第17章(中)--集合
1.ArrayList底层结构和源码分析
ArrayList的全面说明
1) Resizable-array implementation of the List interface [ArrayList实现了List的接口,底层是一个数组,并实现可变的功能.]
ArrayList 属性 : transient
Object[] elementData;
2)
Implements
all optional list operations [ArrayList实现了List所有的操作。
3) permits all elements, including null [ArrayList 可以添加任意的元素,包括null]
4) this class provides methods to manipulate the size of the array that is used internally to store the list[ArrayList的数据是保存到array ]
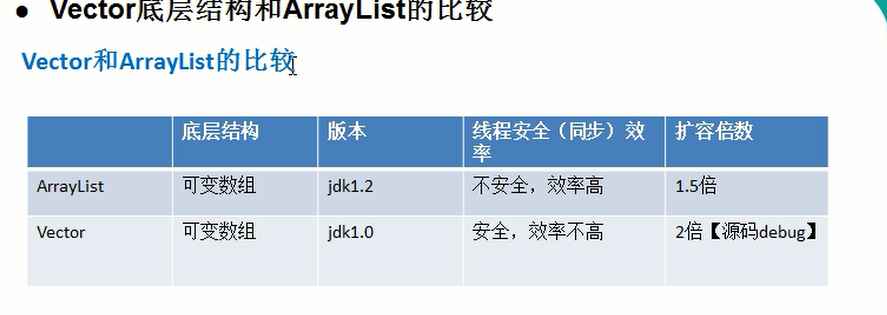
5) This class is roughly equivalent to Vector, except that it is unsynchronized [ArrayList 和Vector基本相同,除了Vector是线程同步的,ArrayList不是线程同步.]

2. Vector底层结构和ArrayList的比较
Vector的基本介绍
1) Vector类的定义说明
2) The Vector class implements a growable array of objects [Vector底层也是一个可变对象数组]
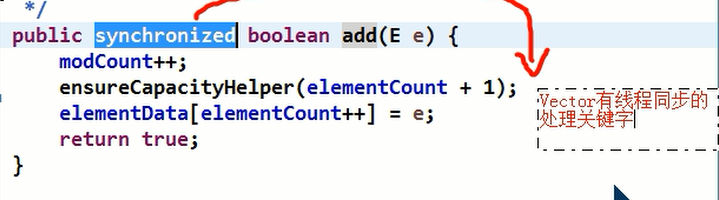
3) Vector 是线程同步的,即线程安全, Vector类的操作方法带有synchronized
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return elementData(index);
}
4) 在开发中,主要使用ArrayList ,只有在确实需要线程同步安全时,才考虑使用Vector(坦克大战)
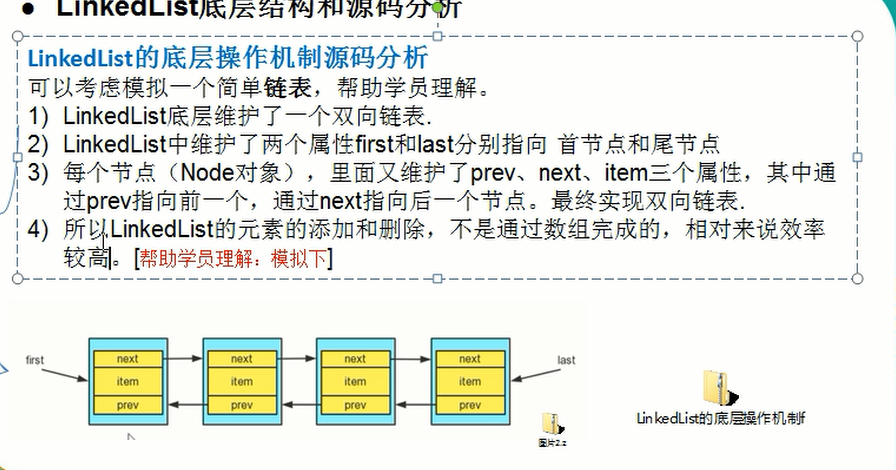
3.LinkedList

4. ArrayList和LinkedList的比较【记住】

如何选择ArrayList和LinkedList:
1) 如果我们改查的操作多,选择ArrayList
2) 如果我们增删的操作多,选择LinkedList
3) 一般来说,在程序中,80%-90%都是查询,因此大部分情况下会选择ArrayList
4) 在一个项目中,根据业务灵活选择,也可能这样,一个模块使用的是ArrayList,另外一个模块是LinkedList.

