02-Spring、注解IOC配置、整合Junit
一、使用spring的IOC的实现账户的CRUD

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 配置Service --> <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"> <!-- 注入dao --> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property> </bean> <!--配置Dao对象--> <bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"> <!-- 注入QueryRunner --> <property name="runner" ref="runner"></property> </bean> <!--配置QueryRunner--> <bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype"> <!--注入数据源--> <constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- 配置数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <!--连接数据库的必备信息--> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property> <property name="user" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="1234"></property> </bean> </beans>
二、基于注解的IOC配置
2.1、明确
注解配置和 xml 配置要实现的功能都是一样 的,都是要降低程序间的耦合。只是配置的形式不一样。
2.2、环境搭建
2.2.1、引入依赖
2.2.2、使用 @Component 注解配置管理的资源

//几种写法 @Service //1 @Service("accountService ") //只有一个属性,且属性为value时,可以省略 public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService { private IAccountDao accountDao ; public AccountServiceImpl(){ System.out.println("对象创建了"); } public void saveAccount(){ accountDao.saveAccount(); } }
2.2.3、创建spring的xml配置文件并开启对注解的支持
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--告知spring在创建容器时要扫描的包,配置所需要的标签不是在beans的约束中,而是一个名称为 context名称空间和约束中--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan> </beans>
2.3、常用注解
2.3.1、用于创建对象
相当于配置文件中的:<bean id=" " class=" ">
2.3.1.1、@Component
把资源让 spring 来管理。相当于在 xml 中配置一个 bean。
属性:
value:指定 bean 的 id。如果不指定 value 属性,默认 bean 的 id 是当前类的类名。首字母小写。
2.3.1.2、@Controllere @Service @Repository
以上三个注解都是针对一个的衍生注解,作用及属性都是一模一样的。
提供了更加明确的语义化。
@Controller:一般用于表现层的注解。
@Service:一般用于业务层的注解。
@Repository:一般用于持久层的注解。
