(原創) 如何用管線(Pipeline)實作無號數乘加運算? (IC Design) (Verilog)
Abstract
之前使用過組合電路實現無號數與有號數的乘加運算,本文我們使用循序電路配合管線(Pipeline)實作無號數的乘加運算。
Introduction
在(原創) 無號數及有號數的乘加運算電路設計 (IC Design) (Verilog) (Linux)中,我們使用了組合電路,並且比較了無號數與有號數程式上的差別,本文我們將使用循序電路,並配合上Pipeline來實作Σai * bi + ci。
Verilog
2 (C) OOMusou 2008 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3
4 Filename : Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic.v
5 Compiler : ModelSim SE 6.1f
6 Description : Demo how to use pipeline with unsigned arithmetic
7 Release : 02/12/2008 1.0
8 */
9
10
11 `timescale 1 ns/1 ns
12
13 module Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic (
14 clk,
15 reset_n,
16 i_a,
17 i_b,
18 i_c,
19 o_answer
20 );
21
22 input clk, reset_n;
23 input [3:0] i_a, i_b, i_c;
24 output [7:0] o_answer;
25
26 reg [3:0] r_a0; // reg 4 i_a
27 reg [3:0] r_b0; // reg 4 i_b
28 reg [3:0] r_c0; // reg 4 i_c
29 reg [3:0] r_c1; // reg 4 r_c0
30
31 reg [7:0] r_mul; // reg 4 a * b
32 reg [7:0] r_acc; // reg 4 a * b + c
33 reg [7:0] r_answer; // reg 4 o_answer
34
35 always@(posedge clk or negedge reset_n) begin
36 if (!reset_n) begin
37 r_a0 <= #1 4'h0;
38 r_b0 <= #1 4'h0;
39 r_c0 <= #1 4'h0;
40 r_c1 <= #1 4'h0;
41 r_mul <= #1 8'h00;
42 r_acc <= #1 8'h00;
43 r_answer <= #1 8'h00;
44 end
45 else begin
46 r_a0 <= #1 i_a;
47 r_b0 <= #1 i_b;
48 r_c0 <= #1 i_c;
49 r_c1 <= #1 r_c0;
50 r_mul <= #1 r_a0 * r_b0;
51 r_acc <= #1 r_mul + r_c1;
52 r_answer <= #1 r_answer + r_acc;
53 end
54 end
55
56 assign o_answer = r_answer;
57
58 endmodule
Waveform
26行
reg [3:0] r_b0; // reg 4 i_b
reg [3:0] r_c0; // reg 4 i_c
reg [3:0] r_c1; // reg 4 r_c0
reg [7:0] r_mul; // reg 4 a * b
reg [7:0] r_acc; // reg 4 a * b + c
reg [7:0] r_answer; // reg 4 o_answer
宣告always block所要用到的register,r_c0表示第一個pipeline stage的register,r_c1表是第二個pipeline stage的register,為什麼r_c要兩個stage呢?後面會解釋。剩下r_開頭的,皆為pipeline會用到的register。
46行
 else begin
else begin r_a0 <= #1 i_a;
r_a0 <= #1 i_a; r_b0 <= #1 i_b;
r_b0 <= #1 i_b; r_c0 <= #1 i_c;
r_c0 <= #1 i_c; r_c1 <= #1 r_c0;
r_c1 <= #1 r_c0; r_mul <= #1 r_a0 * r_b0;
r_mul <= #1 r_a0 * r_b0; r_acc <= #1 r_mul + r_c1;
r_acc <= #1 r_mul + r_c1; r_answer <= #1 r_answer + r_acc;
r_answer <= #1 r_answer + r_acc; end
end
真正開始做pipeline了,由於我們要做a * b + c,所以先做a * b,等a * b求出結果後,再算 + c,由於c必須一直等到a * b才用的到,所以必須r_c0 <= #1 i_c,又 r_c1 <= #1 r_c0;如此i_c才能維持到 r_acc <= #1 r_mul + r_c1時運算。這裡是pipeline比較tricky的地方。
Testbench
2 (C) OOMusou 2008 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3
4 Filename : Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb.v
5 Compiler : ModelSim SE 6.1f
6 Description : Demo how to use pipeline with unsigned arithmetic testbench
7 Release : 02/12/2008 1.0
8 */
9
10 `timescale 1 ns/1 ns
11 module Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb;
12
13 reg clk, reset_n;
14 reg [3:0] i_a, i_b, i_c;
15 wire [7:0] o_answer;
16
17 Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic u0 (
18 .clk(clk),
19 .reset_n(reset_n),
20 .i_a(i_a),
21 .i_b(i_b),
22 .i_c(i_c),
23 .o_answer(o_answer)
24 );
25
26 // 50ns = 20MHz
27 parameter clkper = 50;
28 initial begin
29 clk = 1;
30 end
31
32 always begin
33 #(clkper/2) clk = ~clk;
34 end
35
36 initial begin
37 // time = 0
38 reset_n = 1'b0;
39 i_a = 8'h00;
40 i_b = 8'h00;
41 i_c = 8'h00;
42
43 // time = 75
44 #75
45 reset_n = 1'b1;
46
47 // time = 101
48 #26
49 i_a = 8'h01;
50 i_b = 8'h02;
51 i_c = 8'h03;
52 // o_answer = 8'h05;
53
54 // time = 151
