集美大学课程实验报告-实验4:树、二叉树与查找
集美大学课程实验报告-实验4:树、二叉树与查找
| 项目名称 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 课程名称 | 数据结构 |
| 班级 | 网安2413 |
| 指导教师 | 郑如滨 |
| 学生姓名 | 许晴 |
| 学号 | 202421336069 |
| 实验项目名称 | 实验4-树、二叉树与查找 |
| 上机实践日期 | |
| 上机实践时间 | 2学时 |
一、目的(本次实验所涉及并要求掌握的知识点)
- 掌握创建二叉树与树及二叉树上的基本操作
- 熟练掌握熟练掌握树的递归结构及在其上的递归算法
- 掌握二叉树的层次遍历
- 掌握BST树上的搜索、创建与删除
- 掌握哈希表的应用
二、实验内容与设计思想
题目1:先序序列创建二叉树
函数相关伪代码
中序遍历函数
void InOrderTraverse(BiTree T) {
if (T) {
InOrderTraverse(T->lchild);
printf("%c ", T->data);
InOrderTraverse(T->rchild);
}
}
函数代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
char val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(char x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
TreeNode* createTree(const string& str, int& index) {
if (str[index] == '#') {
index++;
return NULL;
}
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(str[index]);
index++;
node->left = createTree(str, index);
node->right = createTree(str, index);
return node;
}
void inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root) {
inorderTraversal(root->left);
