netty支持的各种socketchannel实现及比较
性能上从低到高如下:
- OioSocketChannel:传统,阻塞式编程。
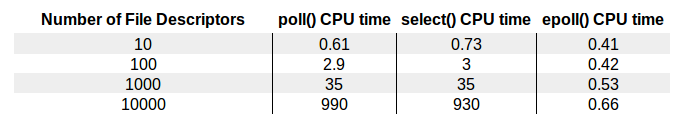
- NioSocketChannel:select/poll或者epoll,jdk 7之后linux下会自动选择epoll。epoll原理及与select/poll的伸缩性性能测试基准
- EpollSocketChannel:epoll,仅限linux,提供更多额外选项。
- EpollDomainSocketChannel:ipc模式,仅限客户端、服务端在相同主机的情况,从4.0.26版本开始支持,见https://github.com/netty/netty/pull/3344。
select示例(监听标准输入)
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/select.h> int main(void) { int retval; fd_set rfds; struct timeval tv; /* Wait up to five seconds. */ tv.tv_sec = 5; tv.tv_usec = 0; // 每次都需要重置,限制1024 /* Watch stdin (fd 0) to see when it has input. */ FD_ZERO(&rfds); FD_SET(0, &rfds); retval = select(1, &rfds, NULL, NULL, &tv); /* Don't rely on the value of tv now! */ if (retval == -1) perror("select()"); else if (retval) { printf("Data is available now.\n"); printf("%d\n",FD_ISSET(0,&rfds)); /* FD_ISSET(0, &rfds) will be true. */ } else printf("No data within five seconds.\n"); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
poll示例(监听文件修改)
/* poll_input.c Licensed under GNU General Public License v2 or later. */ #include <fcntl.h> #include <poll.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <malloc.h> #include <string.h> #define errExit(msg) do { perror(msg); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \ } while (0) // 从文件读取,文件写入内容后会读取最新的内容,适合于日志监听 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int ready; char buf[10]; nfds_t num_open_fds, nfds; ssize_t s; struct pollfd *pfds; if (argc < 2) { fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s file...\n", argv[0]); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } num_open_fds = nfds = argc - 1; pfds = (pollfd *)calloc(nfds, sizeof(struct pollfd)*num_open_fds); if (pfds == NULL) errExit("malloc"); /* Open each file on command line, and add it to 'pfds' array. */ char err_msg[256] = {}; for (nfds_t j = 0; j < nfds; j++) { pfds[j].fd = open(argv[j + 1], O_RDONLY); if (pfds[j].fd == -1) { memset(err_msg, 0, sizeof(err_msg)); snprintf(err_msg,256,"open %s failed",argv[j+1]); errExit(err_msg); } printf("Opened \"%s\" on fd %d\n", argv[j + 1], pfds[j].fd); pfds[j].events = POLLIN; } /* Keep calling poll() as long as at least one file descriptor is open. */ while (num_open_fds > 0) { printf("About to poll()\n"); ready = poll(pfds, nfds, -1); if (ready == -1) errExit("poll"); printf("Ready: %d\n", ready); /* Deal with array returned by poll(). */ for (nfds_t j = 0; j < nfds; j++) { if (pfds[j].revents != 0) { printf(" fd=%d; events: %s%s%s\n", pfds[j].fd, (pfds[j].revents & POLLIN) ? "POLLIN " : "", (pfds[j].revents & POLLHUP) ? "POLLHUP " : "", (pfds[j].revents & POLLERR) ? "POLLERR " : ""); if (pfds[j].revents & POLLIN) { s = read(pfds[j].fd, buf, sizeof(buf)); if (s == -1) errExit("read"); printf(" read %zd bytes: %.*s\n", s, (int) s, buf); } else { /* POLLERR | POLLHUP */ printf(" closing fd %d\n", pfds[j].fd); if (close(pfds[j].fd) == -1) errExit("close"); num_open_fds--; } } } sleep(5); } printf("All file descriptors closed; bye\n"); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
pollin模拟简单,客户端输入即可。pollout呢?可以看下这里。
poll监听socket
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <assert.h> #include <signal.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <errno.h> #include <poll.h> // https://blog.csdn.net/fengasdfgh/article/details/64920120 int start_up(sockaddr_in &addr) { int socketi = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); printf("%d\n", socketi); if (socketi < 0) { printf("%d, %s", errno, strerror(errno)); exit(1); } int flag = bind(socketi, (sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)); if (flag < 0) { printf("%d, %s", errno, strerror(errno)); exit(2); } flag = listen(socketi, 5); if (flag < 0) { printf("%d, %s", errno, strerror(errno)); exit(2); } return socketi; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc < 3) { printf("can sgu error"); exit(0); } struct sockaddr_in addr; bzero(&addr, sizeof(addr)); addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); addr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); addr.sin_family = PF_INET; int socketi = start_up(addr); / // printf("%d\n", socketi); char fd[100] = {0}; // memset(&fd, sizeof(fd), -1); struct pollfd pfd[100]; pfd[0].fd = socketi; pfd[0].events = POLLIN; for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) { pfd[i].fd = -1; } /// int flag = 1; int max = socketi; char buf[100] = {0}; socklen_t len = sizeof(addr); for (;;) { int timeout = 5000; if (false == flag) { max = 0; for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) { if (pfd[i].fd > max) max = pfd[i].fd; } } int ret = poll(pfd, max + 1, timeout); if (pfd[0].revents & POLLIN) { struct sockaddr_in client; socklen_t client_len = sizeof(client); int connfd = accept(socketi, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &client_len); if (connfd < 0) { printf("%d, %s\n", errno, strerror(errno)); } for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) { if (pfd[i].fd < 0) { pfd[i].fd = connfd; max++; break; } } if (connfd > max) max = connfd; } for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) { if (pfd[i].fd > 0 && (pfd[i].revents & POLLIN)) { ssize_t size = read(pfd[i].fd, buf, 20); if (size <= 0) { printf("client is quit\n"); pfd[i].fd = -1; if (pfd[i].fd == max) flag = false; continue; } buf[size - 1] = 0; printf("client:%s\n", buf); } } } return 0; }
epoll示例
#define MAX_EVENTS 5 #define READ_SIZE 10 #include <stdio.h> // for fprintf() #include <unistd.h> // for close(), read() #include <sys/epoll.h> // for epoll_create1(), epoll_ctl(), struct epoll_event #include <string.h> // for strncmp int main() { int running = 1, event_count, i; size_t bytes_read; char read_buffer[READ_SIZE + 1]; struct epoll_event event, events[MAX_EVENTS];
// epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC) 是一个用于创建 epoll 实例的系统调用,它用于异步事件通知。EPOLL_CLOEXEC 是一个标志,它告诉操作系统在创建 epoll 实例时将其设置为 close-on-exec(CLOEXEC)模式。
在 CLOEXEC 模式下,当一个进程调用 fork() 创建子进程或调用 exec() 执行一个新程序时,内核会自动关闭 epoll 实例,以防止在子进程或新程序中泄漏 epoll 文件描述符。这是一种安全措施,确保 epoll 文件描述符不会在不应该的地方被误用。 int epoll_fd = epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC); if (epoll_fd == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "Failed to create epoll file descriptor\n"); return 1; } event.events = EPOLLIN; event.data.fd = 0; if(epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 0, &event)) { fprintf(stderr, "Failed to add file descriptor to epoll\n"); close(epoll_fd); return 1; } while (running) { printf("\nPolling for input...\n"); event_count = epoll_wait(epoll_fd, events, MAX_EVENTS, 30000); printf("%d ready events\n", event_count); for (i = 0; i < event_count; i++) { printf("Reading file descriptor '%d' -- ", events[i].data.fd); bytes_read = read(events[i].data.fd, read_buffer, READ_SIZE); printf("%zd bytes read.\n", bytes_read);
// trim last \n from stdin
read_buffer[bytes_read-1] = '\0'; printf("Read '%s'\n", read_buffer); if(!strncmp(read_buffer, "stop\n", 5)) running = 0; } } if (close(epoll_fd)) { fprintf(stderr, "Failed to close epoll file descriptor\n"); return 1; } return 0; }
epoll各种事件的含义(man手册和头文件没有枚举)
The events member is a bit mask composed by ORing together zero or more of the following
available event types:
EPOLLIN
The associated file is available for read(2) operations.
EPOLLOUT
The associated file is available for write(2) operations.
EPOLLRDHUP (since Linux 2.6.17)
Stream socket peer closed connection, or shut down writing half of connection.
(This flag is especially useful for writing simple code to detect peer shutdown
when using Edge Triggered monitoring.)
EPOLLPRI
There is an exceptional condition on the file descriptor. See the discussion of
POLLPRI in poll(2).
EPOLLERR
Error condition happened on the associated file descriptor. This event is also
reported for the write end of a pipe when the read end has been closed.
epoll_wait(2) will always report for this event; it is not necessary to set it in
events.
EPOLLHUP
Hang up happened on the associated file descriptor. epoll_wait(2) will always wait
for this event; it is not necessary to set it in events.
