反射机制
反射是框架的框架的灵魂。
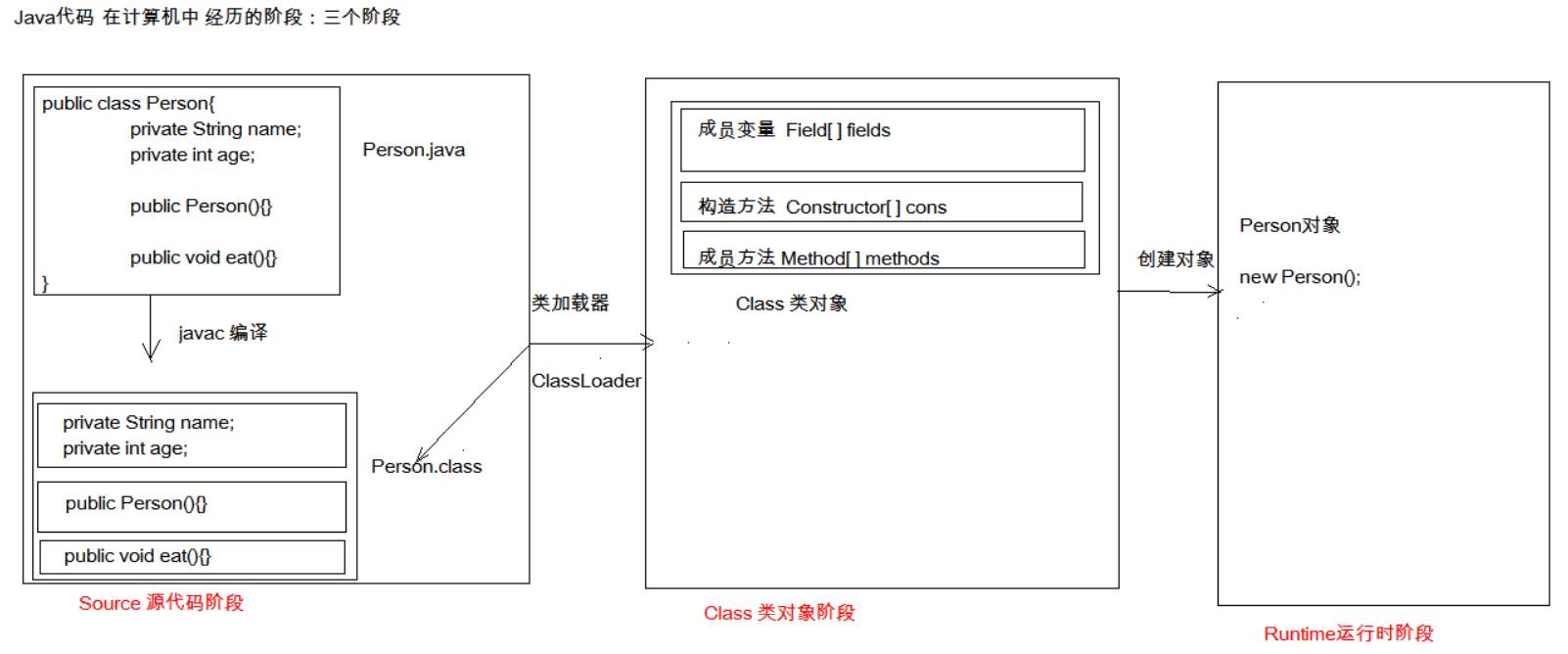
反射:
将类的各个组成部分封装成其他对象(Field、Constructor、Method),即反射机制。
优点:
1、可以在程序运行过程操作这些对象。
2、解耦。提高程序的可扩展性。
java反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能知道该类的所有的属性和方法。并可以实现调用。
Class对象的功能概述
在Class类中关联了 Field、Constructor、Method 类。
以Field 属性对象为例:
Field(Class<?> declaringClass, String name, Class<?> type, int modifiers, //访问修饰符 int slot, String signature, byte[] annotations) //注解
获取功能
1、获取成员变量们
Field[] getFields() :获取所有public修饰的成员变量
Field getField(String name) 获取指定名称的 public修饰的成员变量
Field[] getDeclaredFields() 获取所有的成员变量,不考虑修饰符
Field getDeclaredField(String name)
2、获取构造方法们
Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() Constructor<T> getConstructor(类<?>... parameterTypes) --->这也是为什么要写无参构造方法。 Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(类<?>... parameterTypes) Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors()
3、获取成员方法们
Method[] getMethods() Method getMethod(String name, 类<?>... parameterTypes) Method[] getDeclaredMethods() Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, 类<?>... parameterTypes)
4、获取全类名
String getName()
总结:
通过class字节码对象,获取个各类的组成部分的对象形式(属性,构造方法,成员方法)。
使用method.getParameterTypes();可以获取该方法的参数 ---> 返回的时String.class,int.class...
反射的常见场景:框架
在不改变代码的前提下,帮助我们创建任意的类,并执行其中的方法。
public class TestRef { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException { Properties pro = new Properties(); ClassLoader classLoader = TestRef.class.getClassLoader(); InputStream in = classLoader.getResourceAsStream("pro.properties"); pro.load(in); String className = pro.getProperty("classname"); String methodname = pro.getProperty("methodname"); Class<?> cls = Class.forName(className); Method method = cls.getMethod(methodname); Object o = cls.newInstance(); method.invoke(o); } }
pro.properties 文件需要编译后是放在 classes 文件夹中。
反射机制存在的缺点
单例模式 的破解
可以通过暴力反射进行破解。-->可以预防



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号