5.set接口
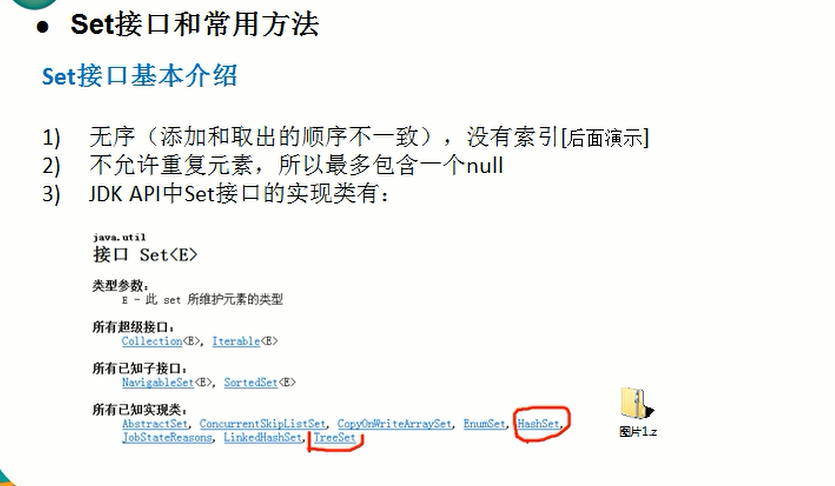

6. Set接口实现类-HashSet


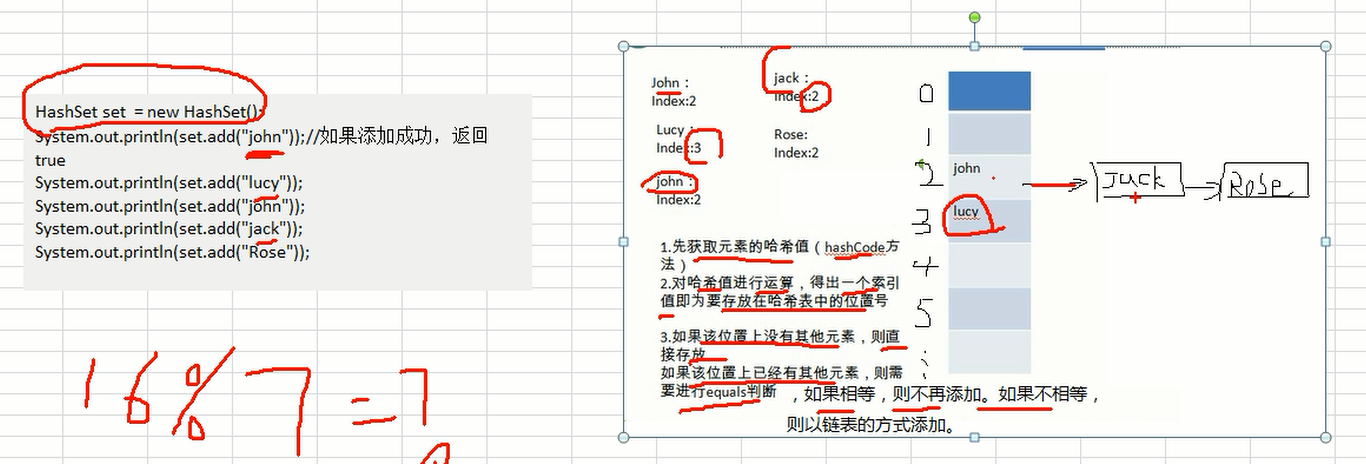
7.HashSet注意事项

 、
、
1 import java.util.HashSet; 2 3 public class HashSetOverrideHashCodeEq { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 //需求是如果Car 的name 和price 一样,也就是说某个对象的属性完全一样, 8 //我们认为是同一个对象。这时需要重写hashCode和equals 9 10 //System.out.println(new Car("奥迪", 300000).hashCode()); 11 //System.out.println(new Car("奥迪", 300000).hashCode()); 12 13 //System.out.println(new Car("奥迪", 300000).equals(new Car("奥迪", 300000)));//true 14 15 HashSet set = new HashSet(); 16 set.add(new Car("奥拓", 1000)); 17 set.add(new Car("奥迪", 300000)); 18 set.add(new Car("法拉利", 10000000)); 19 set.add(new Car("保时捷", 70000000)); 20 set.add(new Car("奥迪", 300000)); 21 for (Object object : set) { 22 System.out.println(object); 23 } 24 25 } 26 27 } 28 29 class Car { 30 private String name; 31 private double price; 32 33 34 //使用eclipse生成 35 //这里hashCode将属性考虑到. 如果我们的属性相同,则hashCode就相同 36 // @Override 37 public int hashCode() { 38 final int prime = 31; 39 int result = 1; 40 result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); 41 long temp; 42 temp = Double.doubleToLongBits(price); 43 result = prime * result + (int) (temp ^ (temp >>> 32)); 44 return result; 45 } 46 47 //这里比较时重写equals 48 // @Override 49 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 50 if (this == obj) 51 return true; 52 if (obj == null) 53 return false; 54 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 55 return false; 56 Car other = (Car) obj; 57 if (name == null) { 58 if (other.name != null) 59 return false; 60 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) 61 return false; 62 if (Double.doubleToLongBits(price) != Double.doubleToLongBits(other.price)) 63 return false; 64 return true; 65 } 66 67 68 public Car(String name, double price) { 69 super(); 70 this.name = name; 71 this.price = price; 72 } 73 74 75 public String getName() { 76 return name; 77 } 78 79 public void setName(String name) { 80 this.name = name; 81 } 82 83 public double getPrice() { 84 return price; 85 } 86 87 public void setPrice(double price) { 88 this.price = price; 89 } 90 91 @Override 92 public String toString() { 93 return "Car [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]"; 94 }
8.HashSet案例

1 import java.util.HashSet; 2 3 public class HashSetExercise { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 HashSet set = new HashSet(); 8 set.add(new Employee("jack", (short)80, new MyDate((short)2011, (short)11, (short)11))); 9 set.add(new Employee("jack", (short)81, new MyDate((short)2011, (short)11, (short)11))); 10 set.add(new Employee("jack", (short)82, new MyDate((short)2011, (short)11, (short)11))); 11 set.add(new Employee("jack", (short)83, new MyDate((short)2011, (short)11, (short)11))); 12 set.add(new Employee("jack", (short)83, new MyDate((short)2011, (short)11, (short)12))); 13 set.add(new Employee("jack2", (short)83, new MyDate((short)2011, (short)11, (short)11))); 14 15 for (Object object : set) { 16 System.out.println(object); 17 } 18 } 19 20 } 21 22 //HashSet课堂练习 23 // 24 //定义一个Employee类, 25 //该类包含:private成员属性name,age,birthday,其中 birthday 为 MyDate类(属性包括:year, month, day)的对象, 要求: 26 //为每一个属性定义 getter, setter 方法; 27 //并重写 toString 方法输出 name, age, birthday 28 //认为 name和birthday一样的为同一个员工 29 //要求MyDate的hashCode 和 equals使用自动生成重写 30 //Employee 的hashCode和 equals 我们自己手动重写。 