates DESC
OPTION (RECOMPILE);
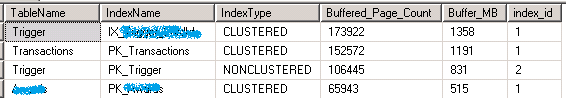
查看 Index 所使用的 Buffer 数量
SELECT TOP 25 obj.[name] AS TableName
,i.[name] AS IndexName
,i.[type_desc] AS IndexType
,count(*) AS Buffered_Page_Count
,count(*) * 8192 / (1024 * 1024) AS Buffer_MB
,obj.index_id
FROM sys.dm_os_buffer_descriptors AS bd
INNER JOIN (
SELECT object_name(object_id) AS NAME
,index_id
,allocation_unit_id
,object_id
FROM sys.allocation_units AS au
INNER JOIN sys.partitions AS p ON au.container_id = p.hobt_id
AND (
au.type = 1
OR au.type = 3
)
UNION ALL
SELECT object_name(object_id) AS NAME
,index_id
,allocation_unit_id
,object_id
FROM sys.allocation_units AS au
INNER JOIN sys.partitions AS p ON au.container_id = p.hobt_id
AND au.type = 2
) AS obj ON bd.allocation_unit_id = obj.allocation_unit_id
LEFT JOIN sys.indexes i ON i.object_id = obj.object_id
AND i.index_id = obj.index_id
WHERE database_id = db_id()
GROUP BY obj.NAME
,obj.index_id
,i.[name]
,i.[type_desc]
ORDER BY Buffered_Page_Count DESC
按照 IO Latch 等待请求对索引进行排行
SELECT OBJECT_SCHEMA_NAME(ios.object_id) + '.' + OBJECT_NAME(ios.object_id) AS table_name
,i.[name] AS index_name
,page_io_latch_wait_count
,page_io_latch_wait_in_ms
,CAST(1. * page_io_latch_wait_in_ms / NULLIF(page_io_latch_wait_count, 0) AS DECIMAL(12, 2)) AS page_io_avg_lock_wait_ms
,page_latch_wait_count
,page_latch_wait_in_ms
,CAST(1. * page_latch_wait_in_ms / NULLIF(page_latch_wait_count, 0) AS DECIMAL(12, 2)) AS page_avg_lock_wait_ms
FROM sys.dm_db_index_operational_stats(DB_ID(), NULL, NULL, NULL) ios
INNER JOIN sys.indexes i ON i.object_id = ios.object_id
AND i.index_id = ios.index_id
WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(ios.object_id, 'IsUserTable') = 1
ORDER BY 3 DESC

《人人都是 DBA》系列文章索引:







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号