JAVAEE学习——hibernate01:简介、搭建、配置文件详解、API详解和CRM练习:保存客户
今日学习:hibernate是什么
一、hibernate是什么
框架是什么:
1.框架是用来提高开发效率的
2.封装了好了一些功能.我们需要使用这些功能时,调用即可.不需要再手动实现.
3.所以框架可以理解成是一个半成品的项目.只要懂得如何驾驭这些功能即可.
hibernate框架是什么:
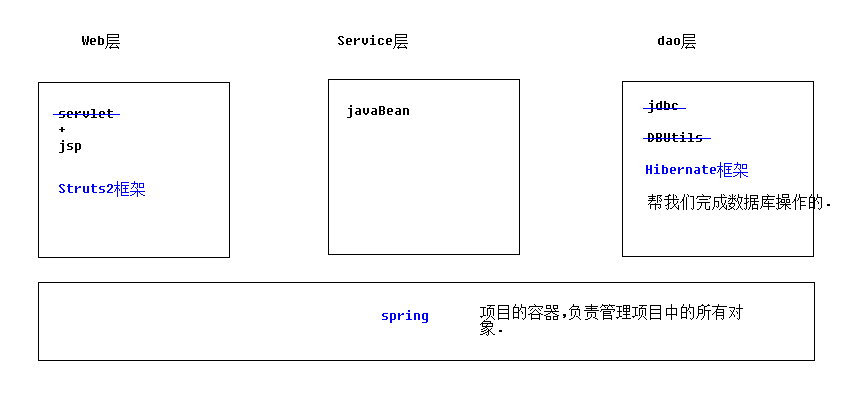
hibernate的好处:
操作数据库的时候,可以以面向对象的方式来完成.不需要书写SQL语句
hibernate是一款orm框架:
orm:object relationg mapping. 对象关系映射