31 32 class MyDate{ 33 private short year; 34 private short month; 35 private short day; 36 public MyDate(short year, short month, short day) { 37 super(); 38 this.year = year; 39 this.month = month; 40 this.day = day; 41 } 42 public short getYear() { 43 return year; 44 } 45 public void setYear(short year) { 46 this.year = year; 47 } 48 public short getMonth() { 49 return month; 50 } 51 public void setMonth(short month) { 52 this.month = month; 53 } 54 public short getDay() { 55 return day; 56 } 57 public void setDay(short day) { 58 this.day = day; 59 } 60 @Override 61 public String toString() { 62 return "MyDate [year=" + year + ", month=" + month + ", day=" + day + "]"; 63 } 64 @Override 65 public int hashCode() { 66 final int prime = 31; 67 int result = 1; 68 result = prime * result + day; 69 result = prime * result + month; 70 result = prime * result + year; 71 return result; 72 } 73 @Override 74 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 75 if (this == obj) 76 return true; 77 if (obj == null) 78 return false; 79 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 80 return false; 81 MyDate other = (MyDate) obj; 82 if (day != other.day) 83 return false; 84 if (month != other.month) 85 return false; 86 if (year != other.year) 87 return false; 88 return true; 89 } 90 91 92 93 } 94 95 class Employee{ 96 private String name; 97 private short age; 98 private MyDate birthday; 99 100 //认为 name和birthday一样的为同一个员工 101 102 103 public Employee(String name, short age, MyDate birthday) { 104 super(); 105 this.name = name; 106 this.age = age; 107 this.birthday = birthday; 108 } 109 @Override 110 public int hashCode() { 111 return name.hashCode() + birthday.hashCode(); 112 } 113 @Override 114 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 115 if(this == obj){ 116 return true; 117 } 118 if(!(obj instanceof Employee)){ 119 return false; 120 } 121 Employee e = (Employee)obj; 122 return name.equals(e.name) && birthday.equals(e.getBirthday()); 123 } 124 public String getName() { 125 return name; 126 } 127 public void setName(String name) { 128 this.name = name; 129 } 130 public short getAge() { 131 return age; 132 } 133 public void setAge(short age) { 134 this.age = age; 135 } 136 public MyDate getBirthday() { 137 return birthday; 138 } 139 public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) { 140 this.birthday = birthday; 141 } 142 @Override 143 public String toString() { 144 return "Employee [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", birthday=" + birthday + "]"; 145 } 146 147 }
9. Set接口实现类-TreeSet


