Promise实现小球的运动
Promise简要说明
Promise可以处理一些异步操作;如像setTimeout、ajax处理异步操作是一函数回调的方式;当然ajax在jQuery版本升级过程中,编写方式也有所变动.
Promise是抽象异步处理对象以及对其进行各种操作的组件.
Promise最初被提出是在 E语言中, 它是基于并列/并行处理设计的一种编程语言。
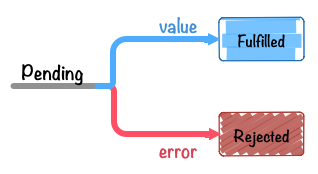
创建promise对象的流程如下所示。
-
new Promise(fn)返回一个promise对象 -
在
fn中指定异步等处理-
处理结果正常的话,调用
resolve(处理结果值) -
处理结果错误的话,调用
reject(Error对象)
-

resolve("new Promise value......"); 会让这个promise对象立即进入确定(即resolved)状态,并将 "new Promise value......" 传递给后面then里所指定的 onFulfilled 函数
Promise.resolve(value); 的返回值也是一个promise对象,所以我们可以像下面那样接着对其返回值进行 .then 调用
Promise 实现小球的运动
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Animate Ball</title>
<style type="text/css">
.ball {
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
border-radius: 20px;
margin-left: 0;
}
.ball1 {
background-color: yellow;
}
.ball2 {
background-color: red;
}
.ball3 {
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="ball ball1" style="margin-left:0px;"></div>
<div class="ball ball2" style="margin-left:0px;"></div>
<div class="ball ball3" style="margin-left:0px;"></div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/bluebird/js/browser/bluebird.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" >
/*function animateBall(ball, distance, callback){
//setTimeout过渡效果
setTimeout(function(){
var marginLeft = parseInt(ball.style.marginLeft, 10);
console.log(marginLeft);
if(marginLeft==distance){
callback && callback();
}else{
if(marginLeft<distance){
marginLeft ++;
}
if(marginLeft>distance){
marginLeft--;
}
ball.style.marginLeft = marginLeft +'px';
//callback
animateBall(ball, distance, callback);
}
}, 13);
}
var ball1 = document.querySelector('.ball1');
var ball2 = document.querySelector('.ball2');
var ball3 = document.querySelector('.ball3');
animateBall(ball1, 150, function(){
animateBall(ball2, 250, function(){
animateBall(ball3, 350, function(){
animateBall(ball3, 200, function(){
animateBall(ball2, 100, function(){
animateBall(ball1, 50, function(){
})
})
})
})
})
})*/
var ball1 = document.querySelector('.ball1');
var ball2 = document.querySelector('.ball2');
var ball3 = document.querySelector('.ball3');
//promise
var Promise = window.Promise;
//使用 promise 替代回调函数
function promiseAnimate(ball, distance){
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
function _animate(){
//setTimeout过渡效果
setTimeout(function(){
var marginLeft = parseInt(ball.style.marginLeft, 10);
console.log(marginLeft);
if(marginLeft==distance){
//resolve函数:将Promise对象的状态从 “未完成”变为 “成功”(Pending ->Resolved),在异步操作成功时调用,并将异步操作的结果,作为参数传递出去
resolve(ball, distance);
}else{
if(marginLeft<distance){
marginLeft ++;
}
if(marginLeft>distance){
marginLeft--;
}
ball.style.marginLeft = marginLeft +'px';
//callback
_animate();
}
}, 13);
}
_animate();
});
}
promiseAnimate(ball1, 150)
.then(function(){
return promiseAnimate(ball2, 250);
}).then(function(){
return promiseAnimate(ball3, 300);
}).then(function(){
return promiseAnimate(ball3, 200);
}).then(function(){
return promiseAnimate(ball2, 100);
}).then(function(){
return promiseAnimate(ball1, 50);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
总结 : Promise链式的编写方式解决回调函数深度嵌套问题
效果演示如下
资料参考
http://liubin.org/promises-book/#how-to-write-promise
http://ejohn.org/blog/how-javascript-timers-work/
http://www.cnblogs.com/zichi/p/4604053.html
谷歌翻译api http://translate.hotcn.top/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号