cout << root->val << " ";
inorderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
int main() {
string str;
while (cin >> str) {
int index = 0;
TreeNode* root = createTree(str, index);
inorderTraversal(root);
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
题目2:先序输出叶结点
函数相关伪代码
- 函数 PreorderPrintLeaves 接收二叉树指针 BT 。
- 若 BT 为空,直接返回。
- 检查 BT 是否为叶节点(即左子树指针 Left 和右子树指针 Right 都为 NULL ):
- 若是叶节点,按格式输出节点数据(先输出空格,再输出节点数据)。
- 递归调用 PreorderPrintLeaves 处理左子树。
- 递归调用 PreorderPrintLeaves 处理右子树。
函数代码
void PreorderPrintLeaves(BinTree BT) {
if (BT == NULL) {
return;
}
if (BT->Left == NULL && BT->Right == NULL) {
printf(" %c", BT->Data);
}
PreorderPrintLeaves(BT->Left);
PreorderPrintLeaves(BT->Right);
}
题目3:求二叉树高度
函数相关伪代码
- 函数 GetHeight 接收二叉树指针 BT 。
- 若 BT 为空,返回0,因为空树高度为0。
- 递归计算左子树高度,记为 leftHeight 。
- 递归计算右子树高度,记为 rightHeight 。
- 返回 max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1 ,其中加1是因为要算上当前节点所在层。
函数代码
int GetHeight(BinTree BT) {
if (BT == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = GetHeight(BT->Left);
int rightHeight = GetHeight(BT->Right);