orm分4级:
hibernate属于4级:完全面向对象操作数据库
mybatis属于2级
dbutils属于1级
二、hibernate框架的搭建
1.导包

驱动包

2.创建数据库,准备表,实体

3.书写orm元数据(对象与表的映射配置文件)
4.书写主配置文件(hibernate.cfg.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- #hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect #hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect #hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLMyISAMDialect #hibernate.connection.driver_class com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #hibernate.connection.url jdbc:mysql:///test #hibernate.connection.username gavin #hibernate.connection.password --> <!-- 数据库驱动 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <!-- 数据库url --> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///hibernate_32</property> <!-- 数据库连接用户名 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <!-- 数据库连接密码 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">1234</property> <!-- 数据库方言 不同的数据库中,sql语法略有区别. 指定方言可以让hibernate框架在生成sql语句时.针对数据库的方言生成. sql99标准: DDL 定义语言 库表的增删改查 DCL 控制语言 事务 权限 DML 操纵语言 增删改查 注意: MYSQL在选择方言时,请选择最短的方言. --> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> <!-- #hibernate.show_sql true #hibernate.format_sql true --> <!-- 将hibernate生成的sql语句打印到控制台 --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <!-- 将hibernate生成的sql语句格式化(语法缩进) --> <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property> <!-- ## auto schema export 自动导出表结构. 自动建表 #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create 自动建表.每次框架运行都会创建新的表.以前表将会被覆盖,表数据会丢失.(开发环境中测试使用) #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create-drop 自动建表.每次框架运行结束都会将所有表删除.(开发环境中测试使用) #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto update(推荐使用) 自动生成表.如果已经存在不会再生成.如果表有变动.自动更新表(不会删除任何数据). #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto validate 校验.不自动生成表.每次启动会校验数据库中表是否正确.校验失败. --> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <!-- 引入orm元数据 路径书写: 填写src下的路径 --> <mapping resource="cn/xyp/domain/Customer.hbm.xml" /> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
5.书写代码测试
//测试Hibernate框架 public class Demo { @Test //保存客户 public void fun1(){ Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure(); SessionFactory sessionFactory = conf.buildSessionFactory(); Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); //---------------------------------------------- Customer c = new Customer(); c.setCust_name("google公司"); session.save(c);//执行保存 //---------------------------------------------- tx.commit(); session.close(); sessionFactory.close(); } }
三、配置文件详解
orm元数据
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 配置表与实体对象的关系 --> <!-- package属性:填写一个包名.在元素内部凡是需要书写完整类名的属性,可以直接写简答类名了. --> <hibernate-mapping package="cn.xyp.domain" > <!-- class元素: 配置实体与表的对应关系的 name: 完整类名 table:数据库表名 --> <class name="Customer" table="cst_customer" > <!-- id元素:配置主键映射的属性 name: 填写主键对应属性名 column(可选): 填写表中的主键列名.默认值:列名会默认使用属性名 type(可选):填写列(属性)的类型.hibernate会自动检测实体的属性类型. 每个类型有三种填法: java类型|hibernate类型|数据库类型 not-null(可选):配置该属性(列)是否不能为空. 默认值:false length(可选):配置数据库中列的长度. 默认值:使用数据库类型的最大长度 --> <id name="cust_id" > <!-- generator:主键生成策略(明天讲) --> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <!-- property元素:除id之外的普通属性映射 name: 填写属性名 column(可选): 填写列名 type(可选):填写列(属性)的类型.hibernate会自动检测实体的属性类型. 每个类型有三种填法: java类型|hibernate类型|数据库类型 not-null(可选):配置该属性(列)是否不能为空. 默认值:false length(可选):配置数据库中列的长度. 默认值:使用数据库类型的最大长度 --> <property name="cust_name" column="cust_name" > <!-- <column name="cust_name" sql-type="varchar" ></column> --> </property> <property name="cust_source" column="cust_source" ></property> <property name="cust_industry" column="cust_industry" ></property> <property name="cust_level" column="cust_level" ></property> <property name="cust_linkman" column="cust_linkman" ></property> <property name="cust_phone" column="cust_phone" ></property> <property name="cust_mobile" column="cust_mobile" ></property> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
hibernate主配置:
必选属性配置(5个)
<!-- 数据库驱动 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <!-- 数据库url --> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///hibernate_32</property> <!-- 数据库连接用户名 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <!-- 数据库连接密码 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">1234</property> <!-- 数据库方言 不同的数据库中,sql语法略有区别. 指定方言可以让hibernate框架在生成sql语句时.针对数据库的方言生成. sql99标准: DDL 定义语言 库表的增删改查 DCL 控制语言 事务 权限 DML 操纵语言 增删改查 注意: MYSQL在选择方言时,请选择最短的方言. --> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
可选属性配置(3个)
<!-- #hibernate.show_sql true #hibernate.format_sql true --> <!-- 将hibernate生成的sql语句打印到控制台 --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <!-- 将hibernate生成的sql语句格式化(语法缩进) --> <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property> <!-- ## auto schema export 自动导出表结构. 自动建表 #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create 自动建表.每次框架运行都会创建新的表.以前表将会被覆盖,表数据会丢失.(开发环境中测试使用) #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create-drop 自动建表.每次框架运行结束都会将所有表删除.(开发环境中测试使用) #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto update(推荐使用) 自动生成表.如果已经存在不会再生成.如果表有变动.自动更新表(不会删除任何数据). #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto validate 校验.不自动生成表.每次启动会校验数据库中表是否正确.校验失败. --> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
元数据引入配置
<!-- 引入orm元数据 路径书写: 填写src下的路径 --> <mapping resource="cn/xyp/domain/Customer.hbm.xml" />
四、hibernateAPI详解
学习Configuration对象
//学习Configuration对象 // Configuration功能: 配置加载类.用于加载主配置,orm元数据加载 public class Demo { @Test public void fun1(){ //1 创建,调用空参构造 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //2 读取指定主配置文件 => 空参加载方法,加载src下的hibernate.cfg.xml文件 conf.configure(); //3 读取指定orm元数据(扩展),如果主配置中已经引入映射配置.不需要手动加载 //conf.addResource(resourceName); //conf.addClass(persistentClass); //4 根据配置信息,创建 SessionFactory对象 SessionFactory sf = conf.buildSessionFactory(); } }
学习SessionFactory对象
//学习SessionFactory对象 // SessionFactory功能: 用于创建操作数据库核心对象session对象的工厂. // 简单说功能就一个---创建session对象 //注意:1.sessionfactory 负责保存和使用所有配置信息.消耗内存资源非常大. // 2.sessionFactory属于线程安全的对象设计. //结论: 保证在web项目中,只创建一个sessionFactory. public class Demo2 { @Test public void fun1(){ //1 创建,调用空参构造 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //2 读取指定主配置文件 => 空参加载方法,加载src下的hibernate.cfg.xml文件 conf.configure(); //3 读取指定orm元数据(扩展),如果主配置中已经引入映射配置.不需要手动加载 //conf.addResource(resourceName); //conf.addClass(persistentClass); //4 根据配置信息,创建 SessionFactory对象 SessionFactory sf = conf.buildSessionFactory(); //-------------------------------------------------- //5 获得session //打开一个新的session对象 sf.openSession(); //获得一个与线程绑定的session对象(明天讲解) sf.getCurrentSession(); } }
学习Session对象:增删查改
//学习Session对象 //session对象功能: 表达hibernate框架与数据库之间的连接(会话).session类似于 // JDBC年代的connection对象. 还可以完成对数据库中数据的增删改查操作. // session是hibernate操作数据库的核心对象 public class Demo3 { @Test //事务操作 public void fun1(){ //1 创建,调用空参构造 Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure(); //2 根据配置信息,创建 SessionFactory对象 SessionFactory sf = conf.buildSessionFactory(); //3 获得session Session session = sf.openSession(); //4 session获得操作事务的Transaction对象 //获得操作事务的tx对象 //Transaction tx = session.getTransaction(); //开启事务并获得操作事务的tx对象(建议使用) Transaction tx2 = session.beginTransaction(); //---------------------------------------------- //---------------------------------------------- tx2.commit();//提交事务 tx2.rollback();//回滚事务 session.close();//释放资源 sf.close();//释放资源 } @Test //session的新增 public void fun2(){ //1 创建,调用空参构造 Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure(); //2 根据配置信息,创建 SessionFactory对象 SessionFactory sf = conf.buildSessionFactory(); //3 获得session Session session = sf.openSession(); //4 session获得操作事务的Transaction对象 //获得操作事务的tx对象 //Transaction tx = session.getTransaction(); //开启事务并获得操作事务的tx对象(建议使用) Transaction tx2 = session.beginTransaction(); //---------------------------------------------- Customer c = new Customer(); c.setCust_name("传智播客"); session.save(c); //---------------------------------------------- tx2.commit();//提交事务 session.close();//释放资源 sf.close();//释放资源 } @Test //session的查询 //查询id为1的customer对象 public void fun3(){ //1 创建,调用空参构造 Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure(); //2 根据配置信息,创建 SessionFactory对象 SessionFactory sf = conf.buildSessionFactory(); //3 获得session Session session = sf.openSession(); //4 session获得操作事务的Transaction对象 //获得操作事务的tx对象 //Transaction tx = session.getTransaction(); //开启事务并获得操作事务的tx对象(建议使用) Transaction tx2 = session.beginTransaction(); //---------------------------------------------- Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1l); System.out.println(customer); //---------------------------------------------- tx2.commit();//提交事务 session.close();//释放资源 sf.close();//释放资源 } @Test //session的修改 //修改id为1的customer对象的name属性为黑马程序员 public void fun4(){ //1 创建,调用空参构造 Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure(); //2 根据配置信息,创建 SessionFactory对象 SessionFactory sf = conf.buildSessionFactory(); //3 获得session Session session = sf.openSession(); //4 session获得操作事务的Transaction对象 //获得操作事务的tx对象 //Transaction tx = session.getTransaction(); //开启事务并获得操作事务的tx对象(建议使用) Transaction tx2 = session.beginTransaction(); //---------------------------------------------- //1 获得要修改的对象 Customer c = session.get(Customer.class, 1l); //2 修改 c.setCust_name("黑马程序员"); //3 执行update session.update(c); //---------------------------------------------- tx2.commit();//提交事务 session.close();//释放资源 sf.close();//释放资源 } @Test //session的删除 //删除id为1的customer对象 public void fun5(){ //1 创建,调用空参构造 Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure(); //2 根据配置信息,创建 SessionFactory对象 SessionFactory sf = conf.buildSessionFactory(); //3 获得session Session session = sf.openSession(); //4 session获得操作事务的Transaction对象 //获得操作事务的tx对象 Transaction tx = session.getTransaction(); tx.begin(); //开启事务并获得操作事务的tx对象(建议使用) Transaction tx2 = session.beginTransaction(); //---------------------------------------------- //1 获得要修改的对象 Customer c = session.get(Customer.class, 1l); //2 调用delete删除对象 session.delete(c); //---------------------------------------------- tx2.commit();//提交事务 session.close();//释放资源 sf.close();//释放资源 } }
五、CRM练习:保存客户