如果注解中有且只有一个属性要赋值时,且名称是 value,value在赋值是可以不写。
2.3.2、用于注入数据
相当于:
<property name="" ref="">
<property name="" value="">
2.3.2.1、@Autowired
作用:
自动按照类型注入。只要容器中有唯一的一个bean对象类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,就可以注入成功。
如果 ioc 容器中没有任何 bean 的类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,则报错。
如果 ioc 容器中有多个类型匹配时,-->按照属性名进行查找,没有,则报错:
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: Unexpected exception parsing XML document from class path resource [bean.xml]; nested exception is org.springframework.context.annotation.ConflictingBeanDefinitionException: Annotation-specified bean name 'accountDao' for bean class [com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl2] conflicts with existing, non-compatible bean definition of same name and class [com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl]
Caused by: org.springframework.context.annotation.ConflictingBeanDefinitionException: Annotation-specified bean name 'accountDao' for bean class [com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl2] conflicts with existing, non-compatible(兼容的) bean definition of same name and class [com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl]
可以是变量上,也可以是方法上。 --->可以写在成员变量或者 set/get 方法上。
细节:
在使用注解注入时,set方法就不是必须的了。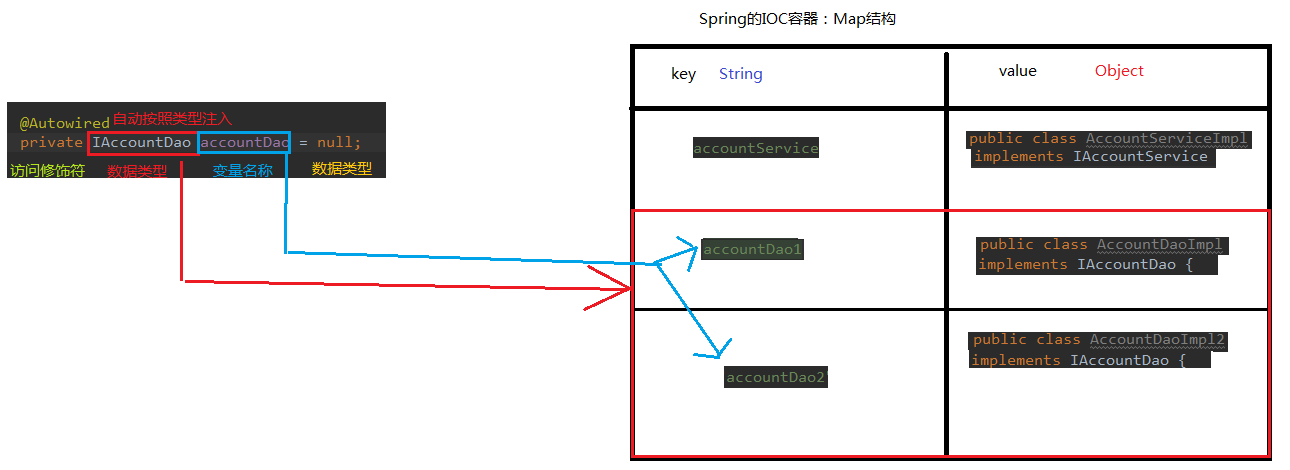
2.3.2.2:@Qualifier
在按照类中注入的基础之上再按照名称注入。它在给类成员注入时不能单独使用(需要配合@Autowired使用)。但是在给方法参数注入时可以。
属性:
value:用于指定注入bean的id。
在容器中寻找对应需要注入的对象的规则:
方法中需要注入的参数,形参名与该数据类型的bean的名称都不相同,先在所有存储在容器中的bean中找到与其数据类型相同的bean。
如果形参名与其中的一个相同数据类型的bean名称相同,则使用形参名作为id,在容器中进行查找,进行注入。
如果在形参中存在 @Qualifier 注解,则是用注解后的名称作为bean的id进行注入。如:
public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(@Qualifier("ds02") DataSource dataSource){ return new QueryRunner(dataSource); }
Qualifier源码:
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Inherited @Documented public @interface Qualifier { String value() default ""; }
ElementType.PARAMETER --->允许写在参数列表中
2.3.2.3、@Resource --->javax.annotaion.Resource 存在两个属性name、type
直接按照bean的id注入。它可以独立使用。
属性:
name:用于指定 bean 的 id 。
以上三个注入都只能注入其他bean类型的数据,而基本类型和String类型无法使用上述注解实现。
另外,集合类型的注入只能通过XML来实现。
2.3.2.4、@Value
用于注入基本类型和String类型的数据。
属性:
value:用于指定数据的值。它可以使用spring中SpEL(也就是spring的el表达式)。
SpEL的写法:${表达式}
2.3.3、用于改变作用范围的
相当于:
<bean id="" class="" scope="">
2.3.3.1、@Scope
作用:
指定 bean 的作用范围。
属性:
value:指定范围的值。
取值:
singleton prototype request session globalsession
2.3.4、和声明周期相关的
相当于:
<bean id="" class="" init-method="" destroy-method="" />
2.3.4.1、@PostConstruct
用于指定初始化方法。
2.3.4.2、@PreDestroy
用于指定销毁方法。
2.3.5、关于Spring注解和XML的选择问题
注解的优势:
配置简单,维护方便(找到类,就相当于找到了对应的配置)。
XML 的优势:
修改时,不用改源码。不涉及重新编译和部署。
Spring 管理 Bean方式的比较: 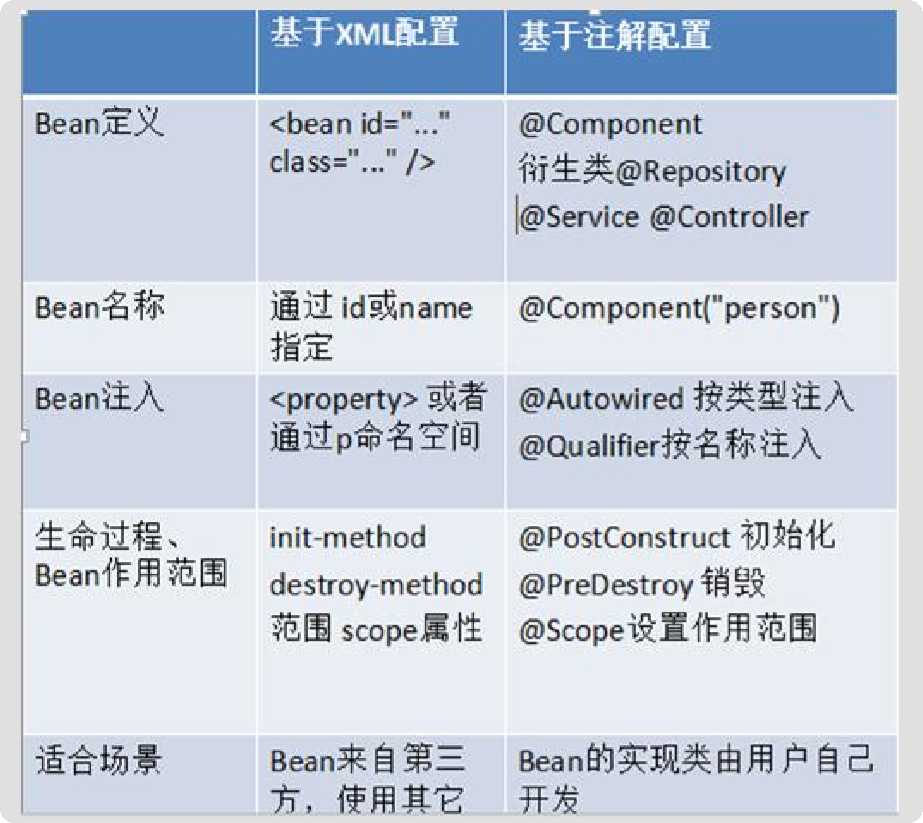
2.4、spring管理对象细节
基于注解的 spring IoC 配置中,bean 对象的特点和基于 XML 配置是一样的。
2.5、spring纯注解配置

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property> </bean> <bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"> <property name="runner" ref="runner"></property> </bean>--> <!--告知spring在创建容器时要扫描的包--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima" ></context:component-scan> <!--配置QueryRunner--> <bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype"> <!--注入数据源--> <constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- 配置数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <!--连接数据库的必备信息--> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy_spring"></property> <property name="user" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="root"></property> </bean> </beans> =========================== 在实现类中使用@Service和@Reposity注解 和@Autowired 进行注解配置。
上述代码中,依然离不开 spring 的 xml 配置文件,那么能不能不写这个 bean.xml,所有配置都用注解来实现呢?
