hdu 1254 推箱子 很好的嵌套搜索 双层BFS
推箱子
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3897 Accepted Submission(s): 1060
Problem Description
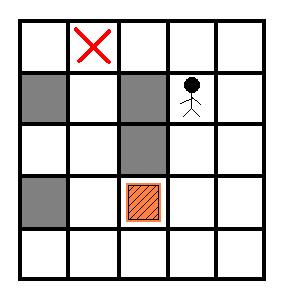
推箱子是一个很经典的游戏.今天我们来玩一个简单版本.在一个M*N的房间里有一个箱子和一个搬运工,搬运工的工作就是把箱子推到指定的位置,注意,搬运工只能推箱子而不能拉箱子,因此如果箱子被推到一个角上(如图2)那么箱子就不能再被移动了,如果箱子被推到一面墙上,那么箱子只能沿着墙移动.
现在给定房间的结构,箱子的位置,搬运工的位置和箱子要被推去的位置,请你计算出搬运工至少要推动箱子多少格.
![]()
现在给定房间的结构,箱子的位置,搬运工的位置和箱子要被推去的位置,请你计算出搬运工至少要推动箱子多少格.
Input
输入数据的第一行是一个整数T(1<=T<=20),代表测试数据的数量.然后是T组测试数据,每组测试数据的第一行是两个正整数M,N(2<=M,N<=7),代表房间的大小,然后是一个M行N列的矩阵,代表房间的布局,其中0代表空的地板,1代表墙,2代表箱子的起始位置,3代表箱子要被推去的位置,4代表搬运工的起始位置.
Output
对于每组测试数据,输出搬运工最少需要推动箱子多少格才能帮箱子推到指定位置,如果不能推到指定位置则输出-1.
Sample Input
1
5 5
0 3 0 0 0
1 0 1 4 0
0 0 1 0 0
1 0 2 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
Sample Output
4
Author
Ignatius.L & weigang Lee
Recommend
Ignatius.L
思路:
参考了大神们的思路
分成2部分 ,首先bfs 搜索箱子能够移动到的地方 然后对人进行bfs 看人是否能走到箱子边上 并且让箱子移动到新的位置
用vis[30][30][30][30]去标记 当人在某个位置箱子在某个位置时的状态 一共有8*8*8*8种状态
by hnust_xiehonghao
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int map[30][30];
bool pvis[30][30],bvis[30][30],vis[30][30][30][30];//四维 前2维是箱子的位置 后2维是人的位置 表示在人在某个位置而箱子在某个位置这个状态是否走过
int n,m,dir[4][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
struct Person
{
int x;
int y;
}pq,ptemp;
struct Box
{
int x;
int y;
int px;
int py;
int step;
}q,temp;
bool pok(int xx,int yy)
{
if(xx<0||xx>=n||yy<0||yy>=m||pvis[xx][yy]||map[xx][yy]==1||(xx==temp.x&&yy==temp.y)) return false ;
return true;// 最后一个条件保证人不会穿越箱子
}
int p_bfs(int x,int y,int fx)//x y是 推动后箱子的位置
{
int i,j;
memset(pvis,0,sizeof(pvis));
queue<struct Person>que;
pq.x=temp.px;pq.y=temp.py;
pvis[pq.x][pq.y]=1;
que.push(pq);
while(!que.empty())
{
ptemp=que.front();
que.pop();
if(ptemp.x==temp.x-dir[fx][0]&&ptemp.y==temp.y-dir[fx][1]) return 1;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
pq.x=ptemp.x+dir[i][1];
pq.y=ptemp.y+dir[i][0];
if(pok(pq.x,pq.y))
{
que.push(pq);
}
pvis[pq.x][pq.y]=1;
}
}
return 0;
}
bool ok(int xx,int yy)
{
if(xx<0||xx>=n||yy<0||yy>=m||map[xx][yy]==1||vis[xx][yy][temp.px][temp.py]) return false;
return true;
}
void BFS()
{
int i,j;
q.step=0;
queue<struct Box>que;
que.push(q);
vis[q.x][q.y][q.px][q.py]=true;
while(!que.empty())
{
temp=que.front();
que.pop();
if(map[temp.x][temp.y]==3) {printf("%d\n",temp.step);return ;}
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int xx,yy;
xx=temp.x+dir[i][0];yy=temp.y+dir[i][1];
if(ok(xx,yy))// 箱子能走
{
if(p_bfs(xx,yy,i))//如果人能走到箱子边上并且能推动箱子
{
q.px=temp.x;
q.py=temp.y;
q.step=temp.step+1;
q.x=xx;
q.y=yy;
que.push(q);
}
vis[xx][yy][temp.px][temp.py]=1;
}
}
}
printf("-1\n");
}
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
scanf("%d",&k);
while(k--)
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=0;j<m;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&map[i][j]);
if(map[i][j]==2) {q.x=i;q.y=j;}
else if(map[i][j]==4) {q.px=i;q.py=j;}
}
BFS();
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号