OpenCV--任意多边形最大内接圆python实现
任意多边形内接圆
算法思路:
推荐
在多边形形成的二维平面区域中,高度为H,宽度为WW。将空间进行等分, 高度为n份, 宽度为m份;
在空间形成网格,将多边形区域外的点剔除掉。在剩下的点中对每个点,找到边最近的距离。在这样
很多点中找出最大距离点。以种子点为中心的区域再剖分,循环迭代。
"""
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
@desc: 获取最大内接圆
"""
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from shapely.geometry import Polygon, MultiPolygon, Point
from math import sqrt
N_CELLS = 20 # 高等分
M_CELLS = 20 # 宽等分
def geometry_find_pia(polygon_coord, bounds):
"""
找到多边形内接圆
:param polygon_coord:
:param bounds:
:return:
"""
increment_x = (bounds[1] - bounds[0]) / N_CELLS
increment_y = (bounds[3] - bounds[2]) / M_CELLS
# 获取圆心
max_distance = 0
circle_center_x = 0
circle_center_y = 0
for i in range(N_CELLS):
tmp_x = bounds[0] + i * increment_x
for j in range(M_CELLS):
tmp_y = bounds[2] + j * increment_y
distance = cv.pointPolygonTest(np.array(polygon_coord), (tmp_x, tmp_y), True) # 里面为正,外面为负,边界为0
if distance > max_distance:
max_distance = distance
circle_center_x = tmp_x
circle_center_y = tmp_y
return [circle_center_x, circle_center_y], max_distance
def find_inscribed_circle_center(polygon_coord):
"""
获取任意多边形,内接圆
:param polygon_coord: 多边形坐标
:return:
"""
polygon = Polygon(polygon_coord)
if polygon.area <= 0:
return None
# 默认图片所在的区域, 像素左下 右上
bounds = polygon.bounds
bounds = [bounds[0],bounds[2],bounds[1],bounds[3]] # 表示x的范围,y的范围[xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax]
img = np.zeros((512, 512, 3), np.uint8)
cv.polylines(img, [np.array(polygon_coord)], True, (0, 255, 255), 5)
# 调整图片区域
count = 1
while True:
count += 1
circle_cent, radius = geometry_find_pia(polygon_coord, bounds) # 初略得到内接圆的圆心和半径,不精准
circle_center_x, circle_center_y = circle_cent
# 更新边界,调整边界值,来对圆心和半径,进行调整
flt_tmp = (bounds[1] - bounds[0]) / (sqrt(2) * 2)
bounds[0] = circle_center_x - flt_tmp
bounds[1] = circle_center_x + flt_tmp
flt_tmp = (bounds[3] - bounds[2]) / (sqrt(2) * 2)
bounds[2] = circle_center_y - flt_tmp
bounds[3] = circle_center_y + flt_tmp
if (bounds[1] - bounds[0]) < 0.001 or (bounds[3] - bounds[2]) < 0.001:
print(f'一共循环{count}次')
break
cv.circle(img, (int(circle_center_x), int(circle_center_y)), int(radius), (255, 255, 0),2)
cv.imshow('image', img)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
return [circle_center_x, circle_center_y, radius]
if __name__ == '__main__':
rec_coord = [[100,100],[300,80],[150,150],[100,300],[100,100]]
rec = Polygon(rec_coord)
cir_center = find_inscribed_circle_center(rec_coord)
print(cir_center)
结果:
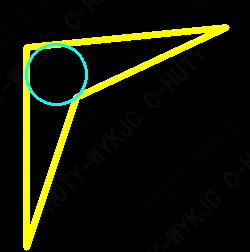
参考博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/u011533238/article/details/88844092
方法二:
使用图像
"""
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
@desc: 获取不规则图形的最大内接圆 此方法依赖图片比较耗时
"""
import cv2
import numpy as np
mask_path = r"D:\workplace\data\opencv\circle_test.png"
mask = cv2.imread(mask_path)
mask_gray = cv2.cvtColor(mask, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 三通道BGR转为灰度图
# 识别轮廓
if '3.4' in cv2.__version__:
_, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(mask_gray, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
else:
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(mask_gray, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 计算到轮廓的距离
raw_dist = np.empty(mask_gray.shape, dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(mask_gray.shape[0]):
for j in range(mask_gray.shape[1]):
raw_dist[i, j] = cv2.pointPolygonTest(contours[0], (j, i), True)
# 获取最大值,内接圆半径, 中心坐标
min_val, max_val, _, max_dist_pt = cv2.minMaxLoc(raw_dist)
min_val = abs(min_val)
max_val = abs(max_val)
# 画出最大内接圆
result = cv2.cvtColor(mask_gray, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
radius = np.int(max_val)
center_of_circle = max_dist_pt
cv2.circle(result, max_dist_pt, radius, (255, 0, 255), 6, 1, 0)
cv2.imshow('Maximum inscribed circle', result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
此种方法比较耗时,不太建议使用。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号