2.5.1、待改造的问题
1、<!-- 告知spring框架在读取配置文件,创建容器时,扫描注解,依据注解创建对象,并存入容器中 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan>
2、另外,数据源和jdbc的匹配值也需要靠注解来实现。
2.5.2、注解说明
2.5.2.1、@Configuration
用于指定当前类是一个 spring 配置类,当创建容器时会从该类上加载注解。
获取容器时需要使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (有@Configuration 注解的类.class)。
属性:
value:用于指定配置类的字节码 。
细节:
当配置类作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建的参数时,该注解可以不写。
-->即:ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
在类SpringConfiguration可以不写Configuration注解。
不能扫描到的情况:
将jdbc相关的配置移动到JdbcConfig.java中。
解决方式:
1)@ComponentScan({"com.itheima","config"})添加扫描的路径+添加@Configuration标志是配置类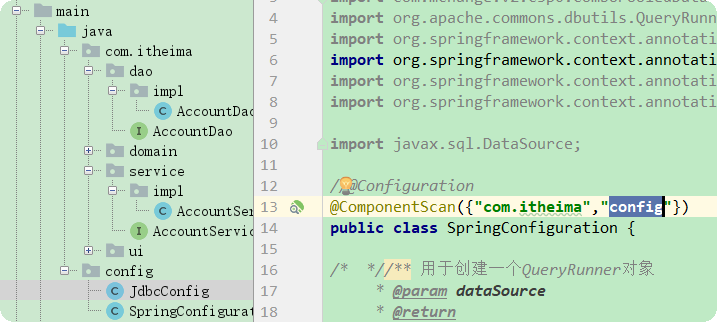

2)直接使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class, JdbcConfig.class);
但是没有体现出层级关系。
@Import
用于导入其他的配置类。
属性:
value:用于指定其他配置类的字节码。
当我们使用Import的注解之后,有Import注解的类就父配置类,而导入的都是子配置类。
3)使用import标签
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
其中:@ComponentScan({"com.itheima"})不能完全省略。因为包下存在其他的注解配置信息。
2.5.2.2、@ComponentScan
用于通过注解指定 spring 在创建容器时要扫描的包。
属性:
value:它和 basePackages 的作用是一样的,都是用于指定创建容器时要扫描的包。
使用此注解就等同于在xml中配置了:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.payn"></context:component-scan>
2.5.2.3、@Bean
用于把当前方法的返回值作为 bean 对象存入 spring 的 ioc 容器中。
属性:
name:用于指定 bean 的 id 。当不写时,默认值是当前方法的名称。
细节:
当我们使用注解配置方法时,如果方法有参数,spring框架会去容器中查找有没有可用的bean对象。
查找的方式和 @Autowired 注解的作用是一样的。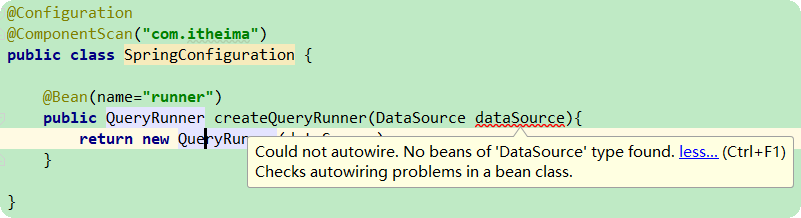

此时bean.xml中的内容可以去除。实现纯注解的方式实现。
2.5.2.4、@PropertySource
用于指定 properties 文件的位置。
属性:
value:指定文件的名称和路径。
关键字:classpath,表示类路径下。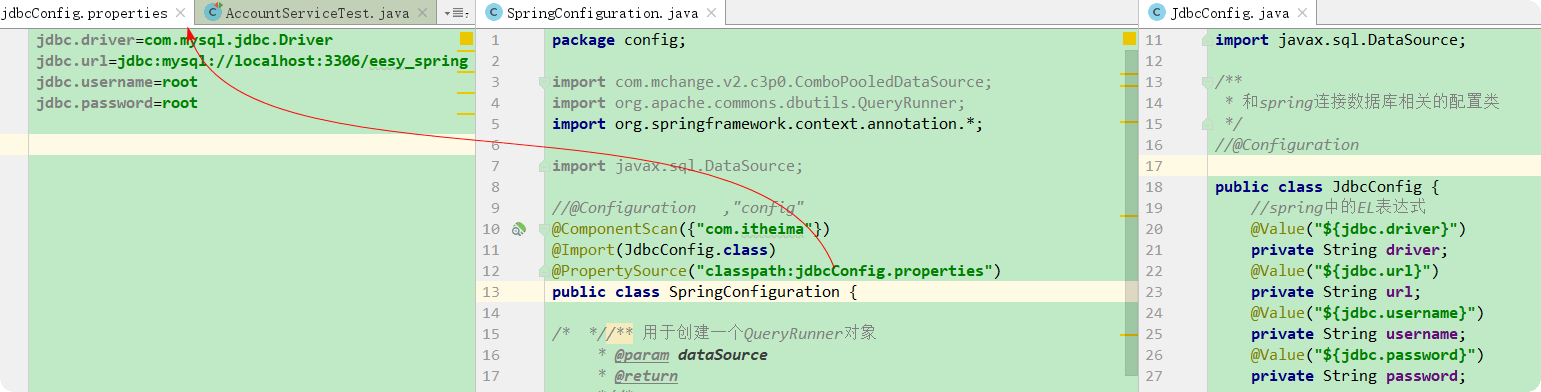
classpath: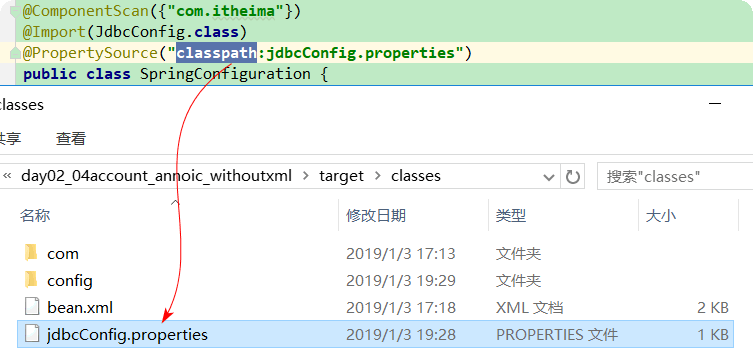
三、Spring整合Junit
junit单元测试中,没有main方法
junit集成了一个main方法。
该方法就会判断当前测试类中哪些方法。有 @Test注解 -->有的话,junit使用method.invoke来执行。
junit就让有 @Test 注解的方法执行。
junit不会管我们是否采用spring框架
在执行测试方法时,junit不知道我们是不是使用了spring框架。
所以也就不会为我们 读取配置文件/配置类 创建spring核心容器。
当测试方法执行时,没有IoC容器,就算写了Autowired注解,也无法实现注入。
3.1、测试类中的问题和解决思路
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); AccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