return (leftHeight > rightHeight? leftHeight : rightHeight) + 1;
}
题目4:二叉树层次遍历(广度优先)
函数相关伪代码
- 定义一个结构体表示二叉树节点,包含数据成员和指向左右子节点的指针成员。
- 遍历输入字符串,对于每个非空字符,创建一个二叉树节点对象。
- 根据顺序存储结构中节点的位置关系(如完全二叉树的节点索引对应关系),设置节点的左右子节点指针。
- 创建一个队列,将根节点入队。
- 当队列不为空时:
- 取出队首节点并输出其数据。
- 若队首节点的左子节点存在,将其入队。
- 若队首节点的右子节点存在,将其入队。
函数代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct tree {
char a;
tree* lchild;
tree* rchild;
};
tree* Createtree(string k, int i)
{
tree* node = new tree;
node->a = k[i];
node->lchild = NULL;
node->rchild = NULL;
return node;
}
tree* Buildtree(string k, int i)
{
if (k.empty()||k.length() <=i || k[i] == '#') {
return NULL;
}
tree* root = Createtree(k,i);
root->lchild = Buildtree(k, 2 * i);
root->rchild = Buildtree(k, 2 * i + 1);
return root;
}
void Showtree(tree* node)
{
if (node == NULL) {
cout << "NULL";
return;
}
queue<tree*> q;
q.push(node);
int f = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
tree* current = q.front();
q.pop();
if (f != 1) {
cout << " ";
}
f = 0;
cout << current->a;
if (current->lchild != NULL) {