Note that when reading from a channel such as a pipe or a stream socket, this event
merely indicates that the peer closed its end of the channel. Subsequent reads
from the channel will return 0 (end of file) only after all outstanding data in the
channel has been consumed.
EPOLLET
Sets the Edge Triggered behavior for the associated file descriptor. The default
behavior for epoll is Level Triggered. See epoll(7) for more detailed information
about Edge and Level Triggered event distribution architectures.
EPOLLONESHOT (since Linux 2.6.2)
Sets the one-shot behavior for the associated file descriptor. This means that
after an event is pulled out with epoll_wait(2) the associated file descriptor is
internally disabled and no other events will be reported by the epoll interface.
The user must call epoll_ctl() with EPOLL_CTL_MOD to rearm the file descriptor with
a new event mask.
EPOLLWAKEUP (since Linux 3.5)
If EPOLLONESHOT and EPOLLET are clear and the process has the CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND
capability, ensure that the system does not enter "suspend" or "hibernate" while
this event is pending or being processed. The event is considered as being
"processed" from the time when it is returned by a call to epoll_wait(2) until the
next call to epoll_wait(2) on the same epoll(7) file descriptor, the closure of
that file descriptor, the removal of the event file descriptor with EPOLL_CTL_DEL,
or the clearing of EPOLLWAKEUP for the event file descriptor with EPOLL_CTL_MOD.
See also BUGS.
EPOLLEXCLUSIVE (since Linux 4.5)
Sets an exclusive wakeup mode for the epoll file descriptor that is being attached
to the target file descriptor, fd. When a wakeup event occurs and multiple epoll
file descriptors are attached to the same target file using EPOLLEXCLUSIVE, one or
more of the epoll file descriptors will receive an event with epoll_wait(2). The
default in this scenario (when EPOLLEXCLUSIVE is not set) is for all epoll file
descriptors to receive an event. EPOLLEXCLUSIVE is thus useful for avoiding
thundering herd problems in certain scenarios.
If the same file descriptor is in multiple epoll instances, some with the
EPOLLEXCLUSIVE flag, and others without, then events will be provided to all epoll
instances that did not specify EPOLLEXCLUSIVE, and at least one of the epoll
instances that did specify EPOLLEXCLUSIVE.
The following values may be specified in conjunction with EPOLLEXCLUSIVE: EPOLLIN,
EPOLLOUT, EPOLLWAKEUP, and EPOLLET. EPOLLHUP and EPOLLERR can also be specified,
but this is not required: as usual, these events are always reported if they occur,
regardless of whether they are specified in events. Attempts to specify other
values in events yield the error EINVAL.
EPOLLEXCLUSIVE may be used only in an EPOLL_CTL_ADD operation; attempts to employ
it with EPOLL_CTL_MOD yield an error. If EPOLLEXCLUSIVE has been set using
epoll_ctl(), then a subsequent EPOLL_CTL_MOD on the same epfd, fd pair yields an
error. A call to epoll_ctl() that specifies EPOLLEXCLUSIVE in events and specifies
the target file descriptor fd as an epoll instance will likewise fail. The error
in all of these cases is EINVAL.
总结
| select | poll | epoll | |
| 文件描述符限制 | 1024 | 65536 | 无限制 |
| 每次需要重新设置监听对象和事件 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 找到变化的对象 |
当数据准备好后,select需要再次遍历表,找出准备好的文件描述符,效率低 O(n) |
当数据准备好之后,poll需要遍历表,找出准备好的文件描述符,效率低 O(n) |
当数据准备好之后,epoll直接能够找出准备好的文件描述符,不需要遍历表,效率高 O(1) |
| 适用场景 |
socket活跃,连接数一两千 |
socket活跃,连接数一两千 |
大量socket,活跃比例低,如http长连接 |
| 工作模式 |
LT |
LT |
LT ET |
| 阻塞与否 |
轮训同步阻塞 |
轮训同步阻塞,性能和select差不多,唯一的就是句柄数多 |
异步模式,但也是在epoll_wait上等待。 |
服务器软件如postgresql中select/poll/epoll一般都有在使用,监听事件用poll和epoll居多,select主要是历史原因,网络编程用的多。
关于unix domain socket的详细解释,可参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/guxch/article/details/7041052
关于epoll/poll/select的白话文解释,可参考:
https://my.oschina.net/dclink/blog/287198
epoll用法以及帮助手册:
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/epoll.7.html
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-311680-id-2439723.html
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/y6je2yf
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/373835207
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/mQ3iAr
关于epoll模式下连接的超时时间设置可参考:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/6590531/how-do-i-implement-epoll-timeout



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号