前面的步骤参考前面的笔记。
5.思路分析

在完成作业之前可以先编写一个方便操作的工具类,免去重复的代码:
public class HibernateUtils { private static SessionFactory sf; static{ //1 创建,调用空参构造 Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure(); //2 根据配置信息,创建 SessionFactory对象 sf = conf.buildSessionFactory(); } //获得session => 获得全新session public static Session openSession(){ //3 获得session Session session = sf.openSession(); return session; } //获得session => 获得与线程绑定的session public static Session getCurrentSession(){ //3 获得session Session session = sf.getCurrentSession(); return session; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(HibernateUtils.openSession()); } }
作业核心代码:
web层:
/** * Servlet implementation class AddCustomerServlet */ public class AddCustomerServlet extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private CustomerService customerService = new CustomerServiceImpl(); protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { //1 获得参数并封装到Customer对象 Customer c = new Customer(); try { BeanUtils.populate(c, request.getParameterMap()); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //2 调用Service保存客户 customerService.save(c); //3 重定向到客户列表 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/ListCustomerServlet"); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
service层:
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService { private CustomerDao customerDao = new CustomerDaoImpl(); public void save(Customer c) { //调用Dao保存客户 customerDao .save(c); } }
dao层:
public class CustomerDaoImpl implements CustomerDao { public void save(Customer c) { //1 获得session Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); //2 打开事务 Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); //3 执行保存 session.save(c); //4 提交事务 tx.commit(); //5 关闭资源 session.close(); } }
作者: kent鹏
出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/xieyupeng/
关于作者:专注JAVAEE领域,请多多赐教!
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号