q.push(current->lchild);
}
if (current->rchild != NULL) {
q.push(current->rchild);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
string k;
tree* root = NULL;
getline(cin, k);
root = Buildtree(k, 1);
Showtree(root);
return 0;
}
题目5: 创建二叉排序树并遍历
函数相关伪代码
插入节点函数
- 函数接收二叉排序树的根节点指针和要插入的数据。
- 如果根节点为空,创建一个新节点并返回。
- 若要插入的数据小于根节点数据,递归插入到左子树;若大于根节点数据,递归插入到右子树。
中序遍历函数
- 函数接收二叉排序树的根节点指针。
- 如果根节点不为空:
- 递归遍历左子树。
- 输出根节点数据。
- 递归遍历右子树。
主函数
- 初始化二叉排序树为空(根节点为 nullptr )。
- 依次读取输入数据,调用插入节点函数构建二叉排序树。
- 调用中序遍历函数对构建好的二叉排序树进行中序遍历并输出结果。
函数代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
TreeNode* insert(TreeNode* root, int data) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return new TreeNode(data);
}
if (data < root->val) {
root->left = insert(root->left, data);
}
else {
root->right = insert(root->right, data);
}
return root;
}
void inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root) {
inorderTraversal(root->left);
cout << root->val << " ";
inorderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = nullptr;
int num;
while (cin >> num) {