10. TreeSet的自然排序

1.1.1 TreeSet实现Comprable 接口指定排序规则
1 package com.atguigu.chapter15.treeset; 2 3 import java.util.TreeSet; 4 5 6 //按名字的升序排序,再按照价格的降序. 7 public class TreeSetCompareableDemo { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 11 TreeSet set = new TreeSet(); 12 set.add(new Book("摆渡人",30)); 13 set.add(new Book("嫌疑人X的献身",45)); 14 set.add(new Book("小时代",23)); 15 set.add(new Book("小时代",23)); 16 set.add(new Book("小时代",23)); 17 set.add(new Book("摆渡人",31)); 18 set.add(new Book("摆渡人",32)); 19 set.add(new Book("流浪地球",45.8)); 20 set.add(new Book("摆渡人",33)); 21 22 for (Object object : set) { 23 System.out.println(object); 24 } 25 26 27 28 29 30 } 31 32 } 33 34 class Book implements Comparable{ 35 private String name; 36 private double price; 37 public Book(String name, double price) { 38 super(); 39 this.name = name; 40 this.price = price; 41 } 42 public String getName() { 43 return name; 44 } 45 public void setName(String name) { 46 this.name = name; 47 } 48 public double getPrice() { 49 return price; 50 } 51 public void setPrice(double price) { 52 this.price = price; 53 } 54 55 //按名字的升序排序,再按照价格的降序. 56 @Override 57 public int compareTo(Object o) { 58 if(!(o instanceof Book)) { 59 return 0; 60 } 61 Book book = (Book)o; 62 if(name.compareTo(book.name) > 0){ 63 return -1; 64 }else if (name.compareTo(book.name) < 0){ 65 return 1; 66 }else { 67 if (price > book.getPrice()){ 68 return 1; 69 }else if(price < book.getPrice()){ 70 return -1; 71 }else { 72 return 0; //返回0,加入不到TreeSet 73 } 74 } 75 } 76 @Override 77 public String toString() { 78 return "Book [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]"; 79 } 80 81 82 83 }
1.1.1 TreeSet通过构造器传入Comparator 匿名对象定制排序
1 mport java.util.Comparator; 2 import java.util.TreeSet; 3 4 public class TreeSetComparatorDemo { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 8 // 要求按照价格从小到大排序即(不考虑书名) 9 TreeSet set = new TreeSet(new Comparator() { 10 11 @Override 12 public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { 13 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 14 Book book1 = (Book)o1; 15 Book book2 = (Book)o2; 16 return Double.compare(book1.getPrice(), book2.getPrice()); 17 } 18 }); 19 20 set.add(new Book("摆渡人",30)); 21 set.add(new Book("嫌疑人X的献身",45)); 22 set.add(new Book("小时代",23)); 23 set.add(new Book("小时代",23)); 24 set.add(new Book("小时代",23)); 25 set.add(new Book("摆渡人",31)); 26 set.add(new Book("摆渡人",32)); 27 set.add(new Book("流浪地球",45.8)); 28 set.add(new Book("摆渡人",33)); 29 30 for (Object object : set) { 31 System.out.println(object); 32 } 33 } 34 35 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号