上述两行代码的作用是获取容器。
3.1.2、解决思路
junit 给我们暴露 了一个注解,可以让我们替换掉它的运行器。
3.2、配置步骤
3.2.2、使用 @RunWith 注解替换原有运行器,替换成spring提供的
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
3.2.3、使用 @ContextConfiguration 指定spring配置文件的位置
locations:指定xml文件的位置,加上classpath关键字,表示在类路径下
classes:指定注解类所在的位置
如:
@ContextConfiguration(locations= {"classpath:bean.xml"})
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfiguration.class)
3.2.4、使用 @AutoWired 给测试类中的变量注入数据

@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfiguration.class) public class AccountServiceTest { /* private ApplicationContext ac; private AccountService accountService; @Before public void init(){ ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class); accountService = ac.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class); }*/ /* @Autowired private AccountService accountService;*/ @Autowired private AccountService accountService; @Test public void testFindAll(){ //1.获取容器 // ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); /* ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class); //2.得到业务层对象 AccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);*/ //3.执行方法 List<Account> accounts = accountService.findAllAccount(); for(Account account:accounts){ System.out.println(account); } } @Test public void testFindById(){ //1.获取容器 ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class); //2.得到业务层对象 AccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class); Account account = accountService.findAccountById(3); System.out.println(account); } @Test public void testSave(){ Account account = new Account(); account.setName("test anno"); account.setMoney(12345F); ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class); AccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class); accountService.saveAccount(account); } }
Q:为什么不把测试类配到XML中
第一:当我们在 xml 中配置了一个 bean,spring 加载配置文件创建容器时,就会创建对象。
第二:测试类只是我们在测试功能时使用,而在项目中它并不参与程序逻辑,也不会解决需求上的问题,所以创建完了,并没有使用。那么存在容器中就会造成资源的浪费。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号