if (num == -1) { // 这里假设输入#时用 -1 表示
break;
}
root = insert(root, num);
}
inorderTraversal(root);
return 0;
}
题目6:航空公司VIP客户查询
函数相关伪代码
定义哈希表结构
- 定义一个哈希表,用于存储身份证号码和对应的里程积分。可以使用 unordered_map ,键为身份证号码(字符串类型),值为里程积分(整数类型)。
读取输入数据并更新哈希表
- 读取会员数量 N 和最低里程 K 。
- 循环 N 次,每次读取一条飞行记录(身份证号码和飞行里程):
- 如果飞行里程小于 K ,将里程更新为 K 。
- 在哈希表中查找该身份证号码,如果存在则累加里程积分,否则在哈希表中插入该身份证号码并设置里程积分为当前里程。
处理查询请求
- 读取查询数量 M 。
- 循环 M 次,每次读取一个查询的身份证号码:
- 在哈希表中查找该身份证号码,如果找到则输出对应的里程积分,否则输出 No Info 。
函数代码
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int N, K;
cin >> N >> K;
unordered_map<string, int> mileageMap;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
string id;
int miles;
cin >> id >> miles;
if (miles < K) {
miles = K;
}
if (mileageMap.find(id) != mileageMap.end()) {
mileageMap[id] += miles;
} else {
mileageMap[id] = miles;
}
}
int M;
cin >> M;
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
string queryId;
cin >> queryId;
if (mileageMap.find(queryId) != mileageMap.end()) {
cout << mileageMap[queryId] << endl;
} else {
cout << "No Info" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