55 #50
56 i_a = 8'h03;
57 i_b = 8'h01;
58 i_c = 8'h04;
59 // o_answer = 8'h0c;
60
61 // time = 201
62 #50
63 i_a = 8'h00;
64 i_b = 8'h00;
65 i_c = 8'h00;
66
67 end
68 endmodule
17行
.clk(clk),
.reset_n(reset_n),
.i_a(i_a),
.i_b(i_b),
.i_c(i_c),
.o_answer(o_answer)
);
對Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic作連線的動作。
26行
parameter clkper = 50;
initial begin
clk = 1;
end
always begin
#(clkper/2) clk = ~clk;
end
為了觀察方便,比例使用20MHz,也就是周期50ns,這裡是產生所需要的50MHz clock。
47行
 // time = 101
// time = 101 #26
#26 i_a = 8'h01;
i_a = 8'h01; i_b = 8'h02;
i_b = 8'h02; i_c = 8'h03;
i_c = 8'h03; // o_answer = 8'h05;
// o_answer = 8'h05; 
 // time = 151
// time = 151  #50
#50 i_a = 8'h03;
i_a = 8'h03; i_b = 8'h01;
i_b = 8'h01; i_c = 8'h04;
i_c = 8'h04; // o_answer = 8'h0c;
// o_answer = 8'h0c;
 // time = 201
// time = 201 #50
#50 i_a = 8'h00;
i_a = 8'h00; i_b = 8'h00;
i_b = 8'h00; i_c = 8'h00;
i_c = 8'h00;
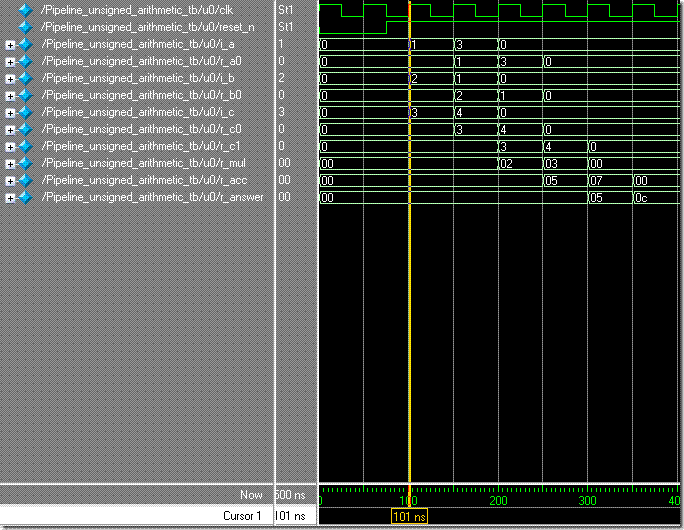
在101ns時產生i_a = 1、i_b = 2、i_c = 3,此時結果預期為 1 * 2 + 3 = 5,在151ns時產生i_a = 3、i_b = 1 、i_c = 4,此時結果預期為 5 + 3 * 1 + 4 = 12,也就是產生了 (1 * 2 +3) + (3 * 1 + 4) = 12。
ModelSim macro
2 #(C) OOMusou 2008 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3
4 #Filename : Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_wave.do
5 #Compiler : ModelSim SE 6.1f
6 #Description : Demo how to use pipeline with unsigned arithmetic batch file
7 #Release : 02/12/2008 1.0
8 #
9
10 #compile
11 vlog Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic.v
12 vlog Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb.v
13
14 #simulate
15 vsim -coverage Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb
16
17 #probe signals
18 add wave -noupdate -format -logic /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/clk
19 add wave -noupdate -format -logic /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/reset_n
20 add wave -noupdate -format -literal -radix hex /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/i_a
21 add wave -noupdate -format -literal -radix hex /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/r_a0
22 add wave -noupdate -format -literal -radix hex /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/i_b
23 add wave -noupdate -format -literal -radix hex /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/r_b0
24 add wave -noupdate -format -literal -radix hex /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/i_c
25 add wave -noupdate -format -literal -radix hex /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/r_c0
26 add wave -noupdate -format -literal -radix hex /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/r_c1
27 add wave -noupdate -format -literal -radix hex /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/r_mul
28 add wave -noupdate -format -literal -radix hex /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/r_acc
29 add wave -noupdate -format -literal -radix hex /Pipeline_unsigned_arithmetic_tb/u0/r_answer
30
31 #500 ns
32 run 500
Conclusion
Pipeline可以增加時脈,也就增加了執行速度,但在本例可以發現,為了使用pipeline,增加了很多register,對FPGA來說就是增加logic element,對ASIC來說就是增加面積,也就是增加成本,這也是為什麼IC不可能毫無限制的使用pipeline增加速度,畢竟速度是靠面積換來的,只能在spec允許下適當的使用pipeline加速。
See Also
(原創) 無號數及有號數的乘加運算電路設計 (IC Design) (Verilog) (Linux)
(原創) 如何處理signed integer的加法運算與overflow? (SOC) (Verilog)
(原創) 如何設計乘加電路? (SOC) (Verilog) (MegaCore)
(原創) 如何設計2數相加的電路? (SOC) (Verilog)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号