三、实验使用环境(本次实验所使用的平台和相关软件)
- 操作系统:Windows 11 professional
- 编程语言:C++
- 开发工具:[Visual Studio 2022]
四、实验步骤和调试过程(实验步骤、测试数据设计、测试结果分析)
题目1:先序序列创建二叉树
本机运行截图
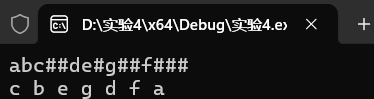
PTA提交截图
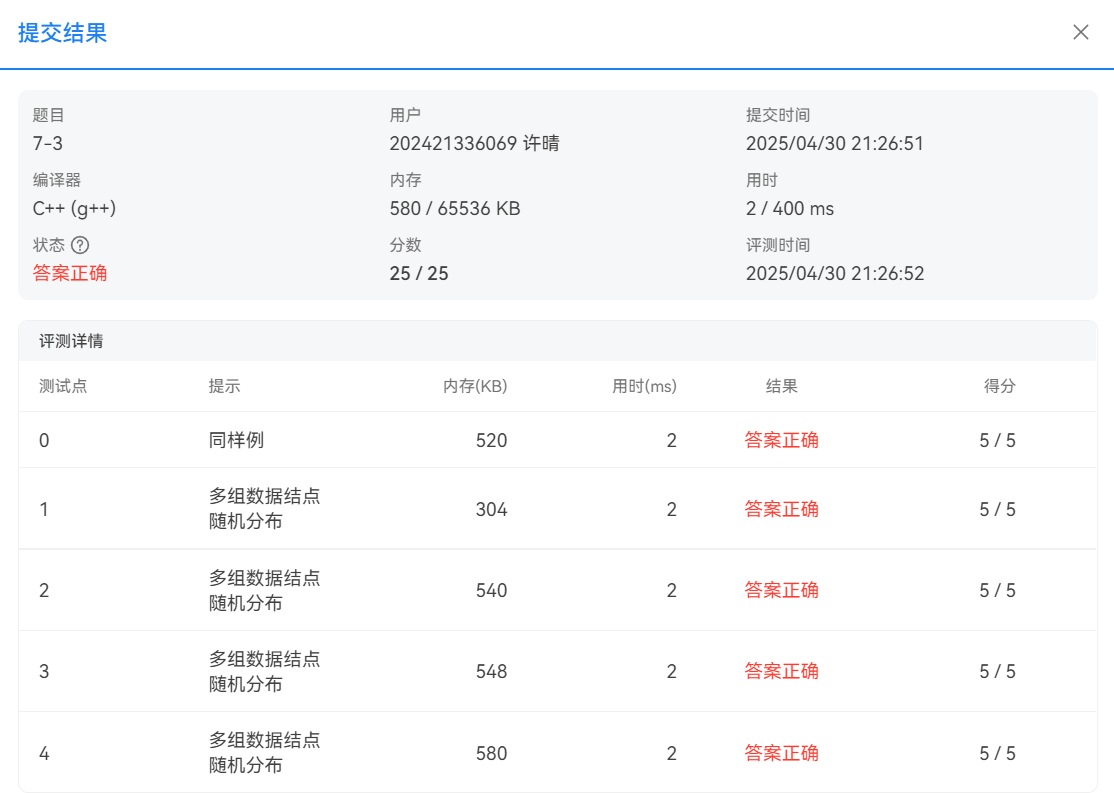
题目2:先序输出叶结点
PTA提交截图
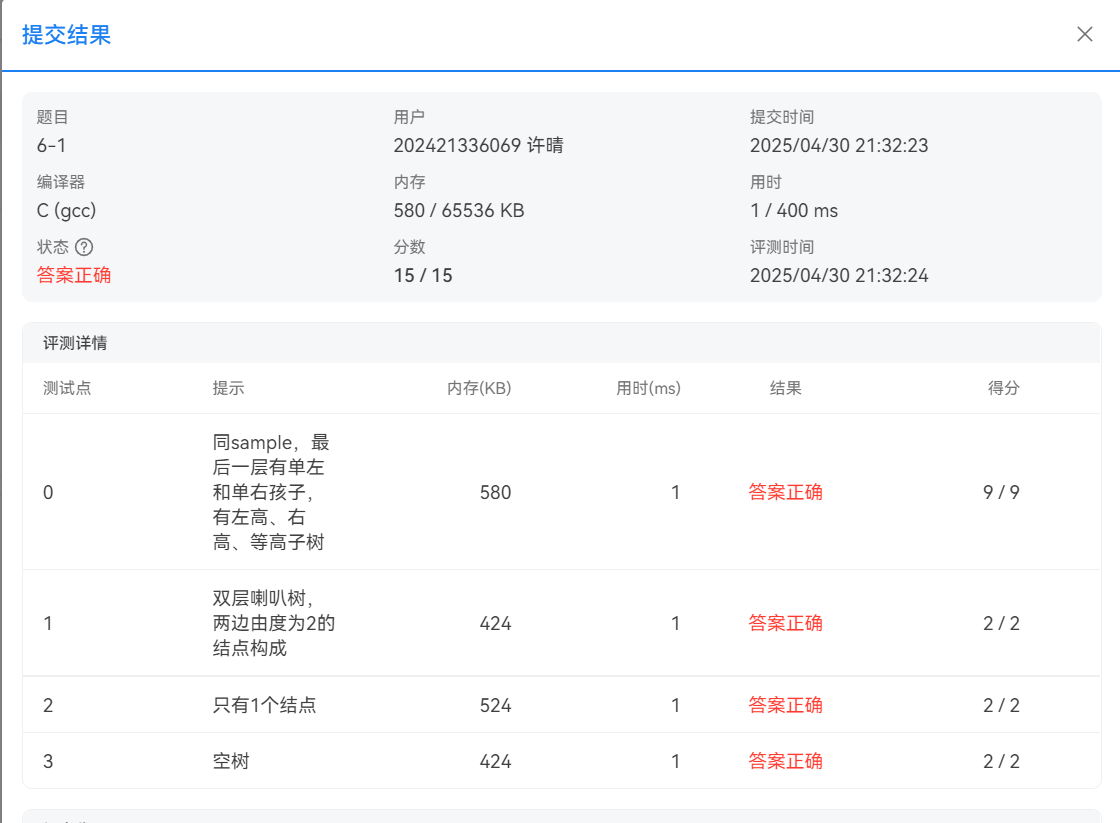
题目3:求二叉树高度
PTA提交截图
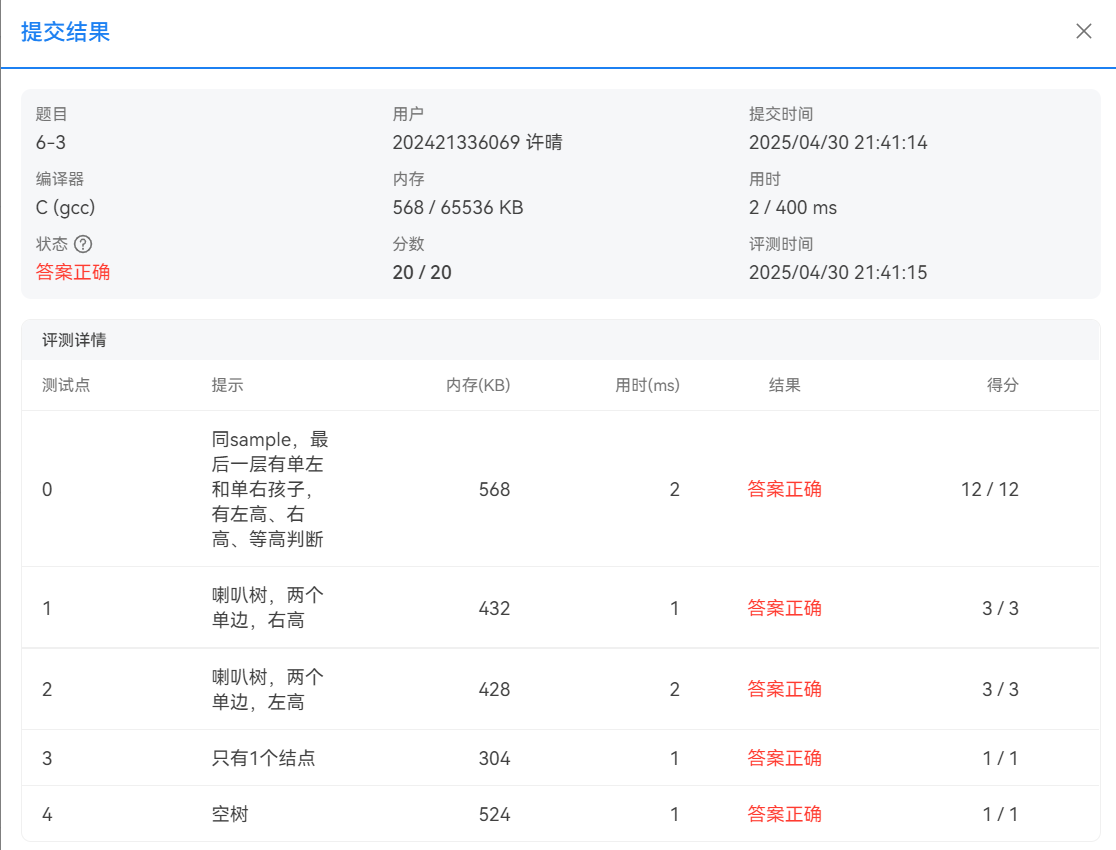
题目4:二叉树层次遍历(广度优先)
本机运行截图
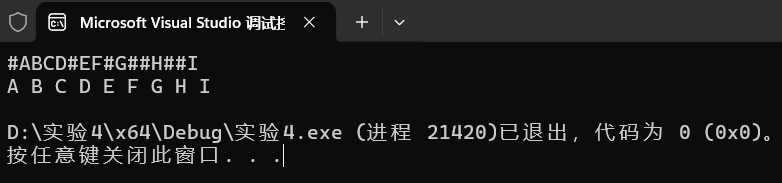
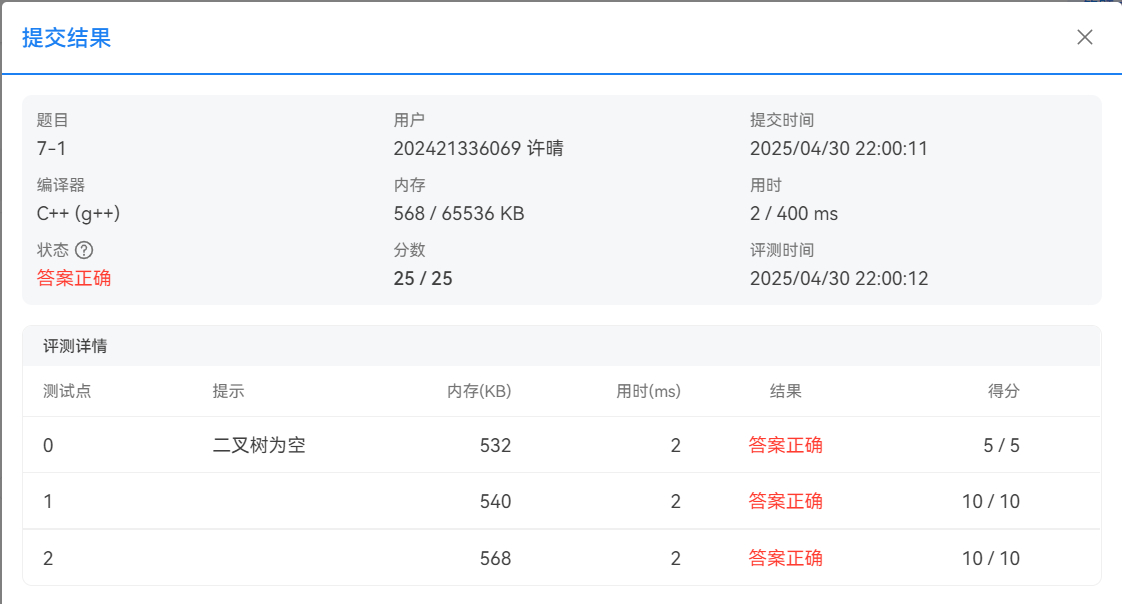
PTA提交截图
题目5: 创建二叉排序树并遍历
本机运行截图
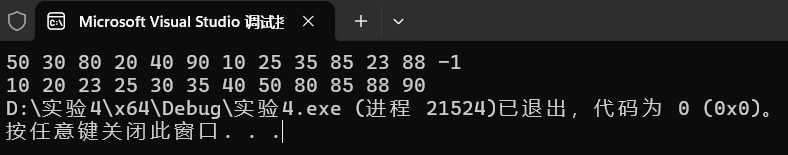
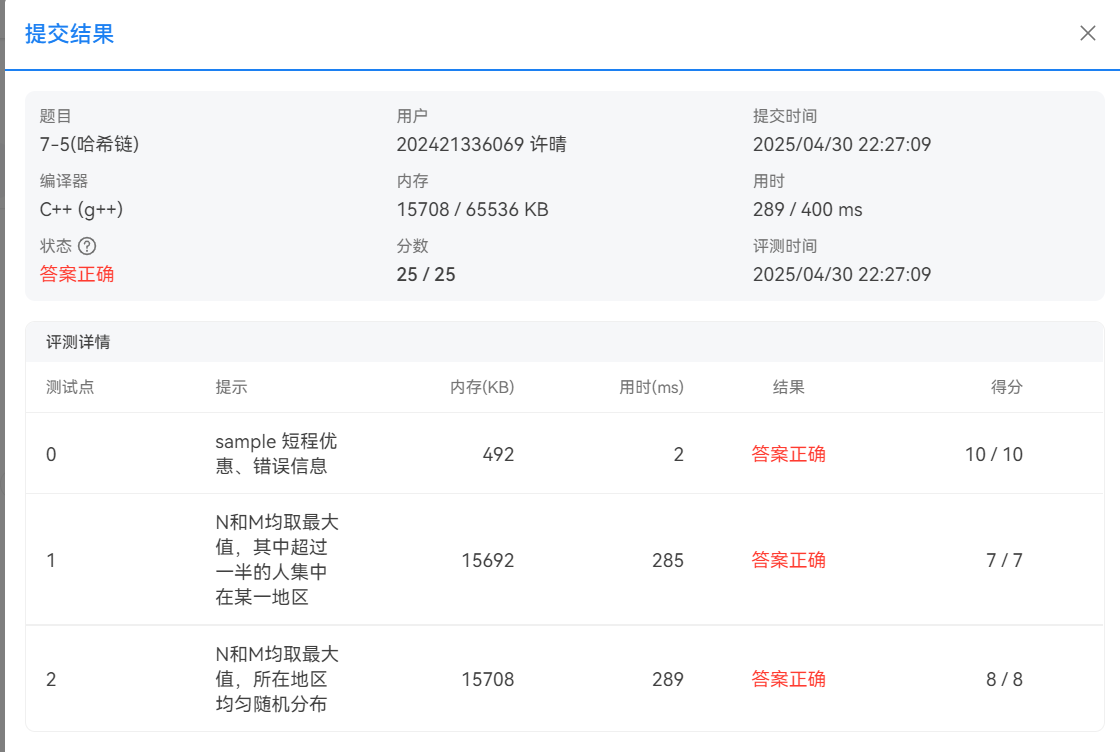
题目6:航空公司VIP客户查询
本机运行截图
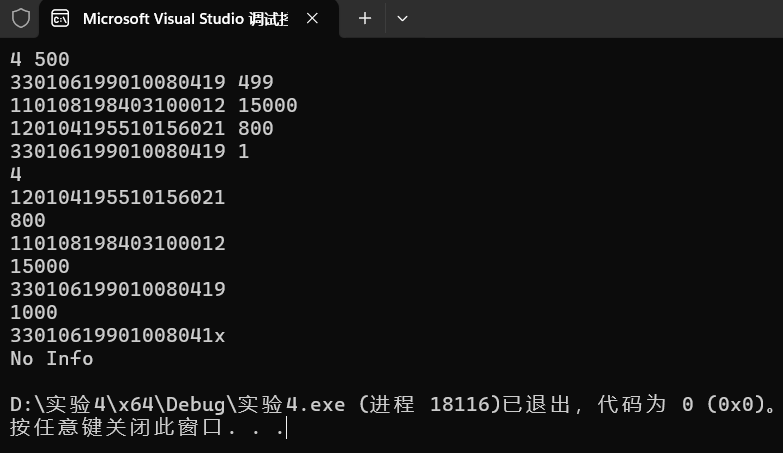
PTA提交截图
五、实验小结(实验中遇到的问题及解决过程、实验体会和收获)
遇到的问题及解决方法:
- 问题:程序崩溃找不到原因,
- 解决方法:使用打断点进行调试的方法。
- 问题:使用 scanf 函数时,编译器提示其不安全(C4996) ,因为 scanf 不检查输入缓冲区溢出,存在安全隐患。
- 解决方法:用 scanf_s 替代 scanf ,并指定输入缓冲区大小,如 scanf_s(" %c", &ch, 1)。
实验体会和收获:
- 学会了如何搭建C++开发环境。
- 掌握了基本的代码调试方法。
- 掌握了Visual Studio调试功能的基本使用
- 了解到像 scanf 这类函数存在缓冲区溢出风险,认识到 scanf_s 等安全版本函数的用法,增强了代码安全意识。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号